理论部分请看自适应矩形卷积(ARConv):突破传统卷积限制的创新设计_arconv routing function-优快云博客
ARConv相比传统的模块,在传入输入X时还需要再传入一个迭代的轮数,因此其他即插即用的模块,与yolov13结合需要更多的调整,本文将重点讲解需额外调整的内容,全部实现代码见文末百度网盘连接
目录
一、如何传递epoch
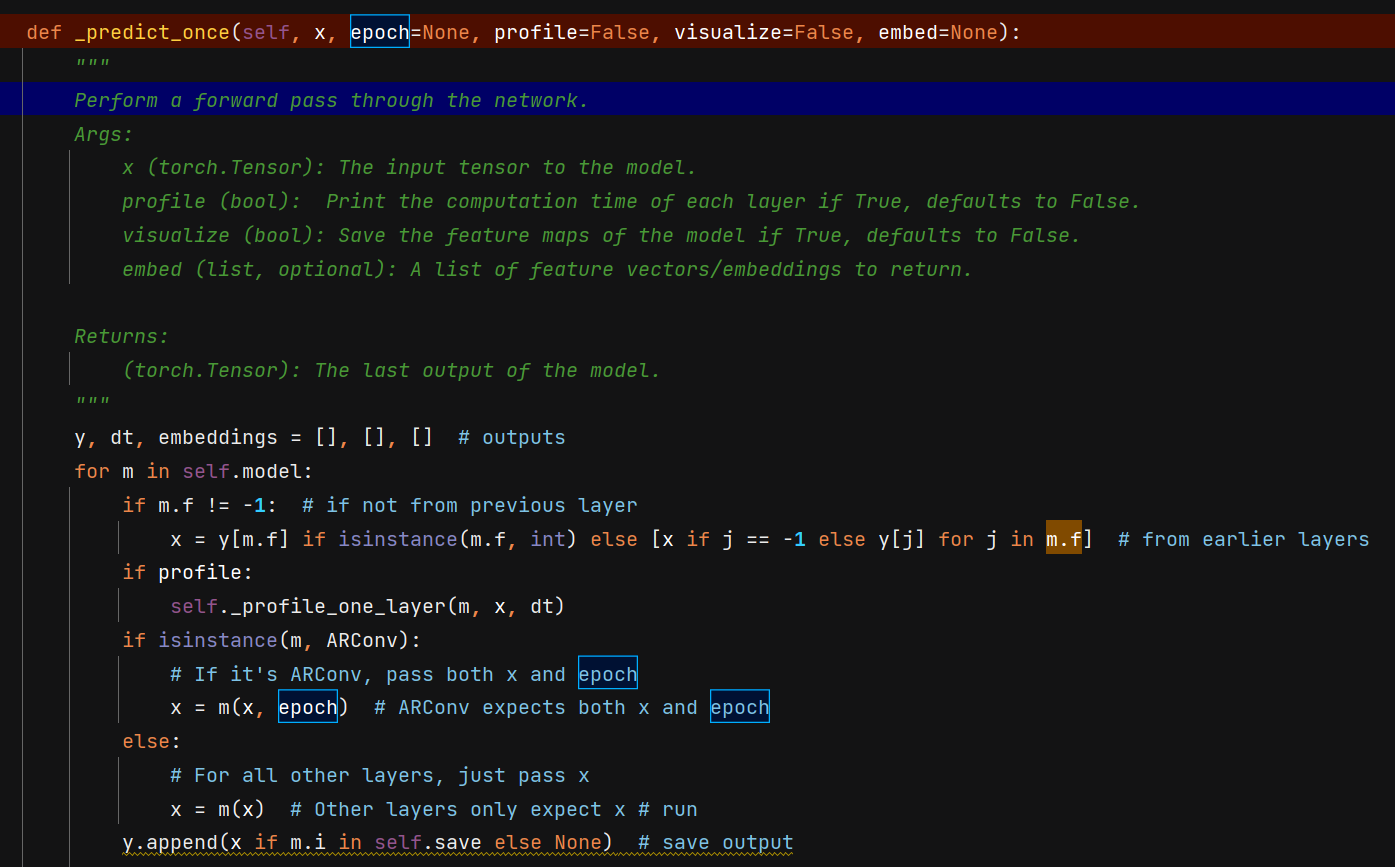
定位到ultralytics/nn/tasks.py中函数_predict_once
增加epoch输入
def _predict_once(self, x, epoch=None, profile=False, visualize=False, embed=None):
"""
Perform a forward pass through the network.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor to the model.
profile (bool): Print the computation time of each layer if True, defaults to False.
visualize (bool): Save the feature maps of the model if True, defaults to False.
embed (list, optional): A list of feature vectors/embeddings to return.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The last output of the model.
"""
y, dt, embeddings = [], [], [] # outputs
for m in self.model:
if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
if isinstance(m, ARConv):
# If it's ARConv, pass both x and epoch
x = m(x, epoch) # ARConv expects both x and epoch
else:
# For all other layers, just pass x
x = m(x) # Other layers only expect x # run
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
if embed and m.i in embed:
embeddings.append(nn.functional.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, (1, 1)).squeeze(-1).squeeze(-1)) # flatten
if m.i == max(embed):
return torch.unbind(torch.cat(embeddings, 1), dim=0)
return x如下图
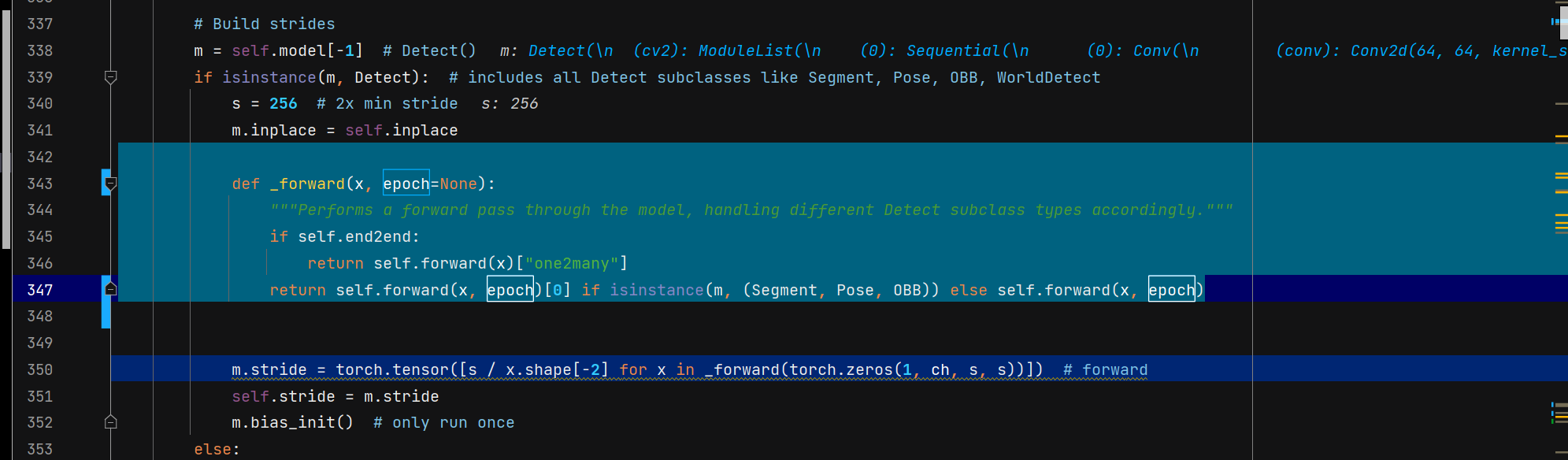
定位到ultralytics/nn/tasks.py,DetectionModel类的__init__函数
增加epoch输入
def _forward(x, epoch=None):
"""Performs a forward pass through the model, handling different Detect subclass types accordingly."""
if self.end2end:
return self.forward(x)["one2many"]
return self.forward(x, epoch)[0] if isinstance(m, (Segment, Pose, OBB)) else self.forward(x, epoch)如下图
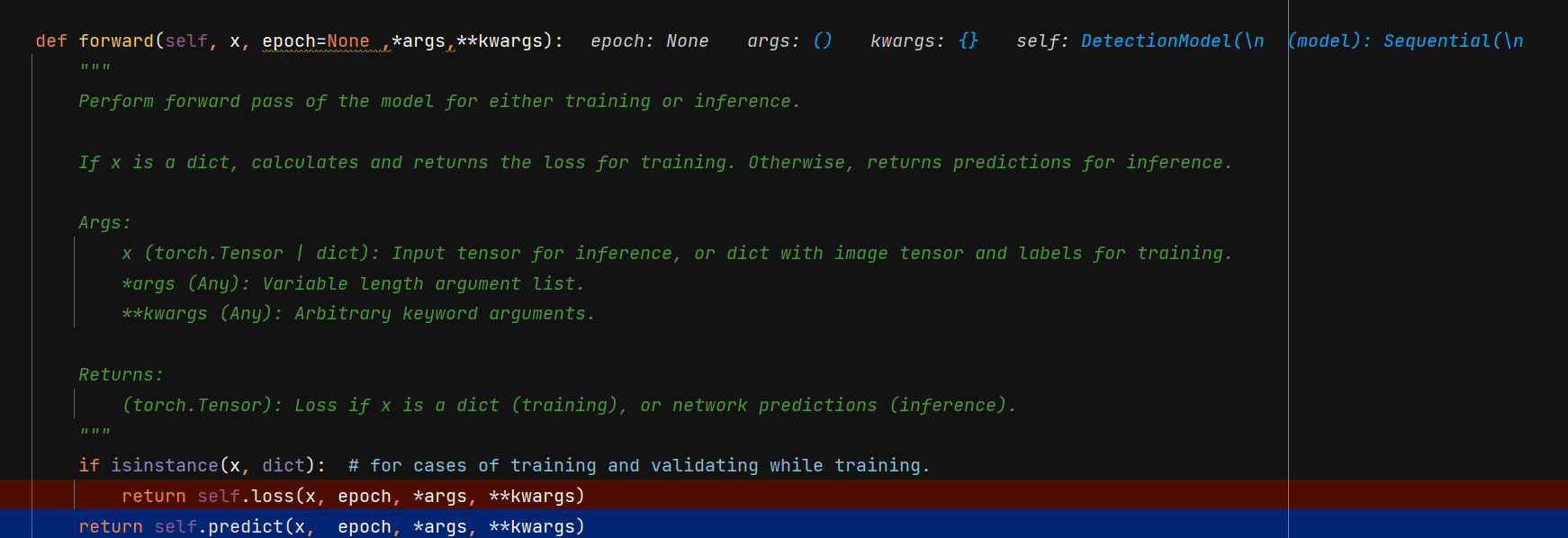
定位到ultralytics/nn/tasks.py,BaseModel类的forward函数、增加epoch输入
def forward(self, x, epoch=None ,*args,**kwargs):
"""
Perform forward pass of the model for either training or inference.
If x is a dict, calculates and returns the loss for training. Otherwise, returns predictions for inference.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor | dict): Input tensor for inference, or dict with image tensor and labels for training.
*args (Any): Variable length argument list.
**kwargs (Any): Arbitrary keyword arguments.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): Loss if x is a dict (training), or network predictions (inference).
"""
if isinstance(x, dict): # for cases of training and validating while training.
return self.loss(x, epoch, *args, **kwargs)
return self.predict(x, epoch, *args, **kwargs)如下图
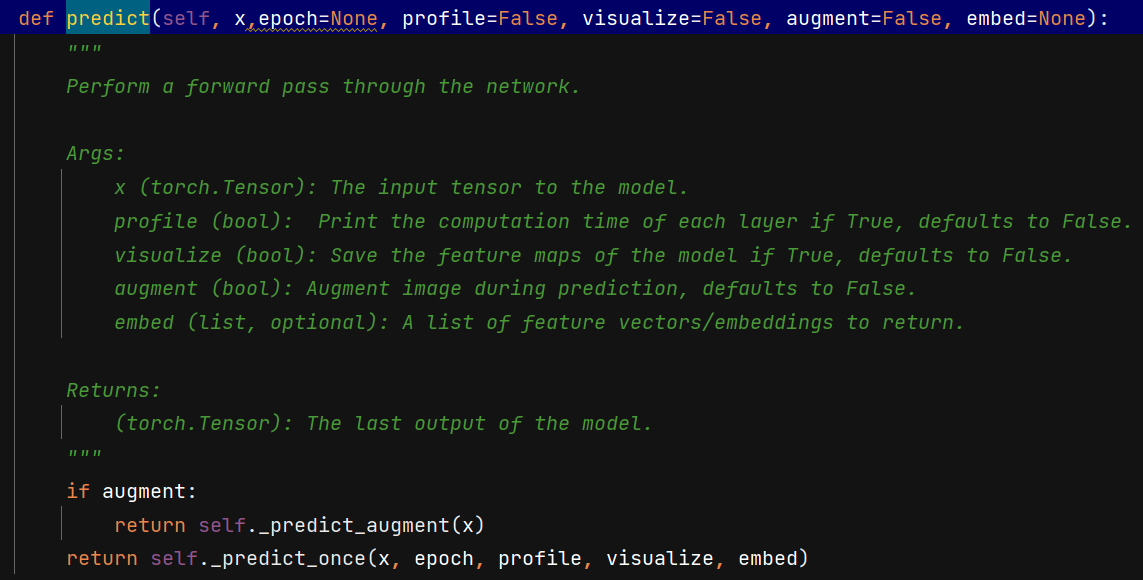
定位到ultralytics/nn/tasks.py,BaseModel类的predict函数、增加epoch输入
def predict(self, x,epoch=None, profile=False, visualize=False, augment=False, embed=None):
"""
Perform a forward pass through the network.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor to the model.
profile (bool): Print the computation time of each layer if True, defaults to False.
visualize (bool): Save the feature maps of the model if True, defaults to False.
augment (bool): Augment image during prediction, defaults to False.
embed (list, optional): A list of feature vectors/embeddings to return.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The last output of the model.
"""
if augment:
return self._predict_augment(x)
return self._predict_once(x, epoch, profile, visualize, embed)如下图
二、添加arconv模块
arconv.py代码如下
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class ARConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inc, outc, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, l_max=9, w_max=9, flag=False, modulation=True):
super(ARConv, self).__init__()
self.lmax = l_max
self.wmax = w_max
self.inc = inc
self.outc = outc
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.padding = padding
self.stride = stride
self.zero_padding = nn.ZeroPad2d(padding)
self.flag = flag
self.modulation = modulation
self.i_list = [33, 35, 53, 37, 73, 55, 57, 75, 77]
self.convs = nn.ModuleList(
[
nn.Conv2d(inc, outc, kernel_size=(i // 10, i % 10), stride=(i // 10, i % 10), padding=0)
for i in self.i_list
]
)
self.m_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inc, outc, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0.3),
nn.Conv2d(outc, outc, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0.3),
nn.Conv2d(outc, outc, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride),
nn.Tanh()
)
self.b_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inc, outc, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0.3),
nn.Conv2d(outc, outc, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0.3),
nn.Conv2d(outc, outc, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride)
)
self.p_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inc, inc, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inc),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0),
nn.Conv2d(inc, inc, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inc),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
)
self.l_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inc, 1, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0),
nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.w_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inc, 1, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0),
nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(0.3)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout2d(0.3)
# self.hook_handles = []
# self.hook_handles.append(self.m_conv[0].register_full_backward_hook(self._set_lr))
# self.hook_handles.append(self.m_conv[1].register_full_backward_hook(self._set_lr))
# self.hook_handles.append(self.b_conv[0].register_full_backward_hook(self._set_lr))
# self.hook_handles.append(self.b_conv[1].register_full_backward_hook(self._set_lr))
# self.hook_handles.append(self.p_conv[0].register_full_backward_hook(self._set_lr))
# self.hook_handles.append(self.p_conv[1].register_full_backward_hook(self._set_lr))
# self.hook_handles.append(self.l_conv[0].register_full_backward_hook(self._set_lr))
# self.hook_handles.append(self.l_conv[1].register_full_backward_hook(self._set_lr))
# self.hook_handles.append(self.w_conv[0].register_full_backward_hook(self._set_lr))
# self.hook_handles.append(self.w_conv[1].register_full_backward_hook(self._set_lr))
self.reserved_NXY = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor([3, 3], dtype=torch.int32), requires_grad=False)
# @staticmethod
# def _set_lr(module, grad_input, grad_output):
# grad_input = tuple(g * 0.1 if g is not None else None for g in grad_input)
# grad_output = tuple(g * 0.1 if g is not None else None for g in grad_output)
# return grad_input
#
# def remove_hooks(self):
# for handle in self.hook_handles:
# handle.remove() # 移除钩子函数
# self.hook_handles.clear() # 清空句柄列表
def forward(self, x, epoch):
hw_range = [1, 18]
assert isinstance(hw_range, list) and len(
hw_range) == 2, "hw_range should be a list with 2 elements, represent the range of h w"
scale = hw_range[1] // 9
if hw_range[0] == 1 and hw_range[1] == 3:
scale = 1
m = self.m_conv(x)
bias = self.b_conv(x)
offset = self.p_conv(x * 100)
l = self.l_conv(offset) * (hw_range[1] - 1) + 1 # b, 1, h, w
w = self.w_conv(offset) * (hw_range[1] - 1) + 1 # b, 1, h, w
if isinstance(epoch, int) and self.training and epoch <= 100 :
mean_l = l.mean(dim=0).mean(dim=1).mean(dim=1)
mean_w = w.mean(dim=0).mean(dim=1).mean(dim=1)
N_X = int(mean_l // scale)
N_Y = int(mean_w // scale)
def phi(x):
if x % 2 == 0:
x -= 1
return x
N_X, N_Y = phi(N_X), phi(N_Y)
N_X, N_Y = max(N_X, 3), max(N_Y, 3)
N_X, N_Y = min(N_X, 7), min(N_Y, 7)
if epoch == 100:
self.reserved_NXY = self.reserved_NXY = nn.Parameter(
torch.tensor([N_X, N_Y], dtype=torch.int32, device=x.device),
requires_grad=False
)
else:
N_X = self.reserved_NXY[0]
N_Y = self.reserved_NXY[1]
N = N_X * N_Y
l = l.repeat([1, N, 1, 1])
w = w.repeat([1, N, 1, 1])
offset = torch.cat((l, w), dim=1)
dtype = offset.data.type()
if self.padding:
x = self.zero_padding(x)
p = self._get_p(offset, dtype, N_X, N_Y) # (b, 2*N, h, w)
p = p.contiguous().permute(0, 2, 3, 1) # (b, h, w, 2*N)
q_lt = p.detach().floor()
q_rb = q_lt + 1
q_lt = torch.cat(
[
torch.clamp(q_lt[..., :N], 0, x.size(2) - 1),
torch.clamp(q_lt[..., N:], 0, x.size(3) - 1),
],
dim=-1,
).long()
q_rb = torch.cat(
[
torch.clamp(q_rb[..., :N], 0, x.size(2) - 1),
torch.clamp(q_rb[..., N:], 0, x.size(3) - 1),
],
dim=-1,
).long()
q_lb = torch.cat([q_lt[..., :N], q_rb[..., N:]], dim=-1)
q_rt = torch.cat([q_rb[..., :N], q_lt[..., N:]], dim=-1)
# clip p
p = torch.cat(
[
torch.clamp(p[..., :N], 0, x.size(2) - 1),
torch.clamp(p[..., N:], 0, x.size(3) - 1),
],
dim=-1,
)
# bilinear kernel (b, h, w, N)
g_lt = (1 + (q_lt[..., :N].type_as(p) - p[..., :N])) * (
1 + (q_lt[..., N:].type_as(p) - p[..., N:])
)
g_rb = (1 - (q_rb[..., :N].type_as(p) - p[..., :N])) * (
1 - (q_rb[..., N:].type_as(p) - p[..., N:])
)
g_lb = (1 + (q_lb[..., :N].type_as(p) - p[..., :N])) * (
1 - (q_lb[..., N:].type_as(p) - p[..., N:])
)
g_rt = (1 - (q_rt[..., :N].type_as(p) - p[..., :N])) * (
1 + (q_rt[..., N:].type_as(p) - p[..., N:])
)
# (b, c, h, w, N)
x_q_lt = self._get_x_q(x, q_lt, N)
x_q_rb = self._get_x_q(x, q_rb, N)
x_q_lb = self._get_x_q(x, q_lb, N)
x_q_rt = self._get_x_q(x, q_rt, N)
# (b, c, h, w, N)
x_offset = (
g_lt.unsqueeze(dim=1) * x_q_lt
+ g_rb.unsqueeze(dim=1) * x_q_rb
+ g_lb.unsqueeze(dim=1) * x_q_lb
+ g_rt.unsqueeze(dim=1) * x_q_rt
)
x_offset = self._reshape_x_offset(x_offset, N_X, N_Y)
x_offset = self.dropout2(x_offset)
x_offset = self.convs[self.i_list.index(N_X * 10 + N_Y)](x_offset)
out = x_offset * m + bias
return out
def _get_p_n(self, N, dtype, n_x, n_y):
p_n_x, p_n_y = torch.meshgrid(
torch.arange(-(n_x - 1) // 2, (n_x - 1) // 2 + 1),
torch.arange(-(n_y - 1) // 2, (n_y - 1) // 2 + 1),
)
p_n = torch.cat([torch.flatten(p_n_x), torch.flatten(p_n_y)], 0)
p_n = p_n.view(1, 2 * N, 1, 1).type(dtype)
return p_n
def _get_p_0(self, h, w, N, dtype):
p_0_x, p_0_y = torch.meshgrid(
torch.arange(1, h * self.stride + 1, self.stride),
torch.arange(1, w * self.stride + 1, self.stride),
)
p_0_x = torch.flatten(p_0_x).view(1, 1, h, w).repeat(1, N, 1, 1)
p_0_y = torch.flatten(p_0_y).view(1, 1, h, w).repeat(1, N, 1, 1)
p_0 = torch.cat([p_0_x, p_0_y], 1).type(dtype)
return p_0
def _get_p(self, offset, dtype, n_x, n_y):
N, h, w = offset.size(1) // 2, offset.size(2), offset.size(3)
L, W = offset.split([N, N], dim=1)
L = L / n_x
W = W / n_y
offsett = torch.cat([L, W], dim=1)
p_n = self._get_p_n(N, dtype, n_x, n_y)
p_n = p_n.repeat([1, 1, h, w])
p_0 = self._get_p_0(h, w, N, dtype)
p = p_0 + offsett * p_n
return p
def _get_x_q(self, x, q, N):
b, h, w, _ = q.size()
padded_w = x.size(3)
c = x.size(1)
x = x.contiguous().view(b, c, -1)
index = q[..., :N] * padded_w + q[..., N:]
index = (
index.contiguous()
.unsqueeze(dim=1)
.expand(-1, c, -1, -1, -1)
.contiguous()
.view(b, c, -1)
)
x_offset = x.gather(dim=-1, index=index).contiguous().view(b, c, h, w, N)
return x_offset
@staticmethod
def _reshape_x_offset(x_offset, n_x, n_y):
b, c, h, w, N = x_offset.size()
x_offset = torch.cat([x_offset[..., s:s + n_y].contiguous().view(b, c, h, w * n_y) for s in range(0, N, n_y)],
dim=-1)
x_offset = x_offset.contiguous().view(b, c, h * n_x, w * n_y)
return x_offset三、注册ARConv
定位到ultralytics/nn/tasks.py
导入模块

四、配置模型yaml
nc: 80 # number of classes scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov13n.yaml' will call yolov13.yaml with scale 'n' # [depth, width, max_channels] n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # Nano s: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # Small l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # Large x: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # Extra Large backbone: # [from, repeats, module, args] - [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2 - [-1, 1, ARConv, [128, 3, 2, 1, 2]] # 1-P2/4 - [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [256, False, 0.25]] - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2, 1, 4]] # 3-P3/8 - [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [512, False, 0.25]] - [-1, 1, DSConv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16 - [-1, 4, A2C2f, [512, True, 4]] - [-1, 1, DSConv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32 - [-1, 4, A2C2f, [1024, True, 1]] # 8 head: - [[4, 6, 8], 2, HyperACE, [512, 8, True, True, 0.5, 1, "both"]] - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]] - [ 9, 1, DownsampleConv, []] - [[6, 9], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] #12 - [[4, 10], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] #13 - [[8, 11], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] #14 - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]] - [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4 - [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [512, True]] # 17 - [[-1, 9], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] #18 - [17, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]] - [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3 - [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [256, True]] # 21 - [10, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]] - [[21, 22], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] #23 - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] - [[-1, 18], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4 - [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [512, True]] # 26 - [[-1, 9], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] - [26, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] - [[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5 - [-1, 2, DSC3k2, [1024,True]] # 30 (P5/32-large) - [[-1, 11], 1, FullPAD_Tunnel, []] - [[23, 27, 31], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
五、执行训练脚本
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
from ultralytics import YOLO
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = YOLO(r'yolov13.yaml') # 续训yaml文件的地方改为lats.pt的地址,需要注意的是如果你设置训练200轮次模型训练了200轮次是没有办法进行续训的.
# 如何切换模型版本, 上面的ymal文件可以改为 yolov13s.yaml就是使用的v13s,
# 类似某个改进的yaml文件名称为yolov13-XXX.yaml那么如果想使用其它版本就把上面的名称改为yolov13l-XXX.yaml即可(改的是上面YOLO中间的名字不是配置文件的)!
# model.load('yolov13n.pt') # 是否加载预训练权重,科研不建议大家加载否则很难提升精度
model.train(data=r"/mnt/gluster/home/huzheng/projects/2023_NP/ipc_sdk_tools/AI_Training/yolov5/data/sleep.yaml", # 数据集的地址也可以填写官方的但是会进行下载ultralytics/cfg/datasets/coco128.yaml
# 如果大家任务是其它的'ultralytics/cfg/default.yaml'找到这里修改task可以改成detect, segment, classify, pose
task='detect',
cache=False,
imgsz=640,
epochs=150,
single_cls=True, # 是否是单类别检测
batch=1,
close_mosaic=0,
workers=0,
device='0',
optimizer='SGD', # using SGD 优化器 默认为auto建议大家使用固定的.
# resume=, # 续训的话这里填写True
amp=True, # 如果出现训练损失为Nan可以关闭amp
project='runs/train',
name='exp',
)
六、结果展示
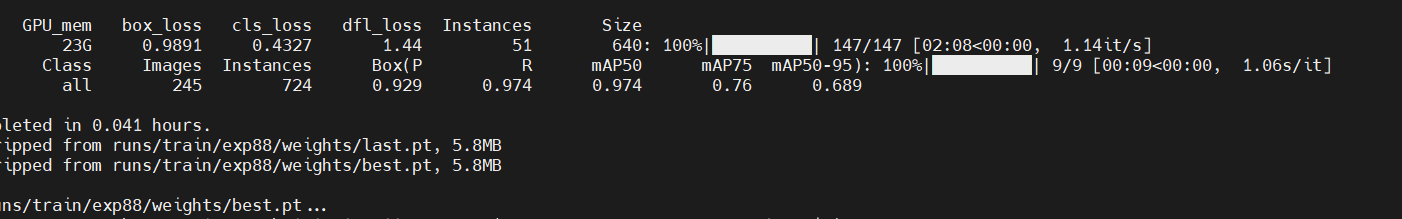





















 623
623

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








