注:部分代码演示如果因长度问题观看不便利,可粘贴到idea中观看
一、API
API,Application Programing interface,应用程序编程接口
其实就是说明书,通过API可以了解到详细内容
https://www.matools.com/api/java8
二、Object
1、概念
(1)Object是所有类的父类,默认继承,可以不写出来
(2)Object有构造方法可以创建对象
| private static void show1() { /** * 演示每个类都继承自Object */ Animal animal = new Animal( ); animal.toString();// Animal只是自定义类,而调用的是继承的Object的父类方法 /** * 演示Object可以创建对象 */ Object o = new Object( ); System.out.println(o ); } |
2、常用方法
(1)hashCode
hashCode方法在Object类中是将十六进制的内存地址转为了十进制的值的表示形式,
一般要和equals一起重写
| private static void show2() { /** * 演示hashCode方法 * hashCode方法返回的是对象的地址值 */ Object o = new Object( ); int i = o.hashCode( ); System.out.println(i ); // 打印十进制的地址值 } |
(2)equals
比较两个Object对象是否相等!!
| public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 演示equals * equals方法是判断两个对象是否相等 * 是通过对象的地址值,使用==判断是否相等 */ Object o1 = new Object( ); Object o2 = new Object( ); boolean equals = o1.equals(o2); System.out.println(equals );//false /** * 这个Object类中的equals方法不好用 * 在实践中,判断地址值无意义,一般是通过判断对象属性是否一致来决定是否相等 * 所以,基本每个子类都会重写equals用于判断对象属性是否相等 */ Animal a1 = new Animal(2, "1101", "小黑"); Animal a2 = new Animal(2, "1101", "小黑"); System.out.println(a1.equals(a2));//false } |
重写equals方法,不需要手写,可以右键generate中直接生成
| public class Animal { int age; String idCard; String name; public Animal() { } public Animal(int age, String idCard, String name) { this.age = age; this.idCard = idCard; this.name = name; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass( ) != o.getClass( )) return false; Animal animal = (Animal) o; return age == animal.age && Objects.equals(idCard, animal.idCard) && Objects.equals(name, animal.name); } // hashCode方法是idea随着equals一起生成的,不用管,删除也行,留着也行,不影响 @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(age, idCard, name); } } |
(3)toString
返回对象的字符串表示形式。一般来说,toString方法官方API建议所有子类覆盖此方法,以保证打印的对象不是一个看不懂的地址而是我们能看的懂的字符串。
| public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 演示toString */ Animal animal = new Animal( ); String string = animal.toString( ); System.out.println("---> "+string ); /** * 输出语句中输出对象其实默认调用toString()将对象以字符串形式返回 * 然后再输出的 */ System.out.println(animal ); System.out.println(animal.toString( ) ); /** * 实战中,一般打印地址值无意义,一般是经常查看对象内的属性值 * 所以:子类都会重写toString,打印对象内容 */ } |
3、总结
(1)以后每个类如果需要判断对象相等那就重写equals
(2)如果需要打印对象信息,那就重写toString
(3)以上两种都可以通过idea里的ptg插件,安装后右键点击下面的javabean一键生成
三、String
1、概念
(1)String代表字符串
(2)程序中出现的任何字符串都是String类对象
(3)字符串是常量,即声明后不可改变
2、构造方法
构造方法很多但是过时了不少只需要了解几个
| public static void main(String[] args) { String s = new String( );// 创建空字符串 String s2 = "";// 创建空字符串 String s3 = new String("a");// 创建字符串副本 // 将字节数组转换为字符串 byte[] bytes = {65,66,67}; String s4 = new String(bytes); System.out.println(s4 );// ABC String msg = "在吗?"; byte[] bytes1 = msg.getBytes( );// 字符串转字节数组的 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes1)); } |
3、字符串常用方法
(1)查找字符串的方法
| public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = “java”; char c = s.charAt(2) //1.在字符串中查找下标为2的字符 System.out.println(c); //v int v = s.indexOf(“a”); // 2.查找字符串第一次出现的位置的下标 System.out.println(v) //1 int a = s.lastIndexOf("a");//3查找字符在字符串中出现的最后一次的下标位置 System.out.println(a);//3 int length = "abcdef".length();//4.字符串的长度 System.out.println(length);//6 } } |
(2)关于字符串判断的方法
| public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { /* 关于字符串判断 */ // 判断是否包含 System.out.println("abc".contains("ab"));//true System.out.println("abc".contains("ac"));//false 看整体 System.out.println("狗蛋".isEmpty());//false System.out.println("".isEmpty());//true System.out.println(" ".isEmpty());//false 空格也有内容的 不为空 // 判断是否以指定字符开头(前缀) System.out.println("张三".startsWith("张"));//true System.out.println("李四".startsWith("张"));//false System.out.println("abcd.txt".startsWith("abc"));//true System.out.println("abcd.txt".startsWith("bcd"));//false // 判断是否以指定字符结尾(后缀) System.out.println("abc.png".endsWith(".png"));//true // 判 断是否相等 System.out.println("abc".equals("abc"));//true // 忽略大小写判断相等 System.out.println("ABcdE".equalsIgnoreCase("abcde"));//true } } |
(3)关于字符串转换的方法
| //转成字节数组 byte[] bytes = “ABC”.getBytes(); //转成字符数组 char[] charArray = “ABC”.tocharArray(); //转大小写 String lowerCase = “ABC”.toLowerCase();//转小写 String upperCase = “abc”.toUpperCase()’;//转大写 //格式刷 String s1 = String.valueof(123); //很重要,能把任何数组类型转为字符串 |
(4)关于字符串拆分、截取、替换的方法
| String[] split = “CN-HN-ZZ-2401-01-01”.split(“-”); for(int i1 = 0; i1 < split.length; i1++){ System,out,println(split[i1]); } // 截取字符串(子字符串),参数 String substring = "41101020000101123-04".substring(6, 14); System.out.println("截取的字符串:" + substring ); // 替换字符串 String replace = "java".replace("av", "AV"); System.out.println(replace ); String replace1 = "我不爱学习".replace("不爱", "**"); System.out.println(replace1 ); |
四、StringBuffer和StringBuilder
1、StringBuffer
StringBuffer是线程安全的可变字符串,重点是知道如何使用方法改变字符串
| public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建空的StringBuffer,后续再拼接字符串 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); // 以指定字符串创建StringBuffer,后续接着改变 StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer(“java”); System.out.println(sb2); // 拼接字符串 sb2.append(“bigdata”); System.out.println(“sb2”);// javabigdata // 插入数据 sb1.insert(2,"狗");//offset偏移量,不是下标 // StringBuffer转成String // 方式1: StringBuffer对象的toString String s1 = sb2.toString(); // 方式2: String.valueOf() String s2 = sb2.value(sb2); // 方式3: String类的构造方法 String s3 = new String(sb2); } |
2、StringBuilder
StringBuilder也是可变字符串,只不过不保证线程安全,于StringBuffer的方法基本一样
3、总结
|
| StringBuffer | StringBuilder | |
| 是字符串? | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 能改变? | 常量 | 能 | 能 |
| 线程安全? | 安全 | 安全 | 不安全 |
| 拼接效率 | 最慢 | 快 | 最快 |
| 出现版本 | JDK1.0 | JDK1.0 | JDK1.5 |
五、包装类
1、概念
包装类是一系列类的统称,将基本类型包装成类。包装成类以后就可以定义属性和方法以及创建对象,比起之前功能更加丰富
基本类型:byte short int long float double boolean char
包装类:Byte Short `Integer` Long Float Double Boolean Character
2、Integer
通过查看API发现这些包装类基本功能一致,就以Integer为例
| // 创建Integer对象 Integer i1 = new Integer(1); Integer i2 = new Integer("1"); // 获得其中的基本类型 int i = i1.intValue( ); // static toString() 可以将包装类变字符串 String s = i1.toString( ); // 字符串变成基本类型[非常重要] // static parseInt() int i3 = Integer.parseInt("1"); |
3、自动装箱拆箱
| public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i = 1;// 自动装箱 int a = i; // 自动拆箱 } |
4、总结
知道有这个包装类就可以,包装类是普通数据类型的上位替代
5、Character(了解)
Character主要是对单个字符操作的
| public static void main(String[] args) { // 判断是否是数字 System.out.println(Character.isDigit('a')); System.out.println(Character.isDigit('1')); // 判断是否是字母 System.out.println(Character.isLetter('a') ); System.out.println(Character.isLetter('1') ); // 判断是否是大写/小写 System.out.println(Character.isUpperCase('a') ); System.out.println(Character.isLowerCase('a') ); // 转换大写小写 char a = Character.toUpperCase('a'); System.out.println(a ); char a1 = Character.toLowerCase('A'); System.out.println(a1 ); } |
六、Math、Random
1、Math数学类
Math类是操作数学运算,方法和属性都是静态的,直接类名调用
| public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Math.abs(-1) );// 求绝对值 System.out.println(Math.min(1,2) );// 取最小值 System.out.println(Math.max(1,2) );// 取最大值 System.out.println(Math.ceil(11.1) );// 向上取整 System.out.println(Math.floor(11.1) );// 向下取整 System.out.println(Math.pow(2,3) );// 次幂 System.out.println(Math.pow(4,0.5) );// 次幂 System.out.println(Math.round(1.4) );// 四舍五入 System.out.println(Math.round(1.5) );// 四舍五入 } |
2、Random随机数
如果不想用Math下面的随机数,可以使用Random,专门做随机数的类
| public class RandomCaptcha { // 生成指定长度的随机数字验证码 public static String generateCaptcha(int length) { // 创建一个随机数生成器 Random random = new Random();
// 用于存储验证码的字符 StringBuilder captcha = new StringBuilder();
// 循环生成验证码的每个字符 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { // 生成一个随机数字,范围是 0 到 9 int digit = random.nextInt(10); captcha.append(digit); }
return captcha.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // 设置验证码长度为 6 int captchaLength = 6;
// 生成验证码 String captcha = generateCaptcha(captchaLength);
// 输出生成的验证码 System.out.println("随机生成的数字验证码: " + captcha); } } |
七、日期类
1、构造方法
| public static void main(String[] args) { // 空参构造,创建当前时间 Date date = new Date( ); System.out.println(date ); // 指定long型毫秒值创建时间 /** * 基础常识: 毫秒值的原点 * 1970-01-01 00:00:00 0.000 * * 1秒 = 1000毫秒 */ // 创建1970-01-02 Date date2 = new Date(1 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000); System.out.println(date2); // 指定年月日创建时间(过时了,不建议)2000-2-3 // 了解: 年份-1900,月份从0-11 Date date3 = new Date(100, 1, 3); System.out.println(date3); } |
2、方法
方法基本都是过时的,但是有两个还没过时
| // 获得毫秒值 long time = date.getTime( ); System.out.println(time ); // 给日期对象设置毫秒值(long型,需要加L),改变时间 date.setTime(1609775621813L); System.out.println(date ); |
3、实战应用场景
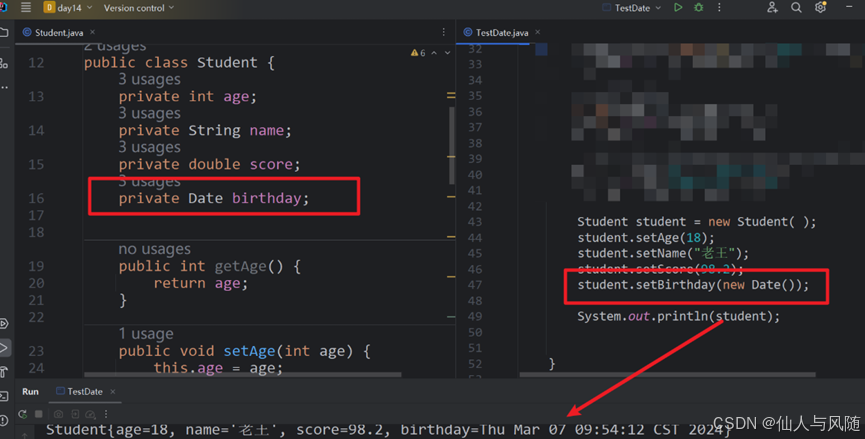
| import java.util.Date; //创建一个类,学生类 属性(整型年龄,字符串姓名,浮点型成绩,`日期型生日`)要封装,创建对象查看效果 class Student { private int age; private String name; private double score; private Date birth; public Student() { } public Student(int age, String name, double score, Date birth) { this.age = age; this.name = name; this.score = score; this.birth = birth; } /** * 获取 * @return age */ public int getAge() { return age; } /** * 设置 * @param age */ public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } /** * 获取 * @return name */ public String getName() { return name; } /** * 设置 * @param name */ public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * 获取 * @return score */ public double getScore() { return score; } /** * 设置 * @param score */ public void setScore(double score) { this.score = score; } /** * 获取 * @return birth */ public Date getBirth() { return birth; } /** * 设置 * @param birth */ public void setBirth(Date birth) { this.birth = birth; } public String toString() { return "Student{age = " + age + ", name = " + name + ", score = " + score + ", birth = " + birth + "}"; } } public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student stu = new Student(); stu.setName("张三"); stu.setAge(18); stu.setScore(98); stu.setBirth(new Date(2006-1900, 2, 11)); System.out.println(stu); } } |
八、SimpleDateFormat
格式化(format):是将日期对象 -> 字符串
解析(parse):是将字符串 -> 日期
日期解析和格式化需要指定模板:
{
y: 年
M: 月
d: 日
H: 24小时制 h是12小时制
m: 分
s: 秒
}
常用模板:
(1)yyyy/MM/dd 2024/03/07
(2)yy年M月d日 24年3月7日
(3)yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss 2024-03-07 10:04:50
| public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException { // 以指定模板创建对象 SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss"); // 格式化(日期 --> 字符串) Date date = new Date( ); String format = sdf.format(date); System.out.println(format ); // 解析(字符串 --> 日期) // parse方法源码中抛出了编译期异常,需要处理 // 解析成功的前提s 是 字符串要与日期模板一致 Date parse = sdf.parse("2020年01月01日"); System.out.println(parse ); } |
九、异常
1、概念
异常(Exception )就是程序中的报错,分为运行时异常和编译时异常。
(1)运行时异常(RuntimeException)时运行时才可能出现的异常,编码阶段不用特殊处理。
(2)编译时异常(除了运行时异常之外的都是编译时异常),编码阶段必须处理
入门案例:
运行时异常
| public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.运行时异常:点击运行的时候控制台会报错 //当Java运行的时候,出现了一些不可与之的错误 //jvm将异常实例化对应的异常对象 int i = 10 / 0;//ArithmeticException算术异常 int[] arr = new int[2]; arr[3] = 90;//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException数组索引越界异常 System.out.println("嘻嘻我来了");
} } |
编译时异常
| import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //2.编译时异常 SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); //Unhandled exception: java.text.ParseException //编译时异常 //Date parse = sdf.parse("2023-12-13 08:09:12"); //System.out.println(parse); //这也是编译时异常!!! //Thread.sleep(3000);//Unhandled exception: java.lang.InterruptedException } } |
2、异常的处理方式——抛出异常
在方法参数列表后、{}之前,使用 throws+异常类名 声明抛出的异常类,可以抛出多个异常,中间用逗号隔开
| public class Demo3 { //语法格式在方法参数列表后,{}前,使用 `throws+异常类名 `声明抛出的异常类 //告知调用者此处有异常 你写代码的时候要小心的!!! //throws 在运行时异常用法不太明朗!!! public static void main(String[] args) throws ArithmeticException{ System.out.println(1); System.out.println(2); System.out.println(3 / 0); System.out.println(4); System.out.println(5); } } |
抛出异常的效果
(1)方法抛出异常前正常执行
(2)抛出异常后会将信息打印到控制台
(3)后续代码不再执行
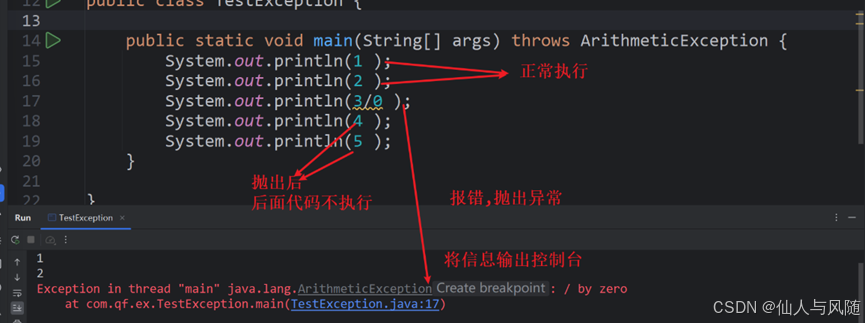
(4)异常是层层抛出的
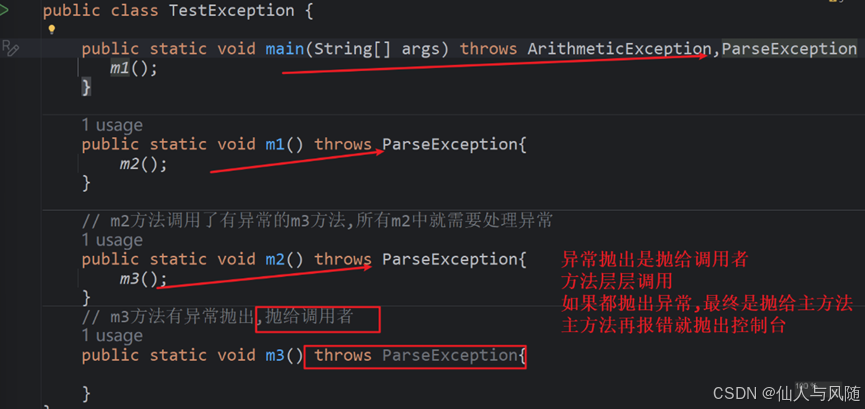
3、异常的处理方式——捕获异常
语法:
try{
//一些可能会出现异常的代码
}catch(异常类 对象名){
//如果上面有异常且能抓住,这里就会执行
}
执行顺序:
(1)try内代码如果没问题,catch内就不执行
(2)try内代码有报错,catch抓住后就执行
(3)try内部如果有报错,try代码从报错处往后不再执行
(4)无论有没有报错,try-catch后代码都会照常执行(比起抛出,捕获的好处)
| public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { test1(); } public static void test1 () { /*try { int i = 1 / 2; // by zero int[] arr = new int[2];//3 arr[3] = 90; }catch (ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("捕捉的异常是:" + e.getMessage()); }catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println("捕捉的异常是:" + e.getMessage()); }*/ //以上写法太麻烦了,写了好多catch //要求只能写一个catch 改进方案 /*try { int i = 1 / 2;// by zero int[] arr = new int[2];//3 arr[3] = 90; }catch (ArithmeticException | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println("捕捉的异常是:" + e.getMessage()); }*/ //太麻烦了, 还得写类。能不能只写一个Exception try { int i = 1 / 2;// by zero int[] arr = new int[2];//3 arr[3] = 90; }catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("捕捉的异常是:" + e.getMessage()); } } } |
4、finally
finally最终的,配合try或者try-catch一起使用,例如
| try{ //代码 }catch(E e) { // 代码 }finally{ // 代码 } |
fianlly里面的代码无论是抛出异常还是捕获异常,最终都会执行。基本用于关闭流的资源通道,释放资源(关闭通道,释放资源)
5、异常API
(1) getMessage(); 获得异常信息
(2) toString();将异常信息以字符串形式返回
(3)
主要使用getMessage();
| public static void main(String[] args) { try { /** * 1/0会报错,java虚拟机会自己创建一个异常对象 * 相对于 new ArithmeticException(); * 这里出错,就是将这个异常对象抛出 */ System.out.println(1/0 ); }catch (Exception e){// 这里抓住异常对象,相对于赋值 String message = e.getMessage( ); System.out.println("异常信息:" + message ); String string = e.toString( ); System.out.println("异常字符串:" + string );
e.printStackTrace();// 将异常信息打印 } } |
十、自定义异常
1、概念
像想一个问题: Java中封装了很多的异常类,但是生活中有很多异常的描述不了的!!!
例如: 没钱 单身 咋办? 自己写!!! 自定义异常
2、创建方法
(1)创建一个异常类,见名知意
(2)找到一个合适父异常类,比如Exception(继承时视为继承编译时异常),RuntimeException(继承时视为继承运行时异常)
(3)设置构造方法,将异常信息通过super传递给父类
(4)使用异常:在方法内部通过判断决定是否抛出异常或者捕获异常
3、案例
| //自定义的异常类 class SingleDogException extends Exception{ public SingleDogException (String message) { super(message);//不报错, 意味着 将message父类的有参构造方法 } } public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws SingleDogException { test1(); } public static void test1 () throws SingleDogException { boolean isSingle = true; if (isSingle) { //代码终止 让其抛出一个单身狗异常 自己造错!!! //throw 动作 抛的动作 模仿jvm虚拟机 自己抛出的异常对象 throw new SingleDogException("单身狗不能进店!!!"); } System.out.println("情侣可以进店购买专属的爱情信物!!!"); } } |
| class PriceOutOfBoundException extends RuntimeException { public PriceOutOfBoundException(double price) { super("价格:" + price + "越界, 钱不能为负数"); } } class Phone { private String name; private double price; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { if (price < 0) { throw new PriceOutOfBoundException(price); } this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Phone{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", price=" + price + '}'; } } public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Phone p1 = new Phone(); p1.setName("狗蛋"); p1.setPrice(1900); //p1.setPrice(-1900); System.out.println(p1); } } |





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








