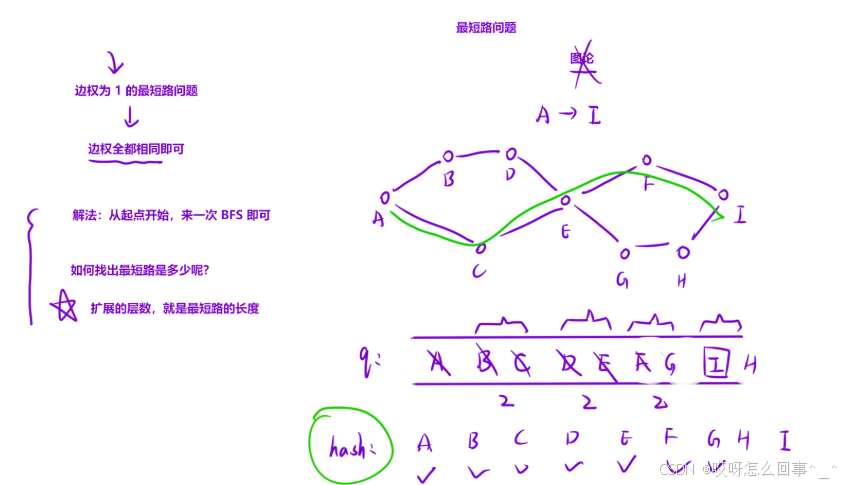
概述:最短路径问题就是边权为一的路径问题,每一次往外走一步步数加上边权,走到目的地步数最少的就是最短路。这种问题一般需要层次遍历来进行辅助,因为层次遍历可以找出本层连接的下一层的地点;一般还要有个哈希表记录地点访问过没有,防止走重复的路。
1926. 迷宫中离入口最近的出口 - 力扣(LeetCode)
每次向外扩展一层,扩展之前提前让总步数加一(下一次向外扩展),若是在下一次扩展中找到了出口就直接返回
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dx = {0, 0, -1, 1};
vector<int> dy = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
vector<vector<bool>> vis{100, vector<bool>(100, false)};
int nearestExit(vector<vector<char>>& maze, vector<int>& entrance) {
int n = maze.size(), m = maze[0].size();
int ans = 0;
queue<pair<int, int>> myq;
myq.push({entrance[0], entrance[1]});
vis[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = true;
while(myq.size())
{
ans++;
//开始向外扩展一层
int size = myq.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
auto [a, b] = myq.front();
myq.pop();
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = a + dx[k], y = b + dy[k];
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && !vis[x][y] && maze[x][y] == '.')
{
if(x == 0 || x == n - 1 || y == 0 || y == m - 1) return ans;
myq.push({x, y});
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};433. 最小基因变化 - 力扣(LeetCode)
新增用法:在unordered_map和unordered_set中取一个用,若是不需要映射值就用unordered_set
思路:
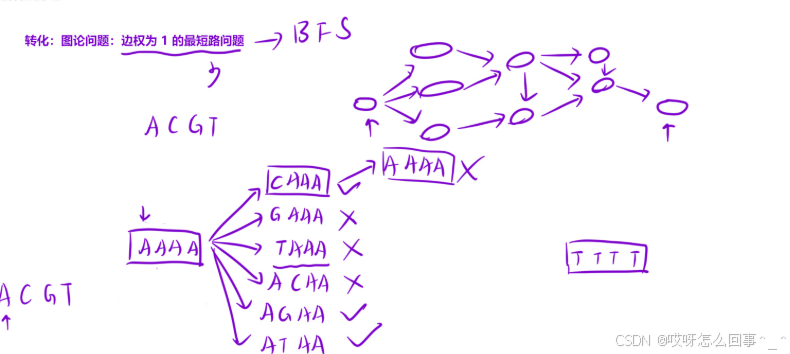
//将问题转换为BFS解决最短路径问题
//由最开始的基因序列一层层扩展查找,每一次扩展的内容为这个基因序列变化的所有可能
//由一个队列记录某一次扩展的基因序列
//只有之前没有被扩展(若是之前已经扩展过再加入队列,那么就重复扩展了,这条路上一定不是最小的次数)的并且在bank里面的才会入队列
class Solution {
public:
int minMutation(string startGene, string endGene, vector<string>& bank)
{
int ans = 0;//最终结果
unordered_set<string> hash_bank(bank.begin(), bank.end()), hash_search;//方便查看某个序列在不在bank内、查看某个序列是否被遍历过
if(startGene == endGene) return ans;
if(hash_bank.find(endGene) == hash_bank.end()) return -1;//最终结果本身不在
queue<string> myq;
myq.push(startGene);
hash_search.insert(startGene);
char genes[4] = {'A', 'G', 'C', 'T'};
while(myq.size())
{
ans++;//准备开始下一次扩展
int size = myq.size();
while(size--)//将上一次的序列全部扩展完
{
string str = myq.front();//将此序列变化,扩展
myq.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
char origin = str[i];
for(auto& gene : genes)
{
if(gene == origin)
continue;//跳过原来的字符串
string next = str;
next[i] = gene;//扩展字符串
//先判断是不是结果字符串,因为之前判断了endGene在不在bank中,走到这一定是在。那么只需要判断next和endGene相同与否即可
if(endGene == next) return ans;
//不是并且没有被访问过并且在bank中就入队列
if(hash_bank.find(next) != hash_bank.end() && hash_search.find(next) == hash_search.end())
{
myq.push(next);
hash_search.insert(next);
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};127. 单词接龙 - 力扣(LeetCode)
和上题类似
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
if(beginWord == endWord) return 1;//相同直接返回0
unordered_set<string> hash_list(wordList.begin(), wordList.end());//简化在wordlist里面查找存不存在的过程
if(hash_list.count(endWord) == 0) return 0;//endWord不存在直接返回0
unordered_set<string> hash_search;//标记访问过
hash_search.insert(beginWord);
queue<string> myq;//层次遍历
myq.push(beginWord);
int ans = 1;
vector<char> words(26, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
words[i] = 'a' + i;
while(myq.size())
{
ans++;
int size = myq.size();
while(size--)//一次扩展
{
string cur = myq.front();
myq.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < cur.size(); i++)
{
char origin = cur[i];
for(auto& ch : words)
{
if(ch == origin) continue;
string next = cur; next[i] = ch;
if(next == endWord) return ans;
//在hash_list里面并且未被访问就进队列并且标记已访问过
if(hash_list.count(next) && !hash_search.count(next))
{
myq.push(next);
hash_search.insert(next);
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};675. 为高尔夫比赛砍树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
因为题意是按照树的高度进行砍树,所以要找出下一次砍树的坐标,需要先将树的坐标按照树的高度排序;
之后将下棵树的下标作为迷宫问题的终点,起点为上一次的终点开始进行bfs查找
class Solution {
public:
//将这个问题分解为多步的迷宫问题,每次的出口换成了下一次应该砍的树的下标,依次统计步数即可
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int n, m;
int cutOffTree(vector<vector<int>>& forest)
{
n = forest.size();
m = forest[0].size();
//首先将砍的树的下标按照树的高度排序
vector<PII> sortindex;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++)
if(forest[i][j] > 1) sortindex.push_back({i, j});
sort(sortindex.begin(), sortindex.end(), [&](const PII& xy1, const PII xy2)->bool{
return forest[xy1.first][xy1.second] < forest[xy2.first][xy2.second];
});//[&]捕捉forest里面的数
//多次进行统计寻找下一颗树所需步数的操作
int ans = 0;
int bx = 0, by = 0;//起点
for(auto& [a, b] : sortindex)
{
int ret = bfs(forest, bx, by, a, b);
if(ret == -1) return -1;//说明下一棵树的位置到不了
ans += ret;
//下一次寻找的起点为上一次寻找的终点
bx = a;
by = b;
}
return ans;
}
int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
bool vis[51][51] = {false};//避免重复回走
int bfs(vector<vector<int>>& forest, int bx, int by, int ex, int ey)
{
if(bx == ex && by == ey) return 0;
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);//每一次都是新的查找,所以要重新标记
int ret = 0;
queue<PII> q;
q.push({bx, by});
vis[bx][by] = true;
while(q.size())
{
ret++;
int sz = q.size();
while(sz--)
{
auto [a, b] = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int x = a + dx[i], y = b+ dy[i];
if(x == ex && y == ey) return ret;
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && !vis[x][y] && forest[x][y] != 0)
{
q.push({x, y});
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};





















 1879
1879

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








