参考:https://github.com/tanluren/yolov3-channel-and-layer-pruning
1.测试集的单独制作:
首先从航线获取的视频中截取,放入data\photos_test_or目录下
cmd命令行运行下面命令将图片重命名:
python rename_photo.py# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import os
def test():
# 源地址和输出地址
cwd = os.getcwd()
photo_test_or_Path = cwd + '\\photos_test_or\\'
photo_test_Path = cwd + '\\photos_test\\'
if not os.path.exists(photo_test_Path):
os.mkdir(photo_test_Path)
filelist = os.listdir(photo_test_or_Path)
label_i = 1
for item in filelist:
if item.endswith('.jpg'):
src = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(photo_test_or_Path), item) #原图的地址
dst = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(photo_test_Path), str(label_i) + '.jpg') #新图的地址
try:
os.rename(src, dst)
print('converting %s to %s ...' % (src, dst))
label_i += 1
except:
continue
if __name__ == '__main__':
test()创建labels_test文件夹(用于存放标签),用labelImg(我的软件在E:\software\win10\exe\labelImg-master\)进行标注,注意将该文件夹下的data\predefined_classes.txt改成你要检测的类别
测试集标注好后cmd命令行运行下面命令将图片和标签放入images和labels文件夹:
python rename_test_photo_label.py# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import os
def test():
# 源地址和输出地址
cwd = os.getcwd()
photo_test_Path = cwd + '\\photos_test\\'
print(photo_test_Path)
photos_Path = cwd + '\\images\\'
print(photos_Path)
filelist = os.listdir(photo_test_Path)
photo_i = 1
for item in filelist:
if item.endswith('.jpg'):
src = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(photo_test_Path), item) #原图的地址
dst = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(photos_Path), '0' + str(photo_i) + '.jpg') #新图的地址
try:
os.rename(src, dst)
print('converting %s to %s ...' % (src, dst))
photo_i += 1
except:
continue
label_test_Path = cwd + '\\labels_test\\'
print(label_test_Path)
labels_Path = cwd + '\\labels\\'
print(labels_Path)
filelist = os.listdir(label_test_Path)
label_i = 1
for item in filelist:
if item.endswith('.txt'):
src = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(label_test_Path), item) #原图的地址
dst = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(labels_Path), '0' + str(label_i) + '.txt') #新图的地址
try:
os.rename(src, dst)
print('converting %s to %s ...' % (src, dst))
label_i += 1
except:
continue
if __name__ == '__main__':
test()
2.训练集和测试集生成脚本的修改
python get_train_test_data.py#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import os
import random
train_list = range(1,235) #训练集(234张图片)
#print(train_list)
test_list = range(1,61) #测试集(60张图片)
#print(test_list)
train = random.sample(train_list, 234)
#print(train)
test = random.sample(test_list, 60)
#print(test)
ftrain = open('ImageSets\\train.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets\\test.txt', 'w') #只生成了训练集和测试集
for train_i in train:
train_name = 'data\\images\\' + str(train_i) + '.jpg' + '\n'
print(train_name)
ftrain.write(train_name)
for test_i in test:
test_name = 'data\\images\\' + '0' + str(test_i) + '.jpg' + '\n'
print(test_name)
ftest.write(test_name)
ftrain.close()
ftest.close()
生成后的train.txt和test.txt文件如下:
3.用yolov3-tiny进行训练
python train.py --cfg cfg/yolov3-tiny_landmark.cfg --data data/landmark.data --weights weights/yolov3-tiny.weights --epochs 400 --batch-size 32Namespace(accumulate=2, adam=False, arc='defaultpw', batch_size=32, bucket='', cache_images=False, cfg='cfg/yolov3-tiny_landmark.cfg', data='data/landmark.data', device='', epochs=400, evolve=False, img_size=416, img_weights=False, multi_scale=False, name='', nosave=False, notest=False, prebias=False, prune=1, rect=False, resume=False, s=0.001, sr=False, t_cfg='', t_weights='', transfer=False, var=None, weights='weights/yolov3-tiny.weights')4.训练完后做视频检测(检测的结果会保存到output,目录下)
python detect.py --cfg cfg/yolov3-tiny_landmark.cfg --data data/landmark.data --weights weights/best.pt --source data/samples/test_mode1.mp4 --conf-thres 0.5Namespace(cfg='cfg/yolov3-tiny_landmark', conf_thres=0.5, data='data/landmark.data', device='', fourcc='mp4v', half=False, img_size=416, nms_thres=0.5, output='output', source='data/samples/test_mode1.mp4', view_img=False, weights='weights/best.pt')5.对测试集进行测试
python test.py --cfg cfg/yolov3-tiny_landmark.cfg --data data/landmark.data --weights weights/best.pt --conf-thres 0.5 –-save-jsonNamespace(batch_size=16, cfg='cfg/yolov3-tiny_landmark.cfg', conf_thres=0.5, data='data/landmark.data', device='', img_size=416, iou_thres=0.5, nms_thres=0.5, save_json=True, weights='weights/best.pt')
tensorboard的使用
tensorboard --logdir runs\Jun03_10-01-06_DESKTOP-3TM1PEM浏览器打开http://localhost:6006/即可查看训练信息
yolov3-tiny 模型剪枝
1.训练保存的pt权重包含epoch信息,可通过python -c "from models import *; convert('cfg/yolov3-tiny_landmark.cfg', 'weights/last.pt')"转换为darknet weights去除掉epoch信息,使用darknet weights从epoch 0开始稀疏训练。转换后的文件在重命名为con_last_yolov3_tiny.weights放到weights文件夹中
2.cmd命令行输入,开始稀疏训练
python train.py --cfg cfg/yolov3-tiny_landmark.cfg --data data/landmark.data --weights weights/con_last_yolov3_tiny.weights --epochs 300 --batch-size 32 -sr --s 0.005 --prune 13.通道剪枝
python slim_prune.py --cfg cfg/yolov3-tiny_landmark.cfg --data data/landmark.data --weights weights/last.pt --global_percent 0.8 --layer_keep 0.01输出结果:
+------------+----------+----------+
| Metric | Before | After |
+------------+----------+----------+
| mAP | 0.725248 | 0.724506 |
| Parameters | 8688356 | 7491720 |
| Inference | 0.0075 | 0.0079 |
+------------+----------+----------+
Config file has been saved: cfg/prune_0.2_keep_0.8_yolov3-tiny_landmark.cfg
Compact model has been saved: weights/prune_0.2_keep_0.8_backup200.weights
4.微调
python train.py --cfg cfg/prune_0.2_keep_0.8_yolov3-tiny_landmark.cfg --data data/landmark.data --weights weights/prune_0.2_keep_0.8_backup200.weights --batch-size 32 --epochs 50将极大值抑制改为最大值抑制
1.由于自己的数据集中每幅图像同一类landmark只会出现一次,故将极大值抑制改为最大值抑制
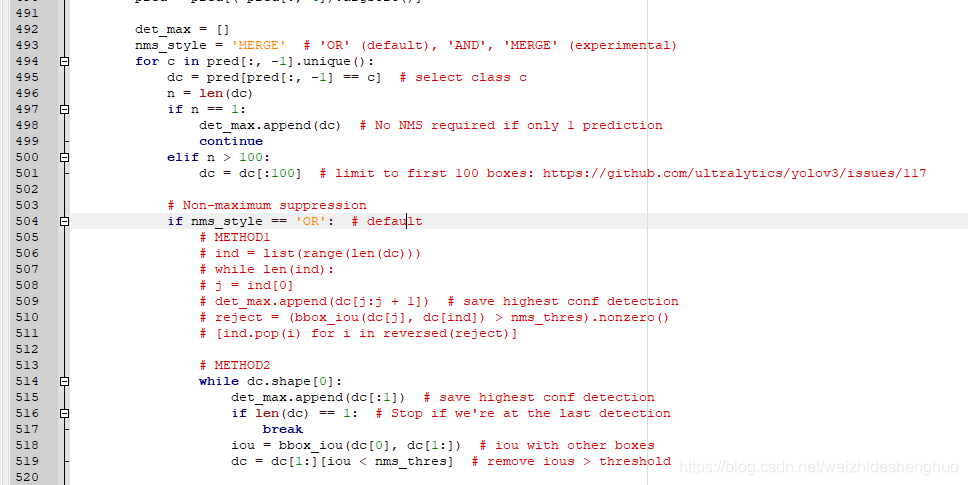
2.修改的文件为utils\utils.py,原文件如下:
修改为:
det_max = []
nms_style = 'OR' # 此处做了修改
for c in pred[:, -1].unique():
dc = pred[pred[:, -1] == c] # select class c
n = len(dc)
if n == 1:
det_max.append(dc) # No NMS required if only 1 prediction
continue
elif n > 100:
dc = dc[:100] # limit to first 100 boxes: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/117
# Non-maximum suppression
if nms_style == 'OR': # default
# METHOD1
# ind = list(range(len(dc)))
# while len(ind):
# j = ind[0]
# det_max.append(dc[j:j + 1]) # save highest conf detection
# reject = (bbox_iou(dc[j], dc[ind]) > nms_thres).nonzero()
# [ind.pop(i) for i in reversed(reject)]
# METHOD2
det_max.append(dc[:1]) # save highest conf detection
'''
while dc.shape[0]:
det_max.append(dc[:1]) # save highest conf detection
if len(dc) == 1: # Stop if we're at the last detection
break
iou = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc[1:]) # iou with other boxes
dc = dc[1:][iou < nms_thres] # remove ious > threshold
'''
自己数据集的k-means聚类
1.根据网络模型选择聚类个数yolov3-tiny为6,yolov3和yolov3-spp为9,labels_train文件夹存放训练数据集的标签
2.命令行输入python k_means.py(以前的版本,暂不采用)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# k-means ++ for YOLOv3 anchors
# 通过k-means ++ 算法获取YOLOv3需要的anchors的尺寸
import numpy as np
import os
import sys
# 定义Box类,描述bounding box的坐标
class Box():
def __init__(self, x, y, w, h):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.w = w
self.h = h
# 计算两个box在某个轴上的重叠部分
# x1是box1的中心在该轴上的坐标
# len1是box1在该轴上的长度
# x2是box2的中心在该轴上的坐标
# len2是box2在该轴上的长度
# 返回值是该轴上重叠的长度
def overlap(x1, len1, x2, len2):
len1_half = len1 / 2
len2_half = len2 / 2
left = max(x1 - len1_half, x2 - len2_half)
right = min(x1 + len1_half, x2 + len2_half)
return right - left
# 计算box a 和box b 的交集面积
# a和b都是Box类型实例
# 返回值area是box a 和box b 的交集面积
def box_intersection(a, b):
w = overlap(a.x, a.w, b.x, b.w)
h = overlap(a.y, a.h, b.y, b.h)
if w < 0 or h < 0:
return 0
area = w * h
return area
# 计算 box a 和 box b 的并集面积
# a和b都是Box类型实例
# 返回值u是box a 和box b 的并集面积
def box_union(a, b):
i = box_intersection(a, b)
u = a.w * a.h + b.w * b.h - i
return u
# 计算 box a 和 box b 的 iou
# a和b都是Box类型实例
# 返回值是box a 和box b 的iou
def box_iou(a, b):
return box_intersection(a, b) / box_union(a, b)
# 使用k-means ++ 初始化 centroids,减少随机初始化的centroids对最终结果的影响
# boxes是所有bounding boxes的Box对象列表
# n_anchors是k-means的k值
# 返回值centroids 是初始化的n_anchors个centroid
def init_centroids(boxes,n_anchors):
centroids = []
boxes_num = len(boxes)
centroid_index = np.random.choice(boxes_num, 1)
centroids.append(boxes[centroid_index[0]])
print(centroids[0].w,centroids[0].h)
for centroid_index in range(0,n_anchors-1):
sum_distance = 0
distance_thresh = 0
distance_list = []
cur_sum = 0
for box in boxes:
min_distance = 1
for centroid_i, centroid in enumerate(centroids):
distance = (1 - box_iou(box, centroid))
if distance < min_distance:
min_distance = distance
sum_distance += min_distance
distance_list.append(min_distance)
distance_thresh = sum_distance*np.random.random()
for i in range(0,boxes_num):
cur_sum += distance_list[i]
if cur_sum > distance_thresh:
centroids.append(boxes[i])
print(boxes[i].w, boxes[i].h)
break
return centroids
# 进行 k-means 计算新的centroids
# boxes是所有bounding boxes的Box对象列表
# n_anchors是k-means的k值
# centroids是所有簇的中心
# 返回值new_centroids 是计算出的新簇中心
# 返回值groups是n_anchors个簇包含的boxes的列表
# 返回值loss是所有box距离所属的最近的centroid的距离的和
def do_kmeans(n_anchors, boxes, centroids):
loss = 0
groups = []
new_centroids = []
for i in range(n_anchors):
groups.append([])
new_centroids.append(Box(0, 0, 0, 0))
for box in boxes:
min_distance = 1
group_index = 0
for centroid_index, centroid in enumerate(centroids):
distance = (1 - box_iou(box, centroid))
if distance < min_distance:
min_distance = distance
group_index = centroid_index
groups[group_index].append(box)
loss += min_distance
new_centroids[group_index].w += box.w
new_centroids[group_index].h += box.h
for i in range(n_anchors):
new_centroids[i].w /= len(groups[i])
new_centroids[i].h /= len(groups[i])
return new_centroids, groups, loss
# 计算给定bounding boxes的n_anchors数量的centroids
# label_path是训练集列表文件地址
# n_anchors 是anchors的数量
# loss_convergence是允许的loss的最小变化值
# grid_size * grid_size 是栅格数量
# iterations_num是最大迭代次数
# plus = 1时启用k means ++ 初始化centroids
def compute_centroids(label_path,n_anchors,loss_convergence,grid_size,iterations_num,plus):
boxes = []
label_files = []
filelist = os.listdir(label_path)
for files in filelist:
#print(files)
f = open(label_path + files)
for line in f:
temp = line.strip().split(" ")
#print(temp)
if len(temp) > 1:
boxes.append(Box(0, 0, float(temp[3]), float(temp[4])))
f.close()
if plus:
centroids = init_centroids(boxes, n_anchors)
else:
centroid_indices = np.random.choice(len(boxes), n_anchors)
centroids = []
for centroid_index in centroid_indices:
centroids.append(boxes[centroid_index])
# iterate k-means
centroids, groups, old_loss = do_kmeans(n_anchors, boxes, centroids)
iterations = 1
while (True):
centroids, groups, loss = do_kmeans(n_anchors, boxes, centroids)
iterations = iterations + 1
print("loss = %f" % loss)
if abs(old_loss - loss) < loss_convergence or iterations > iterations_num:
#if iterations > iterations_num:
break
old_loss = loss
for centroid in centroids:
print(centroid.w * grid_size * 32, centroid.h * grid_size * 32)
# print result
for centroid in centroids:
print("k-means result:")
print(centroid.w * grid_size * 32, centroid.h * grid_size * 32)
cwd = os.getcwd()
label_path = cwd + "\\labels_train\\"
n_anchors = 9
loss_convergence = 1e-6
grid_size = 13
iterations_num = 1000
plus = 1
compute_centroids(label_path,n_anchors,loss_convergence,grid_size,iterations_num,plus)
参考https://www.cnblogs.com/sdu20112013/p/10937717.html和官方https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/scripts/gen_anchors.py,采用的如下版本:
命令行输入python get_anchors.py --num_clusters 9
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from os import listdir
from os.path import isfile, join
import argparse
#import cv2
import numpy as np
import sys
import os
import shutil
import random
import math
width_in_cfg_file = 416.
height_in_cfg_file = 416.
max_avg_IOU = 0
def IOU(x,centroids):
similarities = []
k = len(centroids)
for centroid in centroids: #每一个样本分别与聚类中心点计算IOU
c_w,c_h = centroid
w,h = x
if c_w>=w and c_h>=h: #具有相同的中心点
similarity = w*h/(c_w*c_h)
elif c_w>=w and c_h<=h:
similarity = w*c_h/(w*h + (c_w-w)*c_h)
elif c_w<=w and c_h>=h:
similarity = c_w*h/(w*h + c_w*(c_h-h))
else: #means both w,h are bigger than c_w and c_h respectively
similarity = (c_w*c_h)/(w*h)
similarities.append(similarity) # will become (k,) shape
return np.array(similarities)
def avg_IOU(X,centroids):
n,d = X.shape
sum = 0.
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
#note IOU() will return array which contains IoU for each centroid and X[i] // slightly ineffective, but I am too lazy
sum+= max(IOU(X[i],centroids)) #计算重合度最高的
return sum/n
def write_anchors_to_file(centroids,X,anchor_file):
global max_avg_IOU
return_avg_IOU = avg_IOU(X,centroids) #随机运行1000次,取最大的IOU
print('\n')
print(return_avg_IOU)
print('\n')
if return_avg_IOU > max_avg_IOU:
max_avg_IOU = return_avg_IOU
f = open(anchor_file,'w')
anchors = centroids.copy()
print(anchors.shape)
for i in range(anchors.shape[0]):
anchors[i][0]*=width_in_cfg_file
anchors[i][1]*=height_in_cfg_file
widths = anchors[:,0]
sorted_indices = np.argsort(widths)
print('Anchors = ', anchors[sorted_indices])
for i in sorted_indices[:-1]:
f.write('%0.2f,%0.2f, '%(anchors[i,0],anchors[i,1]))
#there should not be comma after last anchor, that's why
f.write('%0.2f,%0.2f\n'%(anchors[sorted_indices[-1:],0],anchors[sorted_indices[-1:],1])) #换行
f.write('%f\n'%(avg_IOU(X,centroids)))
def kmeans(X,centroids,eps,anchor_file):
N = X.shape[0] #N代表全部样本数量
iterations = 0
k,dim = centroids.shape #k代表聚类的cluster数,dim代表聚类中心点的维度(w,h)
prev_assignments = np.ones(N)*(-1) #N个样本归属于哪个cluster
iter = 0
old_D = np.zeros((N,k))
while True:
D = []
iter+=1 #迭代次数
for i in range(N):
d = 1 - IOU(X[i],centroids)
D.append(d)
D = np.array(D) # D.shape = (N,k) N个样本分别与k个聚类中心点的IOU
print("iter {}: dists = {}".format(iter,np.sum(np.abs(old_D-D))))
#assign samples to centroids
assignments = np.argmin(D,axis=1) #每个样本取最小的IOU,返回的是下标,即该样本所属的cluster
if (assignments == prev_assignments).all() : #每个样本归属的cluster都不再变化了,就退出
print("Centroids = ",centroids)
write_anchors_to_file(centroids,X,anchor_file)
return
#calculate new centroids 重新计算样本中心点
centroid_sums=np.zeros((k,dim),np.float)
for i in range(N):
centroid_sums[assignments[i]]+=X[i] #assignments[i]为每一个样本所属的cluster,将同一cluster的样本相加
for j in range(k):
if np.sum(assignments==j):
centroids[j] = centroid_sums[j]/(np.sum(assignments==j)) #np.sum(assignments==j)为cluster j中的样本总量,重新计算中心点
else:
return
prev_assignments = assignments.copy()
old_D = D.copy()
def main(argv):
cwd = os.getcwd()
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--path_labels', default = cwd + '\\labels_train\\', #标签的文件夹地址
help='path to filelist\n' )
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', default = cwd + '\\anchors\\', type = str,
help='Output anchor directory\n' )
parser.add_argument('--num_clusters', default = 0, type = int,
help='number of clusters\n' )
args = parser.parse_args()
if not os.path.exists(args.output_dir):
os.mkdir(args.output_dir)
annotation_dims = []
filelist = os.listdir(args.path_labels)
for files in filelist:
#print(files)
f = open(args.path_labels + files)
for line in f.readlines():
line = line.rstrip('\n')
w,h = line.split(' ')[3:]
#print(w,h)
annotation_dims.append(tuple(map(float,(w,h))))
f.close()
#print(annotation_dims)
annotation_dims = np.array(annotation_dims)
#print(annotation_dims)
eps = 0.005
if args.num_clusters == 0:
for num_clusters in range(1,11): #we make 1 through 10 clusters
anchor_file = join( args.output_dir,'anchors%d.txt'%(num_clusters))
indices = [random.randrange(annotation_dims.shape[0]) for i in range(num_clusters)]
centroids = annotation_dims[indices]
kmeans(annotation_dims,centroids,eps,anchor_file)
print('centroids.shape', centroids.shape)
else:
anchor_file = join( args.output_dir,'anchors%d.txt'%(args.num_clusters))
for best_i in range(1000):
indices = [random.randrange(annotation_dims.shape[0]) for i in range(args.num_clusters)] #随机选取args.num_clusters个聚类中心
centroids = annotation_dims[indices]
kmeans(annotation_dims,centroids,eps,anchor_file)
print('centroids.shape', centroids.shape)
if __name__=="__main__":
main(sys.argv)
得到27.34,59.93, 30.50,38.86, 46.77,93.98, 51.48,147.72, 51.71,51.65, 53.01,74.68, 64.15,109.78, 66.99,82.44, 94.52,100.05

代码修改说明
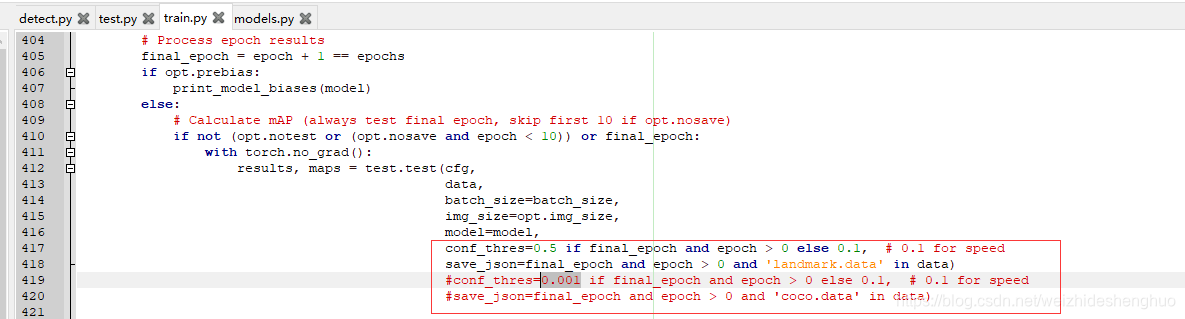
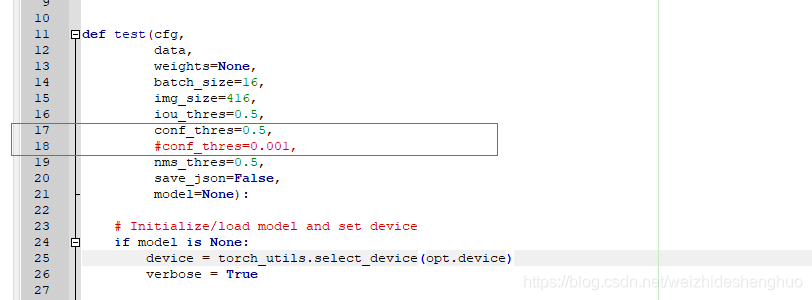
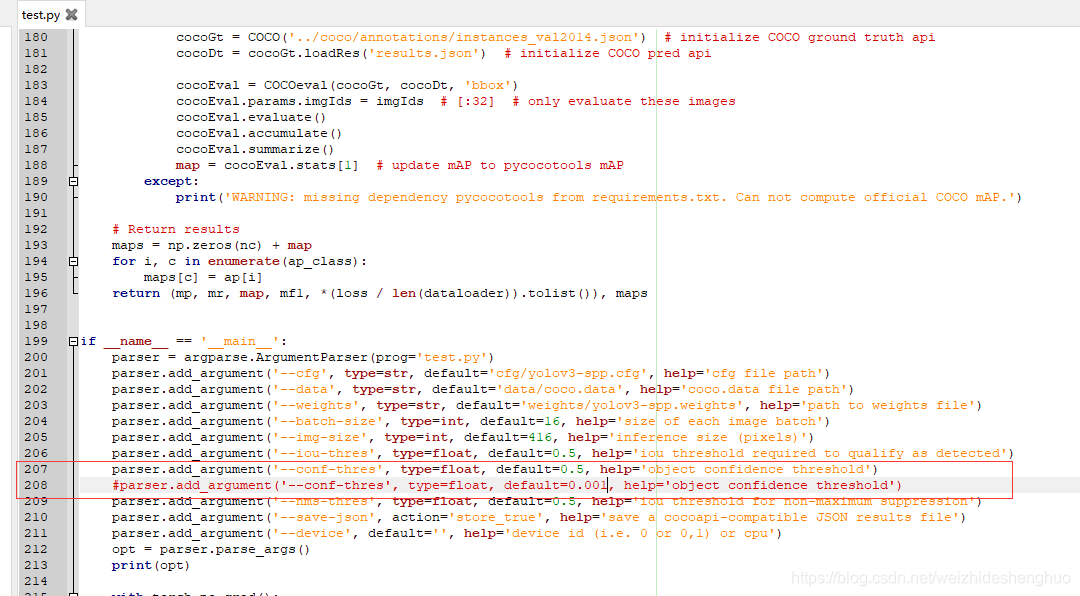
计算mAP等参数时,将conf_thres由0.001改为了0.5





















 1409
1409

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








