先读取数据和查看数据的总体情况
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
print(data.info())
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 7500 entries, 0 to 7499
Data columns (total 18 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Id 7500 non-null int64
1 Home Ownership 7500 non-null object
2 Annual Income 5943 non-null float64
3 Years in current job 7129 non-null object
4 Tax Liens 7500 non-null float64
5 Number of Open Accounts 7500 non-null float64
6 Years of Credit History 7500 non-null float64
7 Maximum Open Credit 7500 non-null float64
8 Number of Credit Problems 7500 non-null float64
9 Months since last delinquent 3419 non-null float64
10 Bankruptcies 7486 non-null float64
11 Purpose 7500 non-null object
12 Term 7500 non-null object
13 Current Loan Amount 7500 non-null float64
14 Current Credit Balance 7500 non-null float64
15 Monthly Debt 7500 non-null float64
16 Credit Score 5943 non-null float64
17 Credit Default 7500 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(12), int64(2), object(4)将Home Ownership 和 Years in current job 转化为数字
先了解特征的分布情况,用字典映射转化类型
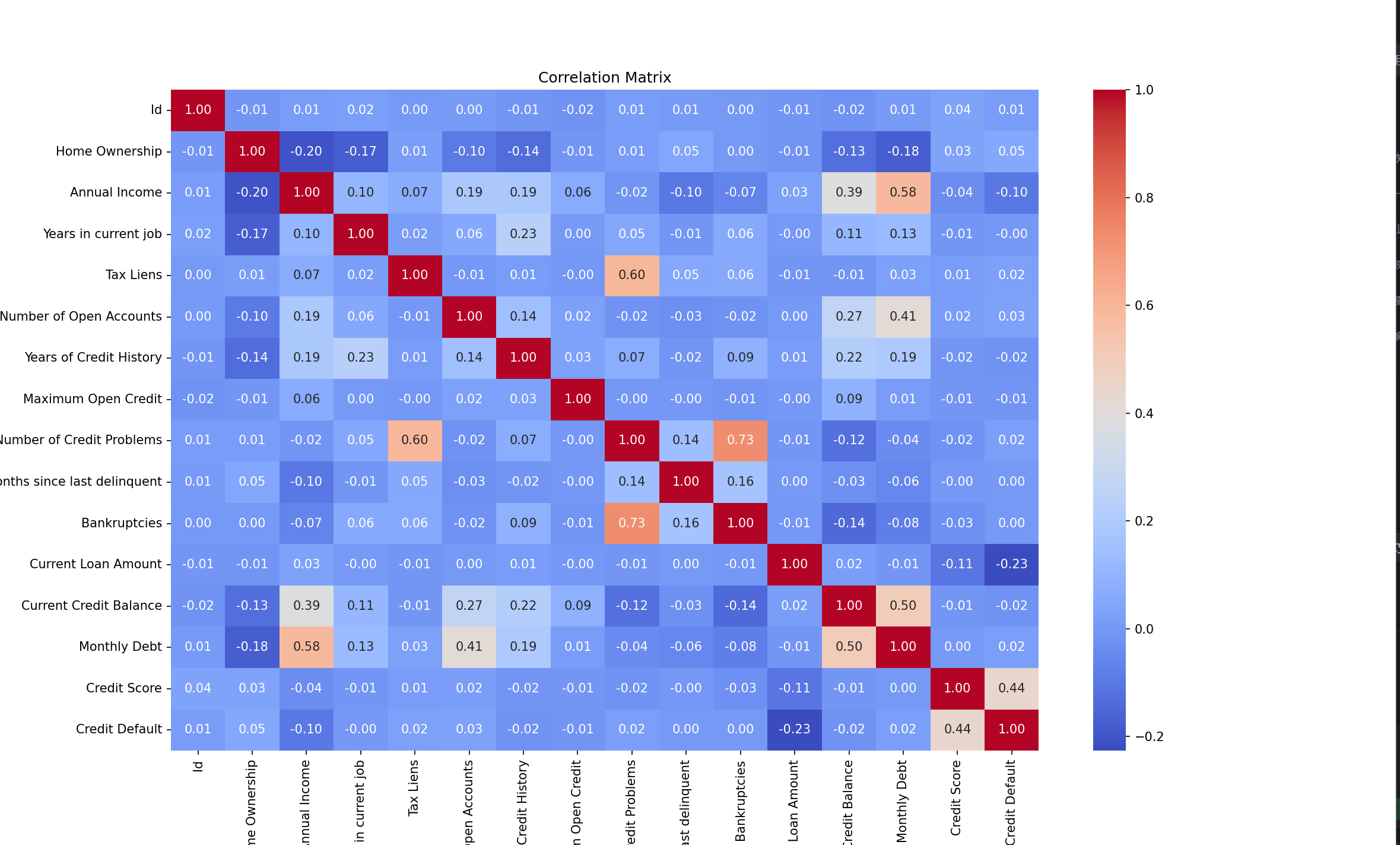
# 提取连续特征,计算相关系数,绘图
continue_feature = []
for feature in data.columns:
if data[feature].dtype != 'object':
continue_feature.append(feature)
# 计算相关系数
corr_matrix = data[continue_feature].corr()
# 绘制相关系数矩阵的热力图
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10))
sns.heatmap(corr_matrix, annot=True, cmap='coolwarm', fmt=".2f")
plt.title("Correlation Matrix")
plt.show()
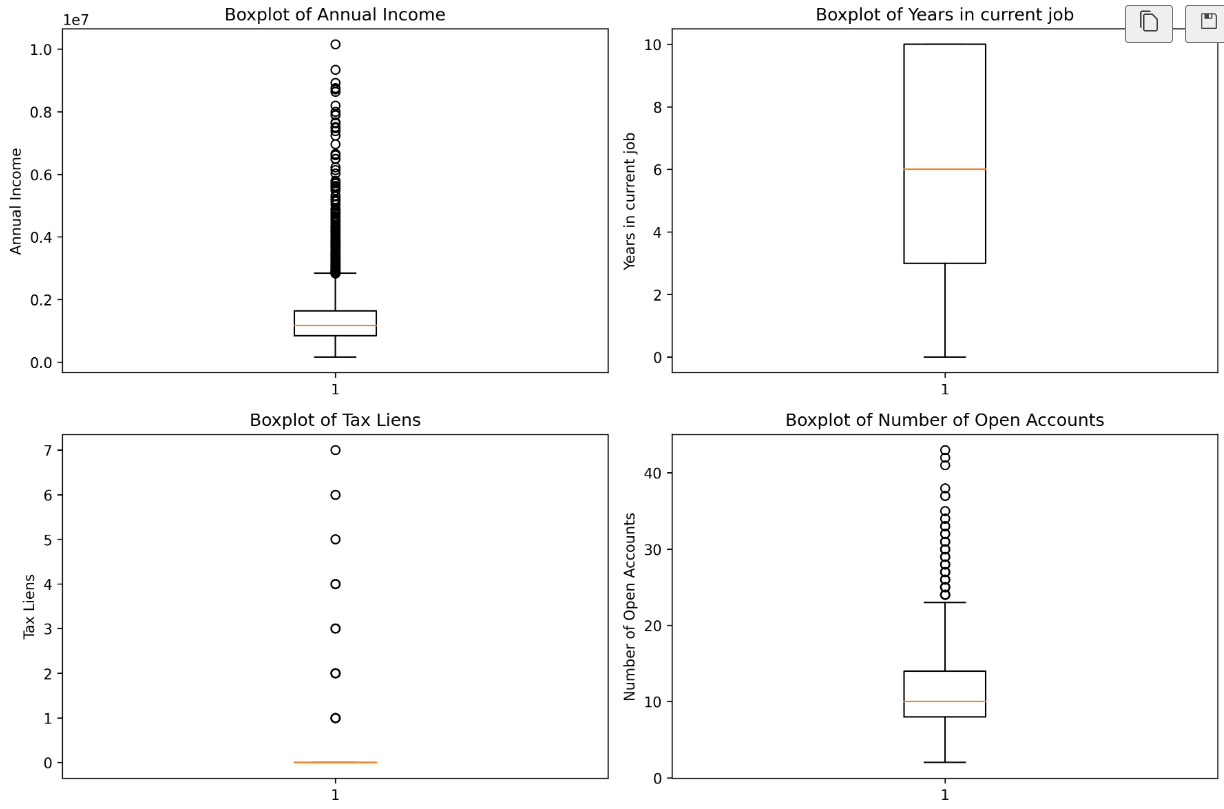
features = ['Annual Income', 'Years in current job', 'Tax Liens', 'Number of Open Accounts']
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 300
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 8))
# 使用 for 循环遍历特征
for i in range(len(features)):
row = i // 2 # 计算当前特征在子图中的行索引,// 是整除,即取整 ,之所以用整除是因为我们要的是行数
# 例如 0//2=0, 1//2=0, 2//2=1, 3//2=1
col = i % 2 # 计算当前特征在子图中的列索引,% 是取余,即取模
# 例如 0%2=0, 1%2=1, 2%2=0, 3%2=1
# 绘制箱线图
feature = features[i]
axes[row, col].boxplot(data[feature].dropna())
axes[row, col].set_title(f'Boxplot of {feature}')
axes[row, col].set_ylabel(feature)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
enumerate()函数:
enumerate()函数返回一个迭代对象,该对象包含索引和值。
语法:
enumerate(iterable, start=0)
参数:
iterable -- 迭代对象,迭代对象可以是列表、元组、字典、字符串等。
start -- 索引的开始值
返回值:
返回一个迭代对象,该对象包含索引和值。
之所以这个函数很有用,是因为它允许我们同时迭代一个序列,并获取每个元素的索引和值。
今日状态一般般,明天再认真跑一下,今天绘制子图时出现不少问题,明天尝试解决





















 431
431

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








