一、模型
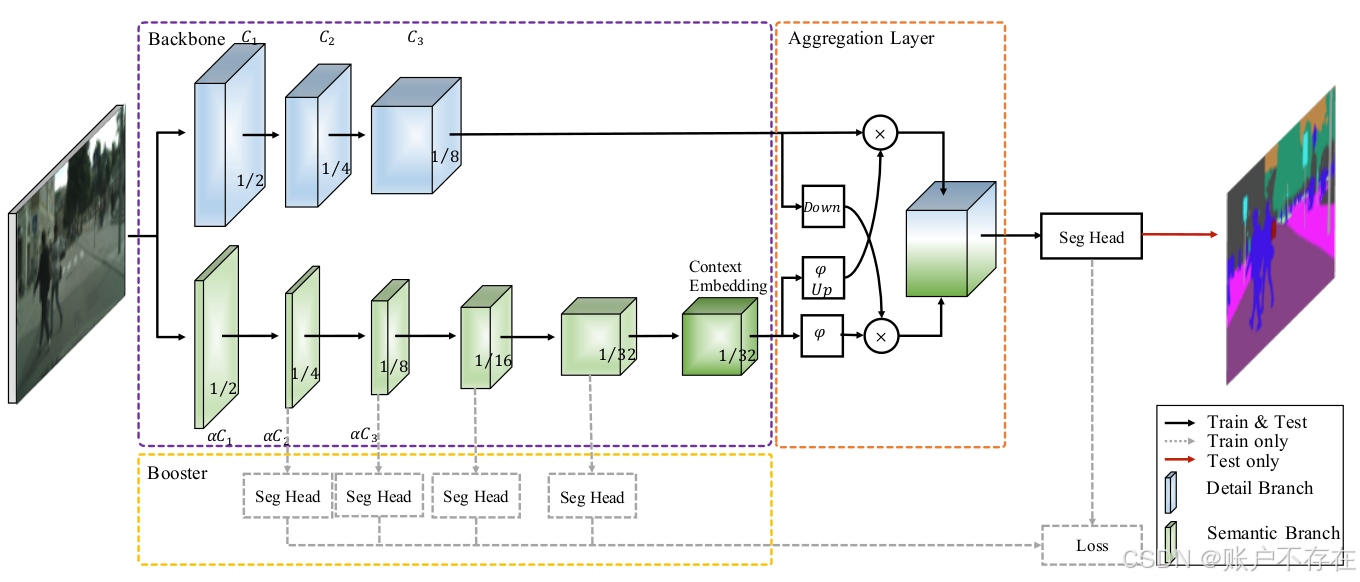
BiSeNetV2主要包含几个结构:
- 紫色框(backbone)内的双路分支,上为Detail Branch分支,下为Semantic Branch分支。
- 橙色框(Aggregation Layer)内的Aggregation Layer聚合层。
- 黄色框(Booster)内的Auxiliary Loss分支。
首先,我们先介绍紫色框backbone部分。
Backbone-Detail Branch
Detail分支的网络结构由三个stage构成,每个stage包含2或3个卷积层,每个卷积层后都有BN和激活函数(RELU)。在每个stage中,第一个卷积层的步幅为2,后面卷积层的步幅为1。因此,Detail分支的输出特征图尺寸为原始图像的1/8,通道数为设计的128,代码部分如下
'''
通过卷积步长stride=2,将原图下采样到原来的1/8
通道数固定为 128
'''
class DetailBranch(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel):
super(DetailBranch, self).__init__()
ch = np.array(np.array([64, 128]), dtype=int)
self.S1 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channel, ch[0], 3, stride=2),
ConvBNReLU(ch[0], ch[0], 3, stride=1),
)
self.S2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(ch[0], ch[0], 3, stride=2),
ConvBNReLU(ch[0], ch[0], 3, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(ch[0], ch[0], 3, stride=1),
)
self.S3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(ch[0], ch[1], 3, stride=2),
ConvBNReLU(ch[1], ch[1], 3, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(ch[1], ch[1], 3, stride=1),
)
def forward(self, x):
feat = self.S1(x)
feat = self.S2(feat)
feat = self.S3(feat)
return feat
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 1024, 2048)
detail = DetailBranch(3)
feat_detail = detail(x)
print('detail', feat_detail.size())
'''detail torch.Size([4, 128, 128, 256])
ch: 128
w,h: 1/8
'''
Backbone-Semantic Branch
Semantic Branch与Detail Branch平行,主要用于捕获高级语义信息.作者在这部分做了较为精心的设计,主要包括三部分:
- Stem Block用于快速下采样(尺寸变为原来的1/4,输出通道代码固定为16);
- Gather-and-Expansion Layer(GE Layer)有两种结构GELayerS1和GELayerS2,用于卷积获取细节信息。
- Context Embedding Block(CE Layer)用于嵌入上下文信息。
Stem Block
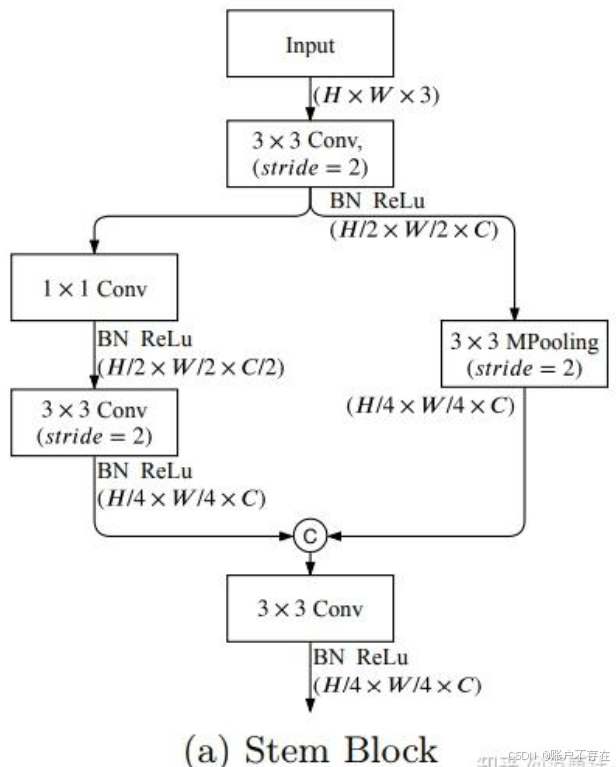
代码部分如下
'''
尺寸变为原来的1/4
输出通道固定为16
'''
class StemBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel):
super(StemBlock, self).__init__()
ch = np.array(np.array([8, 16, 32]), dtype= int)
self.conv = ConvBNReLU(in_channel, ch[1], 3, stride=2)
self.left = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(ch[1], ch[0], 1, stride=1, padding=0),
ConvBNReLU(ch[0], ch[1], 3, stride=2),
)
self.right = nn.MaxPool2d(
kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, ceil_mode=False)
self.fuse = ConvBNReLU(ch[2], ch[1], 3, stride=1)
def forward(self, x):
feat = self.conv(x)
feat_left = self.left(feat)
feat_right = self.right(feat)
feat = torch.cat([feat_left, feat_right], dim=1)
feat = self.fuse(feat)
return feat
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 1024, 2048) #bchw
stem = StemBlock(3) # in_channel由x的channel决定
feat = stem(x)
print(feat.size())
'''torch.Size([4, 16, 256, 512])'''
GE Block结构
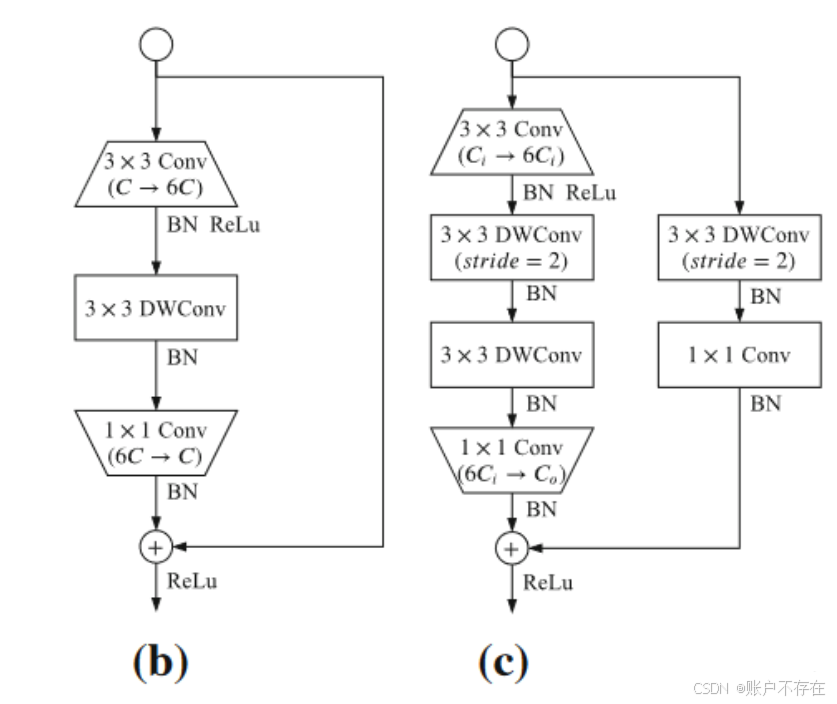
代码部分如下
'''
输出通道与输入通道一样, 图像尺寸不变
'''
class GELayerS1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_chan, out_chan, exp_ratio=6):
super(GELayerS1, self).__init__()
mid_chan = in_chan * exp_ratio
self.conv1 = ConvBNReLU(in_chan, in_chan, 3, stride=1)
self.dwconv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
in_chan, mid_chan, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
padding=1, groups=in_chan, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_chan),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), # not shown in paper
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
mid_chan, out_chan, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chan),
)
self.conv2[1].last_bn = True
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
feat = self.conv1(x)
feat = self.dwconv(feat)
feat = self.conv2(feat)
feat = feat + x
feat = self.relu(feat)
return feat
'''
输出通道为设置的通道out_chan, 图像尺寸变为原来的1/2
'''
class GELayerS2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_chan, out_chan, exp_ratio=6):
super(GELayerS2, self).__init__()
mid_chan = in_chan * exp_ratio
self.conv1 = ConvBNReLU(in_chan, in_chan, 3, stride=1)
self.dwconv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
in_chan, mid_chan, kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, groups=in_chan, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_chan),
)
self.dwconv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
mid_chan, mid_chan, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
padding=1, groups=mid_chan, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_chan),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), # not shown in paper
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
mid_chan, out_chan, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chan),
)
self.conv2[1].last_bn = True
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
in_chan, in_chan, kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, groups=in_chan, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_chan),
nn.Conv2d(
in_chan, out_chan, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chan),
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
feat = self.conv1(x)
feat = self.dwconv1(feat)
feat = self.dwconv2(feat)
feat = self.conv2(feat)
shortcut = self.shortcut(x)
feat = feat + shortcut
feat = self.relu(feat)
return feat
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 1024, 2048) #bchw
ge1 = GELayerS1(3, 3) # in_channel由x的channel决定, out_channel必须与in_channel一致,因为残差连接必须保证通道一致
feat = ge1(x)
print(feat.size())
'''torch.Size([4, 3, 1024, 2048])'''
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 1024, 2048)
ge2 = GELayerS2(3, 16)
feat = ge2(x)
print(feat.size())
'''torch.Size([4, 16, 512, 1024])
h,w: 1/2
out_chan: any
'''
CE Block
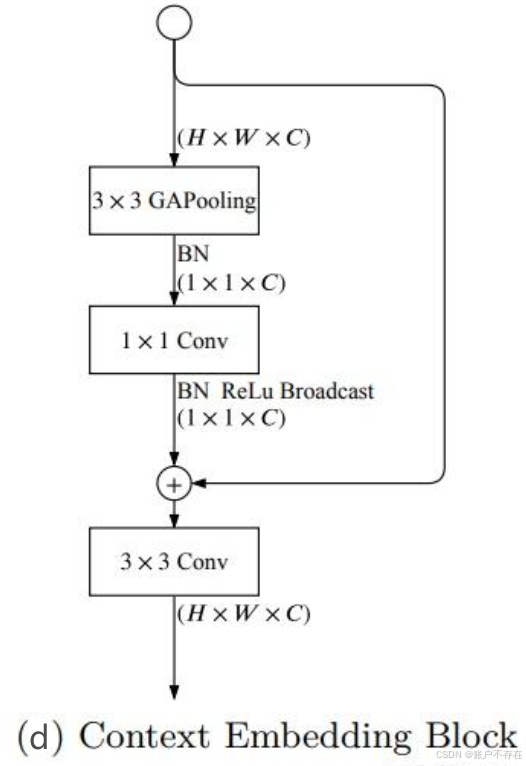
部分代码如下
'''
#NOTE: 源码中channels固定为128, 这里修改为可支持任意值
不改输入特征尺寸和通道
'''
class CEBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels):
super(CEBlock, self).__init__()
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels)
self.conv_gap = ConvBNReLU(channels, channels, 1, stride=1, padding=0)
# TODO: in paper here is naive conv2d, no bn-relu
self.conv_last = ConvBNReLU(channels, channels, 3, stride=1)
def forward(self, x):
feat = torch.mean(x, dim=(2, 3), keepdim=True)
feat = self.bn(feat)
feat = self.conv_gap(feat)
feat = feat + x
feat = self.conv_last(feat)
return feat
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 1024, 2048)
ceb = CEBlock(3) #in_channel由x的channel决定
feat = ceb(x)
print(feat.size())
'''torch.Size([4, 3, 1024, 2048])'''
Semantic Branch的代码
该模块包含了上述StemBlock、GE Block和CE Block。部分代码如下
'''
示例
输入
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 1024, 2048)
输出
torch.Size([4, 16, 256, 512]) ch=16 , w,h:1/4
torch.Size([4, 32, 128, 256]) ch=32 , w,h:1/8
torch.Size([4, 64, 64, 128]) ch=64 , w,h:1/16
torch.Size([4, 128, 32, 64]) ch=128 , w,h:1/32
torch.Size([4, 128, 32, 64]) ch=128 , w,h:1/32
'''
class SegmentBranch(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel):
super(SegmentBranch, self).__init__()
self.S1S2 = StemBlock(in_channel)
ch = np.array(np.array([16, 32, 64, 128]), dtype=int)
self.S3 = nn.Sequential(
GELayerS2(ch[0], ch[1]),
GELayerS1(ch[1], ch[1]),
)
self.S4 = nn.Sequential(
GELayerS2(ch[1], ch[2]),
GELayerS1(ch[2], ch[2]),
)
self.S5_4 = nn.Sequential(
GELayerS2(ch[2], ch[3]),
GELayerS1(ch[3], ch[3]),
GELayerS1(ch[3], ch[3]),
GELayerS1(ch[3], ch[3]),
)
self.S5_5 = CEBlock()
def forward(self, x):
feat2 = self.S1S2(x)
feat3 = self.S3(feat2)
feat4 = self.S4(feat3)
feat5_4 = self.S5_4(feat4)
feat5_5 = self.S5_5(feat5_4)
return feat2, feat3, feat4, feat5_4, feat5_5
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 1024, 2048)
segment = SegmentBranch(3)
feat_seg = segment(x)
for i in feat_seg:
print(i.size())
'''
torch.Size([4, 16, 256, 512]) ch=16, w,h:1/4
torch.Size([4, 32, 128, 256]) ch=32 , w,h:1/8
torch.Size([4, 64, 64, 128]) ch=64, w,h:1/16
torch.Size([4, 128, 32, 64]) ch=128 , w,h:1/32
torch.Size([4, 128, 32, 64]) ch=128, w,h:1/32
'''
Aggregation Layer
Aggregation Layer接收了Detail Branch和Semantic Branch的结果,通过图e中的一系列操作进行特征融合。
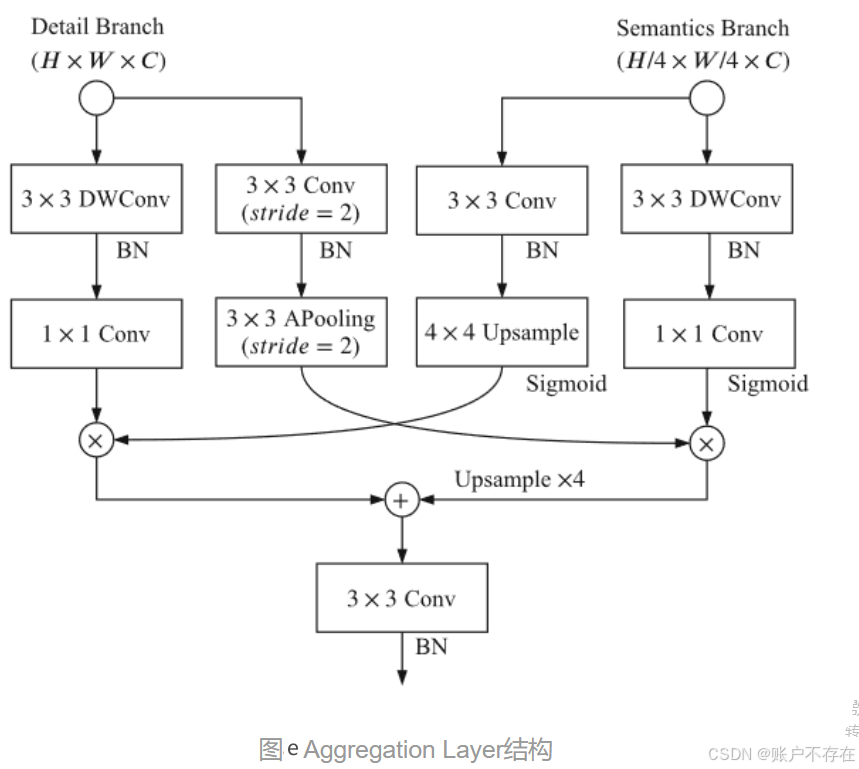
部分代码如下
'''
Aggregation Layer
输入1: H,W,C
输入2: H/4, W/4,C
输出: H,W,C
'''
class BGALayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(BGALayer, self).__init__()
ch = int(128)
self.left1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
ch, ch, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
padding=1, groups=ch, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch),
nn.Conv2d(
ch, ch, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
padding=0, bias=False),
)
self.left2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
ch, ch, kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
self.right1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
ch, ch, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch),
)
self.right2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
ch, ch, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
padding=1, groups=ch, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch),
nn.Conv2d(
ch, ch, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
padding=0, bias=False),
)
self.up1 = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=4)
self.up2 = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=4)
##TODO: does this really has no relu?
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
ch, ch, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), # not shown in paper
)
def forward(self, x_d, x_s):
dsize = x_d.size()[2:]
left1 = self.left1(x_d)
left2 = self.left2(x_d)
right1 = self.right1(x_s)
right2 = self.right2(x_s)
right1 = self.up1(right1)
left = left1 * torch.sigmoid(right1)
right = left2 * torch.sigmoid(right2)
right = self.up2(right)
out = self.conv(left + right)
return out
if __name__ == "__main__":
left = torch.randn(16, 128, 64, 128)
right = torch.randn(16, 128, 16, 32)
bga = BGALayer()
feat = bga(left, right)
print(feat.size())
'''torch.Size([16, 128, 64, 128])'''
分割头SegHead
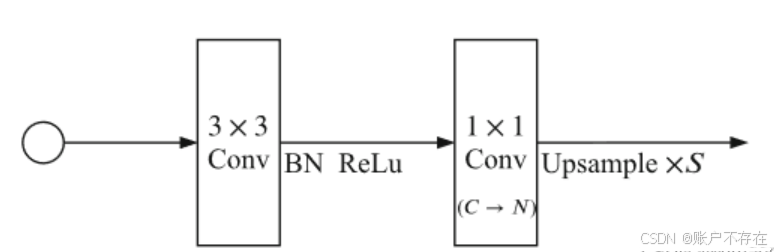
分割头的部分代码如下,其中S是上采样倍率
'''
输入通道变为类别数目
尺寸变成原来的up_factor倍
如: input (6,3,16,16) #bchw
nclass=2
output (6,2,128,128)
'''
class SegmentHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_chan, mid_chan, n_classes, up_factor=8, aux=True):
super(SegmentHead, self).__init__()
self.conv = ConvBNReLU(in_chan, mid_chan, 3, stride=1)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(0.1)
self.up_factor = up_factor
out_chan = n_classes
mid_chan2 = up_factor * up_factor if aux else mid_chan
up_factor = up_factor // 2 if aux else up_factor
self.conv_out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Sequential(
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
ConvBNReLU(mid_chan, mid_chan2, 3, stride=1)
) if aux else nn.Identity(),
nn.Conv2d(mid_chan2, out_chan, 1, 1, 0, bias=True),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=up_factor, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
)
def forward(self, x):
feat = self.conv(x)
feat = self.drop(feat)
feat = self.conv_out(feat)
return feat
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 64, 128)
head = SegmentHead(3, 64, 19) # in_channel由x的channel决定, mid_channel:any, nclass:any
logits = head(x)
print(logits.size())
''' torch.Size([4, 19, 512, 1024])
h,w : 8倍
'''
终极BiseNet v2代码
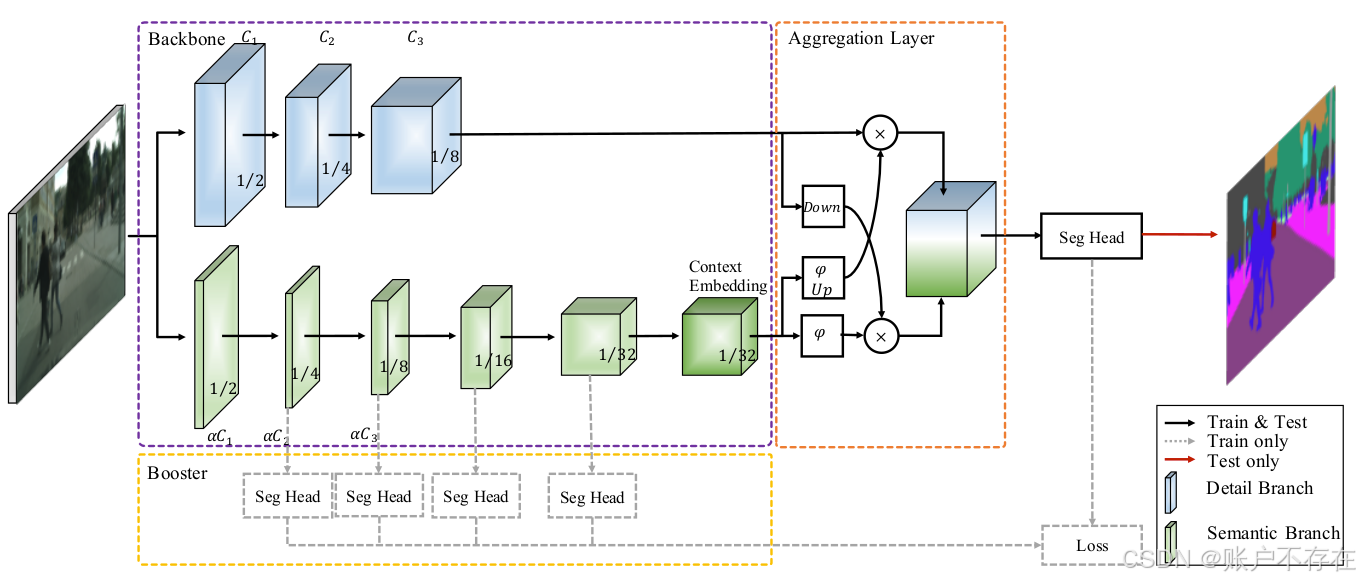
'''
输入通道变为类别数目
图像尺寸不变
如: input (6,3,16,16) #bchw
nclass=2
output (6,2,16,16)
'''
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.model_zoo as modelzoo
DEVICE = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
backbone_url = 'https://github.com/CoinCheung/BiSeNet/releases/download/0.0.0/backbone_v2.pth'
class BiSeNetV2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, n_classes, aux_mode='train', *args, **kwargs):
super(BiSeNetV2, self).__init__()
self.aux_mode = aux_mode
self.detail = DetailBranch(in_channel)
self.segment = SegmentBranch(in_channel)
self.bga = BGALayer()
## TODO: 从 1/8倍尺寸放大回原图, mid_channel(1024)可随意设置, in_channel(128)为DetailBranch输出的通道数
self.head = SegmentHead(int(128), int(1024), n_classes, up_factor=8, aux=False)
if self.aux_mode == 'train': #这几个分割头输入通道为SegmentBranch设置的通道数, mid_chanel=128
self.aux2 = SegmentHead(int(16 ), int(128 ), n_classes, up_factor=4)
self.aux3 = SegmentHead(int(32 ), int(128 ), n_classes, up_factor=8)
self.aux4 = SegmentHead(int(64 ), int(128 ), n_classes, up_factor=16)
self.aux5_4 = SegmentHead(int(128 ), int(128 ), n_classes, up_factor=32)
self.init_weights()
def forward(self, x):
size = x.size()[2:]
feat_d = self.detail(x)
feat2, feat3, feat4, feat5_4, feat_s = self.segment(x)
feat_head = self.bga(feat_d, feat_s)
logits = self.head(feat_head)
if self.aux_mode == 'train':
logits_aux2 = self.aux2(feat2)
logits_aux3 = self.aux3(feat3)
logits_aux4 = self.aux4(feat4)
logits_aux5_4 = self.aux5_4(feat5_4)
return logits, logits_aux2, logits_aux3, logits_aux4, logits_aux5_4
elif self.aux_mode == 'eval':
return logits,
elif self.aux_mode == 'pred':
logits = logits.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
logits = F.softmax(logits, 3)
return logits
else:
raise NotImplementedError
def init_weights(self):
for name, module in self.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, (nn.Conv2d, nn.Linear)):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(module.weight, mode='fan_out')
if module.bias is not None: nn.init.constant_(module.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(module, nn.modules.batchnorm._BatchNorm):
if hasattr(module, 'last_bn') and module.last_bn:
nn.init.zeros_(module.weight)
else:
nn.init.ones_(module.weight)
nn.init.zeros_(module.bias)
# self.load_pretrain()
def load_pretrain(self):
state = modelzoo.load_url(backbone_url)
#state = torch.load(r"D:\pretrain_models\backbone_v2.pth")
for name, child in self.named_children():
if name in state.keys():
child.load_state_dict(state[name], strict=True)
def get_params(self):
def add_param_to_list(mod, wd_params, nowd_params):
for param in mod.parameters():
if param.dim() == 1:
nowd_params.append(param)
elif param.dim() == 4:
wd_params.append(param)
else:
print(name)
wd_params, nowd_params, lr_mul_wd_params, lr_mul_nowd_params = [], [], [], []
for name, child in self.named_children():
if 'head' in name or 'aux' in name:
add_param_to_list(child, lr_mul_wd_params, lr_mul_nowd_params)
else:
add_param_to_list(child, wd_params, nowd_params)
return wd_params, nowd_params, lr_mul_wd_params, lr_mul_nowd_params
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 1024, 2048)
bisnetv2 = BiSeNetV2(3, n_classes=10) #in_channel由x的channel决定
output = bisnetv2(x)
for i in output:
print(i.size())
'''
torch.Size([4, 10, 1024, 2048])
torch.Size([4, 10, 1024, 2048])
torch.Size([4, 10, 1024, 2048])
torch.Size([4, 10, 1024, 2048])
torch.Size([4, 10, 1024, 2048])
'''
由此可见,BiSeNetV2有 5 个输出,其中第一个为主输出,其余4个为辅助输出,训练的时产生的loss关系如下代码所示
net = BiSeNetV2(3, num_classes=10)
net.train()
result = net(X)
pred = result[0] #主输出预测值
seg_loss = loss(result[0], gt) #主loss
aux_loss_1 = loss(result[1], gt) #辅助loss1
aux_loss_2 = loss(result[2], gt) #辅助loss2
aux_loss_3 = loss(result[3], gt)
aux_loss_4 = loss(result[4], gt)

























 873
873

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










