一、序言
这篇文章分享的是cesium中高阶功能淹没分析代码实现的思路,以及一些参考代码,源码开源仓库地址在文末,希望能给各位在生产中提供一些帮助,话不多说,上效果图:
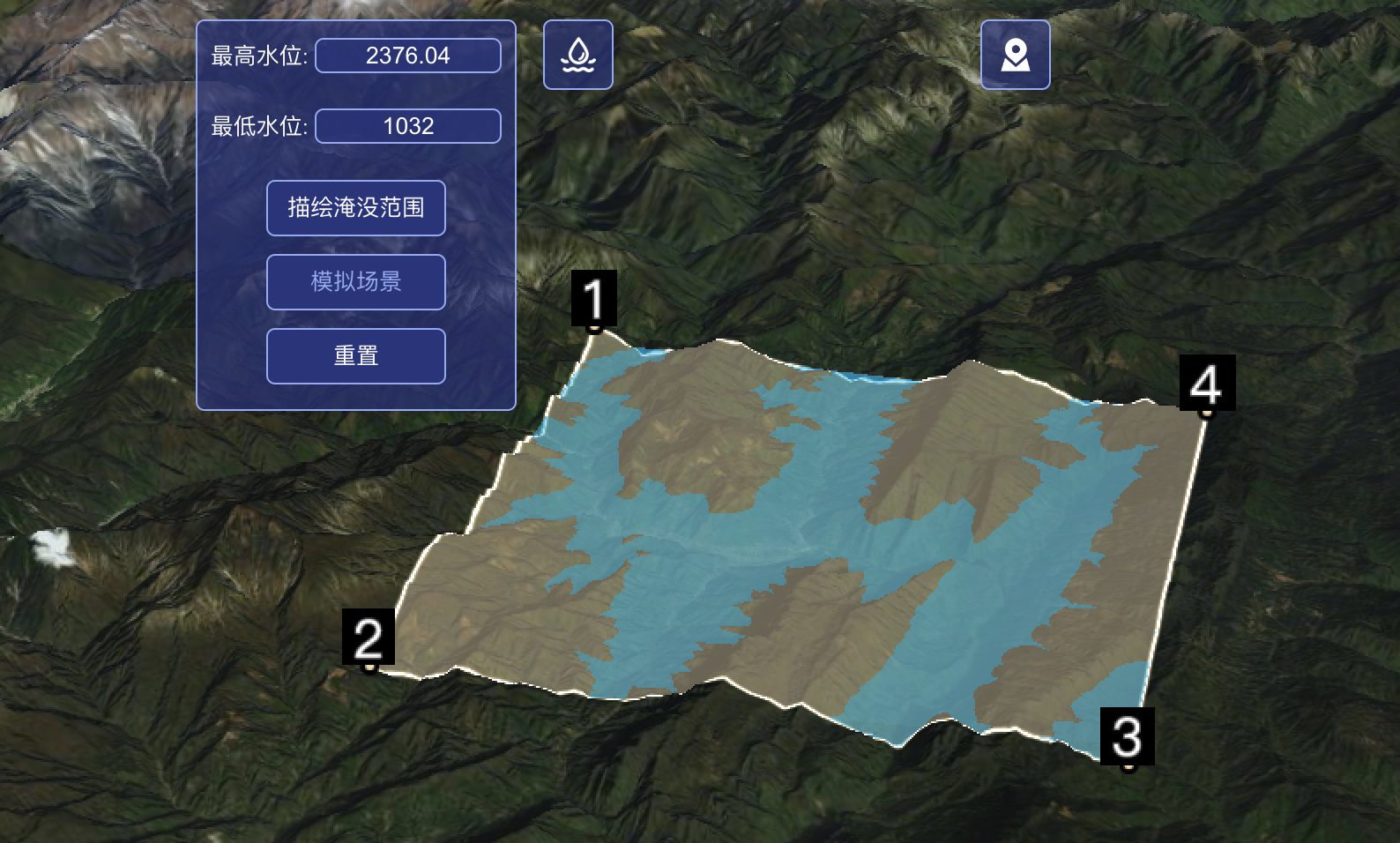
二、应用场景
剖面分析的常见应用场景:
1)根据某区域洪水涨势速度,模拟洪水涨到指定高程的淹没过程,为防洪救灾提供一定的参考。
2)淹没分析结果可为河流区域的水利工程或建筑地选址提供依据。
三、实现思路及代码
看到了效果图之后,我们就来理一下实现的思路:
先通过鼠标左键点击事件获取四个点的位置,把点的位置传给淹没分析的函数,函数需传入起始水位和终止水位,把四点的坐标去除高度后以数组的形式作为画多边形的位置参数,利用extrudeHeight(拉伸高度)机制和属性回调函数来不断拉高多边形的高度,直到达到终止水位,实现淹没效果
1.描绘出淹没范围
要描绘出淹没范围,首先需要点击添加点位以及范围面,下面的代码是过程中涉及的一些添加entity的函数:
//画广告牌
drawPointLabel(position, pointNum) {
let viewer = this.viewer
let Cesium = this.Cesium
// 本质上就是添加一个点的实体
return viewer.entities.add({
name: '测量点',
position: position,
point: {
color: Cesium.Color.WHEAT,
pixelSize: 5,
outlineWidth: 3,
disableDepthTestDistance: Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY, //
heightReference: Cesium.HeightReference.CLAMP_TO_GROUND // 规定贴地
},
label: {
text: pointNum,
font: '30px sans-serif',
fillColor: Cesium.Color.WHITE,
outlineWidth: 2,
backgroundColor: Cesium.Color.BLACK,
showBackground: true,
style: Cesium.LabelStyle.FILL,
verticalOrigin: Cesium.VerticalOrigin.BOTTOM,
horizontalOrigin: Cesium.HorizontalOrigin.CENTER,
disableDepthTestDistance: Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY,
heightReference: Cesium.HeightReference.CLAMP_TO_GROUND
}
})
},
//画线
drawPolyline(positions) {
let viewer = this.viewer
if (positions.length < 1) return
viewer.entities.add({
name: '测量点',
polyline: {
positions: positions,
width: 5.0,
material: new this.Cesium.PolylineGlowMaterialProperty({
// eslint-disable-next-line new-cap
color: this.Cesium.Color.WHEAT
}),
depthFailMaterial: new this.Cesium.PolylineGlowMaterialProperty({
// eslint-disable-next-line new-cap
color: this.Cesium.Color.WHEAT
}),
clampToGround: true
}
})
}
// 方向
Bearing(from, to) {
let Cesium = this.Cesium
let fromCartographic = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(from)
let toCartographic = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(to)
let lat1 = fromCartographic.latitude
let lon1 = fromCartographic.longitude
let lat2 = toCartographic.latitude
let lon2 = toCartographic.longitude
let angle = -Math.atan2(Math.sin(lon1 - lon2) * Math.cos(lat2), Math.cos(lat1) * Math.sin(lat2) - Math.sin(lat1) * Math.cos(lat2) * Math.cos(lon1 - lon2))
if (angle < 0) {
angle += Math.PI * 2.0
}
return angle
},
// 角度
pointAngle(point1, point2, point3) {
let bearing21 = this.Bearing(point2, point1)
let bearing23 = this.Bearing(point2, point3)
let angle = bearing21 - bearing23
if (angle < 0) {
angle += Math.PI * 2.0
}
return angle
},
/* 计算空间面积 */
getArea(positions) {
let res = 0
for (let i = 0; i < positions.length - 2; i++) {
let j = (i + 1) % positions.length
let k = (i + 2) % positions.length
let totalAngle = this.pointAngle(positions[i], positions[j], positions[k])
let tempLength1 = this.getLength(positions[j], positions[0])
let tempLength2 = this.getLength(positions[k], positions[0])
res += tempLength1 * tempLength2 * Math.sin(totalAngle) / 2
}
res = res.toFixed(2)
// console.log(res)
res = parseFloat(res)
// console.log(Math.abs(res))
return Math.abs(res)
},
/* 在最后一个点处添加标签,显示面积 */
addArea(area, positions) {
let viewer = this.viewer
let Cesium = this.Cesium
return viewer.entities.add({
name: '测量点',
position: positions[positions.length - 1],
label: {
text: area + '平方公里',
font: '20px sans-serif',
fillColor: Cesium.Color.WHITE,
outlineWidth: 2,
backgroundColor: Cesium.Color.BLACK,
showBackground: true,
style: Cesium.LabelStyle.FILL,
pixelOffset: new Cesium.Cartesian2(60, -60),
verticalOrigin: Cesium.VerticalOrigin.BOTTOM,
horizontalOrigin: Cesium.HorizontalOrigin.CENTER,
heightReference: Cesium.HeightReference.CLAMP_TO_GROUND,
disableDepthTestDistance: Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY
}
})
},
//画面
drawPolygon(positions) {
let viewer = this.viewer
if (positions.length < 2) return
return viewer.entities.add({
name: '测量点',
polygon: {
hierarchy: positions,
// eslint-disable-next-line new-cap
material: new this.Cesium.ColorMaterialProperty(
this.Cesium.Color.WHEAT.withAlpha(0.4)
)
}
})
},2.水位的高程极值计算
要实现淹没的效果,需要设置水位的最高值和最低值,该值可以直接通过input框输入,但是在实际应用场景中,用户本身并不知到其描述范围的最高值和最低值,如果随便输入,效果并不理想,可能耗费长时间等待水位从0点升高,甚至需要多次尝试才能找到该范围最合适的水位高度,非常的不方便,所以我们需要在描绘出范围的时候,自动计算好该范围内的高程极值并提供给用户,便于用户找到其理想的水位,以下是高程极值算法的实现思路以及代码:
利用四点坐标两两成线,分别迭代求中点得到线上诸多点位,两条线上相同位置点位成线迭代求中点得到点位矩阵,解析矩阵求出每个点的高度,求出高程极值,求出高程极值后可以减少extrudeHeight拉升的距离,减少等待时间且高度更加准确
//求第一条线上的33个点
this.waterArray1.push(tempPoints[0])
this.waterArray1.push(tempPoints[1])
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
this.waterArray2 = []
for (let i in this.waterArray1) {
if (i == this.waterArray1.length - 1) {
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
} else {
let midpoint = this.getMidpoint(this.waterArray1[i], this.waterArray1[i * 1 + 1])
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
this.waterArray2.push(midpoint)
}
}
this.waterArray1 = this.waterArray2
}
let pointOnline1 = this.waterArray1
this.waterArray1 = []
//求平行线上的33个点
this.waterArray1.push(tempPoints[3])
this.waterArray1.push(tempPoints[2])
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
this.waterArray2 = []
for (let i in this.waterArray1) {
if (i == this.waterArray1.length - 1) {
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
} else {
let midpoint = this.getMidpoint(this.waterArray1[i], this.waterArray1[i * 1 + 1])
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
this.waterArray2.push(midpoint)
}
}
this.waterArray1 = this.waterArray2
}
let pointOnline2 = this.waterArray1
let heightarr = []
//33*33矩阵
// let matrix = []
for (let i = 0; i < pointOnline1.length; i++) {
this.waterArray1 = []
this.waterArray1.push(pointOnline1[i])
this.waterArray1.push(pointOnline2[i])
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
this.waterArray2 = []
for (let i in this.waterArray1) {
if (i == this.waterArray1.length - 1) {
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
} else {
let midpoint = this.getMidpoint(this.waterArray1[i], this.waterArray1[i * 1 + 1])
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
this.waterArray2.push(midpoint)
}
}
// this.waterArray1 = this.waterArray2
for (let j in this.waterArray2) {
let categary = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(this.waterArray2[j]);
let height = (viewer.scene.globe.getHeight(categary)).toFixed(2)
heightarr.push(Number(height))
}
}
// matrix.push(this.waterArray1)
}
//解析矩阵求所有点位高度
// let heightarr = []
// for (let i in matrix) {
// let matrix1 = matrix[i]
// for (let j in matrix1) {
// let categary = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(matrix1[j]);
// let height = (viewer.scene.globe.getHeight(categary)).toFixed(2)
// heightarr.push(Number(height))
// }
// }
this.maxWaterHeight = Math.max(...heightarr)
this.minWaterHeight = Math.min(...heightarr)3.淹没效果实现
淹没效果的实现主要利用多面体的拉升机制,利用回调函数不断提高多面体的高度,实现水位上升的效果,话不多说,上码:
该码用于开始淹没分析的点击事件
//开始淹没分析
waterAnalysis(targetHeight1, positions, waterHeight1) {
this.$refs.waterComing.style.color = 'rgb(146, 171, 243)'
let viewer = this.viewer
let Cesium = this.Cesium
let targetHeight = targetHeight1 * 1
let waterHeight = waterHeight1 * 1
// console.log(positions)
let adapCoordi = []
positions.forEach((item) => {
let cartographic = this.Cesium.Ellipsoid.WGS84.cartesianToCartographic(item)
let lon = this.Cesium.Math.toDegrees(cartographic.longitude)
let lat = this.Cesium.Math.toDegrees(cartographic.latitude)
let arr = Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(lon, lat, 0)
adapCoordi.push(arr)
})
// console.log(adapCoordi)
let entity = viewer.entities.add({
name: '测量点',
polygon: {
hierarchy: adapCoordi,
perPositionHeight: true,
extrudedHeight: new Cesium.CallbackProperty(() => {
waterHeight += 3;
if (waterHeight > targetHeight) {
waterHeight = targetHeight;
this.$refs.waterComing.style.color = '#ffffff'
}
return waterHeight
}, false),
material: new Cesium.Color.fromBytes(0, 191, 255, 100),
}
})4.上述代码的应用
let Cesium = this.Cesium
let that = this
let viewer = this.viewer
// let pointNum = 1
// console.log(pointNum)
let tempEntities = this.tempEntities
let floatingPoint = this.floatingPoint
let activeShape = this.activeShape
let position = []
let tempPoints = []
let activeShapePoints = []
// 开启深度检测
viewer.scene.globe.depthTestAgainstTerrain = true
// 创建场景的HTML canvas元素
let handler = new Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventHandler(viewer.scene.canvas)
// 取消鼠标双击事件
viewer.cesiumWidget.screenSpaceEventHandler.removeInputAction(Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventType.LEFT_CLICK)
viewer.cesiumWidget.screenSpaceEventHandler.removeInputAction(Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventType.LEFT_DOUBLE_CLICK)
// 监听鼠标移动
handler.setInputAction(function (movement) {
if (Cesium.defined(floatingPoint)) {
let newPosition = viewer.scene.pickPosition(movement.endPosition)
if (Cesium.defined(newPosition)) {
floatingPoint.position.setValue(newPosition)
activeShapePoints.pop()
activeShapePoints.push(newPosition)
}
}
}, Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventType.MOUSE_MOVE)
// 左键单击开始画线
handler.setInputAction((click) => {
let earthPosition = viewer.scene.pickPosition(click.position)
if (Cesium.defined(earthPosition)) {
if (activeShapePoints.length === 0) {
floatingPoint = that.drawPoint(earthPosition)
activeShapePoints.push(earthPosition)
const dynamicPositions = new Cesium.CallbackProperty(function () {
return new Cesium.PolygonHierarchy(activeShapePoints)
}, false)
activeShape = that.drawPolygon(dynamicPositions)
}
activeShapePoints.push(earthPosition)
}
// 获取位置信息
let ray = viewer.camera.getPickRay(click.position)
position = viewer.scene.globe.pick(ray, viewer.scene)
tempPoints.push(position) // 记录点位
let tempLength = tempPoints.length // 记录点数
that.pointNum += 1
// 调用绘制点的接口
let point = that.drawPointLabel(tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 1], JSON.stringify(that.pointNum))
tempEntities.push(point)
// 存在超过一个点时
if (tempLength > 1) {
// 绘制线
let pointline = that.drawPolyline([tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 2], tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 1]])
tempEntities.push(pointline) // 保存记录
}
if (tempLength == 4) {
let cartesian = viewer.camera.pickEllipsoid(click.position, viewer.scene.globe.ellipsoid)
if (cartesian) {
// 闭合最后一条线
let pointline = that.drawPolyline([tempPoints[0], tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 1]])
const loading = this.$loading({
lock: true,
text: '正在计算高程极值......',
spinner: 'el-icon-loading',
background: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7)'
});
setTimeout(() => { // 以服务的方式调用的 Loading 需要异步关闭
//求第一条线上的33个点
this.waterArray1.push(tempPoints[0])
this.waterArray1.push(tempPoints[1])
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
this.waterArray2 = []
for (let i in this.waterArray1) {
if (i == this.waterArray1.length - 1) {
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
} else {
let midpoint = this.getMidpoint(this.waterArray1[i], this.waterArray1[i * 1 + 1])
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
this.waterArray2.push(midpoint)
}
}
this.waterArray1 = this.waterArray2
}
let pointOnline1 = this.waterArray1
this.waterArray1 = []
//求平行线上的33个点
this.waterArray1.push(tempPoints[3])
this.waterArray1.push(tempPoints[2])
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
this.waterArray2 = []
for (let i in this.waterArray1) {
if (i == this.waterArray1.length - 1) {
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
} else {
let midpoint = this.getMidpoint(this.waterArray1[i], this.waterArray1[i * 1 + 1])
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
this.waterArray2.push(midpoint)
}
}
this.waterArray1 = this.waterArray2
}
let pointOnline2 = this.waterArray1
let heightarr = []
//33*33矩阵
// let matrix = []
for (let i = 0; i < pointOnline1.length; i++) {
this.waterArray1 = []
this.waterArray1.push(pointOnline1[i])
this.waterArray1.push(pointOnline2[i])
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
this.waterArray2 = []
for (let i in this.waterArray1) {
if (i == this.waterArray1.length - 1) {
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
} else {
let midpoint = this.getMidpoint(this.waterArray1[i], this.waterArray1[i * 1 + 1])
this.waterArray2.push(this.waterArray1[i])
this.waterArray2.push(midpoint)
}
}
// this.waterArray1 = this.waterArray2
for (let j in this.waterArray2) {
let categary = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(this.waterArray2[j]);
let height = (viewer.scene.globe.getHeight(categary)).toFixed(2)
heightarr.push(Number(height))
}
}
// matrix.push(this.waterArray1)
}
//解析矩阵求所有点位高度
// let heightarr = []
// for (let i in matrix) {
// let matrix1 = matrix[i]
// for (let j in matrix1) {
// let categary = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(matrix1[j]);
// let height = (viewer.scene.globe.getHeight(categary)).toFixed(2)
// heightarr.push(Number(height))
// }
// }
this.maxWaterHeight = Math.max(...heightarr)
this.minWaterHeight = Math.min(...heightarr)
loading.close();
}, 1000);
tempEntities.push(pointline)
that.drawPolygon(tempPoints)
tempEntities.push(tempPoints)
this.waterArea = tempPoints
handler.destroy()
handler = null
this.$refs.darwWaterRef.style.color = '#ffffff'
}
activeShapePoints.pop()
viewer.entities.remove(activeShapePoints)
viewer.entities.remove(floatingPoint)
floatingPoint = undefined
activeShapePoints = []
this.waterArray1 = []
this.waterArray2 = []
this.pointNum = 0
this.jieliuFlag = true
}
}, Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventType.LEFT_CLICK)总结:
以上内容是我在cesium中淹没分析的实现思路以及一些参考代码,如果伙伴有什么不清楚的地方,欢迎私信,我们共同讨论进步,码字不易,点赞收藏支持一下!!!!
附上源码开源仓库地址:CesiumDemo: cesium的一些基础应用demo,包含点线面绘制、模型加载、地形加载、淹没分析、剖面海拔分析、以及常见的贴地测量、空间测量方法的实现







 文章介绍了使用Cesium进行三维淹没分析的实现思路,包括获取鼠标点击的四点坐标,计算水位高度极值,以及利用多面体拉伸机制模拟水位上升效果。应用场景包括洪水模拟和水利工程选址。提供了源码开源仓库链接。
文章介绍了使用Cesium进行三维淹没分析的实现思路,包括获取鼠标点击的四点坐标,计算水位高度极值,以及利用多面体拉伸机制模拟水位上升效果。应用场景包括洪水模拟和水利工程选址。提供了源码开源仓库链接。

















 2668
2668

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










