一、基本原理
1、线性分类器
线性分类器的判别函数为 ,其中
为一个 n 维列向量,称为权向量或权重;
为一个常数,称为阈值权或偏置 。
2、Fisher线性判别分析
2.1、Fisher线性判别分析的原理
Fisher线性判别分析(Fisher Linear Discriminant Analysis)就是为了求解上述判别函数 中的最优
和
,该方法是利用降维的思想将所有样本点投影到一条直线上,然后选择一个阈值将两类分开(以二分类问题为例),具体如下图所示。
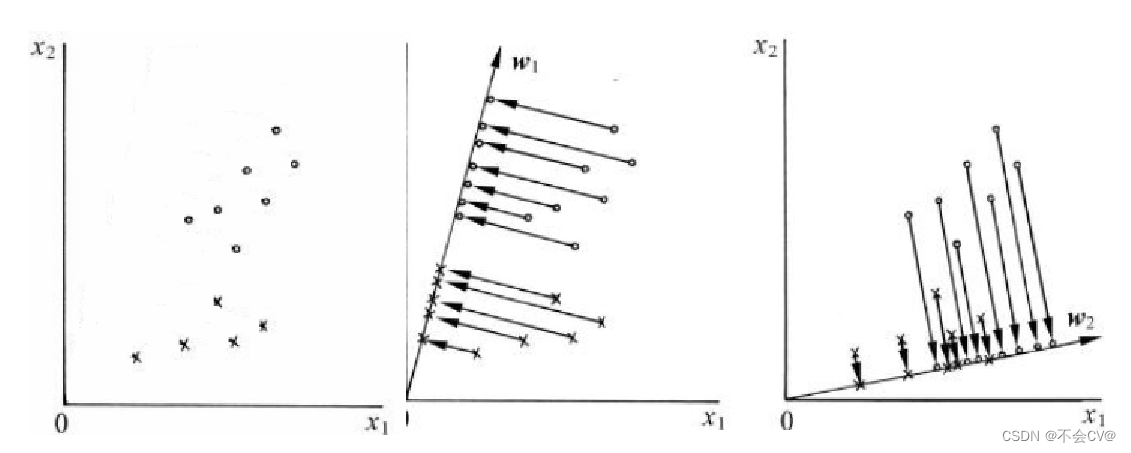
投影的准则: (1)两类之间的距离尽可能远;(2)每一类自身尽可能紧凑。根据上述准则可知图(b)的投影效果图(c)要好。
2.2、求解过程:
2.2.1、权向量求解
以二分类问题为例,现做出如下约定: 和
分别两类(原始)数据的均值向量;
和
分别表示两类(原始)数据的离散度矩阵;
和
分别表示两类(投影后,一维)数据的均值;
和
分别表示两类(投影后,一维)数据的离散度。则上述投影准则中,准则(1)可以用
越大越好来表示,准则(2)用
越小越好来表示。所以Fisher准则函数可用如下的式子来表示:
此时,优化的目标就变成了下式:
定义:(1)类间散度矩阵(给出两种计算方式)
(2)类内散度矩阵
(3)总类内散度矩阵(给出两种计算方式)
则上述的Fisher准则函数可简化为:
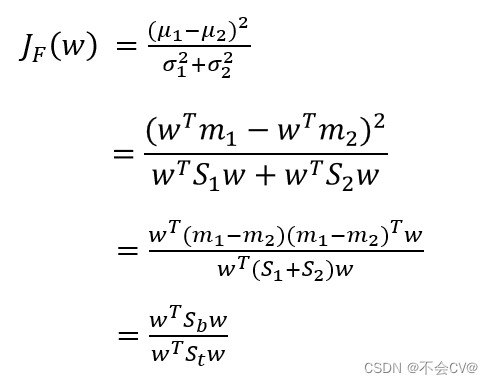
最后求解可得:
2.2.2、分割阈值求解
分割阈值 的求解有两种方法:
(1)取投影后两类均值的中点作为分割阈值
(2)如果投影到一维空间后样本接近正态分布,可以根据样本拟合正态分布,估计分类阈值。
3、具体实例
已知样本点及其label如下,要求使用Fisher分类器对其进行分类,并自己设计一个测试集进行测试。
x = np.array([[2.9500, 6.6300], [2.5300, 7.7900],
[3.5700, 5.6500], [3.1600, 5.4700],
[2.5800, 4.4600], [2.1600, 6.2200],
[3.2700, 3.5200]])
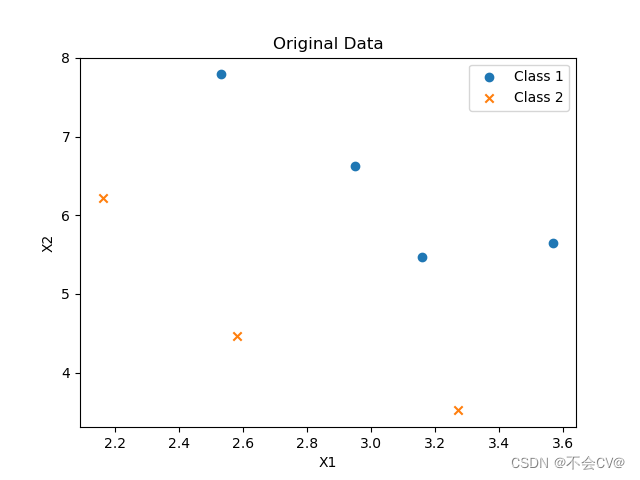
label = np.array([1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2])原始数据:
测试集:
test = np.array([[5.2500, 4.6500], [5.6400, 2.5300],
[2.2400, 2.4500], [3.2100, 2.1800],
[5.4500, 5.6700], [1.2800, 2.2200]])分类结果:
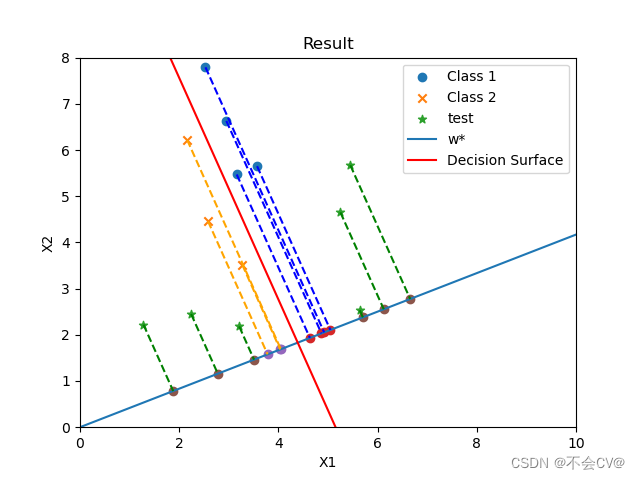
测试集的label预测结果:
![]()
二、代码实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
def calculate_data(x):
"""统计量计算"""
mean_w = np.mean(x, axis=0)
scatter_matrix = np.zeros((x.shape[1], x.shape[1]))
for data in x:
data = data.reshape((-1, 1))
mean_w = mean_w.reshape((-1, 1))
scatter_matrix += (data - mean_w).dot((data - mean_w).T)
return mean_w, scatter_matrix
def predict(x, w, threshold):
"""标签预测"""
predict_label = []
for data in x:
value = w.T.dot(data) + threshold
if value > 0:
predict_label.append(1)
else:
predict_label.append(2)
return predict_label
def subpoint_draw(x, w, color):
"""绘制投影点和投影线"""
subpoints = np.dot(x, w) / np.dot(w.T, w) * w.T
plt.scatter(subpoints[:, 0], subpoints[:, 1])
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
x_i = x[i]
subpoint_i = subpoints[i]
plt.plot([x_i[0], subpoint_i[0]], [x_i[1], subpoint_i[1]],
linestyle='--', color=color)
x = np.array([[2.9500, 6.6300], [2.5300, 7.7900],
[3.5700, 5.6500], [3.1600, 5.4700],
[2.5800, 4.4600], [2.1600, 6.2200],
[3.2700, 3.5200]])
label = np.array([1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2])
test = np.array([[5.2500, 4.6500], [5.6400, 2.5300],
[2.2400, 2.4500], [3.2100, 2.1800],
[5.4500, 5.6700], [1.2800, 2.2200]])
mu1, s1 = calculate_data(x[label == 1])
mu2, s2 = calculate_data(x[label == 2])
# 计算先验概率
p_p1 = len(x[label == 1]) / len(label)
p_p2 = 1 - p_p1
# 计算s_w和s_b
s_w = p_p1 * s1 + p_p2 * s2
s_b = p_p1 * p_p2 * (mu1 - mu2).dot((mu1 - mu2).T)
# 计算最优解w(投影向量)
w = np.linalg.inv(s_w).dot(mu1 - mu2)
projected_data = test.dot(w)
# 设置决策阈值
threshold = -0.5 * \
(mu1 + mu2).T.dot(np.linalg.inv(s_w).dot(mu1 - mu2)) - math.log(p_p2 / p_p1)
# 预测测试数据集的标签
predict_label = predict(test, w, threshold)
print(predict_label)
class_1 = x[label == 1]
class_2 = x[label == 2]
# 计算决策面参数
k = 0 - w[0, 0] / w[1, 0]
b = 0 - threshold[0] / w[1, 0]
data = np.linspace(0, 8, 100)
y = k * data + b
# 添加坐标轴标签
plt.xlabel('X1')
plt.ylabel('X2')
# 确定坐标轴范围
plt.xlim(0, 10)
plt.ylim(0, 8)
# 绘制数据分布
plt.scatter(class_1[:, 0], class_1[:, 1], label='Class 1', marker='o')
plt.scatter(class_2[:, 0], class_2[:, 1], label='Class 2', marker='x')
plt.scatter(test[:, 0], test[:, 1], label='test', marker='*')
# 绘制投影方向w*
plt.plot([0, w[0, 0]], [0, w[1, 0]], label='w*')
# 绘制决策面
plt.plot(data, y, label='Decision Surface', color='red')
# 绘制投影点
subpoint_draw(x[label == 1], w, color='blue')
subpoint_draw(x[label == 2], w, color='orange')
subpoint_draw(test, w, color='green')
plt.title('Result')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
三、参考资料
《模式识别:模式识别与机器学习第4版》第四版,张学工、汪小我编著




 本文介绍了Fisher线性判别分析的基本原理,包括判别函数、投影准则、求解过程,以及如何通过Python实现一个分类实例。文章详细展示了如何计算权向量和分割阈值,并给出了一个具体的代码实现和应用案例。
本文介绍了Fisher线性判别分析的基本原理,包括判别函数、投影准则、求解过程,以及如何通过Python实现一个分类实例。文章详细展示了如何计算权向量和分割阈值,并给出了一个具体的代码实现和应用案例。
















 3595
3595

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








