假设有如下示例代码
import React, { useEffect, useRef, useState } from "react";
export default function App() {
const btn = useRef(null);
const [value, setValue] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
console.log("bind");
return () => console.log("unbind");
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
console.log("bind value");
return () => console.log("unbind value");
}, [value]);
return (
<div>
<button ref={btn} onClick={() => setValue(value + 1)}>
按钮
</button>
</div>
);
}这段代码的执行结果是:
当初始化组件时,输出bind和bind value;
当点击按钮后,输出unbind value和bind value;
当卸载组件时,输出unbind和unbind value。
一、初次挂载
render阶段
我们知道,react存在两个阶段:render阶段和commit阶段,而render阶段又分为beginWork和completeWork阶段,在beginWork阶段,对于IndeterminateComponent,我们会调用到renderWithHooks方法。(不清楚的可以看我之前的博客:react源码解析(一)协调器与渲染器-优快云博客)
当调用该方法时,首先我们会判断当前是否处于mount阶段,指定使用mount hook或者render hook。然后再去调用component方法,这里即是App函数。
export function renderWithHooks<Props, SecondArg>(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: (p: Props, arg: SecondArg) => any,
props: Props,
secondArg: SecondArg,
nextRenderLanes: Lanes,
): any {
currentlyRenderingFiber = workInProgress;
workInProgress.memoizedState = null;
workInProgress.updateQueue = null;
// ...
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
current === null || current.memoizedState === null
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
let children = Component(props, secondArg);
// ...
return children;
}当执行app函数时,我们会调用到useEffect方法,实际上是mount hook的useEffect方法。
export function useEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): void {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useEffect(create, deps);
}function resolveDispatcher() {
const dispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
return ((dispatcher: any): Dispatcher);
}那么mount阶段的useEffect是如何执行的呢?
1. 初始化Hook对象
2. currentlyRenderingFiber的memoizedState指针指向该组件的首个hook,workInProgress指向当前hook,如果当前hook是该组件的首个hook,那么修改currentlyRenderingFiber的memoizedState指针指向当前Hook,如果当前hook不是首个hook,那么就将其连接成链表,并更新workInProgress。
3. 给currentlyRenderingFiber打上PassiveEffect | PassiveStaticEffect flags,后续commit阶段会用到。
4. 初始化effect对象。
5. 对于useEffect而言,hook的memoizedState指向对应的effect对象,所有的effect对象连成单向的环形链表,currentRenderingFiber的updateQueue对象的lastEffect指针指向最后一个effect。
示例中的useRef和useState也会形成对应的hook对象,但不会形成effect对象,他们形成的hook对象的memoizedState会指向其他对象,本文章专注于useEffect,这两块暂且跳过。
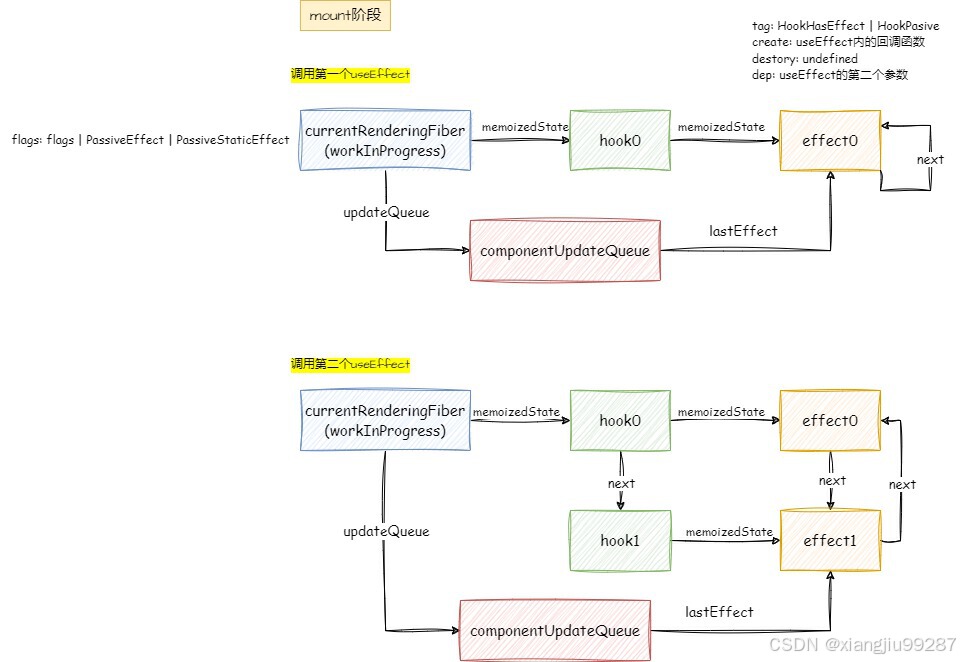
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
// ...
useEffect: mountEffect,
// ...
};function mountEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): void {
return mountEffectImpl(
PassiveEffect | PassiveStaticEffect,
HookPassive,
create,
deps,
);
}function mountEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps): void {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags;
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
create,
undefined,
nextDeps,
);
}function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}function pushEffect(tag, create, destroy, deps) {
const effect: Effect = {
tag,
create,
destroy,
deps,
// Circular
next: (null: any),
};
let componentUpdateQueue: null | FunctionComponentUpdateQueue = (currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue: any);
if (componentUpdateQueue === null) {
componentUpdateQueue = createFunctionComponentUpdateQueue();
currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue = (componentUpdateQueue: any);
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
} else {
const lastEffect = componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect;
if (lastEffect === null) {
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
} else {
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
lastEffect.next = effect;
effect.next = firstEffect;
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect;
}
}
return effect;
}接下来就是调用reconcileChildren,用diff算法创建出子fiber,依照从父节点到子节点的顺序执行beginWork,依照从子节点到父节点的顺序执行completeWork,最终进入commit阶段。
commit阶段
commit阶段会调用到commitRootImpl,这里面有个关键的方法是flushPassiveEffect,负责执行useEffect方法,并收集useEffect的返回值(即销毁时的回调函数)。我们将其传入scheduleCallback,那么调度器就会选择合适的时机执行该方法。
function commitRootImpl(
root: FiberRoot,
recoverableErrors: null | Array<CapturedValue<mixed>>,
transitions: Array<Transition> | null,
renderPriorityLevel: EventPriority,
) {
if (
(finishedWork.subtreeFlags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags ||
(finishedWork.flags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags
) {
if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true;
scheduleCallback(NormalSchedulerPriority, () => {
flushPassiveEffects();
return null;
});
}
}
}flushPassiveEffectsImpl提交了unmount副作用和mount副作用。
export function flushPassiveEffects(): boolean {
// ...
return flushPassiveEffectsImpl();
}function flushPassiveEffectsImpl() {
// ...
commitPassiveUnmountEffects(root.current);
commitPassiveMountEffects(root, root.current, lanes, transitions);
// ...
flushSyncCallbacks();
// ...
return true;
}假设我们存在如下示例代码
// App.jsx
import React, { useEffect, useRef, useState } from "react";
import Home from "./components/Home";
import User from "./components/User";
export default function App() {
const btn = useRef(null);
const [value, setValue] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
console.log("app bind");
return () => console.log("app unbind");
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
console.log("value bind");
return () => console.log("value unbind");
}, [value]);
return (
<div>
<button ref={btn} onClick={() => setValue(!value)}>
按钮
</button>
{value === true ? (
<>
<Home />
<User />
</>
) : (
<></>
)}
</div>
);
}
// Home.jsx
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
import Hello from "./Hello";
export default function Home() {
useEffect(() => {
console.log("home bind");
return () => console.log("home unbind");
}, []);
return <Hello />;
}
// Hello.jsx
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
export default function Hello() {
useEffect(() => {
console.log("hello bind");
return () => {
console.log("hello unbind");
};
}, []);
return <div>Hello</div>;
}
// User.jsx
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
export default function User() {
useEffect(() => {
console.log("user bind");
return () => console.log("user unbind");
}, []);
return <div>User</div>;
}
即页面结构如下。
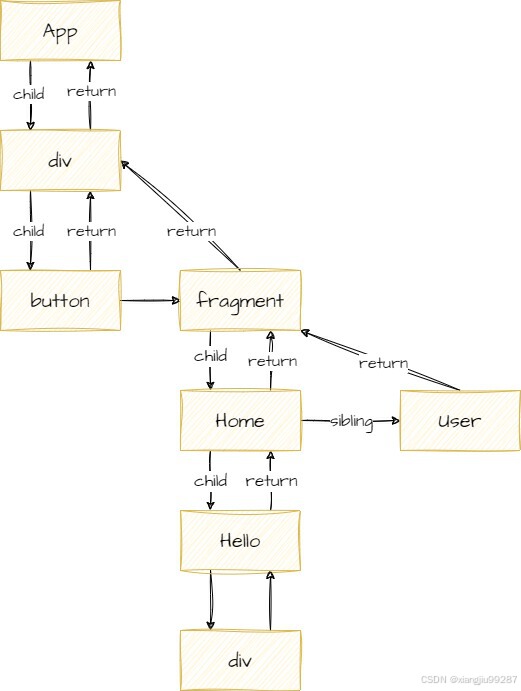
当页面初始化时,打印台输出内容为。

1. 这是因为在页面初始化时,effect.destory被初始化为undefined,所以不会执行umount副作用。
2. 当执行mount副作用时,采用的算法类似后序遍历,向下遍历直到child === null,执行该节点副作用,如果sibling !== null,继续遍历sibling的子节点,如果sibling === null,就向上递归回父节点执行副作用,如果sibling !== null,继续遍历sibling的子节点...直至所有节点的副作用都被执行。
3. 在执行完mount副作用后,返回值即为unmount的副作用函数,react会把其收集在effect.destory中,以便在update阶段调用。
具体实现代码
commitPassiveUnmountEffects
export function commitPassiveUnmountEffects(firstChild: Fiber): void {
nextEffect = firstChild;
commitPassiveUnmountEffects_begin();
}function commitPassiveUnmountEffects_begin() {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const fiber = nextEffect;
const child = fiber.child;
if ((nextEffect.flags & ChildDeletion) !== NoFlags) {
const deletions = fiber.deletions;
if (deletions !== null) {
for (let i = 0; i < deletions.length; i++) {
const fiberToDelete = deletions[i];
nextEffect = fiberToDelete;
commitPassiveUnmountEffectsInsideOfDeletedTree_begin(
fiberToDelete,
fiber,
);
}
// ...
nextEffect = fiber;
}
}
if ((fiber.subtreeFlags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags && child !== null) {
child.return = fiber;
nextEffect = child;
} else {
commitPassiveUnmountEffects_complete();
}
}
}function commitPassiveUnmountEffectsInsideOfDeletedTree_begin(
deletedSubtreeRoot: Fiber,
nearestMountedAncestor: Fiber | null,
) {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const fiber = nextEffect;
commitPassiveUnmountInsideDeletedTreeOnFiber(fiber, nearestMountedAncestor);
const child = fiber.child;
if (child !== null) {
child.return = fiber;
nextEffect = child;
} else {
commitPassiveUnmountEffectsInsideOfDeletedTree_complete(
deletedSubtreeRoot,
);
}
}
}function commitPassiveUnmountInsideDeletedTreeOnFiber(
current: Fiber,
nearestMountedAncestor: Fiber | null,
): void {
switch (current.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case SimpleMemoComponent: {
// ...
commitHookEffectListUnmount(
HookPassive,
current,
nearestMountedAncestor,
);
}
break;
}
// ...
}
}function commitPassiveUnmountEffectsInsideOfDeletedTree_complete(
deletedSubtreeRoot: Fiber,
) {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const fiber = nextEffect;
const sibling = fiber.sibling;
const returnFiber = fiber.return;
if (deletedTreeCleanUpLevel >= 2) {
// Recursively traverse the entire deleted tree and clean up fiber fields.
// This is more aggressive than ideal, and the long term goal is to only
// have to detach the deleted tree at the root.
detachFiberAfterEffects(fiber);
if (fiber === deletedSubtreeRoot) {
nextEffect = null;
return;
}
} else {
// This is the default branch (level 0). We do not recursively clear all
// the fiber fields. Only the root of the deleted subtree.
if (fiber === deletedSubtreeRoot) {
detachFiberAfterEffects(fiber);
nextEffect = null;
return;
}
}
if (sibling !== null) {
sibling.return = returnFiber;
nextEffect = sibling;
return;
}
nextEffect = returnFiber;
}
}function commitPassiveUnmountEffects_complete() {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const fiber = nextEffect;
if ((fiber.flags & Passive) !== NoFlags) {
commitPassiveUnmountOnFiber(fiber);
}
const sibling = fiber.sibling;
if (sibling !== null) {
sibling.return = fiber.return;
nextEffect = sibling;
return;
}
nextEffect = fiber.return;
}
}function commitPassiveUnmountOnFiber(finishedWork: Fiber): void {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case SimpleMemoComponent: {
commitHookEffectListUnmount(
HookPassive | HookHasEffect,
finishedWork,
finishedWork.return,
);
break;
}
}
}function commitHookEffectListUnmount(
flags: HookFlags,
finishedWork: Fiber,
nearestMountedAncestor: Fiber | null,
) {
const updateQueue: FunctionComponentUpdateQueue | null = (finishedWork.updateQueue: any);
const lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null;
if (lastEffect !== null) {
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
let effect = firstEffect;
do {
if ((effect.tag & flags) === flags) {
// Unmount
const destroy = effect.destroy;
effect.destroy = undefined;
if (destroy !== undefined) {
safelyCallDestroy(finishedWork, nearestMountedAncestor, destroy);
}
}
effect = effect.next;
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
}
}function safelyCallDestroy(
current: Fiber,
nearestMountedAncestor: Fiber | null,
destroy: () => void,
) {
// ...
destroy();
// ...
}commitPassiveMountEffects
export function commitPassiveMountEffects(
root: FiberRoot,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedLanes: Lanes,
committedTransitions: Array<Transition> | null,
): void {
nextEffect = finishedWork;
commitPassiveMountEffects_begin(
finishedWork,
root,
committedLanes,
committedTransitions,
);
}function commitPassiveMountEffects_begin(
subtreeRoot: Fiber,
root: FiberRoot,
committedLanes: Lanes,
committedTransitions: Array<Transition> | null,
) {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const fiber = nextEffect;
const firstChild = fiber.child;
if ((fiber.subtreeFlags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags && firstChild !== null) {
firstChild.return = fiber;
nextEffect = firstChild;
} else {
commitPassiveMountEffects_complete(
subtreeRoot,
root,
committedLanes,
committedTransitions,
);
}
}
}function commitPassiveMountEffects_complete(
subtreeRoot: Fiber,
root: FiberRoot,
committedLanes: Lanes,
committedTransitions: Array<Transition> | null,
) {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const fiber = nextEffect;
if ((fiber.flags & Passive) !== NoFlags) {
commitPassiveMountOnFiber(
root,
fiber,
committedLanes,
committedTransitions,
);
}
if (fiber === subtreeRoot) {
nextEffect = null;
return;
}
const sibling = fiber.sibling;
if (sibling !== null) {
sibling.return = fiber.return;
nextEffect = sibling;
return;
}
nextEffect = fiber.return;
}
}function commitPassiveMountOnFiber(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedLanes: Lanes,
committedTransitions: Array<Transition> | null,
): void {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case SimpleMemoComponent: {
commitHookEffectListMount(HookPassive | HookHasEffect, finishedWork);
break;
}
// ...
}
}function commitHookEffectListMount(flags: HookFlags, finishedWork: Fiber) {
const updateQueue: FunctionComponentUpdateQueue | null = (finishedWork.updateQueue: any);
const lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null;
if (lastEffect !== null) {
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
let effect = firstEffect;
do {
if ((effect.tag & flags) === flags) {
// Mount
const create = effect.create;
effect.destroy = create();
}
effect = effect.next;
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
}
}flushSyncCallbacks
执行副作用可能会产生新的副作用,这些新产生的副作用会立即同步执行。
export function flushSyncCallbacks() {
if (!isFlushingSyncQueue && syncQueue !== null) {
// Prevent re-entrance.
isFlushingSyncQueue = true;
let i = 0;
const previousUpdatePriority = getCurrentUpdatePriority();
try {
const isSync = true;
const queue = syncQueue;
setCurrentUpdatePriority(DiscreteEventPriority);
for (; i < queue.length; i++) {
let callback = queue[i];
do {
callback = callback(isSync);
} while (callback !== null);
}
syncQueue = null;
includesLegacySyncCallbacks = false;
} catch (error) {
// If something throws, leave the remaining callbacks on the queue.
if (syncQueue !== null) {
syncQueue = syncQueue.slice(i + 1);
}
// Resume flushing in the next tick
scheduleCallback(ImmediatePriority, flushSyncCallbacks);
throw error;
} finally {
setCurrentUpdatePriority(previousUpdatePriority);
isFlushingSyncQueue = false;
}
}
return null;
}二、更新
render阶段
当我们点击按钮时,会重新进入render阶段和commit阶段,render的beginWork阶段会重新调用renderWithHooks,这导致重新执行App函数,执行useEffect方法。不同的是,这次我们执行的是update hooks。
update hook的流程为:
1. 对于useEffect而言,new hook除next属性以外,其他属性均拷贝自current hook
2. 对比新旧dep依赖值是否改变,决定给effect和fiber打什么标记。如果依赖值改变,effect.tag = HookHasEffect | HookPassive,fiber.flags |= PassiveEffect;如果依赖值未变,effect.tag = HookPassive,fiber.flags不变。该标识跟后面副作用是否执行有关。
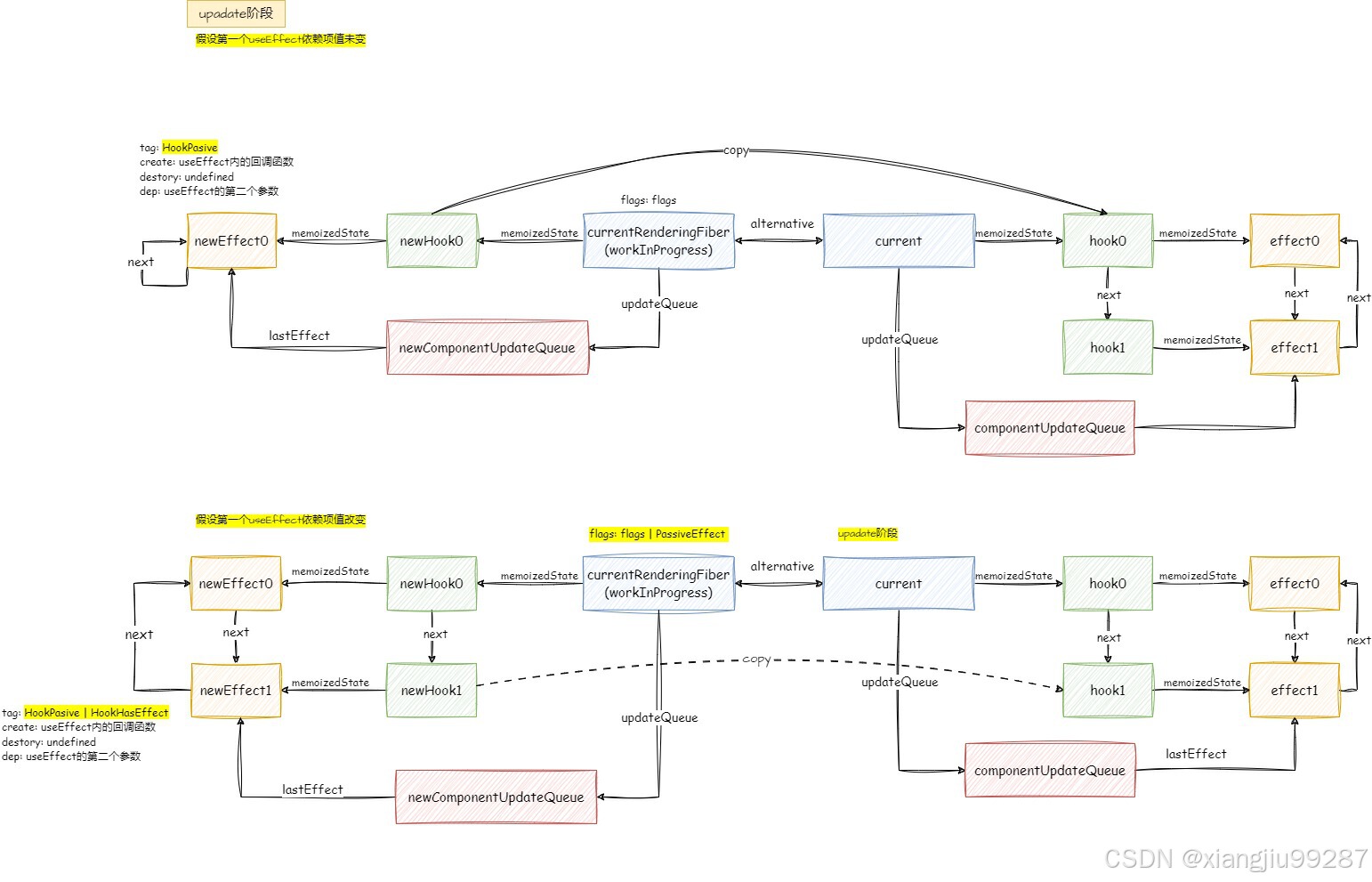
function updateEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): void {
return updateEffectImpl(PassiveEffect, HookPassive, create, deps);
}function updateEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps): void {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
let destroy = undefined;
if (currentHook !== null) {
const prevEffect = currentHook.memoizedState;
destroy = prevEffect.destroy;
if (nextDeps !== null) {
const prevDeps = prevEffect.deps;
if (areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) {
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps);
return;
}
}
}
currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags;
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
create,
destroy,
nextDeps,
);
}function updateWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
let nextCurrentHook: null | Hook;
if (currentHook === null) {
const current = currentlyRenderingFiber.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
nextCurrentHook = current.memoizedState;
} else {
nextCurrentHook = null;
}
} else {
nextCurrentHook = currentHook.next;
}
let nextWorkInProgressHook: null | Hook;
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
nextWorkInProgressHook = currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState;
} else {
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
}
if (nextWorkInProgressHook !== null) {
// There's already a work-in-progress. Reuse it.
workInProgressHook = nextWorkInProgressHook;
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
} else {
// Clone from the current hook.
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
const newHook: Hook = {
memoizedState: currentHook.memoizedState,
baseState: currentHook.baseState,
baseQueue: currentHook.baseQueue,
queue: currentHook.queue,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list.
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = newHook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list.
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = newHook;
}
}
return workInProgressHook;
}commit阶段
还是上面那个例子,当我们点击按钮时,Home组件和User组件都会被卸载,打印台输出如下。

可以看到,前四个是unmount副作用,最后一个是mount的副作用。前三个unmount副作用是组件卸载导致的,第四个mount副作用是value值变化导致的。
unmount
1. unmount副作用的执行顺序是先找到有副作用的最小子树(fragment),发现这个fragment fiber被打上了删除标记,所以先执行被删除子节点的副作用。在执行被删除子节点副作用时,用到的算法类似于前序遍历,即先执行被删除最左子节点Home的副作用,再执行其子节点Hello的副作用,再执行div的副作用,由于div是叶子结点,且其没有兄弟节点,故向上递归,由于Hello也没有兄弟节点,继续向上递归,到达Home,完成第一个被删除子节点Home的副作用执行。继续执行第二个被删除子节点User的副作用...
2. 在执行完被删除子树的副作用后,执行本节点的副作用,不同的是,由于本节点未被卸载,所以只有依赖数组对应的值改变时,我们才会执行其副作用。在执行完本节点副作用后,如果存在右兄弟节点,会执行兄弟节点的删除子树及自身的副作用,如果不存在有兄弟节点,那就向上递归执行父节点副作用。这段执行逻辑就类似于后序遍历。
mount
mount阶段跟上次初次挂载的执行逻辑基本相同,不同的是只有依赖数组值改变的副作用才会被执行。
我们知道,依赖数组值改变的effect会被打上HookHasEffect | HookPassive,依赖数组未改变的effect会被打上HookPassive。对于删除的子树,我们传入的对比标定值是HookPassive,所以无论依赖数组是否改变,都会执行该副作用;对于未删除的子树,我们传入的标定值是HookHasEffect | HookPassive,所以只有依赖数组改变,才会执行副作用。由于在执行完unmount副作用后,我们会断开与删除子树的child连接,所以就算依赖数组改变,也不会执行删除数组的mount副作用。
function commitPassiveUnmountInsideDeletedTreeOnFiber(
current: Fiber,
nearestMountedAncestor: Fiber | null,
): void {
// ...
commitHookEffectListUnmount(
HookPassive,
current,
nearestMountedAncestor,
);
}
// ...
}
function commitPassiveUnmountOnFiber(finishedWork: Fiber): void {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case SimpleMemoComponent: {
commitHookEffectListUnmount(
HookPassive | HookHasEffect,
finishedWork,
finishedWork.return,
);
break;
}
}
}function commitPassiveMountOnFiber(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedLanes: Lanes,
committedTransitions: Array<Transition> | null,
): void {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case SimpleMemoComponent: {
commitHookEffectListMount(HookPassive | HookHasEffect, finishedWork);
break;
}
// ...
}
}






















 418
418

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








