任务1
- 题目
二叉检索树即 BST,是利用二叉树的非线性关系,结合数据之间的大小关系进行存储的一种用于检索数据的数据结构。一般情况下,对信息进行检索时,都需要指定检索关键码(Key),根据该关键字找到所需要的信息(比如学生信息里关键码是学号,而姓名等信息就是该关键码对应的信息),所以当提到检索时,都会有“键值对”这个概念,用(key,value)表示键值和对应信息的关系。
下面的二叉检索树的 ADT 在描述时,依然使用了模板类的方法,并且在这次描述中,使用了两个模板参数 K 和 V(这表明 key 和 value 可以为不同类型的数据)。在本次任务的测试文件中,key 和 value 都是 String 类型,对模板参数运用有困难的同学,可以直接设定 key 和 value 的类型为 String。
在本次实验中,主要完成的任务是:
1、为指定的 BST ADT实现数据结构。
2、用给定的输入数据文件验证所实现的数据结构是否正确。
为了方便进行测试验证,对BST 的各种操作指定了相应的命令符号,具体的符号含义如下:
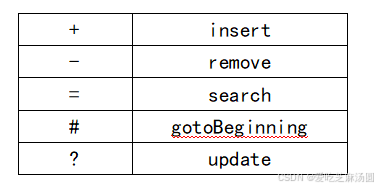
实验完成之后,必须通过实验中提供的测试用例。借助测试用例的运行结果,用来检查所撰写的代码功能是否正确。
测试用例中的每一行的内容都类似于上表中的每一行“命令行内容”列中所指示的内容。要求每执行一行,就调用 List 接口中的 showStructure 行为,用以验证该命令行的执行是否正确。
每行“命令行内容”都不是独立的,是针对同一个 List 类型的对象实例运行的结果。实验包里包括了个文件,一个是“list_testcase.txt”,其内包含了测试用例;另一个是“list_result.txt”,其内包含了对应测试用例的运行结果。
- 数据设计
这个BST的实现是一个通用的、基于泛型的二叉搜索树,支持任何实现了Comparable接口的键类型。递归是实现插入、删除、搜索和更新等操作的主要手段。
BSTNode类包括K key:键,用于比较节点的大小关系;V value:值,存储在节点中的数据;BSTNode<K, V> left:左子节点;BSTNode<K, V> right:右子节点。
- static class BSTNode<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
- K key;
- V value;
- BSTNode<K, V> left;
- BSTNode<K, V> right;
- public BSTNode(K key, V value, BSTNode<K, V> left, BSTNode<K, V> right) {
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- this.left = left;
- this.right = right;
- }
- }
insert(K key, V value) 方法接受一个键值对作为输入,将其插入到二叉搜索树中。方法首先检查输入的键和值是否为 null,如果是则抛出异常。然后,调用 doInsert 方法来执行实际的插入操作,同时更新根节点。
doInsert 方法是一个私有的递归方法,它接受一个节点、一个键和一个值作为输入,并返回更新后的节点。在 doInsert(BSTNode<K, V> node, K key, V value) 方法中,首先检查节点是否为 null。如果节点为 null,说明当前位置是一个合适的插入点,于是创建一个新的节点,并将键值对存储在新节点中,然后返回新节点。如果节点不为 null,那么需要根据键的大小关系选择向左子树或右子树递归插入。如果键小于当前节点的键,则递归调用 doInsert 方法,传入当前节点的左子节点,键和值,并将返回的结果赋值给当前节点的左子节点。如果键大于当前节点的键,则递归调用 doInsert 方法,传入当前节点的右子节点,键和值,并将返回的结果赋值给当前节点的右子节点。如果键等于当前节点的键,则更新当前节点的值。
时间复杂度分析:对于 insert(K key, V value) 方法,除了调用 doInsert 方法外,其他操作都是常数时间操作,不会对时间复杂度产生影响。而 doInsert 方法是一个递归方法,其时间复杂度取决于树的高度。在平衡的情况下,二叉搜索树的高度可以近似为 log(n),其中 n 是树中节点的数量。因此,在平衡的情况下,insert 方法的时间复杂度为 O(log n)。然而,如果二叉搜索树不平衡,即树的高度接近于 n,那么插入操作的时间复杂度可能接近于 O(n)。
- @Override
- public void insert(K key, V value) {
- if (key == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Key cannot be null");
- }
- if (value == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Value cannot be null");
- }
- root = doInsert(root, key, value); // 更新根节点
- }
- private BSTNode<K, V> doInsert(BSTNode<K, V> node, K key, V value) {
- if (node == null) {
- return new BSTNode<>(key, value, null, null); // 创建新节点并返回
- }
- if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0) {
- node.left = doInsert(node.left, key, value); // 递归插入左子树
- } else if (key.compareTo(node.key) > 0) {
- node.right = doInsert(node.right, key, value); // 递归插入右子树
- } else {
- node.value = value; // 更新节点值
- }
- return node;
- }
remove(K key) 方法接受一个键作为输入,从二叉搜索树中删除对应的节点,并返回删除节点的值。方法首先将 removeValue 设置为 null,然后检查输入的键是否为 null,如果是则抛出异常。接着,调用 removeHelp 方法执行实际的删除操作,并更新根节点。最后,返回删除节点的值。
在 removeHelp(BSTNode<K, V> root, K key) 方法中,首先检查根节点是否为 null。如果根节点为 null,说明树为空,直接返回 null。接下来,根据键和根节点的键的大小关系,选择向左子树或右子树递归删除。如果键小于根节点的键,则递归调用 removeHelp 方法,并将返回的结果赋值给根节点的左子节点。如果键大于根节点的键,则递归调用 removeHelp 方法,并将返回的结果赋值给根节点的右子节点。如果键等于根节点的键,那么需要考虑不同情况下的节点删除操作:
如果根节点没有左子节点,将 removeValue 设置为根节点的值,然后将根节点指向其右子节点,完成删除操作。
如果根节点没有右子节点,将 removeValue 设置为根节点的值,然后将根节点指向其左子节点,完成删除操作。
如果根节点既有左子节点又有右子节点,需要找到右子树中的最小节点(即右子树中最左边的节点),将其键和值替换到根节点中,然后递归地删除右子树中的最小节点,并将返回的结果赋值给根节点的右子节点。
此外,还有两个辅助方法 getMinNode 和 removeMinNode。getMinNode 方法用于获取指定树中的最小节点,它通过递归地向左子树寻找最小节点,并返回结果。removeMinNode 方法用于删除指定树中的最小节点,它通过递归地删除左子树中的最小节点,并将返回的结果赋值给当前节点的左子节点。
时间复杂度分析:对于 remove(K key) 方法,除了调用 removeHelp 方法外,其他操作都是常数时间操作,不会对时间复杂度产生影响。而 removeHelp 方法是一个递归方法,其时间复杂度取决于树的高度。在平衡的情况下,二叉搜索树的高度可以近似为 log(n),其中 n 是树中节点的数量。因此,在平衡的情况下,删除操作的时间复杂度为 O(log n)。然而,如果二叉搜索树不平衡,即树的高度接近于 n,那么删除操作的时间复杂度可能接近于 O(n)。
- @Override
- public V remove(K key) {
- removeValue = null;
- if (key == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Key cannot be null");
- }
- root = removeHelp(root, key);
- return removeValue;
- }
- private BSTNode<K, V> removeHelp(BSTNode<K, V> root, K key) {
- if (root == null)
- return null;
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) < 0) {
- root.left = removeHelp(root.left, key);
- } else if (key.compareTo(root.key) > 0) {
- root.right = removeHelp(root.right, key);
- } else {
- if (root.left == null) {
- removeValue = root.value;
- root = root.right;
- } else if (root.right == null) {
- removeValue = root.value;
- root = root.left;
- } else {
- BSTNode<K, V> minNode = getMinNode(root.right);
- removeValue = root.value;
- root.key = minNode.key;
- root.value = minNode.value;
- root.right = removeMinNode(root.right);
- }
- }
- return root;
- }
- private BSTNode<K, V> getMinNode(BSTNode<K, V> root) {
- if (root.left == null)
- return root;
- else
- return getMinNode(root.left);
- }
- private BSTNode<K, V> removeMinNode(BSTNode<K, V> root) {
- if (root.left == null) {
- return root.right;
- }
- root.left = removeMinNode(root.left);
- return root;
- }
search(K key) 方法接受一个键作为输入,从二叉搜索树中查找对应的值,并返回该值。方法首先检查输入的键是否为 null,如果是则抛出异常。接下来,调用私有方法 search,并传入根节点和键进行递归查找。最后,返回查找结果。
在 search(BSTNode<K, V> root, K key) 方法中,首先检查根节点是否为 null。如果根节点为 null,说明树为空,直接返回 null。接下来,根据键和根节点的键的大小关系,选择向左子树或右子树递归查找。如果键小于根节点的键,则递归调用 search 方法,并传入根节点的左子节点和键进行查找。如果键大于根节点的键,则递归调用 search 方法,并传入根节点的右子节点和键进行查找。如果键等于根节点的键,则找到了对应的节点,直接返回该节点的值。
时间复杂度分析:对于 search(K key) 方法,除了调用 search 方法外,其他操作都是常数时间操作,不会对时间复杂度产生影响。而 search 方法是一个递归方法,其时间复杂度取决于树的高度。在平衡的情况下,二叉搜索树的高度可以近似为 log(n),其中 n 是树中节点的数量。因此,在平衡的情况下,搜索操作的时间复杂度为 O(log n)。然而,如果二叉搜索树不平衡,即树的高度接近于 n,那么搜索操作的时间复杂度可能接近于 O(n)。
- @Override
- public V search(K key) {
- if (key == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Key cannot be null");
- }
- return search(root, key);
- }
- private V search(BSTNode<K, V> root, K key) {
- if (root == null)
- return null;
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) < 0)
- return search(root.left, key);//小于当前key值则往左子树查找
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) > 0)
- return search(root.right, key);//大于当前key值则往右子树查找
- return root.value;//找到值
- }
update(K key, V value) 方法接受一个键和一个值作为输入,用于更新二叉搜索树中指定键对应的节点的值,并返回一个布尔值表示更新是否成功。方法首先检查输入的键和值是否为 null,如果是则抛出异常。接下来,调用私有方法 update,并传入根节点、键和值进行递归更新。最后,返回更新结果。
在 update(BSTNode<K, V> root, K key, V value) 方法中,首先检查键是否等于根节点的键。如果相等,说明找到了要更新的节点,将节点的值更新为输入的值,并返回 true 表示更新成功。如果键小于根节点的键,则递归调用 update 方法,并传入根节点的左子节点、键和值进行更新。如果键大于根节点的键,则递归调用 update 方法,并传入根节点的右子节点、键和值进行更新。如果以上情况都不满足,说明树中不存在指定的键,返回 false 表示更新失败。
时间复杂度分析:对于 update(K key, V value) 方法,除了调用 update 方法外,其他操作都是常数时间操作,不会对时间复杂度产生影响。而 update 方法是一个递归方法,其时间复杂度取决于树的高度。在平衡的情况下,二叉搜索树的高度可以近似为 log(n),其中 n 是树中节点的数量。因此,在平衡的情况下,更新操作的时间复杂度为 O(log n)。然而,如果二叉搜索树不平衡,即树的高度接近于 n,那么更新操作的时间复杂度可能接近于 O(n)。
- @Override
- public boolean update(K key, V value) {
- if (key == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Key cannot be null");
- }
- if (value == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Value cannot be null");
- }
- return update(root, key, value);
- }
- public boolean update(BSTNode<K, V> root, K key, V value) {
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) == 0) {
- root.value = value;
- return true;
- }
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) < 0)
- return update(root.left, key, value);
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) > 0)
- return update(root.right, key, value);
- return false;
- }
isEmpty方法:判断树是否为空,即根节点是否为null。时间复杂度为O(1)。
clear方法:将根节点置为null,清空整个树。时间复杂度为O(1)。
- @Override
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return root == null;
- }
- @Override
- public void clear() {
- root = null;
- }
showStructure(PrintWriter pw) 方法用于将二叉搜索树的结构信息输出到给定的 PrintWriter。方法首先调用 countNodes 方法获取二叉搜索树的节点数量,然后调用 getHeight 方法获取二叉搜索树的高度。接下来,输出一些描述性信息,包括节点数量和树的高度。最后,通过调用 pw.flush() 来确保输出立即被写入到目标中。
countNodes(BSTNode<K, V> node) 方法用于递归计算以给定节点为根的二叉搜索树的节点数量。如果节点为 null,则返回 0。否则,递归调用 countNodes 方法计算左子树和右子树的节点数量,并将其加上当前节点的数量(1),然后返回结果。
getHeight(BSTNode<K, V> node) 方法用于递归计算以给定节点为根的二叉搜索树的高度。如果节点为 null,则返回 0。否则,递归调用 getHeight 方法计算左子树和右子树的高度,并取两者中的最大值,然后加上当前节点的高度(1),最后返回结果。
时间复杂度分析:countNodes 和 getHeight 方法都是递归方法,其时间复杂度取决于树的高度。在平衡的情况下,二叉搜索树的高度可以近似为 log(n),其中 n 是树中节点的数量。因此,这两个方法的时间复杂度为 O(log n)。需要注意的是,这里的时间复杂度是在遍历整个树的情况下。对于 showStructure 方法,除了调用 countNodes 和 getHeight 方法外,其他操作都是常数时间操作,不会对时间复杂度产生影响。
- @Override
- public void showStructure(PrintWriter pw) {
- int numberOfNode = countNodes(root);
- int height = getHeight(root);
- pw.println("-----------------------------");
- pw.print("There are ");
- pw.print(numberOfNode);
- pw.println(" nodes in this BST.");
- pw.print("The height of this BST is ");
- pw.print(height);
- pw.println(".");
- pw.println("-----------------------------");
- //使用 pw.flush() 是为了确保 showStructure 方法中的输出被立即写入到目标中,而不是等待缓冲区满或程序结束时才进行写入。
- pw.flush();
- }
- private int countNodes(BSTNode<K, V> node) {
- if (node == null) {
- return 0;
- }
- int leftCount = countNodes(node.left);
- int rightCount = countNodes(node.right);
- return 1 + leftCount + rightCount;
- }
- private int getHeight(BSTNode<K, V> node) {
- if (node == null) {
- return 0;
- }
- int leftHeight = getHeight(node.left);
- int rightHeight = getHeight(node.right);
- return 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
- }
printInorder(PrintWriter pw) 方法用于将二叉搜索树按照中序遍历的顺序输出到给定的 PrintWriter。首先,方法检查传入的 PrintWriter 是否为 null,如果是,则抛出 NullPointerException。接下来,调用私有方法 inorderTraversal,并传入根节点和 PrintWriter 进行中序遍历输出。
inorderTraversal(BSTNode<K, V> node, PrintWriter pw) 方法是一个递归方法,用于实现中序遍历。如果当前节点不为 null,则先递归调用 inorderTraversal 方法遍历当前节点的左子树,然后将当前节点的键和值输出到 PrintWriter,最后再递归调用 inorderTraversal 方法遍历当前节点的右子树。通过这种方式,可以按照中序遍历的顺序输出二叉搜索树的节点。
时间复杂度分析:中序遍历的时间复杂度取决于树的节点数量。在最坏的情况下,即二叉搜索树是一个完全不平衡的链表时,需要遍历所有的节点,时间复杂度为 O(n)。在平衡的情况下,二叉搜索树的高度可以近似为 log(n),其中 n 是树中节点的数量。
- @Override
- public void printInorder(PrintWriter pw) {
- if (pw == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("PrintWriter不能为空");
- }
- inorderTraversal(root, pw);
- }
- private void inorderTraversal(BSTNode<K, V> node, PrintWriter pw) {
- if (node != null) {
- inorderTraversal(node.left, pw);
- pw.println("[" + node.key + " --- <" + node.value + ">]");
- inorderTraversal(node.right, pw);
- }
- }
- 算法设计
当实现了BST的数据结构后,剩下比较难办的就是怎么用StreamTokenizer实现命令行。
每当我们输入一个回车,程序都会相应的作出一系列动作,那么我们可以把根据行读入,根据输入的内容做出回应。
- String line;
- while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
- executeCommand(bstTree, line);
- writer.flush(); // 刷新PrintWriter的缓冲区
- }
为了方便起见,我们把读取标记并进行相对应的动作用方法抽离出来:
- private static <K extends Comparable<K>, V> void executeCommand(BSTTree<K, V> bstTree, String line) throws IOException {
- StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(new StringReader(line));
- int token = st.nextToken();
- while (token != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF) {
- char command = (char) st.ttype;
- switch (command) {
- case '+' -> {
- ......
- }
- case '-' -> {
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- token = st.nextToken();
- }
- }
当读取到+时,分别读取+后面的Key和Value并调用bsttree的insert方法。在bsttree插入对应的key和value。
- case '+' -> {
- //+( conflagration , "n.建筑物或森林大火" )
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- V value = (V) st.sval;
- bstTree.insert(key, value);
- }
当读取到-时,读取-后面的Key并调用bsttree的remove方法。在bsttree删除对应的key和value,并根据是否删除成功输出对应的语句。
- case '-' -> {
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- V value = bstTree.remove(key);
- if (value == null) {
- writer.println("remove unsuccess ---" + key);
- } else {
- writer.println("remove success ---" + key + " " + value);
- }
- }
当读取到?时,读取?后面的Key并调用bsttree的search方法。在bsttree查询对应的key和value,并根据是否查询成功输出对应的语句。
- case '?' -> {
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- V value = bstTree.search(key);
- if (value == null) {
- writer.println("search unsuccess ---" + key);
- } else {
- writer.println("search success ---" + key + " " + value);
- }
- }
当读取到=时,分别读取=后面的key和value并调用bsttree的update方法。在bsttree更新对应的key和value,并输出更新成功的语句。
- case '=' -> {
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- V value = (V) st.sval;
- bstTree.update(key, value);
- writer.println("update success ---" + key + " " + value);
- }
当读取到#就调用showStructure方法。
- case '#' ->bstTree.showStructure(writer);
最后,我们为了验证输出与标准答案是否一致,还需要一个验文本文件比较器。
- package Homework01;
- import java.io.BufferedReader;
- import java.io.FileReader;
- import java.io.IOException;
- public class TextFileComparator {
- public static boolean compareFiles(String filePath1, String filePath2) {
- try (BufferedReader reader1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath1));
- BufferedReader reader2 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath2))) {
- String line1, line2;
- while ((line1 = reader1.readLine()) != null) {
- line2 = reader2.readLine();
- if (!line1.equals(line2)) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- // Check if file2 has additional lines
- return reader2.readLine() == null;
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- return false;
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String file1 = "D:\\develop\\projects\\dataStructure\\homework03\\file\\homework3_result.txt";
- String file2 = "D:\\develop\\projects\\dataStructure\\homework03\\file\\output.txt";
- boolean areEqual = compareFiles(file1, file2);
- if (areEqual) {
- System.out.println("两个文件的内容相同");
- } else {
- System.out.println("两个文件的内容不同");
- }
- }
- }
- 运行结果展示
我们可以直接把输出打印在控制台,部分结果如下:
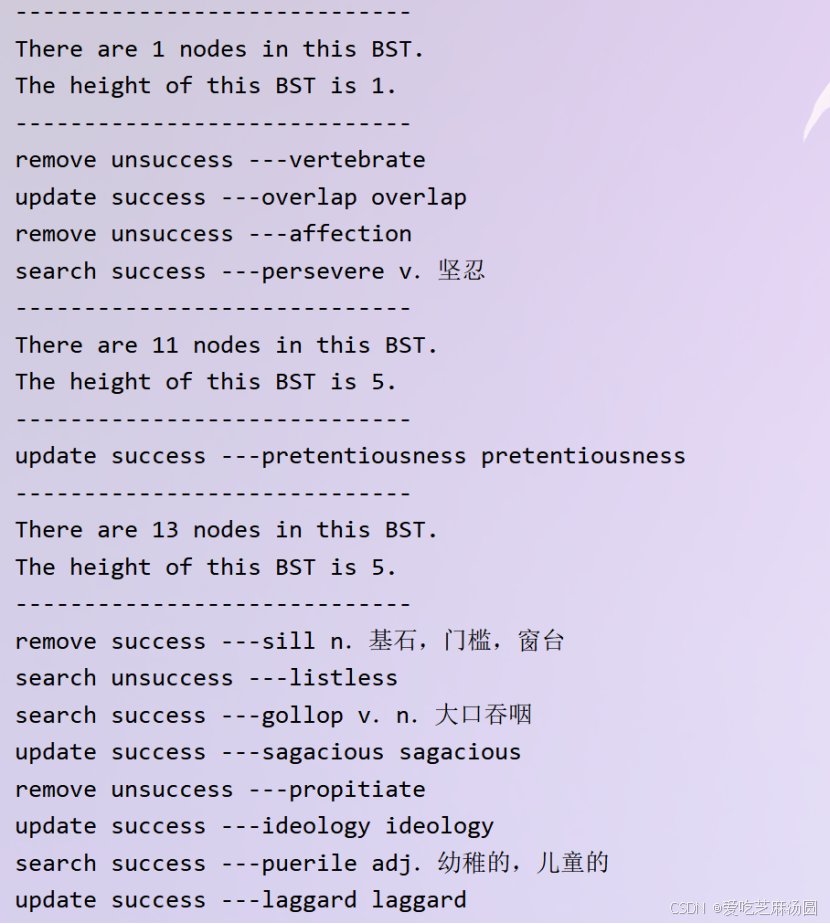
图1 测试结果图(部分)
用人眼无法看出来我们打印在控制台的和答案是否相同,所以我们将PrintWriter打印到一个文件output.txt中,再比较两个文件是否相同。为此写了一个类TextFileComparator。
- package Homework01;
- import java.io.BufferedReader;
- import java.io.FileReader;
- import java.io.IOException;
- public class TextFileComparator {
- public static boolean compareFiles(String filePath1, String filePath2) {
- try (BufferedReader reader1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath1));
- BufferedReader reader2 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath2))) {
- String line1, line2;
- while ((line1 = reader1.readLine()) != null) {
- line2 = reader2.readLine();
- if (!line1.equals(line2)) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- // Check if file2 has additional lines
- return reader2.readLine() == null;
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- return false;
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String file1 = "D:\\develop\\projects\\dataStructure\\homework03\\file\\homework3_result.txt";
- String file2 = "D:\\develop\\projects\\dataStructure\\homework03\\file\\output.txt";
- boolean areEqual = compareFiles(file1, file2);
- if (areEqual) {
- System.out.println("两个文件的内容相同");
- } else {
- System.out.println("两个文件的内容不同");
- }
- }
- }
结果如下:

图2 用TextFileComparator文件比较器对比结果图
- 总结和收获
通过这个实验,首先练习了BST这种数据结构,并复习了泛型的使用,学习了StreamTokenizer类的使用,学会了文件相关的方法和流。收获很大。
附录:
- 任务1
- BST的ADT:
- package Homework01;
- import java.io.PrintWriter;
- public interface BST <K extends Comparable<K>, V>{
- /**
- * @Precondition 二叉查找树未满。
- * Key和value不能为null。
- * @Postcondition 向二叉查找树中插入一个新元素(包括键和值)。
- * 如果树中已经存在具有相同键值的元素,则使用newElement的value字段更新该元素的value字段。
- * @return none
- */
- public void insert(K key, V value);
- /**
- * @Precondition Key不为空。
- * @Postcondition 从二叉查找树中删除具有相同键值的元素。
- * 如果树中不存在具有相同键值的元素,则返回null。
- * 否则,返回元素的value字段。
- * @return value
- */
- public V remove(K key);
- /**
- * @Precondition Key不为空。
- * @Postcondition 在二叉查找树中查找具有相同键值的元素。
- * 如果找到该元素,则返回该元素的value字段。
- * 否则,返回null。
- * @return value
- */
- public V search(K key);
- /**
- * @Precondition Key和value不能为null。
- * @Postcondition 在二叉查找树中查找具有相同键值的元素。
- * 如果没有找到该元素,则返回false。
- * 否则,用参数的值更新元素的value字段,并返回true。
- * @return 布尔值
- */
- public boolean update(K key,V value);
- /**
- * @Precondition none
- * @Postcondition
- * @return 布尔值
- */
- public boolean isEmpty();
- /**
- * @Precondition none
- * @Postcondition 删除二叉查找树中的所有元素。
- * @return none
- */
- public void clear();
- /**
- * @Precondition PrintWriter不为null。
- * @Postcondition 输出二叉查找树的相关信息。
- * 这些信息包括二叉查找树的节点数和高度。
- * 输出内容的格式应该是如图2所示(在下一页)。
- * @return none
- */
- public void showStructure(PrintWriter pw);
- /**
- * @Precondition PrintWriter不为null。
- * @Postcondition 按发送顺序asending order输出二叉查找树中的所有节点。
- * 每行输出一个元素。
- * 每个元素的输出格式如下:
- * [key --- < value >]
- * @return none
- */
- public void printInorder(PrintWriter pw);
- }
- BSTtree:
- package Homework01;
- import java.io.PrintWriter;
- public class BSTTree<K extends Comparable<K>, V> implements BST<K, V> {
- private V removeValue;
- BSTNode<K, V> root;
- static class BSTNode<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
- K key;
- V value;
- BSTNode<K, V> left;
- BSTNode<K, V> right;
- public BSTNode(K key, V value, BSTNode<K, V> left, BSTNode<K, V> right) {
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- this.left = left;
- this.right = right;
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void insert(K key, V value) {
- if (key == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Key cannot be null");
- }
- if (value == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Value cannot be null");
- }
- root = doInsert(root, key, value); // 更新根节点
- }
- private BSTNode<K, V> doInsert(BSTNode<K, V> node, K key, V value) {
- if (node == null) {
- return new BSTNode<>(key, value, null, null); // 创建新节点并返回
- }
- if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0) {
- node.left = doInsert(node.left, key, value); // 递归插入左子树
- } else if (key.compareTo(node.key) > 0) {
- node.right = doInsert(node.right, key, value); // 递归插入右子树
- } else {
- node.value = value; // 更新节点值
- }
- return node;
- }
- @Override
- public V remove(K key) {
- removeValue = null;
- if (key == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Key cannot be null");
- }
- root = removeHelp(root, key);
- return removeValue;
- }
- private BSTNode<K, V> removeHelp(BSTNode<K, V> root, K key) {
- if (root == null)
- return null;
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) < 0) {
- root.left = removeHelp(root.left, key);
- } else if (key.compareTo(root.key) > 0) {
- root.right = removeHelp(root.right, key);
- } else {
- if (root.left == null) {
- removeValue = root.value;
- root = root.right;
- } else if (root.right == null) {
- removeValue = root.value;
- root = root.left;
- } else {
- BSTNode<K, V> minNode = getMinNode(root.right);
- removeValue = root.value;
- root.key = minNode.key;
- root.value = minNode.value;
- root.right = removeMinNode(root.right);
- }
- }
- return root;
- }
- private BSTNode<K, V> getMinNode(BSTNode<K, V> root) {
- if (root.left == null)
- return root;
- else
- return getMinNode(root.left);
- }
- private BSTNode<K, V> removeMinNode(BSTNode<K, V> root) {
- if (root.left == null) {
- return root.right;
- }
- root.left = removeMinNode(root.left);
- return root;
- }
- @Override
- public V search(K key) {
- if (key == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Key cannot be null");
- }
- return search(root, key);
- }
- private V search(BSTNode<K, V> root, K key) {
- if (root == null)
- return null;
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) < 0)
- return search(root.left, key);//小于当前key值则往左子树查找
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) > 0)
- return search(root.right, key);//大于当前key值则往右子树查找
- return root.value;//找到值
- }
- @Override
- public boolean update(K key, V value) {
- if (key == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Key cannot be null");
- }
- if (value == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("Value cannot be null");
- }
- return update(root, key, value);
- }
- public boolean update(BSTNode<K, V> root, K key, V value) {
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) == 0) {
- root.value = value;
- return true;
- }
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) < 0)
- return update(root.left, key, value);
- if (key.compareTo(root.key) > 0)
- return update(root.right, key, value);
- return false;
- }
- @Override
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return root == null;
- }
- @Override
- public void clear() {
- root = null;
- }
- @Override
- public void showStructure(PrintWriter pw) {
- int numberOfNode = countNodes(root);
- int height = getHeight(root);
- pw.println("-----------------------------");
- pw.print("There are ");
- pw.print(numberOfNode);
- pw.println(" nodes in this BST.");
- pw.print("The height of this BST is ");
- pw.print(height);
- pw.println(".");
- pw.println("-----------------------------");
- //使用 pw.flush() 是为了确保 showStructure 方法中的输出被立即写入到目标中,而不是等待缓冲区满或程序结束时才进行写入。
- pw.flush();
- }
- private int countNodes(BSTNode<K, V> node) {
- if (node == null) {
- return 0;
- }
- int leftCount = countNodes(node.left);
- int rightCount = countNodes(node.right);
- return 1 + leftCount + rightCount;
- }
- private int getHeight(BSTNode<K, V> node) {
- if (node == null) {
- return 0;
- }
- int leftHeight = getHeight(node.left);
- int rightHeight = getHeight(node.right);
- return 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
- }
- @Override
- public void printInorder(PrintWriter pw) {
- if (pw == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("PrintWriter不能为空");
- }
- inorderTraversal(root, pw);
- }
- private void inorderTraversal(BSTNode<K, V> node, PrintWriter pw) {
- if (node != null) {
- inorderTraversal(node.left, pw);
- pw.println("[" + node.key + " --- <" + node.value + ">]");
- inorderTraversal(node.right, pw);
- }
- }
- }
- SystemInTest:
- package Homework01;
- import java.io.*;
- public class SystemInTest {
- private static PrintWriter writer;
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- BSTTree<String, String> bstTree = new BSTTree<>();
- InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
- BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
- writer = new PrintWriter(System.out); // 创建PrintWriter对象
- String line;
- while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
- executeCommand(bstTree, line);
- writer.flush(); // 刷新PrintWriter的缓冲区
- }
- writer.close(); // 在循环结束后关闭PrintWriter对象
- }
- //泛型方法
- private static <K extends Comparable<K>, V> void executeCommand(BSTTree<K, V> bstTree, String line) throws IOException {
- StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(new StringReader(line));
- int token = st.nextToken();
- while (token != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF) {
- char command = (char) st.ttype;
- switch (command) {
- case '+' -> {
- //+( conflagration , "n.建筑物或森林大火" )
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- V value = (V) st.sval;
- bstTree.insert(key, value);
- }
- case '-' -> {
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- V value = bstTree.remove(key);
- if (value == null) {
- writer.println("remove unsuccess ---" + key);
- } else {
- writer.println("remove success ---" + key + " " + value);
- }
- }
- case '?' -> {
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- V value = bstTree.search(key);
- if (value == null) {
- writer.println("search unsuccess ---" + key);
- } else {
- writer.println("search success ---" + key + " " + value);
- }
- }
- case '=' -> {
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- V value = (V) st.sval;
- bstTree.update(key, value);
- writer.println("update success ---" + key + " " + value);
- }
- case '#' ->
- bstTree.showStructure(writer);
- }
- token = st.nextToken();
- }
- }
- }
- FileTest:
- package Homework01;
- import java.io.*;
- public class FileTest {
- private static PrintWriter writer;
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- BSTTree<String, String> bstTree = new BSTTree<>();
- FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("D:\\develop\\projects\\dataStructure\\homework03\\file\\homework3_testcases.txt");
- BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
- writer = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\develop\\projects\\dataStructure\\homework03\\file\\output.txt")); // 创建PrintWriter对象,并将输出定向到文件
- String line;
- while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
- executeCommand(bstTree, line);
- writer.flush(); // 刷新PrintWriter的缓冲区
- }
- writer.close(); // 在循环结束后关闭PrintWriter对象
- br.close(); // 关闭输入流
- }
- //泛型方法
- private static <K extends Comparable<K>, V> void executeCommand(BSTTree<K, V> bstTree, String line) throws IOException {
- StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(new StringReader(line));
- int token = st.nextToken();
- while (token != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF) {
- char command = (char) st.ttype;
- switch (command) {
- case '+' -> {
- //+( conflagration , "n.建筑物或森林大火" )
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- V value = (V) st.sval;
- bstTree.insert(key, value);
- }
- case '-' -> {
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- V value = bstTree.remove(key);
- if (value == null) {
- writer.println("remove unsuccess ---" + key);
- } else {
- writer.println("remove success ---" + key + " " + value);
- }
- }
- case '?' -> {
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- V value = bstTree.search(key);
- if (value == null) {
- writer.println("search unsuccess ---" + key);
- } else {
- writer.println("search success ---" + key + " " + value);
- }
- }
- case '=' -> {
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- K key = (K) st.sval;
- st.nextToken();
- st.nextToken();
- V value = (V) st.sval;
- bstTree.update(key, value);
- writer.println("update success ---" + key + " " + value);
- }
- case '#' ->
- bstTree.showStructure(writer);
- }
- token = st.nextToken();
- }
- }
- }
- TextFileComparator:
- package Homework01;
- import java.io.BufferedReader;
- import java.io.FileReader;
- import java.io.IOException;
- public class TextFileComparator {
- public static boolean compareFiles(String filePath1, String filePath2) {
- try (BufferedReader reader1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath1));
- BufferedReader reader2 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath2))) {
- String line1, line2;
- while ((line1 = reader1.readLine()) != null) {
- line2 = reader2.readLine();
- if (!line1.equals(line2)) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- // Check if file2 has additional lines
- return reader2.readLine() == null;
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- return false;
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String file1 = "D:\\develop\\projects\\dataStructure\\homework03\\file\\homework3_result.txt";
- String file2 = "D:\\develop\\projects\\dataStructure\\homework03\\file\\output.txt";
- boolean areEqual = compareFiles(file1, file2);
- if (areEqual) {
- System.out.println("两个文件的内容相同");
- } else {
- System.out.println("两个文件的内容不同");
- }
- }
- }






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








