如何调用
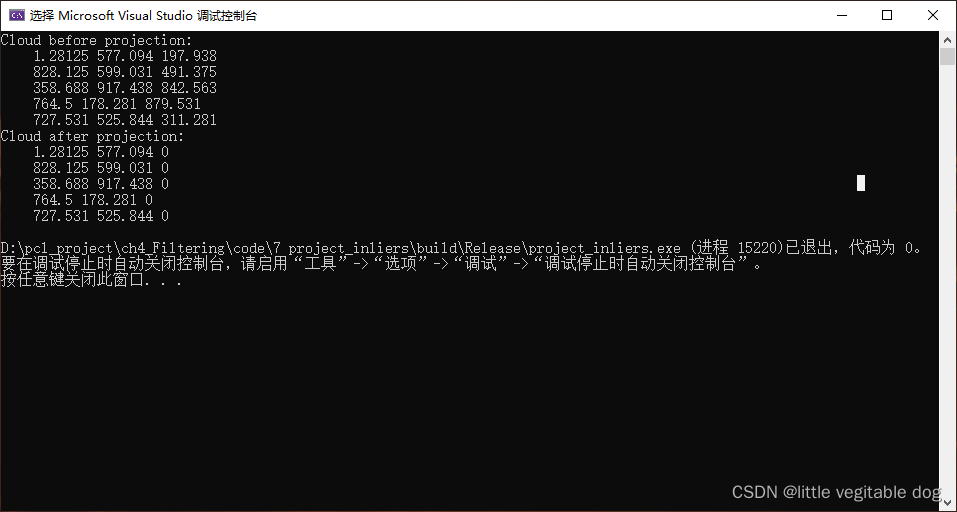
cloud是输入的点云指针,cloud_projected是输出的点云指针,调用PCL滤波函数将cloud投影到Z=0的平面。之后输出cloud_projected即可看到Z坐标归零了。
// 本例使用ax+by+cz+d=0的平面模型创健一个系数为a=b=d=0,c=1的平面,也就是X-Y平面
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients ());
coefficients->values.resize (4);
coefficients->values[0] = coefficients->values[1] = 0;
coefficients->values[2] = 1.0;
coefficients->values[3] = 0;
// 创建滤波器对象
pcl::ProjectInliers<pcl::PointXYZ> proj;
proj.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
proj.setInputCloud (cloud);
proj.setModelCoefficients (coefficients);
proj.filter (*cloud_projected);
结果附图:
源码探究
我们主要关注这一行,因为之前的函数都是向滤波器对象输入参数,这一步是通过之前输入的参数进行计算
proj.filter (*cloud_projected);
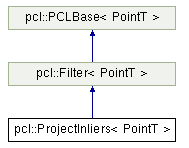
Ctrl+左键,点进去发现是一个filter基类,在pcl官网可以看到类之间的继承关系。如下图
细看发现,在filter基类中有filter函数,执行filter函数会调用
virtual void applyFilter (PointCloud &output) = 0;
此函数为虚函数,在继承类中需要重新定义,所以我们要看ProjectInliers的filter函数需要去ProjectInliers的类定义中去找,去pcl安装的地方找project_inliers.hpp文件,我的位置如下
C:\Program Files\PCL 1.12.0\include\pcl-1.12\pcl\filters\impl\project_inliers.hpp
打开之后找到函数
template <typename PointT> void pcl::ProjectInliers<PointT>::applyFilter (PointCloud &output)
这里面就是刚才调用的filter函数实际执行的位置。
template <typename PointT> void
pcl::ProjectInliers<PointT>::applyFilter (PointCloud &output)
{
//滤波器对象是否为空
if (indices_->empty ())
{
PCL_WARN ("[pcl::%s::applyFilter] No indices given or empty indices!\n", getClassName ().c_str ());
output.width = output.height = 0;
output.clear ();
return;
}
//Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXf, Eigen::Aligned> model_coefficients (&model_->values[0], model_->values.size ());
// More expensive than a map but safer (32bit architectures seem to complain)
//这里的model_已经在之前的函数中赋值为我们设定的平面模型了
//转化为Eigen::VectorXf格式
Eigen::VectorXf model_coefficients (model_->values.size ());
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < model_->values.size (); ++i)
model_coefficients[i] = model_->values[i];
// Initialize the Sample Consensus model and set its parameters
//这里根据model_type_调用不同的投影函数,进行不同的计算,我们定义的是平面所以model_type_为plane
if (!initSACModel (model_type_))
{
PCL_ERROR ("[pcl::%s::applyFilter] Error initializing the SAC model!\n", getClassName ().c_str ());
output.width = output.height = 0;
output.clear ();
return;
}
//投影计算
if (copy_all_data_)
sacmodel_->projectPoints (*indices_, model_coefficients, output, true);
else
sacmodel_->projectPoints (*indices_, model_coefficients, output, false);
}
现在需要找到调用的projectPoints 函数,但是发现Ctrl+左键跳转不过去,这时候就和之前说的一样,遇到了虚函数,编译器不知道跳转到哪个函数,于是我们从调用它的对象入手,点击sacmodel_,点击SampleConsensusModelPtr,点击SampleConsensusModel,跳转到了sac_model.h
找到函数projectPoints
/** \brief Create a new point cloud with inliers projected onto the model. Pure virtual.
* \param[in] inliers the data inliers that we want to project on the model
* \param[in] model_coefficients the coefficients of a model
* \param[out] projected_points the resultant projected points
* \param[in] copy_data_fields set to true (default) if we want the \a
* projected_points cloud to be an exact copy of the input dataset minus
* the point projections on the plane model
*/
virtual void
projectPoints (const Indices &inliers,
const Eigen::VectorXf &model_coefficients,
PointCloud &projected_points,
bool copy_data_fields = true) const = 0;
想再次跳转的时候发现很多类都继承了SampleConsensusModel类,比如我们需要投影到平面上,我们就用到SampleConsensusModelPlane类,找到projectPoints函数,这就是PCL 点云投影到平面实际的计算函数!
template <typename PointT> void
pcl::SampleConsensusModelPlane<PointT>::projectPoints (
const Indices &inliers, const Eigen::VectorXf &model_coefficients, PointCloud &projected_points, bool copy_data_fields) const
{
// Needs a valid set of model coefficients
if (!isModelValid (model_coefficients))
{
PCL_ERROR ("[pcl::SampleConsensusModelPlane::projectPoints] Given model is invalid!\n");
return;
}
projected_points.header = input_->header;
projected_points.is_dense = input_->is_dense;
//mc是平面的法向量
Eigen::Vector4f mc (model_coefficients[0], model_coefficients[1], model_coefficients[2], 0.0f);
// normalize the vector perpendicular to the plane...
mc.normalize ();
// ... and store the resulting normal as a local copy of the model coefficients
//tmp_mc是归一化的平面的法向量,模为1
Eigen::Vector4f tmp_mc = model_coefficients;
tmp_mc[0] = mc[0];
tmp_mc[1] = mc[1];
tmp_mc[2] = mc[2];
// Copy all the data fields from the input cloud to the projected one?
//是否将所有数据字段从输入点云中复制到投影点云中
if (copy_data_fields)
{
// Allocate enough space and copy the basics
projected_points.resize (input_->size ());
projected_points.width = input_->width;
projected_points.height = input_->height;
//这一步是将所有数据字段从输入点云中复制到投影点云中
using FieldList = typename pcl::traits::fieldList<PointT>::type;
// Iterate over each point
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < input_->size (); ++i)
// Iterate over each dimension
pcl::for_each_type <FieldList> (NdConcatenateFunctor <PointT, PointT> ((*input_)[i], projected_points[i]));
//计算点云上的点到平面的距离
// Iterate through the 3d points and calculate the distances from them to the plane
for (const auto &inlier : inliers)
{
// Calculate the distance from the point to the plane
Eigen::Vector4f p ((*input_)[inlier].x,
(*input_)[inlier].y,
(*input_)[inlier].z,
1);
// use normalized coefficients to calculate the scalar projection
//将距离乘以平面的标准法向量,变成有方向的距离矢量
float distance_to_plane = tmp_mc.dot (p);
//定义输出vector
pcl::Vector4fMap pp = projected_points[inlier].getVector4fMap ();
//mc * distance_to_plane:将距离乘以平面的标准法向量,变成垂直于平面的距离矢量
//点在平面的投影矢量 = 点坐标矢量 - 点垂直于平面的距离矢量
//这里用到的是pcl::Vector的矢量减法(重载运算符),需要自己想一下
pp.matrix () = p - mc * distance_to_plane; // mc[3] = 0, therefore the 3rd coordinate is safe
}
}
//和上面代码基本相同
//不将所有数据字段从输入点云中复制到投影点云中
else
{
// Allocate enough space and copy the basics
projected_points.resize (inliers.size ());
projected_points.width = inliers.size ();
projected_points.height = 1;
using FieldList = typename pcl::traits::fieldList<PointT>::type;
// Iterate over each point
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < inliers.size (); ++i)
{
// Iterate over each dimension
pcl::for_each_type <FieldList> (NdConcatenateFunctor <PointT, PointT> ((*input_)[inliers[i]], projected_points[i]));
}
// Iterate through the 3d points and calculate the distances from them to the plane
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < inliers.size (); ++i)
{
// Calculate the distance from the point to the plane
Eigen::Vector4f p ((*input_)[inliers[i]].x,
(*input_)[inliers[i]].y,
(*input_)[inliers[i]].z,
1.0f);
// use normalized coefficients to calculate the scalar projection
float distance_to_plane = tmp_mc.dot (p);
pcl::Vector4fMap pp = projected_points[i].getVector4fMap ();
pp.matrix () = p - mc * distance_to_plane; // mc[3] = 0, therefore the 3rd coordinate is safe
}
}
}
以上就是PCL 点云投影到平面的源码解释








 该博客深入解析了如何使用PCL库将点云投影到Z=0平面,实现Z坐标归零。通过创建平面模型系数、设置滤波器对象、调用ProjectInliers滤波函数,最终利用SampleConsensusModelPlane类的projectPoints函数完成点云投影。博客详细分析了PCL源码,展示了从输入参数到实际计算的整个过程。
该博客深入解析了如何使用PCL库将点云投影到Z=0平面,实现Z坐标归零。通过创建平面模型系数、设置滤波器对象、调用ProjectInliers滤波函数,最终利用SampleConsensusModelPlane类的projectPoints函数完成点云投影。博客详细分析了PCL源码,展示了从输入参数到实际计算的整个过程。


















 1335
1335

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










