1.什么是shell
在 Linux 系统中,Shell 是连接用户与操作系统内核(Kernel)的 “桥梁”,它本质上是一个命令行解释器—— 接收用户输入的命令,将其翻译成内核能理解的语言,再将内核执行后的结果反馈给用户。没有 Shell,普通用户无法直接操作 Linux 内核(内核是操作系统的核心,负责管理硬件、内存、进程等底层资源,不直接与用户交互)。
2. 基于模拟实现shell
2.1 实现输出命令行
我们要实现一个这样的命令行:
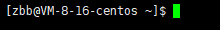
这样一个命令行中包括了[用户名,主机名,目录]用户类型,这些信息。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 512
char* getuser()
{
char* user=getenv("USER"); //从系统中获取用户名
return user;
}
char* gethostname()
{
char* hostname=getenv("HOSTNAME"); //从系统中获取主机名
return hostname;
}
char* getpwd()
{
char* pwd=getenv("PWD"); //从系统中获取路径名
return pwd;
}
void MakeConmandLineAndPrintf(char arr[],size_t size)
{
snprintf(arr,size,"[%s@%s %s]$",getuser(),gethostname(),getpwd());
printf("%s",arr);
fflush(stdout); //刷新屏幕的缓冲区
}
int main()
{
char ConmandLine [SIZE];
MakeConmandLineAndPrintf(ConmandLine,sizeof(ConmandLine));
return 0;
}
2.2 获取用户命令字符串
#include<string.h>
#define ZERO '\0'
int GetCommand(char arr[],size_t size)
{
char* comand=fgets(arr,size,stdin);//从键盘中获取字符到arr中,返回获取字符数量
if(comand==NULL) return -1; //文件为空,则获取失败,返回-1.
comand[strlen(comand)-1]=ZERO; //使字符串最后一个字符为‘0’,否则我们从键盘获取字符时,回车键结束,打印时会相当于一个换行。
return strlen(arr); //成功获取字符,就返回字符数量。
}
int main()
{
char usercommand[SIZE];
GetCommand(usercommand,sizeof(usercommand));
}
2.3 命令行字符串分割
在 Linux 系统中,进程的命令行参数(包括程序名本身)会被存储在 argv 数组 中,同时配套的 argc 变量用于标识该数组的元素个数。这两个变量是 C 语言(Linux 下多数系统程序的开发语言)中 main 函数的标准参数,也是操作系统向进程传递命令行参数的核心载体。
./app arg1 arg2
就会分别存在argv[0],argv[1],argv[2]中,他们的分割依据就是空格" "。
我们需要用到函数,strtok 是 C 语言标准库 <string.h> 中用于字符串分割的函数,它可以将一个字符串按照指定的分隔符拆分成多个子串(令牌)。
函数原型:
char *strtok(char *str, const char *delim);
功能说明:
str:第一次调用时传入要分割的字符串,后续调用传入 NULL。
delim:包含分隔符的字符串(多个分隔符)。
返回值:指向当前分割出的子串的指针,若没有更多子串则返回 NULL。
工作原理:
- 第一次调用时,strtok 会在 str 中查找第一个非分隔符字符作为子串的起始位置
- 然后继续查找下一个分隔符,找到后将其替换为 \0 作为子串的结束
- 同时保存下一个字符的位置作为内部状态
- 后续调用传入 NULL 时,函数会从上次保存的位置继续分割
#define DELIM " "//命令行参数的分隔符是空格。
char *Argv[30];//存储分割后的命令行参数。
void splitcommand(char command[],size_t size)
{
Argv[0]= strtok(command,DELIM);
int i=1;
while((Argv[i++]=strtok(NULL,DELIM)));//直到无法分割了,返回一个NULL。
}
int main()
{
char ConmandLine [SIZE];
MakeConmandLineAndPrintf(ConmandLine,sizeof(ConmandLine));
char usercommand[SIZE];
GetCommand(usercommand,sizeof(usercommand));
splitcommand(usercommand,sizeof(usercommand));
return 0;
}
2.4 执行命令
这里我们执行命令可以选择创建子进程,让子进程去执行命令。
#include<errno.h>
void ExucuteCommand()
{
pid_t id=fork();
if(id<0) Die();//创建子进程执行命令
else if(id==0)
{
execvp(Argv[0],Argv);//进程替换,替换成我们要执行的命令的文件代码。
exit(errno);//errno由系统记录最近的一次错误退出,如果execvp替换错误返回-1,就会被errno记录
}
else{//父进程
int status=0;
pid_t rid=waitpid(id,&status,0);//等待子进程退出
}
}
int main()
{
int quit=0;
char ConmandLine [SIZE];
char usercommand[SIZE];
while(!quit)
{
MakeConmandLineAndPrintf(ConmandLine,sizeof(ConmandLine));
GetCommand(usercommand,sizeof(usercommand));
splitcommand(usercommand,sizeof(usercommand));
ExucuteCommand();
}
return 0;
}
改内容涉及大量进程和进程替换的知识,建议不会的朋友可以移步我另两篇文章:
Linux进程控制(进程的创建退出,等待与进程替换)
Linux进程概念(内容涵盖操作系统,进程,环境变量,地址空间,进程调度队列)
2.5 完善执行命令
在 Linux 系统中,内建命令(Built-in Commands) 是指由 Shell(如 Bash、Zsh 等)直接解释执行的命令,而非独立的可执行文件(外部命令通常存放在 /bin、/usr/bin 等目录下)。由于内建命令无需创建子进程,无需磁盘 I/O,其执行效率远高于外部命令,同时能直接操作 Shell 的内部环境(如变量、进程状态)。
例:cd 是 Bash 的内建命令,执行 which cd 会提示 “cd: shell 内建命令”,而外部命令 ls 可通过 which ls 找到路径(如 /bin/ls)。
这里内建命令可以理解为我们shell程序中的内部函数,而并非通过进程创建和进程替换的文件。
例如我们写一个cd内建命令的函数:
char cwd[SIZE*2]
int CheckBuildin()//先判断是否为内建命令
{
int yes=0;
char* enter_cmd=Argv[0];
if(strcmp(enter_cmd,"cd")==0)//判断是内建命令中哪一个
{
yes=1;//是的话,返回非0
cd();
}
return yes;
}
void cd()
{
char*path=Argv[1];//获取cd后地址。
if(path==NULL) path=Gethome();//若cd后什么都没跟,则返回家目录。
chdir(path);//chdir更改该进程所在的工作目录。
getcwd(cwd,sizeof(cwd));//使用getcwd获取当前目录。
setenv("PWD", cwd, 1);//更改进程环境变量中的PWD当前地址。
}
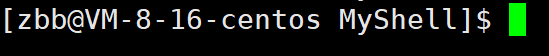
2.6 截取路径
在linux中命令行显示的路径只有MyShell这种,只显示最后一个地址位置,我们将我们的shell也改成这样,就需要截取我们的路径。
#define SkipPath(p) do{p=p+strlen(p)-1;while(*p!='/'){p--;}}while(0)
//获取最后的地址
void MakeConmandLineAndPrintf(char arr[],size_t size)
{
char* Cwd=Getpwd();
SkipPath(Cwd); //宏函数
snprintf(arr,size,"[%s@%s %s]>",Getuser(),Gethostname(),strlen(Cwd)==1?"/":Cwd+1);
//如果地址只有“/”就直接打印“/”
printf("%s",arr);
fflush(stdout);
}
2.7 内建命令echo $?
内建命令echo $?可以查看最近一次进程的退出码:
int lastcode;全局整型存储退出码。
int CheckBuildin()
{
int yes=0;
const char* enter_cmd=Argv[0];
if(strcmp(enter_cmd,"cd")==0)
{
yes=1;
cd();
}
if(strcmp(enter_cmd,"echo")==0&&strcmp(Argv[1],"$?")==0)
//检查是否为内建命令。
{
echo_stast(); //执行该内建命令。
yes =1;
}
return yes;
}
void echo_stast()//打印退出码。
{
printf("%d\n",lastcode);
}
void ExucuteCommand()
{
pid_t id=fork();
if(id<0) Die();
else if(id==0)
{
execvp(Argv[0],Argv);
exit(errno);
}
else{
int status=0;
pid_t rid=waitpid(id,&status,0);
if(rid>0)
{
lastcode= WEXITSTATUS(status);//子进程等待成功后,获得退出码。
}
}
}
3. 所有代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 512
#define ZERO '\0'
#include<errno.h>
#define DELIM " "
#include<unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define SkipPath(p) do{p=p+strlen(p)-1;while(*p!='/'){p--;}}while(0)
char *Argv[30];
char ConmandLine [SIZE];
char cwd[SIZE*2];
int lastcode;
char* Getuser()
{
char* user=getenv("USER");
return user;
}
char* Gethostname()
{
char* hostname=getenv("HOSTNAME");
return hostname;
}
char* Getpwd()
{
char* pwd=getenv("PWD");
return pwd;
}
void MakeConmandLineAndPrintf(char arr[],size_t size)
{
char* Cwd=Getpwd();
SkipPath(Cwd);
snprintf(arr,size,"[%s@%s %s]>",Getuser(),Gethostname(),strlen(Cwd)==1?"/":Cwd+1);
printf("%s",arr);
fflush(stdout);
}
int GetCommand(char arr[],size_t size)
{
char* comand=fgets(arr,size,stdin);
if(comand==NULL) return -1;
comand[strlen(comand)-1]=ZERO;
return strlen(arr);
}
void splitcommand(char command[],size_t size)
{
Argv[0]= strtok(command,DELIM);
int i=1;
while((Argv[i++]=strtok(NULL,DELIM)));
}
void Die()
{
exit(-1);
}
void ExucuteCommand()
{
pid_t id=fork();
if(id<0) Die();
else if(id==0)
{
execvp(Argv[0],Argv);
exit(errno);
}
else{
int status=0;
pid_t rid=waitpid(id,&status,0);
if(rid>0)
{
lastcode= WEXITSTATUS(status);
}
}
}
char* Gethome()
{
char*tmp= getenv("HOME");
return tmp;
}
void cd()
{
char*path=Argv[1];
printf("cd : %s\n", path);
if(path==NULL) path=Gethome();
chdir(path);
getcwd(cwd,sizeof(cwd));
setenv("PWD", cwd, 1);
}
void echo_stast()
{
printf("%d\n",lastcode);
}
int CheckBuildin()
{
int yes=0;
const char* enter_cmd=Argv[0];
if(strcmp(enter_cmd,"cd")==0)
{
yes=1;
cd();
}
if(strcmp(enter_cmd,"echo")==0&&strcmp(Argv[1],"$?")==0)
{
echo_stast();
printf("AAAA");
yes =1;
}
return yes;
}
int main()
{
int quit=0;
char usercommand[SIZE];
while(!quit)
{
MakeConmandLineAndPrintf(ConmandLine,sizeof(ConmandLine));
GetCommand(usercommand,sizeof(usercommand));
splitcommand(usercommand,sizeof(usercommand));
int n=CheckBuildin();
if(n!=0) continue;
ExucuteCommand();
}
return 0;
}





















 243
243

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










