目录
事件介绍

事件是允许类或对象的某些状态发生改变时通知其它类或对象。在 C# 编程中,在客户端开发中,事件(Event)可以看作是用户的一系列操作,例如按下键盘的某个按键、单击界面上一个按钮或选择某个选项等,当事件发生时我们可以针对事件做出一系列的响应,例如显示一个界面、退出程序、记录日志等等。
事件需要在一个类中声明和触发,并通过委托与事件处理程序关联。
事件可以分为发布器和订阅器两个部分:
发布器类 是一个包含事件和委托的类,事件和委托之间的联系也定义在这个类中,发布器类的对象可以触发事件,并使用委托通知其他的对象。
订阅器类 则是一个接收事件并提供事件处理程序的类,发布器类中的委托调用订阅器类中的方法(事件处理程序)。有关事件我们需要注意:
- 发布器才能触发事件,订阅器决定对事件作出何种响应;
- 一个事件可以拥有多个订阅器,同时订阅器也可以处理来自多个发布器的事件;
- 没有订阅器的事件永远也不会触发;
- 事件通常用于定义针对用户的操作,例如单击某个按钮;
- 如果事件拥有多个订阅器,当事件被触发时会同步调用所有的事件处理程序;
- 在 .NET 类库中,事件基于 EventHandler 委托和 EventArgs 基类。
事件声明

事件是基于委托的两层意思:
第一层:事件需要委托类型来做一个约束。约束既规定事件能发送什么样的消息给响应者,也规定事件响应者能收到什么样的事件消息。这就决定了事件响应者的事件处理器,必须能够和这个约束匹配上,才能够订阅这个事件。
第二层意思:当事件响应者向事件拥有者提供了能够匹配这个事件的事件处理器之后,需要把事件处理器保存或者记录下来。能够记录或者说引用方法的任务,只有委托类型的实例能够做到。
总结来说,事件这类成员无论从表层约束还是从底层的实现都是依赖委托类型的。
委托是底层基础,事件是上层建筑。
事件声明的完整格式:
三个普通类,一个委托类,事件拥有者类,事件处理者类,事件信息类,事件添加器和处理器同属的委托类。
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace event1
{
/// <summary>
/// 事件完整的声明
/// 点菜的案例:点菜事件是顾客为主体对象
///
/// 事件的拥有者customer
/// 事件customer.Order
/// 事件的响应者waiter
/// 事件处理器waiter.Action
/// 事件订阅customer.Order += waiter.Action;
/// </summary>
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
customer.Order += waiter.Action;
//触发事件,一定是事件拥有者的一些内部逻辑触发了事件
customer.Action();
customer.PayTheBill();
}
}
//按照规定,如果class是为了传递事件信息,应该是事件的名字+EventArgs
//如果一个类作为EventArgs使用,它需要派生于EventArgs
public class OrderEventArgs: EventArgs
{
public string DishName { get; set; }
public string Size { get; set; }
}
//按照规定,如果委托是为了声明事件,需要在最后加上EventHander
//使用这个后缀是用来约束事件处理器的
//使用这个后缀是用来表明这个委托是用来存储事件处理器
//委托类型的声明是不能放在类体里的,委托是一个独立的类型
public delegate void OrderEventHander(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);
public class Customer
{
//声明一个委托类型的字段,不需要外部访问到
private OrderEventHander orderEventHander;
//声明一个事件,public需要外部访问到,Event是关键字,后面的委托是必要的约束,
//也就是事件基于委托。Order是他的事件名字。
public event OrderEventHander Order
{
//事件处理器的添加器
add
{
this.orderEventHander += value;
}
//事件处理器的移除器
remove
{
this.orderEventHander -= value;
}
}
//付账的钱
public double Bill { get; set; }
public void PayTheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("l will pay ${0}",this.Bill);
}
//添加一些方法来触发逻辑、事件
public void Walkln()
{
Console.WriteLine("walk into the restaurant.");
}
public void SitDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("Sit down.");
}
public void Think()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Let me think...");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
if (this.orderEventHander != null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = "Yu";
e.Size = "large";
//Invoke是间接调用这个委托,this表示当前这个类,
this.orderEventHander.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
public void Action()
{
Console.ReadKey();
this.Walkln();
this.SitDown();
this.Think();
}
}
//事件的响应器
public class Waiter
{
public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("l will serve you the dish-{0}.",e.DishName);
double price = 10;
switch (e.Size)
{
case "small":
price = price * 0.8;
break;
case "large":
price = price * 1.2;
break;
default:
break;
}
customer.Bill += price;
}
}
}事件声明的简约格式:
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace event1
{
/// <summary>
/// 事件简化的声明
/// 点菜的案例:点菜事件是顾客为主体对象
///
/// 事件的拥有者customer
/// 事件customer.Order
/// 事件的响应者waiter
/// 事件处理器waiter.Action
/// 事件订阅customer.Order += waiter.Action;
/// </summary>
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
customer.Order += waiter.Action;
//触发事件,一定是事件拥有者的一些内部逻辑触发了事件
customer.Action();
customer.PayTheBill();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
//按照规定,如果class是为了传递事件信息,应该是事件的名字+EventArgs
//如果一个类作为EventArgs使用,它需要派生于EventArgs
public class OrderEventArgs: EventArgs
{
public string DishName { get; set; }
public string Size { get; set; }
}
//按照规定,如果委托是为了声明事件,需要在最后加上EventHander
//使用这个后缀是用来约束事件处理器的
//使用这个后缀是用来表明这个委托是用来存储事件处理器
//委托类型的声明是不能放在类体里的,委托是一个独立的类型
public delegate void OrderEventHander(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);
public class Customer
{
//事件简化声明,这里的order是一个事件,事件里包含着一个委托字段
public event OrderEventHander Order;
//付账的钱
public double Bill { get; set; }
public void PayTheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("l will pay ${0}",this.Bill);
}
//添加一些方法来触发逻辑、事件
public void Walkln()
{
Console.WriteLine("walk into the restaurant.");
}
public void SitDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("Sit down.");
}
public void Think()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Let me think...");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
if (this.Order != null)//这里使用事件名来代替前面的字段名,这样用情非得已
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = "Yu";
e.Size = "large";
//Invoke是间接调用这个委托,this表示当前这个类,
this.Order.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
public void Action()
{
Console.ReadKey();
this.Walkln();
this.SitDown();
this.Think();
}
}
//事件的响应器
public class Waiter
{
public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("l will serve you the dish-{0}.",e.DishName);
double price = 10;
switch (e.Size)
{
case "small":
price = price * 0.8;
break;
case "large":
price = price * 1.2;
break;
default:
break;
}
customer.Bill += price;
}
}
}- 事件只能用在+=/-=操作符的左边,不能用在其他操作符的左边。
- 为了防止委托字段有可能在类的外面滥用,微软推出了事件。
- 事件的本质是委托字段的一个包装器。
EventHandler委托是最常用的委托(平台已经准备好了的),使用EventHandler实现上述案例:
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace event1
{
/// <summary>
/// 事件EventHandler使用
/// 点菜的案例:点菜事件是顾客为主体对象
///
/// 事件的拥有者customer
/// 事件customer.Order
/// 事件的响应者waiter
/// 事件处理器waiter.Action
/// 事件订阅customer.Order += waiter.Action;
/// </summary>
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
customer.Order += waiter.Action;
//触发事件,一定是事件拥有者的一些内部逻辑触发了事件
customer.Action();
customer.PayTheBill();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
//按照规定,如果class是为了传递事件信息,应该是事件的名字+EventArgs
//如果一个类作为EventArgs使用,它需要派生于EventArgs
public class OrderEventArgs : EventArgs
{
public string DishName { get; set; }
public string Size { get; set; }
}
public class Customer
{
//事件简化声明,这里的order是一个事件,事件里包含着一个委托字段
public event EventHandler Order;
//付账的钱
public double Bill { get; set; }
public void PayTheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("l will pay ${0}", this.Bill);
}
//添加一些方法来触发逻辑、事件
public void Walkln()
{
Console.WriteLine("walk into the restaurant.");
}
public void SitDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("Sit down.");
}
public void Think()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Let me think...");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
if (this.Order != null)//这里使用事件名来代替前面的字段名,这样用情非得已
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = "Yu";
e.Size = "large";
//Invoke是间接调用这个委托,this表示当前这个类,
this.Order.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
public void Action()
{
Console.ReadKey();
this.Walkln();
this.SitDown();
this.Think();
}
}
//事件的响应器
public class Waiter
{
public void Action(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//类型转换
Customer customer = sender as Customer;
OrderEventArgs orderlnfo = e as OrderEventArgs;
Console.WriteLine("l will serve you the dish-{0}.", orderlnfo.DishName);
double price = 10;
switch (orderlnfo.Size)
{
case "small":
price = price * 0.8;
break;
case "large":
price = price * 1.2;
break;
default:
break;
}
customer.Bill += price;
}
}
}事件与委托的关系

- 事件本不可以使用!=和.运算符,但是这里简略声明的时候把委托字段给隐藏了,所以迫不得已使用事件。
- 面试题,为什么事件是基于委托的:source事件拥有者,subscriber事件响应者处理者

- 属性不是字段,很多时候属性是字段的包装器,包装器保护字段不被滥用;
事件不是委托字段,是委托字段的包装器,保护委托字段不被滥用;
包装器永远都不可能是被包装的东西
事件应用
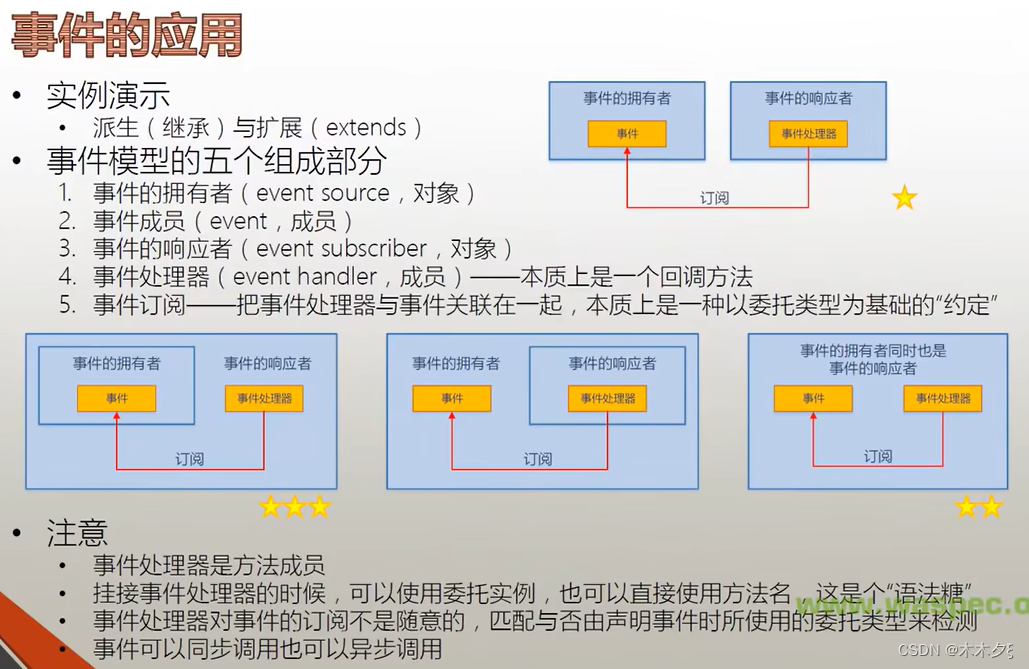
click点击事件过程:用户的操作通过windows操作系统调用按钮的内部逻辑,最终按钮的内部逻辑触发了click事件。
三星案例(windows默认使用的):窗口响应按钮事件,按钮是窗口的一部分。
案例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Timers;
namespace CombinationMode1
{
/// <summary>
/// 事件拥有者timer
/// 事件Elapsed
/// 事件的响应者boy,girl
/// 事件处理器Action
/// 事件订阅timer.Elapsed += boy.Action
/// </summary>
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//一个类最重要的三类成员,小扳手是属性,小方块是方法,小闪电是事件
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.Interval = 1000;
Boy boy = new Boy();
Girl girl = new Girl();
//timer.Elapsed达到事件间隔后发生什么
timer.Elapsed += boy.Action;
timer.Elapsed += girl.Action;
timer.Start();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Boy
{
//internal表示在访问权限是在同一个程序集下
internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now);
}
}
class Girl
{
internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Today);
}
}
}组合方式:事件拥有者和事件响应者是完全不同的两个对象(1星)
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CombinationMode_1
{
/// <summary>
/// 组合方式:事件拥有者和事件响应者是完全不同的两个对象
/// 事件拥有者form
/// 事件click
/// 事件响应者controller
/// 事件处理器FormClicked
/// 事件订阅this.form.Click += this.FormClicked
/// </summary>
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Form form = new Form();
Controller controller = new Controller(form);
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class Controller
{
public Form form;
public Controller(Form form)
{
//如果form非空就为Click添加一个处理器
if (form != null)
{
//this表示当前Controller的字段,没有this表示传进来的参数
this.form = form;
this.form.Click += this.FormClicked;
}
}
private void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//显示当前时间
this.form.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}组合方式:事件拥有者和事件响应者是同一个的对象,也就是说一个对象用自己的方法处理订阅自己的事件(2星)。
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CombinationMode_2
{
/// <summary>
/// 组合方式:事件拥有者和事件响应者是同一个的对象
/// 事件的拥有者form,类型是MyForm
/// 事件是click
/// 事件的响应者是form
/// 事件处理器Clicked
/// 事件订阅form.Click += form.Clicked
/// </summary>
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyForm form = new MyForm();
form.Click += form.Clicked;
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyForm : Form//继承于Form这个类
{
//事件处理器
internal void Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}组合方式:事件的拥有者是事件的响应者的一个字段成员(3星)
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CombinationMode_3
{
/// <summary>
/// 事件的拥有者是事件的响应者的一个字段成员,
/// 事件的响应者用自己的方法订阅着自己的字段成员的某个事件
/// 事件的拥有者是button,button是form的一个字段成员
/// 事件是button.Click
/// 事件的响应者是myform的对象
/// 事件处理器是ButtonClicked
/// 事件的订阅是this.button.Click += this.ButtonClicked
/// </summary>
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyForm form = new MyForm();
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyForm : Form
{
private TextBox textBox;
private Button button;
public MyForm()
{
this.textBox = new TextBox();
this.button = new Button();
this.Controls.Add(this.button);
this.Controls.Add(this.textBox);
this.button.Click += this.ButtonClicked;
this.button.Text = "Time";
this.button.Top = 50;
}
private void ButtonClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.textBox.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}




















 1983
1983

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








