融合改进结果预览
总体改进成效
通过架构优化与模块融合,实现了参数量减少10.8%的同时关键精度指标全面提升的卓越效果,完美实现了"更少参数、更高精度"的优化目标。
计算效率提升分析
| 指标 | 改进前 | 改进后 | 提升幅度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 网络层数 | 648层 | 608层 | -6.2% |
| 参数量 | 2,460,106 | 2,193,282 | -10.8% |
| 梯度数量 | 2,460,090 | 2,193,266 | -10.8% |
| 计算复杂度 | 6.4 GFLOPs | 5.9 GFLOPs | -7.8% |
关键改进:通过引入CG块的上下文感知机制,在减少参数的同时提升了特征表示能力,实现了计算效率的显著优化。
| 评估指标 | 改进前 | 改进后 | 提升值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 精确率(P) | 0.933 | 0.955 | +0.022 |
| 召回率(R) | 0.977 | 0.9786 | +0.0016 |
| mAP50 | 0.975 | 0.985 | +0.010 |
| mAP75 | 0.749 | 0.759 | +0.010 |
| mAP50-95 | 0.681 | 0.695 | +0.014 |
改进价值总结
本次融合改进实现了三重突破:
- 效率优化:参数量减少26.8万,计算量降低0.5 GFLOPs,更适合移动端部署
- 精度提升:关键指标mAP50达到0.985,较原模型提升1个百分点
- 架构创新:CG块与DSC3k2的成功融合为轻量级网络设计提供了新思路
一、DSC3k2 模块解析
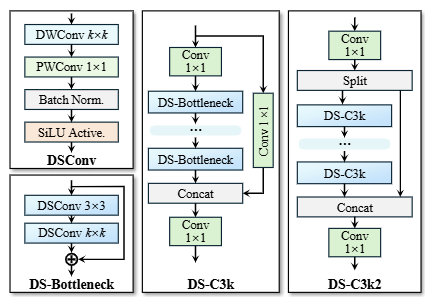
DS-C3k2 模块是一个为计算效率而设计的深度学习卷积模块。其核心思想是通过深度可分离卷积(DSConv)大幅减少参数量和计算量,同时通过并行分支结构来保持或增强特征提取能力。
以下是分层级的详细分析:
1. 核心构建块:DS-Bottleneck
这是整个架构中最基础的运算单元,位于左栏。
- 组成:
DWConv k×k->Batch Norm.&SiLU Active.->PWConv 1×1-> (Batch Norm. & SiLU) - 技术分析:
- DWConv (Depthwise Convolution): 这是深度可分离卷积的第一部分。它每个卷积核只负责一个输入通道,极大地减少了计算量和参数。
k×k是卷积核大小(常见为3x3)。 - PWConv (Pointwise Convolution): 这是深度可分离卷积的第二部分。使用
1×1卷积来融合不同通道的信息,负责创建新的特征图。 - 优势: 一个标准的
k×k卷积的计算成本大约是DWConv + PWConv组合的k²倍。因此,DS-Bottleneck 是构建轻量化模型的基石。
- DWConv (Depthwise Convolution): 这是深度可分离卷积的第一部分。它每个卷积核只负责一个输入通道,极大地减少了计算量和参数。
2. 中间模块:DS-C3k
这是 DS-C3k2 的并行分支之一,它本身也是一个串联结构,位于中栏。
- 数据流:
Conv 1×1-> 多个串联的 DS-Bottleneck ->Concat->Conv 1×1 - 技术分析:
- **第一个
Conv 1×1**: 对输入特征图进行降维,进一步减少后续多个DS-Bottleneck处理所需的数据量。 - 串联的 DS-Bottleneck: 这是特征提取的核心。多个Bottleneck的堆叠允许网络学习更复杂、更深层的特征,同时保持了低计算成本。
- **
Concat: 这里并非拼接其他分支,而是残差连接(Shortcut Connection)** 的体现。它将第一个1×1卷积降维前的输入(或等价的投影后特征)与经过多个Bottleneck处理后的特征在通道维度上进行拼接。这有效缓解了深层网络中的梯度消失问题,确保了梯度的有效回传。 - **最后一个
Conv 1×1**: 对拼接后的特征进行融合并调整到所需的输出通道数。 - 与经典C3模块的关联: 此结构类似于YOLOv5中的C3模块,但将其中的标准Bottleneck替换为了更轻量的DS-Bottleneck,故得名DS-C3k。
- **第一个
3. 主体模块:DS-C3k2
这是最终的复合模块,其设计体现了“拆分-并行处理-合并”的思想,位于右栏。
- 数据流:
Conv 1×1-> **Split -> 2个并行的 DS-C3k 分支 -> Concat** ->Conv 1×1 - 技术分析:
- **第一个
Conv 1×1**: 对输入特征进行初步的通道调整和特征编码。 - **
Split操作: 将特征图在通道维度上平均拆分成两部分**(例如,256个通道被拆成两个128通道的组)。 - 并行分支处理:
- 两个分支独立地进行特征提取。每个分支都是一个完整的DS-C3k模块。
- 这种并行结构允许网络同时捕捉不同类型的特征模式。由于两个分支的参数是独立学习的,它们可以特化到不同的特征表示,从而增强模型的表征能力,类似于一种轻量级的“集成学习”。
- 与单纯的堆叠更深的DS-C3k相比,并行结构在增加模型容量的同时,计算路径更短,训练更高效。
- **
Concat操作: 将两个并行DS-C3k分支输出的特征图重新在通道维度上拼接起来**,融合它们学习到的不同特征信息。 - **最后一个
Conv 1×1**: 对拼接后的融合特征进行最终的整合与非线性变换,输出模块的最终结果。
- **第一个
4 . 总结与优势
| 特性 | 分析 | 带来的优势 |
|---|---|---|
| 核心操作 | 广泛使用深度可分离卷积 (DSConv) | 极致的轻量化:参数量和计算量(FLOPs)远少于使用标准卷积的同等模块。 |
| 结构设计 | 并行分支结构 | 强大的特征提取:两个独立分支能够捕捉丰富且多样化的特征,提升了模型的表征能力。 |
| 梯度流动 | 内部包含残差连接(DS-C3k内) | 训练稳定性:缓解梯度消失,使网络可以更容易地训练得更深。 |
| 整体流程 | 拆分->处理->合并 | 效率与性能的平衡:在不过度增加计算复杂度的前提下,通过增加网络宽度(并行分支)来提升性能。 |
二、改进的核心动机与问题背景
尽管 DSC3k2 模块在轻量化方面表现优异,但它也存在一些固有的缺点:
特征融合能力可能不足:深度卷积和逐点卷积是顺序执行的。深度卷积阶段缺乏跨通道的信息交互,这可能限制模型捕获复杂特征关系和全局上下文的能力。在处理需要精细识别或复杂场景的任务时,其表现可能不如标准卷积。
因此我们引入Context Guided (CG) 块,其设计灵感来源于人类视觉系统利用上下文辅助识别的机制需同时处理像素级分类和目标定位,上下文信息至关重要。改模块能很好的整合全局与上下文信息,并且更加轻量,
三、核心创新:Context Guided (CG) 块
Context Guided Network
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.08201.pdf
代码地址:https://github.com/wutianyiRosun/CGNet
1. Context Guided Network (CGNet) 深度分析
CGNet 是一种专为移动设备设计的轻量级语义分割网络,其核心创新在于Context Guided (CG) 块的提出及整体网络结构的优化。以下从网络动机、核心模块、架构设计、实验性能及创新对比等方面展开分析:
CG块是CGNet的基础单元,其设计灵感来源于人类视觉系统利用上下文辅助识别的机制。结构如下:
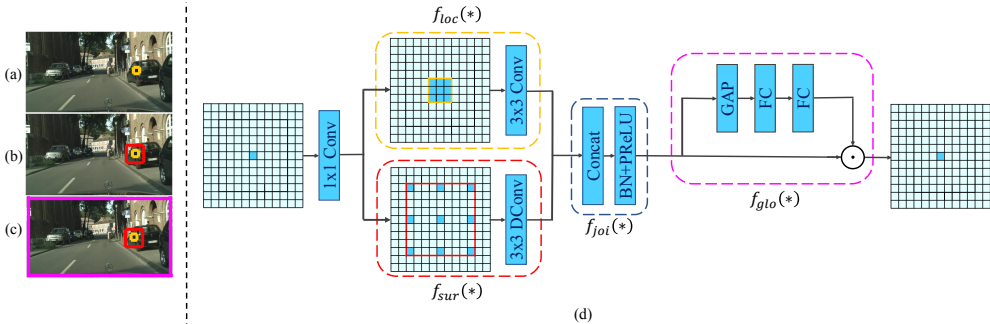
- 局部特征提取(floc(∗)):
使用3×3标准卷积捕获局部细节(对应图3a黄色区域)。
- 周围上下文提取(fsur(∗)):
采用3×3空洞卷积(dilation rate=2或4)扩大感受野,捕获目标周围环境信息(红色区域),增强空间依赖性。
- 联合特征融合(fjoi(∗)):
将局部特征与周围上下文拼接后经BN和PReLU激活,形成联合特征。
- 全局上下文优化(fglo(∗)):
借鉴SENet思想,通过全局平均池化提取全局上下文(紫色区域),生成通道注意力权重,对联合特征进行重校准,突出有用信息。
四、YOLOv13 中DSC3k2模块与Context Guided Network(CGNet)的代码融合改进
1.Context Guided Network核心代码
复制下面的代码,进入ultralytics/nn/modules到该目录下,创建一个py文件粘贴进去,名为ContextGuided.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
__all__ = ['C2f_Context', 'ContextGuidedBlock_Down']
class ConvBNPReLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nIn, nOut, kSize, stride=1):
"""
args:
nIn: number of input channels
nOut: number of output channels
kSize: kernel size
stride: stride rate for down-sampling. Default is 1
"""
super().__init__()
if isinstance(kSize, tuple):
kSize = kSize[0]
padding = int((kSize - 1) / 2)
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(nIn, nOut, (kSize, kSize), stride=stride, padding=(padding, padding), bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(nOut, eps=1e-03)
self.act = nn.PReLU(nOut)
def forward(self, input):
"""
args:
input: input feature map
return: transformed feature map
"""
output = self.conv(input)
output = self.bn(output)
output = self.act(output)
return output
class BNPReLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nOut):
"""
args:
nOut: channels of output feature maps
"""
super().__init__()
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(nOut, eps=1e-03)
self.act = nn.PReLU(nOut)
def forward(self, input):
"""
args:
input: input feature map
return: normalized and thresholded feature map
"""
output = self.bn(input)
output = self.act(output)
return output
class ConvBN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nIn, nOut, kSize, stride=1):
"""
args:
nIn: number of input channels
nOut: number of output channels
kSize: kernel size
stride: optinal stide for down-sampling
"""
super().__init__()
if isinstance(kSize, tuple):
kSize = kSize[0]
padding = int((kSize - 1) / 2)
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(nIn, nOut, (kSize, kSize), stride=stride, padding=(padding, padding), bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(nOut, eps=1e-03)
def forward(self, input):
"""
args:
input: input feature map
return: transformed feature map
"""
output = self.conv(input)
output = self.bn(output)
return output
class Conv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nIn, nOut, kSize, stride=1):
"""
args:
nIn: number of input channels
nOut: number of output channels
kSize: kernel size
stride: optional stride rate for down-sampling
"""
super().__init__()
if isinstance(kSize, tuple):
kSize = kSize[0]
padding = int((kSize - 1) / 2)
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(nIn, nOut, (kSize, kSize), stride=stride, padding=(padding, padding), bias=False)
def forward(self, input):
"""
args:
input: input feature map
return: transformed feature map
"""
output = self.conv(input)
return output
class ChannelWiseConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nIn, nOut, kSize, stride=1):
"""
Args:
nIn: number of input channels
nOut: number of output channels, default (nIn == nOut)
kSize: kernel size
stride: optional stride rate for down-sampling
"""
super().__init__()
if isinstance(kSize, tuple):
kSize = kSize[0]
padding = int((kSize - 1) / 2) # 填充 (kSize - 1) / 2 层(取整)可以抵消卷积核带来的尺寸缩减 H_out = floor( (H_in - K + 2P) / S ) + 1
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(nIn, nOut, (kSize, kSize), stride=stride, padding=(padding, padding), groups=nIn,
bias=False)
def forward(self, input):
"""
args:
input: input feature map
return: transformed feature map
"""
output = self.conv(input)
return output
class DilatedConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nIn, nOut, kSize, stride=1, d=1):
"""
args:
nIn: number of input channels
nOut: number of output channels
kSize: kernel size
stride: optional stride rate for down-sampling
d: dilation rate
"""
super().__init__()
if isinstance(kSize, tuple):
kSize = kSize[0]
padding = int((kSize - 1) / 2) * d #为了在指定空洞率 d 和步长 stride=1 的情况下,保持输出特征图的空间尺寸(高度和宽度)与输入一致。
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(nIn, nOut, (kSize, kSize), stride=stride, padding=(padding, padding), bias=False,
dilation=d)
#空洞卷积通过向卷积核的元素间注入空格(值为零)来实现这一点。例如,一个 3x3 的卷积核在 dilation=2 时,其感受野等效于一个 5x5 的标准卷积核。
def forward(self, input):
"""
args:
input: input feature map
return: transformed feature map
"""
output = self.conv(input)
return output
class ChannelWiseDilatedConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nIn, nOut, kSize, stride=1, d=1):
"""
args:
nIn: number of input channels
nOut: number of output channels, default (nIn == nOut)
kSize: kernel size
stride: optional stride rate for down-sampling
d: dilation rate
"""
super().__init__()
if isinstance(kSize, tuple):
kSize = kSize[0]
padding = int((kSize - 1) / 2) * d
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(nIn, nOut, (kSize, kSize), stride=stride, padding=(padding, padding), groups=nIn,
bias=False, dilation=d)
def forward(self, input):
"""
args:
input: input feature map
return: transformed feature map
"""
output = self.conv(input)
return output
class FGlo(nn.Module):
"""
the FGlo class is employed to refine the joint feature of both local feature and surrounding context.
"""
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(FGlo, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c) #view() 通常要求输入张量在内存中是连续存储的,对于非连续张量,需先调用 .contiguous()
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y
class ContextGuidedBlock_Down(nn.Module):
"""
the size of feature map divided 2, (H,W,C)---->(H/2, W/2, 2C)
"""
def __init__(self, nIn, dilation_rate=2, reduction=16):
"""
args:
nIn: the channel of input feature map
nOut: the channel of output feature map, and nOut=2*nIn
"""
super().__init__()
# print(f"nIn value: {nIn}, type: {type(nIn)}")
nOut = nIn
self.conv1x1 = ConvBNPReLU(nIn, nOut, 3, 2) # size/2, channel: nIn--->nOut
self.F_loc = ChannelWiseConv(nOut, nOut, 3, 1)
self.F_sur = ChannelWiseDilatedConv(nOut, nOut, 3, 1, dilation_rate)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * nOut, eps=1e-3)
self.act = nn.PReLU(2 * nOut)
self.reduce = Conv(2 * nOut, nOut, 1, 1) # reduce dimension: 2*nOut--->nOut
self.F_glo = FGlo(nOut, reduction)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.conv1x1(input)
loc = self.F_loc(output)
sur = self.F_sur(output)
joi_feat = torch.cat([loc, sur], 1) # the joint feature
joi_feat = self.bn(joi_feat)
joi_feat = self.act(joi_feat)
joi_feat = self.reduce(joi_feat) # channel= nOut
output = self.F_glo(joi_feat) # F_glo is employed to refine the joint feature
return output
class ContextGuidedBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nIn, nOut, dilation_rate=2, reduction=16, add=True):
"""
args:
nIn: number of input channels
nOut: number of output channels,
add: if true, residual learning
"""
super().__init__()
n = int(nOut / 2)
self.conv1x1 = ConvBNPReLU(nIn, n, 1, 1) # 1x1 Conv is employed to reduce the computation
self.F_loc = ChannelWiseConv(n, n, 3, 1) # local feature
self.F_sur = ChannelWiseDilatedConv(n, n, 3, 1, dilation_rate) # surrounding context
self.bn_prelu = BNPReLU(nOut)
self.add = add
self.F_glo = FGlo(nOut, reduction)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.conv1x1(input)
loc = self.F_loc(output)
sur = self.F_sur(output)
joi_feat = torch.cat([loc, sur], 1)
joi_feat = self.bn_prelu(joi_feat)
output = self.F_glo(joi_feat) # F_glo is employed to refine the joint feature
# if residual version
if self.add:
output = input + output
return output
class Bottleneck_Context(nn.Module):
"""Standard bottleneck."""
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5):
"""Initializes a bottleneck module with given input/output channels, shortcut option, group, kernels, and
expansion.
"""
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k[0], 1)
self.cv2 = ContextGuidedBlock_Down(c_)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x):
"""'forward()' applies the YOLO FPN to input data."""
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
class C2f_Context(nn.Module):
"""Faster Implementation of CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions."""
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):
"""Initialize CSP bottleneck layer with two convolutions with arguments ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups,
expansion.
"""
super().__init__()
self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv((2 + n) * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(ContextGuidedBlock(self.c, self.c) for _ in range(n))
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward pass through C2f layer."""
y = list(self.cv1(x).chunk(2, 1)) #torch.chunk函数将卷积输出张量沿着维度1(通道维)分割成两个大小相等的块
y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m) #extend() 方法,将多个处理后的特征张量依次添加到列表 y 的末尾
return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))
def forward_split(self, x):
"""Forward pass using split() instead of chunk()."""
y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1))
y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))
class C3_Context(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
"""Initialize the CSP Bottleneck with given channels, number, shortcut, groups, and expansion values."""
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(ContextGuidedBlock(c_, c_) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward pass through the CSP bottleneck with 2 convolutions."""
return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), 1))
2. 导入并添加模块
进入ultralytics/nn/tasks.py
导入模块:
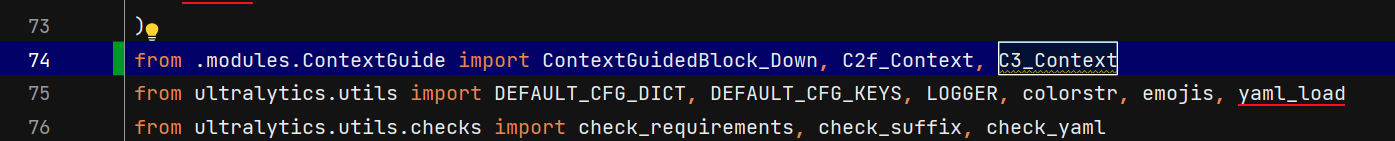
添加模块:
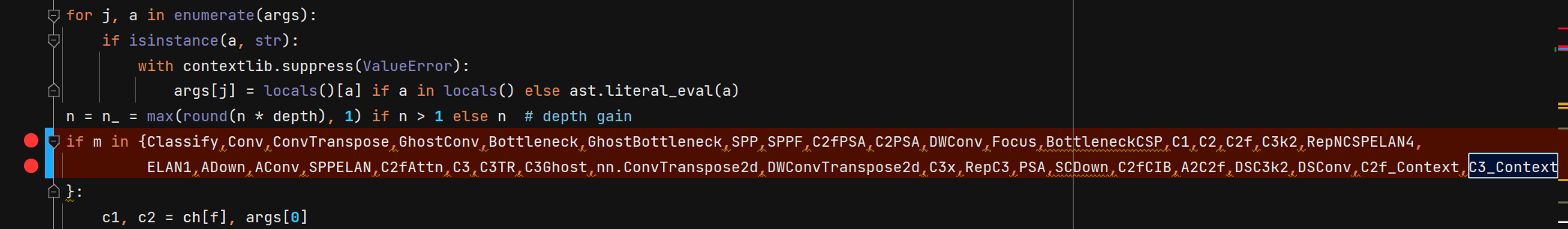
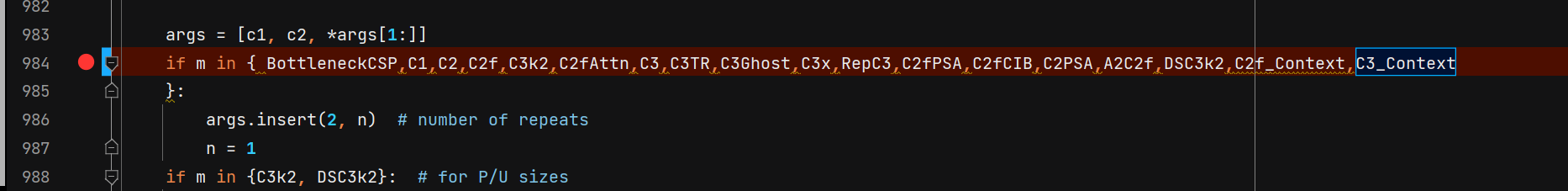
3.修改模型结构配置文件
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov13n.yaml' will call yolov13.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # Nano
s: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # Small
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # Large
x: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # Extra Large
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2, 1, 2]] # 1-P2/4
#- [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [256, False, 0.25]]
- [-1, 2, C3_Context, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2, 1, 4]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 2, C3_Context, [512, True]]
#- [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [512, False, 0.25]]
- [-1, 1, DSConv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 4, A2C2f, [512, True, 4]]
- [-1, 1, DSConv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 4, A2C2f, [1024, True, 1]] # 8
head:
- [[4, 6, 8], 2, HyperACE, [512, 8, True, True, 0.5, 1, "both"]]
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [ 9, 1, DownsampleConv, []]
- [[6, 9], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] #12
- [[4, 10], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] #13
- [[8, 11], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] #14
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 2, C3_Context, [512, True]]
#- [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [512, True]] # 17
- [[-1, 9], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] #18
- [17, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 2, C3_Context, [256, True]]
#- [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [256, True]] # 21
- [10, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]]
- [[21, 22], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] #23
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 18], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 2, C3_Context, [512, True]]
#- [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [512, True]] # 26
- [[-1, 9], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []]
- [26, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 2, C3_Context, [1024, True]]
#- [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [1024,True]] # 30 (P5/32-large)
- [[-1, 11], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []]
- [[23, 27, 31], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
4.执行运行脚本
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
from ultralytics import YOLO
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = YOLO(r'yolov13n.yaml') # 续训yaml文件的地方改为lats.pt的地址,需要注意的是如果你设置训练200轮次模型训练了200轮次是没有办法进行续训的.
# 如何切换模型版本, 上面的ymal文件可以改为 yolov13s.yaml就是使用的v13s,
# 类似某个改进的yaml文件名称为yolov13-XXX.yaml那么如果想使用其它版本就把上面的名称改为yolov13l-XXX.yaml即可(改的是上面YOLO中间的名字不是配置文件的)!
# model.load('yolov13n.pt') # 是否加载预训练权重,科研不建议大家加载否则很难提升精度
model.train(data=r"/mnt/gluster/home//AI_Training/yolov5/data/sleep.yaml", # 数据集的地址也可以填写官方的但是会进行下载ultralytics/cfg/datasets/coco128.yaml
# 如果大家任务是其它的'ultralytics/cfg/default.yaml'找到这里修改task可以改成detect, segment, classify, pose
task='detect',
cache=False,
imgsz=640,
epochs=100,
single_cls=True, # 是否是单类别检测
batch=10,
close_mosaic=0,
workers=0,
device='3',
optimizer='SGD', # using SGD 优化器 默认为auto建议大家使用固定的.
# resume=, # 续训的话这里填写True
amp=True, # 如果出现训练损失为Nan可以关闭amp
project='runs/train',
name='exp',
)
 YOLOv13中DSC3k2与CGNet融合创新
YOLOv13中DSC3k2与CGNet融合创新






















 184
184

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








