今天分享一篇关于cesium高阶功能剖面海拔分析的文章,希望能够为各位在生产中提供一定参考作用,在cesium的实际开发应用中我们会涉及到各种各样关于测量工具的需求,剖面海拔分析便是其中一种,通过点位选择出要测量的山体部分,分析其高度,并用echarts图可视化的表现出来,话不多说,直接上图:
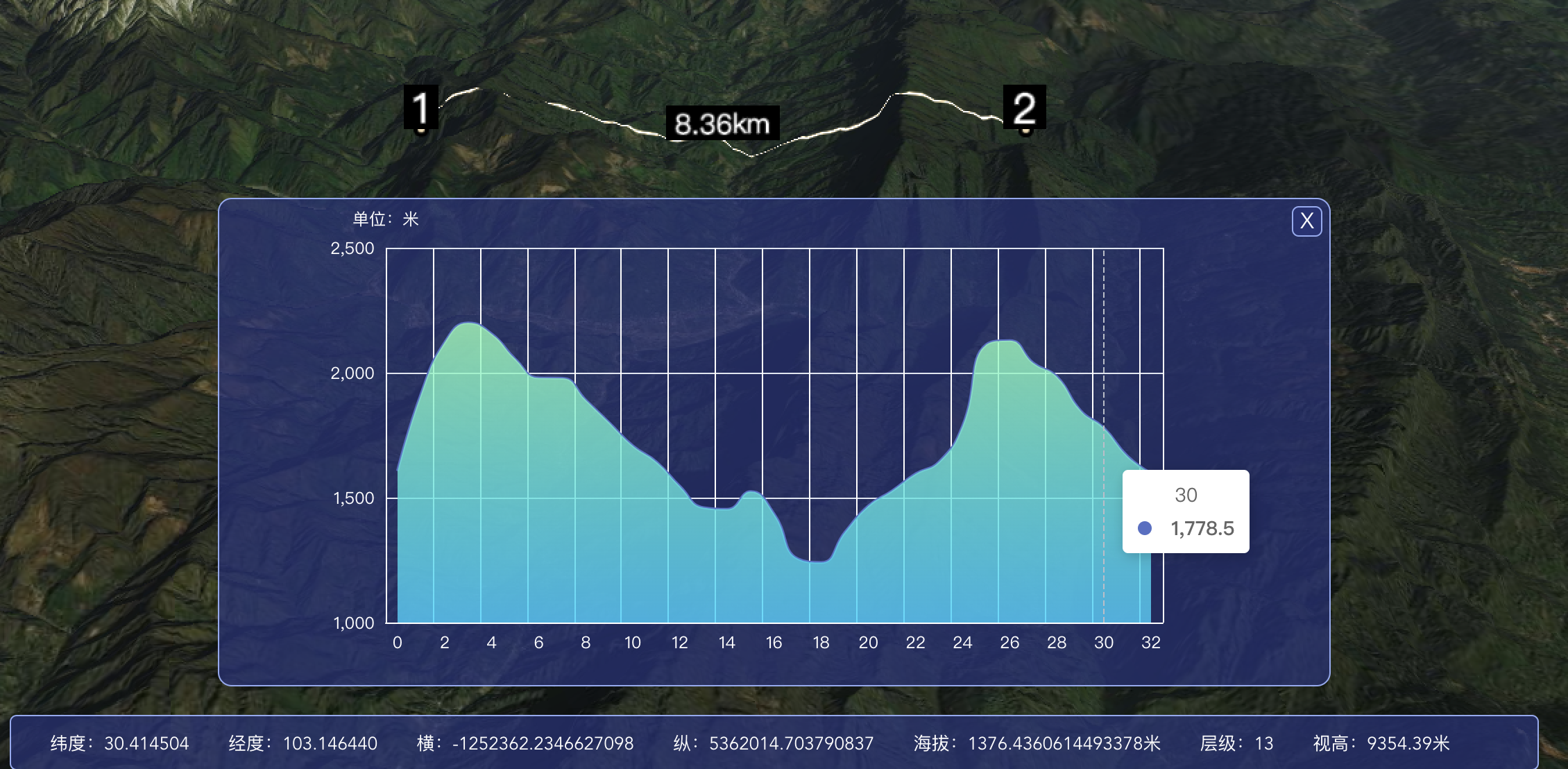
这是我们想要的效果,接下来就理一下思路:
1.我们需要一个方法可以通过点击,描绘出我们需要测量的山体部分
既然需要描绘,那就会涉及到entity的添加,直接上码:
//画点
drawPoint(position) {
let viewer = this.viewer
// 本质上就是添加一个点的实体
viewer.entities.add({
name: '测量点',
position: position,
point: {
color: this.Cesium.Color.WHEAT,
pixelSize: 5,
outlineWidth: 3,
disableDepthTestDistance: Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY,
heightReference: this.Cesium.HeightReference.CLAMP_TO_GROUND // 规定贴地
}
})
},
//画广告牌
drawPointLabel(position, pointNum) {
let viewer = this.viewer
let Cesium = this.Cesium
// 本质上就是添加一个点的实体
return viewer.entities.add({
name: '测量点',
position: position,
point: {
color: Cesium.Color.WHEAT,
pixelSize: 5,
outlineWidth: 3,
disableDepthTestDistance: Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY, //
heightReference: Cesium.HeightReference.CLAMP_TO_GROUND // 规定贴地
},
label: {
text: pointNum,
font: '30px sans-serif',
fillColor: Cesium.Color.WHITE,
outlineWidth: 2,
backgroundColor: Cesium.Color.BLACK,
showBackground: true,
style: Cesium.LabelStyle.FILL,
verticalOrigin: Cesium.VerticalOrigin.BOTTOM,
horizontalOrigin: Cesium.HorizontalOrigin.CENTER,
disableDepthTestDistance: Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY,
heightReference: Cesium.HeightReference.CLAMP_TO_GROUND
}
})
},
//画线
drawPolyline(positions) {
let viewer = this.viewer
if (positions.length < 1) return
viewer.entities.add({
name: '测量点',
polyline: {
positions: positions,
width: 5.0,
material: new this.Cesium.PolylineGlowMaterialProperty({
// eslint-disable-next-line new-cap
color: this.Cesium.Color.WHEAT
}),
depthFailMaterial: new this.Cesium.PolylineGlowMaterialProperty({
// eslint-disable-next-line new-cap
color: this.Cesium.Color.WHEAT
}),
clampToGround: true
}
})
}有了测绘方法之后,我们就需要用这些方法,画出一条贴地直线,所有的方法操作,皆在以下代码中应用:
let Cesium = this.Cesium
let that = this
let viewer = this.viewer
let tempEntities = this.tempEntities
let floatingPoint = this.floatingPoint
let activeShape = this.activeShape
let position = []
let tempPoints = []
let activeShapePoints = []
// 开启深度检测
viewer.scene.globe.depthTestAgainstTerrain = true
// 创建场景的HTML canvas元素
let handler = new Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventHandler(viewer.scene.canvas)
// 取消鼠标双击事件
viewer.cesiumWidget.screenSpaceEventHandler.removeInputAction(Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventType.LEFT_CLICK)
viewer.cesiumWidget.screenSpaceEventHandler.removeInputAction(Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventType.LEFT_DOUBLE_CLICK)
// 监听鼠标移动
handler.setInputAction(function (movement) {
if (Cesium.defined(floatingPoint)) {
let newPosition = viewer.scene.pickPosition(movement.endPosition)
if (Cesium.defined(newPosition)) {
floatingPoint.position.setValue(newPosition)
activeShapePoints.pop()
activeShapePoints.push(newPosition)
}
}
}, Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventType.MOUSE_MOVE)
// 左键单击开始画线
handler.setInputAction((click) => {
let earthPosition = viewer.scene.pickPosition(click.position)
if (Cesium.defined(earthPosition)) {
floatingPoint = that.drawPoint(earthPosition)
}
// 获取位置信息
// 从相机位置创建一条射线,这条射线通过世界中movement.position像素所在的坐标,返回Cartesian3坐标
let ray = viewer.camera.getPickRay(click.position)
// 找到射线与渲染的地球表面之间的交点。射线必须以世界坐标给出。返回Cartesian3坐标
position = viewer.scene.globe.pick(ray, viewer.scene)
tempPoints.push(position) // 记录点位
that.pointNum += 1
let tempLength = tempPoints.length // 记录点数
// 调用绘制点的接口
let point = that.drawPointLabel(tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 1], JSON.stringify(that.pointNum))
tempEntities.push(point)
// 存在超过一个点时
if (tempLength > 1) {
// 绘制线
let pointLength = that.getLength(tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 2], tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 1])
let midPosition = that.getMidpoint(tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 2], tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 1])
let pointline = that.drawPolyline([tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 2], tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 1]])
let pointLabel = that.addLabel(midPosition, pointLength)
tempEntities.push(pointline) // 保存记录
tempEntities.push(pointLabel)
this.poumianArray1.push(tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 2])
this.poumianArray1.push(tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 1])
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
this.profileloop()
}
// for (let i = 0; i < this.poumianArray1.length; i++) {
// this.poumianArray1[i]
// }
let heightarr = []
let newHeightarr = []
// let startPoint = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 2])
// let endPoint = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(tempPoints[tempPoints.length - 1])
// let geodesic = new Cesium.EllipsoidGeodesic()
// geodesic.setEndPoints(startPoint, endPoint)
// this.poumianArray1 = geodesic.interpolateUsingFraction(0.1)
// console.log(this.poumianArray1)
for (let i in this.poumianArray1) {
let categary = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(this.poumianArray1[i]);
let height = viewer.scene.globe.getHeight(categary)
heightarr.push((height).toFixed(2))
}
this.profilechart(heightarr)
this.$refs.profileboxRef.style.display = 'block'
this.$refs.profileRef.style.color = '#ffffff'
activeShapePoints.pop()
viewer.entities.remove(activeShapePoints)
viewer.entities.remove(floatingPoint)
tempPoints = [] // 清空点位记录
handler.destroy()
handler = null
floatingPoint = undefined
activeShape = undefined
activeShapePoints = []
this.jieliuFlag = true
this.pointNum = 0
this.poumianArray1 = []
}
}, Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventType.LEFT_CLICK)2.我们需要计算出两点之间的距离
我们在描绘的过程中通过该方法计算出两点之间的距离
/* 空间两点表面距离计算函数 */
getLength(start, end) {
// 将起点与终点位置信息从笛卡尔坐标形式转换为Cartographic形式
let startCartographic = this.Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(start)
let endCartographic = this.Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(end)
// 初始化测地线
let geodesic = new this.Cesium.EllipsoidGeodesic()
// 设置测地线起点和终点,EllipsoidGeodesic中setEndPoints常与surfaceDistance搭配使用
geodesic.setEndPoints(startCartographic, endCartographic)
// 获取起点和终点之间的表面距离,单位为km,规定四舍五入保留两位小数
// surfaceDistance返回number 单位为m,带小数
// console.log((geodesic.surfaceDistance / 1000).toFixed(2))
return (geodesic.surfaceDistance / 1000).toFixed(2)
},3.我们需要把山体的高度走势用echarts图描绘出来
既然要描绘出山体高度的走势,那么我们就需要获得起始点位之间n个点位的高度集合,我们利用一个求始末两点之间中点的函数,求得两点之间中点的坐标,再把始末点位与中点加入到新的数组中,再两两求中点,反复迭代,可以求出两点间的n个点位集合,该过程在贴地直线描绘中进行,参考第一点中画贴地直线的代码:
/* 空间两点计算贴地中点函数 */
getMidpoint(start, end) {
let Cesium = this.Cesium
let startPoint = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(start)
let endPoint = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(end)
let geodesic = new Cesium.EllipsoidGeodesic()
geodesic.setEndPoints(startPoint, endPoint)
let geoPoint = geodesic.interpolateUsingFraction(0.5)
// console.log(Cesium.Ellipsoid.WGS84.cartographicToCartesian(geoPoint))
return Cesium.Ellipsoid.WGS84.cartographicToCartesian(geoPoint)
}最后,我们把求到的点集通过遍历求出高度集,传给echarts用图表的形式描绘出来:
for (let i in this.poumianArray1) {
let categary = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(this.poumianArray1[i]);
let height = viewer.scene.globe.getHeight(categary)
heightarr.push((height).toFixed(2))
}echarts函数:
//剖面分析的表格加载
profilechart(heightarr) {
let myEchart = this.$echarts.init(document.getElementById("profile"))
let option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
axisLine: {
show: true,
lineStyle: {
color: "#fff",
width: 1,
type: "solid"
}
},
axisTick: {
show: false
},
splitLine: {
show: true,
lineStyle: {
color: "#fff",
width: 1,
type: "solid"
}
},
axisLabel: {//y轴文字的配置
textStyle: {
color: "#fff",
margin: 15
},
}
},
yAxis: {
minInterval: 500,
scale: true,
type: 'value',
splitLine: {
show: true
},
name: "单位:米",//y轴上方的单位
nameTextStyle: {//y轴上方单位的颜色
color: '#fff'
},
axisLabel: {//y轴文字的配置
textStyle: {
color: "#fff",
margin: 15
},
}
},
tooltip: {
trigger: 'axis',
axisPointer: {
type: 'line'
},
},
series: [
{
data: heightarr,
type: 'line',
symbol: 'none',
smooth: true,
areaStyle: {
opacity: 0.8,
color: new this.$echarts.graphic.LinearGradient(0, 0, 0, 1, [
{
offset: 0,
color: 'rgb(128, 255, 165)'
},
{
offset: 1,
color: 'rgb(1, 191, 236)'
}
])
}
}
]
}
myEchart.setOption(option)
}以上就是我在cesium中剖面海拔的整体思路以及部分参考代码,希望能够给各位伙伴提供一些帮助,码字不易,期待点赞收藏!!!T-T💕







 本文介绍了如何在Cesium中进行剖面海拔分析,通过点击测量山体部分的高度,并使用Echarts进行可视化展示。文章提供了从绘制点、线到计算距离和高度走势的代码示例,展示了完整的实现思路。
本文介绍了如何在Cesium中进行剖面海拔分析,通过点击测量山体部分的高度,并使用Echarts进行可视化展示。文章提供了从绘制点、线到计算距离和高度走势的代码示例,展示了完整的实现思路。

















 1085
1085

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










