课程内容
1、集合的概述,体系结构
2、单列集合Collection
3、List有序的。ArrayList,LinkedList
4、泛型
1、集合分类:
单列集合:每个元素都是一个单独的个体。
双列集合:每个操作都是针对一对数据来进行的,一对数据作为一个整体。键值对。
2、单列集合的体系:
Collection 单列集合的顶层接口
List 有序的子接口
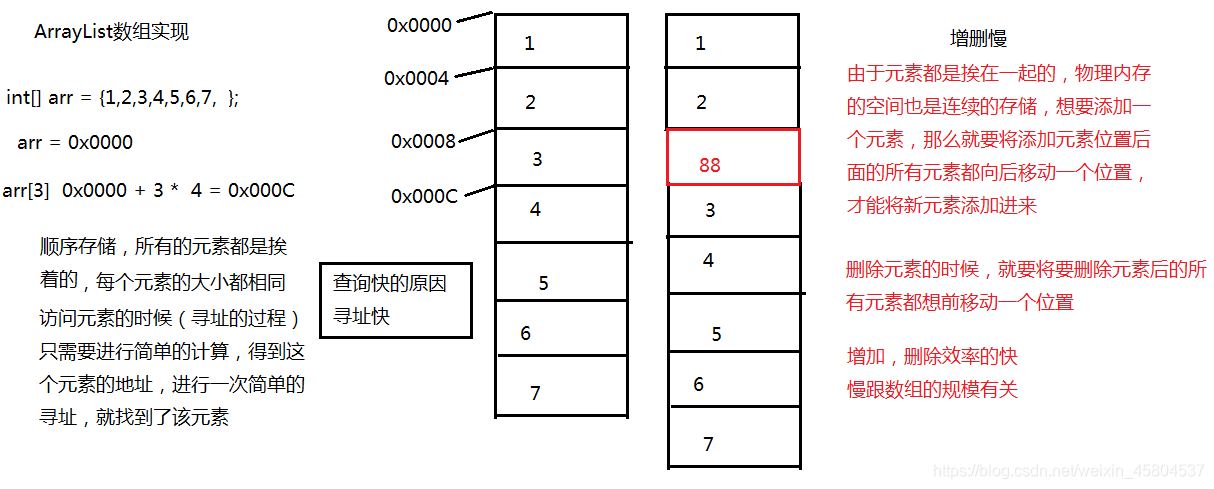
ArrayList 顺序存储的实现类,查询快,增删慢
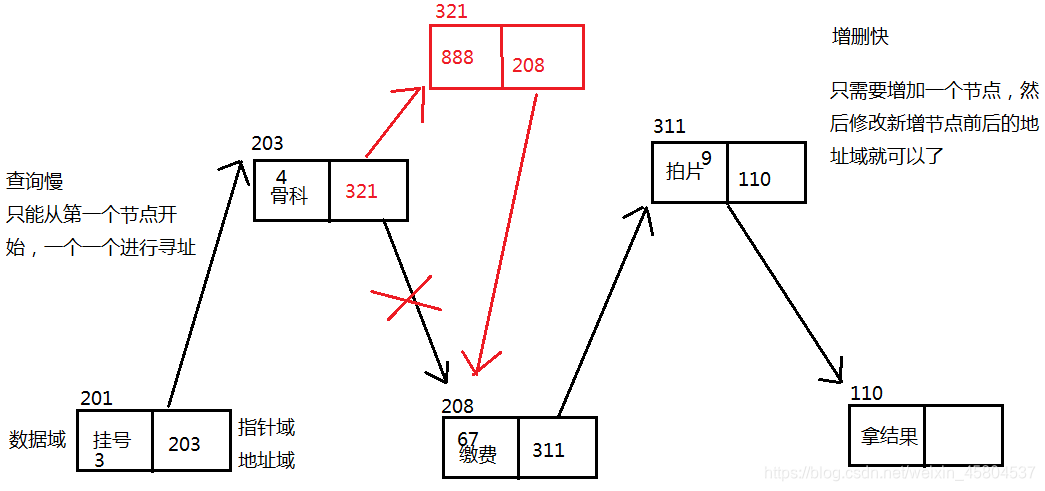
LinkedList 链式存储,查询慢,增删块
Set 无序的子接口
HashSet 哈希表存储
LinkedHashSet HashSet的子类
3、双列集合的体系:
Map 双列集合的顶层接口
HashMap 哈希表存储Map的实现类
LinkedHashMap HashMap的子类
1、单词:收集,集合
2、单列集合的顶层接口:定义的所有单列集合中共有的功能。
3、Collection是一个接口,不能实例化,不能创建对象,找一个该接口的实现类对象。
使用接口类型的引用,指向实现类的对象
Collection类型的引用,指向ArrayList类型的对象(只能调用接口中的方法)
4、常用的方法
add(Object obj):将obj这个元素添加到集合中
remove(Object obj):将obj元素从集合中移除
contains(Object obj)判断集合中是否包含obj这个元素
isEmpty()就是集合为空就返回true
size()返回就是集合中元素的个数
clear();清空集合中的元素
package com. ujiuye. homework ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. Collection ;
public class Demo_1 {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
Collection coll = new ArrayList ( ) ;
coll. add ( 123 ) ;
coll. add ( "hello" ) ;
coll. add ( 1.2 ) ;
coll. add ( true ) ;
coll. add ( 'a' ) ;
System . out. println ( coll) ;
coll. remove ( true ) ;
System . out. println ( coll) ;
System . out. println ( coll. contains ( 'a' ) ) ;
System . out. println ( coll. contains ( 'p' ) ) ;
System . out. println ( coll. isEmpty ( ) ) ;
System . out. println ( coll. size ( ) ) ;
coll. clear ( ) ;
System . out. println ( coll) ;
System . out. println ( coll. isEmpty ( ) ) ;
System . out. println ( coll. size ( ) ) ;
}
}
1、转成数组,通过遍历数组,来间接的访问集合
2、方法:Object[] toArray():将调用者集合转成Object类型的数组
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. Collection ;
public class Demo_2 {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
Collection coll = new ArrayList ( ) ;
coll. add ( 520 ) ;
coll. add ( "成都" ) ;
coll. add ( true ) ;
coll. add ( 9.9 ) ;
System . out. println ( coll) ;
Object [ ] objs = coll. toArray ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < objs. length; i++ ) {
System . out. println ( objs[ i] ) ;
}
}
}
1、addAll(Collection c):将参数c中的所有元素,都添加到调用者集合中
2、removeAll(Collection c):将参数集合c中的元素都从调用者集合中移除
3、containsAll(Collection c):判断调用者集合中是否全部包含参数集合c中的元素
4、retainAll(Collection<?> c) 参数c中有哪些元素,就在调用者集合中保留哪些元素(参数c集合和调用者集合中共有的元素)
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. Collection ;
public class Demo_3 {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
Collection coll1 = new ArrayList ( ) ;
coll1. add ( "赵云" ) ;
coll1. add ( "关羽" ) ;
coll1. add ( "张飞" ) ;
System . out. println ( coll1) ;
Collection coll2 = new ArrayList ( ) ;
coll2. add ( 897 ) ;
coll2. add ( 520 ) ;
coll2. add ( 520 ) ;
coll2. add ( 825 ) ;
coll2. add ( 825 ) ;
System . out. println ( "coll2 " + coll2) ;
coll1. addAll ( coll2) ;
System . out. println ( "coll1:AddAll " + coll1) ;
System . out. println ( "containsAll: " + coll1. containsAll ( coll2) ) ;
Collection coll3 = new ArrayList ( ) ;
coll3. add ( 825 ) ;
coll3. add ( 520 ) ;
coll3. add ( "张飞" ) ;
System . out. println ( "coll3 : " + coll3) ;
coll1. removeAll ( coll3) ; ‘
System . out. println ( "coll1 :removeAll: " + coll1) ;
System . out. println ( "====================================" ) ;
Collection coll4 = new ArrayList ( ) ;
coll4. add ( 520 ) ;
coll4. add ( "王祖贤" ) ;
coll4. add ( "王祖蓝" ) ;
coll4. add ( "王宝强" ) ;
System . out. println ( coll4) ;
Collection coll5 = new ArrayList ( ) ;
coll5. add ( 520 ) ;
coll5. add ( "王祖贤" ) ;
coll5. add ( "周润发" ) ;
coll5. add ( "马蓉" ) ;
System . out. println ( coll5) ;
coll4. retainAll ( coll5) ;
System . out. println ( coll4) ;
}
}
1、迭代:更新迭代,从某一个到下一个的过程的含义
2、迭代器:专门用于将集合中的元素,一个到另一个逐个进行迭代的过程,就是提供一个方法对集合容器对象都进行访问。而又不去暴露对象容器的内部细节。集合容器内部结构不同,很多时候不知道怎样去遍历一个容器中所有的元素是。所以为了容器中的元素操作起来更为简单,java引入了迭代器模式,把访问不同逻辑从不同类型集合类中抽取出来,避免了向外部暴露集合内部的内部结构。
3、获取:集合自己内部有一个可以迭代自己的对象,从集合中获取即可
Iterator iterator()
4、迭代器的使用:
方法iterator()返回是一个Iterator接口的实现类对象可以使用Iterator接口中提供的方法。
hastNext():判断集合中是否还有下一个元素
next():获取集合中的下一个元素,让迭代器指针发生一次移动
remove();删除迭代器正在遍历的那个元素
5、迭代器在使用时候的注意事项
(1)迭代器对象虽然多次调用next方法,都是同样的名称,但是每次调用方法返回的内容是不一样的。
next方法既可以获取下一个元素,也会让迭代器对象,向前移动一步。
(2)如果没有下一个元素,仍然调用next方法,出现NoSuchElementException(没有当前元素异常)可以使用hasNext方法进行判断,如果为true就调用next方法,为flalse就不调用next方法
(3)hastNext方法不会移动迭代器指针的位置
(4)next()会移动迭代器指针的位置
(5)不要只判断一次hasNext方法,就调用多次next方法
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. Collection ;
import java. util. Iterator ;
public class Demo_5 {
private static final Object Person = null ;
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
Collection coll = new ArrayList ( ) ;
coll. add ( new Person ( "张三" , 23 ) ) ;
coll. add ( new Person ( "李四" , 24 ) ) ;
coll. add ( new Person ( "王五" , 25 ) ) ;
coll. add ( new Person ( "赵六" , 26 ) ) ;
coll. add ( new Person ( "小七" , 27 ) ) ;
Iterator it = coll. iterator ( ) ;
while ( it. hasNext ( ) ) {
Object obj = it. next ( ) ;
Person p = ( Person ) obj;
System . out. println ( p. getName ( ) + " " + p. getAge ( ) ) ;
}
}
}
1、概述:
是Collection有序的子接口
2、特点:
有序:每个元素都有自己位置,不同的位置有区别的
有索引:每个元素都有自己的编号
可以重复:即使是值相同的元素,位置和索引是不同的,可以区分相同的值
3、特有方法:
add(int index,Object obj): 在指定索引上,添加指定的元素
remove(int index):删除指定索引上的元素
set(int intdex,Object obj):将指定索引上的值,修改为指定的值
get(int index):获取指定索引上的值
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. List ;
public class Demo_6 {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
List list = new ArrayList ( ) ;
list. add ( 0 , 123 ) ;
list. add ( 1 , 521 ) ;
list. add ( 0 , "java" ) ;
list. add ( "hello" ) ;
System . out. println ( list) ;
list. remove ( 1 ) ;
System . out. println ( list) ;
list. set ( 2 , "约会" ) ;
System . out. println ( list) ;
System . out. println ( list. get ( 2 ) ) ;
}
}
1、针对就是List集合特有的遍历方式
2、可以通过集合中的size方法获取集合中元素的个数,List集合有索引,结合get方法就能够获取List集合中所有的元素。
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. List ;
public class Demo_7 {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
List list = new ArrayList ( ) ;
list. add ( 0 , 123 ) ;
list. add ( 1 , 521 ) ;
list. add ( 0 , "java" ) ;
list. add ( "hello" ) ;
System . out. println ( list) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < list. size ( ) ; i++ ) {
System . out. println ( list. get ( i) ) ;
}
}
}
1、ConcurrentModificationException
并发修改异常
2、出现的原因:在使用【迭代器对象】遍历集合的同时,使用【集合对象】增加或删除集合的元素
3、避免的方式:两种方式都是针对list集合
方式1:迭代器遍历,迭代器增加
方法2:集合遍历,集合增加
4、方式1:迭代器遍历,迭代器增加:问题普通的迭代器中没有增加的方法,需要使用List中特有的迭代器
迭代器增加:问题普通的迭代器中没有增加的方法,需要使用List中特有的迭代器
列表迭代器:ListIterator是Iterator的子接口,拥有Iterator中所有的方法,还要特有的方法
列表迭代器的获取:listIterator();
方式2:集合遍历,集合增加
list特有的遍历方式,size和get方法相结合
5、不是所有的集合在进行迭代器遍历,迭代器增删的时候都会出现并发修改异常
集合中的倒数第二个元素是不会发生的,其他都是会发生了。
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. Iterator ;
import java. util. List ;
import java. util. ListIterator ;
public class Demo_8 {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
List list = new ArrayList ( ) ;
list. add ( "hello" ) ;
list. add ( "java" ) ;
list. add ( "php" ) ;
list. add ( "C" ) ;
list. add ( "Python" ) ;
System . out. println ( list) ;
Iterator it = list. iterator ( ) ;
while ( it. hasNext ( ) ) {
Object obj = it. next ( ) ;
if ( obj. equals ( "C" ) ) {
list. remove ( "java" ) ;
}
}
System . out. println ( list) ;
}
private static void solve_1 ( List list) {
System . out. println ( "-----------解决方式1---------------------" ) ;
ListIterator lit = list. listIterator ( ) ;
while ( lit. hasNext ( ) ) {
Object obj = lit. next ( ) ;
if ( obj. equals ( "java" ) ) {
lit. add ( "go" ) ;
}
}
System . out. println ( list) ;
System . out. println ( "-----------解决方式2---------------------" ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < list. size ( ) ; i++ ) {
if ( list. get ( i) . equals ( "java" ) ) {
list. add ( "go" ) ;
}
}
System . out. println ( list) ;
}
}
1、概述
List是一个接口,根据底层的实现方式不同,具有不同的实现类
2、ArrayList:数组实现,顺序存储
3、LinkedList:节点实现,链式存储
1、也是List一个实现类
2、没有特有方法
存储的方式数组实现,顺序存储
通过物理内存位置的关系,来表述逻辑顺序的相邻
3、图示
1、List的一个实现类
2、存储方式:
节点实现,链式存储
不通过物理位置的相邻,来表示逻辑位置的相邻
每个元素都在一个节点中,节点除了元素数据本身以外,还需要存储是下一个节点内存地址
3、图示
4、特点:
查询速度慢,需要根据前面的节点来获取后一个节点的地址,前面所有的节点都要访问一遍,节点越多,查询速度就越慢
增删速度快:增删一个元素,只需要修改前后两个节点的指针域即可,与集合的规模没有关系
5、LinkedList中特有的方法
addFirst(Object obj)在头部添加元素
addLast(Object obj)在尾部添加元素
removeFirst() 移除头部元素
removeLast() 移除尾部元素
getFirst() 获取头部元素
getLast() 获取尾部元素
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. LinkedList ;
public class Demo_9 {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
LinkedList ll = new LinkedList ( ) ;
ll. addFirst ( "hello" ) ;
ll. addFirst ( "java" ) ;
ll. addFirst ( "php" ) ;
System . out. println ( ll) ;
ll. addLast ( "C" ) ;
ll. addLast ( "GO" ) ;
System . out. println ( ll) ;
ll. removeFirst ( ) ;
ll. removeLast ( ) ;
System . out. println ( ll) ;
System . out. println ( ll. getFirst ( ) ) ;
System . out. println ( ll. getLast ( ) ) ;
}
}
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. LinkedList ;
public class Demo_10 {
final static int NUM = 99999 ;
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
linkedListFind ( ) ;
}
public static void linkedListFind ( ) {
LinkedList alist = new LinkedList ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < NUM; i++ ) {
alist. addFirst ( i) ;
}
long start = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < alist. size ( ) ; i++ ) {
alist. get ( i) ;
}
long end = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
System . out. println ( "LinkedList查询元素的时间:" + ( end - start) ) ;
}
public static void arrayListFind ( ) {
ArrayList alist = new ArrayList ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < NUM; i++ ) {
alist. add ( i) ;
}
long start = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < alist. size ( ) ; i++ ) {
alist. get ( i) ;
}
long end = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
System . out. println ( "ArrayList查询元素的时间:" + ( end - start) ) ;
}
public static void arrayListAdd ( ) {
long start = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
ArrayList alist = new ArrayList ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < NUM; i++ ) {
alist. add ( 0 , i) ;
}
long end = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
System . out. println ( "ArrayList添加元素的时间:" + ( end - start) ) ;
}
public static void linkedListAdd ( ) {
long start = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
LinkedList alist = new LinkedList ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < NUM; i++ ) {
alist. addFirst ( i) ;
}
long end = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
System . out. println ( "LinkedList添加元素的时间:" + ( end - start) ) ;
}
public static void arrayListDel ( ) {
ArrayList alist = new ArrayList ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < NUM; i++ ) {
alist. add ( i) ;
}
long start = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
while ( ! alist. isEmpty ( ) ) {
alist. remove ( 0 ) ;
}
long end = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
System . out. println ( "ArrayList删除元素的时间:" + ( end - start) ) ;
}
public static void linkedListDel ( ) {
LinkedList alist = new LinkedList ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < NUM; i++ ) {
alist. addFirst ( i) ;
}
long start = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
while ( ! alist. isEmpty ( ) ) {
alist. removeFirst ( ) ;
}
long end = System . currentTimeMillis ( ) ;
System . out. println ( "LinkedList删除元素的时间:" + ( end - start) ) ;
}
}
1、泛型的概述和使用
2、泛型:广泛的类型,在定义一个类的时候,类型中有些方法参数,返回值类型不确定,就使用一个符号,来表示那些尚未确定的类型,这个符号就称为泛型。
3、使用:对于有泛型类,在这些类型后面跟上了一个尖括号,尖括号中写上泛型的确定类型的(在使用该类型创建对象的时候,就可以写出具体类型)
4、泛型的好处:
(1)提高了数据的安全性,将运行时的问题,提前暴露在编译时期
(2)避免向下转型的问题
5、注意事项:
(1)前后一致:在创建对象的时候,赋值符号前后中尖括号中的类型要一致
(2)泛型推断:如果创建对象的时候,前面已经写好了泛型,后面创建对象的类型就可以只写一个尖括号。“菱形泛型”
jdk1.7特性
(3)不能定义泛型数组,发生泛型擦除问题,失去了泛型存在的意义
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. Iterator ;
import java. util. List ;
public class Demo_11 {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
List list = new ArrayList ( ) ;
list. add ( 123 ) ;
list. add ( "hello" ) ;
list. add ( 43 ) ;
Iterator it = list. iterator ( ) ;
while ( it. hasNext ( ) ) {
Object next = it. next ( ) ;
}
List < String > = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
list2. add ( "php" ) ;
list2. add ( "java" ) ;
List < Integer > = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
list3. add ( 123 ) ;
list3. add ( 345 ) ;
Iterator < Integer > = list3. iterator ( ) ;
while ( iterator. hasNext ( ) ) {
Integer next = iterator. next ( ) ;
System . out. println ( next) ;
}
}
}
1、泛型类:带着泛型的类
2、格式:
class 类名<泛型类型1,泛型类型2,泛型类型3,....>{
}
3、说明
(1)类名后面跟着的泛型类型,是泛型的声明,一旦泛型声明出来,就相当于这个类型成为了已知类型,这个类型就可以在整个类中使用
(2)泛型声明的名称:只需要是一个合法的标识符即可,通常我们使用单个大写字母来表示。E,Q ,T,M,K,V
(3)泛型确定的时机:将来在使用这个类,创建对象的时候
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
public class FXclass < qq> {
public ArrayList < qq> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
public void addData ( qq t) {
alist. add ( t) ;
}
public qq getData ( ) {
return alist. get ( 0 ) ;
}
}
1、在方法声明中,带着泛型声明的方法,就是泛型方法
2、格式
修饰符 <泛型的声明1,泛型声明2,。。。> 返回值类型 方法名称(参数列表){
}
3、说明
(1)在方法上声明的泛型,可以在整个方法中使用,当做已知类型去使用
(2)如果是非静态方法,在方法上没有任何泛型的声明,可以使用类上声明的泛型
(3)如果是静态方法,在方法上没有任何泛型的声明,不可以使用类上声明的泛型,只能在静态方法上,声明泛型
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. Arrays ;
public class Demo_13 {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
String [ ] strs = { "hello" , "java" , "C" , "Php" } ;
swap ( strs, 0 , 1 ) ;
System . out. println ( Arrays . toString ( strs) ) ;
Integer [ ] arr = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 } ;
swap ( arr, 0 , 3 ) ;
System . out. println ( Arrays . toString ( arr) ) ;
}
public static < T > void swap ( T [ ] arr, int index1, int index2) {
T temp = arr[ index1] ;
arr[ index1] = arr[ index2] ;
arr[ index2] = temp;
}
}
1、使用泛型的时候,没有使用具体的泛型声明T,而是使用了和声明的某个泛型T有关的一类类型,就称为泛型的通配符
三种形式
2、第一种形式,使用?来表示可以是任意的类型
removeAll(Collection<?> c) 表示可以接受任意泛型类型的集合c
作为该方法的参数,参数集合的泛型可以和调用者集合泛型E没有任何关系
3、第二种形式,使用? extends E来表示某个泛型类型或是该泛型类型的子类
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 表示的是参数集合c中的泛型,必须是调用者集合泛型E的子类类型或者是本类类型,作为该方法的参数
4、第三种形式:使用?super E来表示必须是某个泛型类型或者是该泛型类型的父类类型
Arrays工具类中排序方法sort(T[] t,Comparator<? super T> c)
T就是该方法的泛型,T表示的就是数组中元素的类型<? super T>,表示的是可以接受泛型的类型必须是T类型或者是T类型的父类类型
package com. ujiuye. demos ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. Collection ;
public class Demo_14 {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
Collection < CharSequence > = new ArrayList < CharSequence > ( ) ;
coll1. add ( "java" ) ;
coll1. add ( "C" ) ;
coll1. add ( "python" ) ;
coll1. add ( "go" ) ;
System . out. println ( coll1) ;
Collection < Integer > = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
coll2. add ( 123 ) ;
coll2. add ( 234 ) ;
coll2. add ( 554 ) ;
coll1. removeAll ( coll2) ;
System . out. println ( coll1) ;
Collection < String > = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
coll3. add ( "123" ) ;
coll3. add ( "as" ) ;
coll3. add ( "asdf" ) ;
coll1. addAll ( coll3) ;
}
}





 本文深入解析了集合的体系结构,包括单列集合如ArrayList、LinkedList的特点与应用场景,双列集合Map的介绍,以及List的特性和遍历方法。同时,详细阐述了泛型的概念、使用方法和好处,包括泛型类、泛型方法的定义与使用。
本文深入解析了集合的体系结构,包括单列集合如ArrayList、LinkedList的特点与应用场景,双列集合Map的介绍,以及List的特性和遍历方法。同时,详细阐述了泛型的概念、使用方法和好处,包括泛型类、泛型方法的定义与使用。
















 716
716










