一:R console input and evolution
>x <-5 ##将5赋值给x
>x ##自动输出
[1] 5 注意:【1】的意思是数字5是这个向量的第一个元素
>print(x) ##expliciting print
[1] 5
二:R data types
(1)objects(对象)
- character(字符型)
- numeric(real number)(数值型)
- integer(整型) 在数字后加L可以表示为整型
- complex(复数型)
- logical(逻辑型)
向量只能包含同种类型的元素(列表是一个例外)
inf表示 infinity(无穷),且inf是一个real number。
NAN OR Nan 表示一个不确定的值。
(2)attributes (attributes can be part of an object in R. )(属性)
-
names
-
dim names/dimension names(维度名字)
解释:A dimension, so a matrix will have dimensions for
example it will have a number of rows and a number of columns if you
have a multidimensional array you'll have more than two dimensions.
-
class(类)
解释:every object will have a class.
So for example, numeric objects their class is numeric and
integer objects, their class is integer.
-
length
-
other user-defined attributes
解释:There is a general function called attributes which allows you to set or
modify the attributes for an R object.
(3)vectors(向量)
c function is another function that can be used to create vectors of object
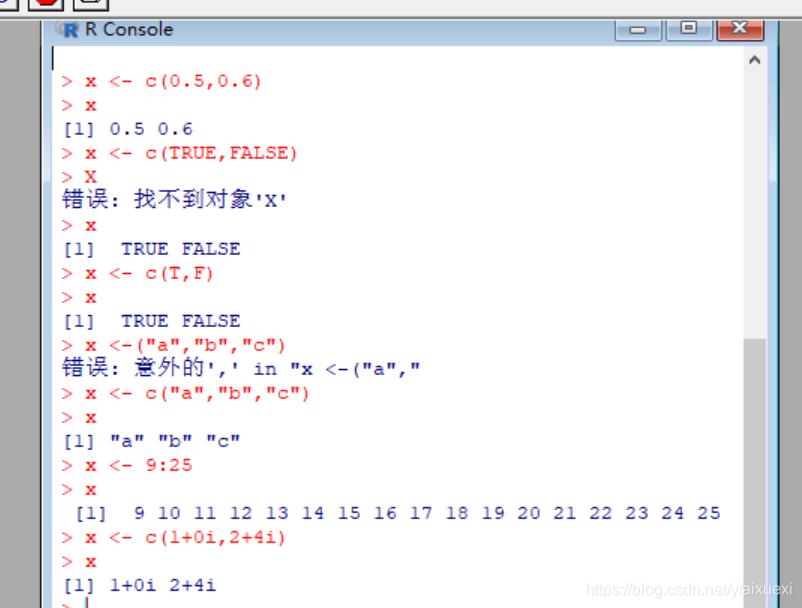
using the vector function you can also create
a vector of a certain type and a certain length
Example: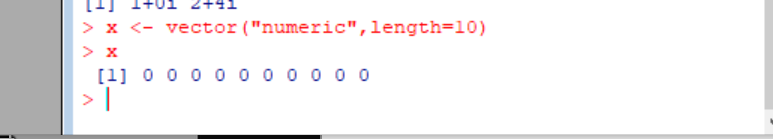
在默认情况下,向量会被初始化为一个默认值,对数值向量而言,这个默认值为0。
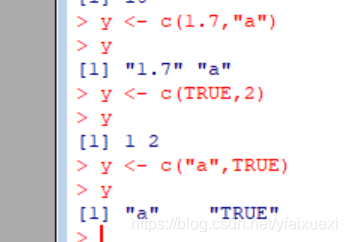
(4)Mixing Objects
if you take a vect you create a vector and
you mix two different types of objects and so the general it that is that r.
Will kind of create the least common denominator vector so, will not give you
an error but what will happen is that it will coerce(强制转换) the vector to be the
class that's kind of the least common denominator(最低级公共形式)
即字符型《数值型《整型《复数型《逻辑型。
(5)explicit coercion(强制类型转换)
使用as.objects()将对象的类型进行转换

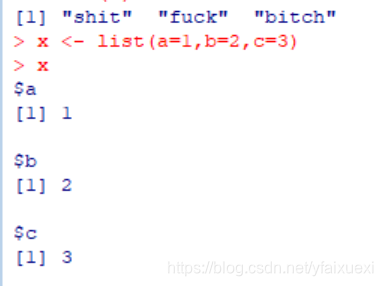
(6)LIST

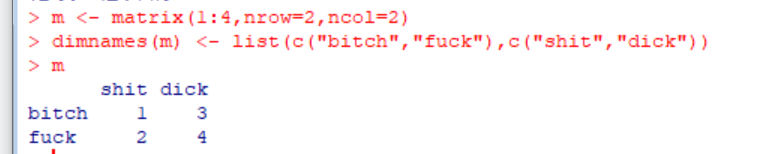
(7)Matrices(矩阵)
①Matrices are vectors with a dimension attribute. The dimension attribute is itself an integer vector of length 2 (nrow, ncol)
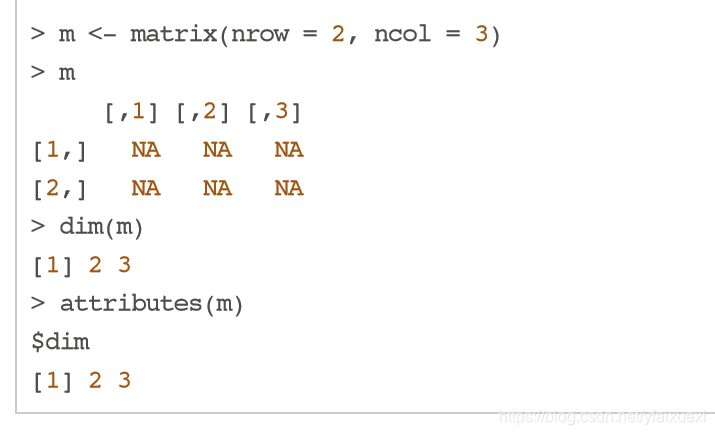
dim()是维度函数
②Matrices are constructed column-wise, so entries can be thought of starting in the “upper left” corner and running down the columns.矩阵是按列排列的,把一个向量中元素按列排入矩阵中,先排满第一列,然后第二列。。。。
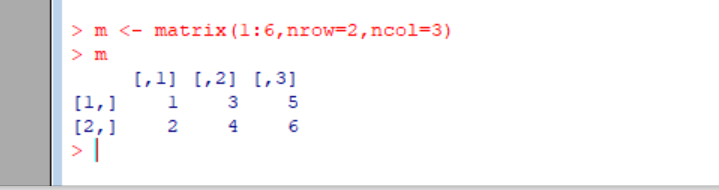
③Matrices can also be created directly from vectors by adding a dimension attribute.

④cbind-ing and rbind-ing(列绑定和行绑定)
Matrices can be created by column-binding or row-binding with cbind() and rbind().

(8)Factors(因子)
因子是一种特殊的向量类型,它通常用来记录分类数据。因子可以被分为有序的和无序的
无序因子可以被用来标记那些可以分类但是没有顺序的数据,而有序因子用来标记那些有先后顺序的数据。

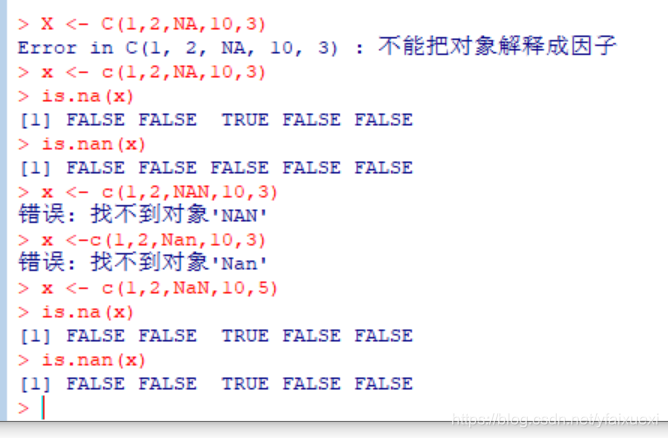
(9)Missing values(缺失值)
- Missing values are denoted by NA or NaN for undefined mathematical operations.(NAN用来表示未定义的数学运算,NA用来表示其他的缺失值。)
- is.na() is used to test objects if they are NA。
- is.nan() is used to test for NaN .
- NA values have a class also, so there are integer NA, character NA, etc.
- A NaN value is also NA but the converse is not true
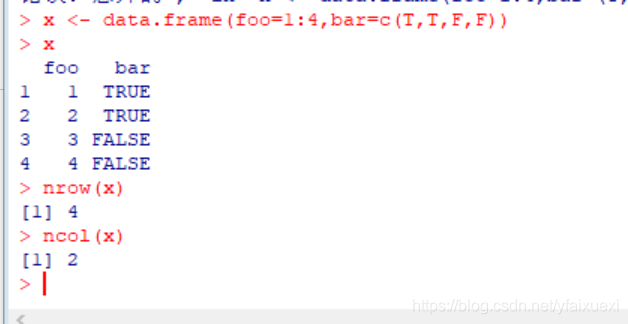
(10)Data Frames(数据框)
Data Frames Data frames are used to store tabular data(表格数据)
- They are represented as a special type of list where every element of the list has to have the same length,
- Each element of the list can be thought of as a column and the length of each element of the list is the number of rows
- Unlike matrices, data frames can store different classes of objects in each column (just like lists); matrices must have every element be the same class
- Data frames also have a special attribute called row.names
- Data frames are usually created by calling read.table() or read.csv()
- Can be converted to a matrix by calling data.matrix()
(11)Names
R objects can also have names, which is very useful for writing readable code and self-describing objects.
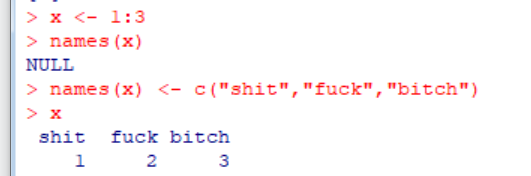
Lists can also have names.And matrices.





 本文详细介绍R语言的基础概念,包括变量赋值、数据类型如字符、数值、整数、复数和逻辑型,向量操作,混合对象处理,强制类型转换,列表、矩阵和因子的使用,以及数据框和缺失值的管理。
本文详细介绍R语言的基础概念,包括变量赋值、数据类型如字符、数值、整数、复数和逻辑型,向量操作,混合对象处理,强制类型转换,列表、矩阵和因子的使用,以及数据框和缺失值的管理。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








