Hunter
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1589 Accepted Submission(s): 469
Problem Description
One day, a hunter named James went to a mysterious area to find the treasures. James wanted to research the area and brought all treasures that he could.
The area can be represented as a N*M rectangle. Any points of the rectangle is a number means the cost of research it,-1 means James can't cross it, James can start at any place out of the rectangle, and explore point next by next. He will move in the rectangle and bring out all treasures he can take. Of course, he will end at any border to go out of rectangle(James will research every point at anytime he cross because he can't remember whether the point are researched or not).
Now give you a map of the area, you must calculate the least cost that James bring out all treasures he can take(one point up to only one treasure).Also, if nothing James can get, please output 0.
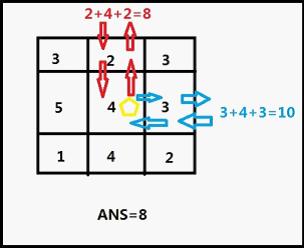
The area can be represented as a N*M rectangle. Any points of the rectangle is a number means the cost of research it,-1 means James can't cross it, James can start at any place out of the rectangle, and explore point next by next. He will move in the rectangle and bring out all treasures he can take. Of course, he will end at any border to go out of rectangle(James will research every point at anytime he cross because he can't remember whether the point are researched or not).
Now give you a map of the area, you must calculate the least cost that James bring out all treasures he can take(one point up to only one treasure).Also, if nothing James can get, please output 0.

Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases T is given in the first line of the input. Each test case begins with a line containing 2 integers N M , (1<=N,M<=200), that represents the rectangle. Each of the following N lines contains M numbers(0~9),represent the cost of each point. Next is K(1<=K<=13),and next K lines, each line contains 2 integers x y means the position of the treasures, x means row and start from 0, y means column start from 0 too.
Output
For each test case, you should output only a number means the minimum cost.
Sample Input
2 3 3 3 2 3 5 4 3 1 4 2 1 1 1 3 3 3 2 3 5 4 3 1 4 2 2 1 1 2 2
Sample Output
8 11
Source
Recommend
zhoujiaqi2010 | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you:
5498
5497
5495
5494
5493
TSP问题,
先BFS建下图,然后。。。人家的解释
一个整数i就表示了一个点集;
整数i可以表示一个点集,也可以表示是第i个点。
状态表示:dp[i][j]表示经过点集i中的点恰好一次,不经过其它的点,并且以j点为终点的路径,权值和的最小值,如果这个状态不存在,就是无穷大。
状态转移:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define min(a,b) (a>b?b:a)
using namespace std;
int dp[1<<14][14];
int u[14],v[14];
int map[220][220],vis[220][220],id[220][220],dis[220][220];
int n,m,k;
int dx[4]={0,1,0,-1};
int dy[4]={1,0,-1,0};
struct s
{
int x,y,step;
friend bool operator < (s a, s b)
{
return a.step>b.step;
}
}a,temp;
int jud(struct s a)
{
if(a.x<1||a.x>n||a.y<1||a.y>m)
return 0;
return 1;
}
void bfs(int x,int y,int xx)
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
priority_queue<struct s>q;
int flag=0;
a.x=x;
a.y=y;
a.step=0;
q.push(a);
vis[a.x][a.y]=1;
while(!q.empty())
{
a=q.top();
q.pop();
if(id[a.x][a.y]!=-1)
{
dis[xx][id[a.x][a.y]]=a.step;
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
temp.x=a.x+dx[i];
temp.y=a.y+dy[i];
if(!jud(temp))
{
if(!flag)
{
flag=1;
dp[1<<xx][xx]=a.step+map[u[xx]][v[xx]];
}
continue;
}
if(vis[temp.x][temp.y]||map[temp.x][temp.y]==-1)
continue;
temp.step=a.step+map[temp.x][temp.y];
vis[temp.x][temp.y]=1;
q.push(temp);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
//int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=m;j++)
scanf("%d",&map[i][j]);
}
scanf("%d",&k);
memset(id,-1,sizeof(id));
memset(dp,INF,sizeof(dp));
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&u[i],&v[i]);
u[i]++;
v[i]++;
id[u[i]][v[i]]=i;
}
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
{
bfs(u[i],v[i],i);
}
int rt=(1<<k)-1,p;
for(i=0;i<=rt;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<k;j++)
{
if(dp[i][j]==INF)
continue;
for(p=0;p<k;p++)
{
if(p==j||(i&(1<<p)))
continue;
int st=i|(1<<p);
dp[st][p]=min(dp[st][p],dp[i][j]+dis[j][p]);
}
}
}
int ans=INF;
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
{
ans=min(ans,dp[rt][i]+dp[1<<i][i]-map[u[i]][v[i]]);
}
if(ans==INF)
{
ans=0;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}







 本文介绍了一种解决旅行商问题(TSP)的方法,通过构建辅助图并运用动态规划技巧来寻找收集所有宝藏所需的最低成本路径。
本文介绍了一种解决旅行商问题(TSP)的方法,通过构建辅助图并运用动态规划技巧来寻找收集所有宝藏所需的最低成本路径。
















 486
486

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








