
原创,转载请著名作者和出处,谢谢!
接续上一篇TensorFlow DLL官方下载:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/weixin_44029053/article/details/114206494
这篇是关于TF C API 训练(python)和推理(C语言)一条龙流程,具有工业部署价值,非常可贵,且看且珍惜,诸君!

本文的测试环境:
Win10x64;
cuda101~102(同时安装三个版本);
TF1.15.0 GPU DLL(CPU版本DLL 亦可!且理论上以下C推理代码支持所有版本,因为TF C版本的DLL都把C++API封装好了,也就是高级api封装为低级api,调用的套路(接口)都是一致的!);
宇宙第一的IDE:VS2019
干趴atom的VSCODE,不错,还是微软的!
首先我们还是一经典的mnist为例,训练为冻结的pb文件用于c推理
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import absolute_import, unicode_literals
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import tensorflow as tf
import shutil
import os.path
export_dir = './models/'
if os.path.exists(export_dir):
shutil.rmtree(export_dir)
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("./MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
with tf.Graph().as_default():
## 变量占位符定义
x = tf.placeholder("float", shape=[None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", shape=[None, 10])
## 定义网络结构
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
#
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
#
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
#
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
#
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
#
y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
## 定义损失及优化器
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
with tf.Session() as sess:
## 初始化变量
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(1000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i % 100 == 0:
## 验证阶段dropout比率为1
train_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 1.0})
print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy))
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
print('test accuracy %g' % sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1.0}))
## 将网络中的权值变量取出来
_W_conv1 = sess.run(W_conv1)
_b_conv1 = sess.run(b_conv1)
_W_conv2 = sess.run(W_conv2)
_b_conv2 = sess.run(b_conv2)
_W_fc1 = sess.run(W_fc1)
_b_fc1 = sess.run(b_fc1)
_W_fc2 = sess.run(W_fc2)
_b_fc2 = sess.run(b_fc2)
## 创建另外一个图,验证权值的正确性并save model
with tf.Graph().as_default():
## 定义变量占位符
x_2 = tf.placeholder("float", shape=[None, 784], name="input")
y_2 = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 10])
## 网络的权重用上一个图中已经学习好的对应值
W_conv1_2 = tf.constant(_W_conv1, name="constant_W_conv1")
b_conv1_2 = tf.constant(_b_conv1, name="constant_b_conv1")
x_image_2 = tf.reshape(x_2, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
h_conv1_2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image_2, W_conv1_2) + b_conv1_2)
h_pool1_2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1_2)
#
W_conv2_2 = tf.constant(_W_conv2, name="constant_W_conv2")
b_conv2_2 = tf.constant(_b_conv2, name="constant_b_conv2")
h_conv2_2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1_2, W_conv2_2) + b_conv2_2)
h_pool2_2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2_2)
#
W_fc1_2 = tf.constant(_W_fc1, name="constant_W_fc1")
b_fc1_2 = tf.constant(_b_fc1, name="constant_b_fc1")
h_pool2_flat_2 = tf.reshape(h_pool2_2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1_2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat_2, W_fc1_2) + b_fc1_2)
#
# DropOut is skipped for exported graph.
## 由于是验证过程,所以dropout层去掉,也相当于keep_prob为1
#
W_fc2_2 = tf.constant(_W_fc2, name="constant_W_fc2")
b_fc2_2 = tf.constant(_b_fc2, name="constant_b_fc2")
#
y_conv_2 = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_2, W_fc2_2) + b_fc2_2, name="output")
with tf.Session() as sess_2:
sess_2.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
tf.train.write_graph(sess_2.graph_def, export_dir, 'expert-graph.pb', as_text=False)
correct_prediction_2 = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv_2, 1), tf.argmax(y_2, 1))
accuracy_2 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction_2, "float"))
print('check accuracy %g' % sess_2.run(accuracy_2, feed_dict={x_2: mnist.test.images, y_2: mnist.test.labels}))
PS:这里我们用了纯TensorFlow python API训练模冻结模型的,其实一般可以用Keras来训练和冻结(.h5转.pb),网上有相应代码,这里仅仅是演示,只要最后的x,y的张量名称记住以及输入输出的张量格式清楚就可以了
python部分推理测试:
我们的示例图片:
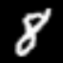


# import tensorflow as tf
# import cv2
# import numpy as np
# import os
# os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'
# frozen_graph_path="./model/"+"mnist_model_freeze_graph.pb"
# print(frozen_graph_path)
# # 读取模型并保存到序列化模型对象中
# with open(frozen_graph_path, "rb") as f:
# graph_def = tf.compat.v1.GraphDef()#tf.GraphDef()
# graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
# # 导入计算图
# graph = tf.Graph()
# with graph.as_default():
# tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, name="")
# for op in graph.get_operations():
# print(op.name)
# x_tensor = graph.get_tensor_by_name("input:0")
# y_tensor = graph.get_tensor_by_name("output:0")
# img1 = cv2.imread(r'H:\CPPProjects\TFDemo\x64\Release\mnist\00.PNG',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# img1 = cv2.resize(img1,(28,28),) # 为图片重新指定尺寸
# img1=(img1-1)/255.0
# # gray = cv2.cvtColor(img1,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# # gray = np.float(gray)
# # print(type(img1),img1)
# inputTensor=tf.convert_to_tensor(img1,dtype=float)
# # inputTensor=tf.expand_dims(inputTensor, 0, name=None)
# inputTensor=tf.reshape(inputTensor,[-1,784])
# print(inputTensor,type(inputTensor))
# with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
# res = sess.run(y_tensor, feed_dict={x_tensor:inputTensor})
# print(res)
#! -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import absolute_import, unicode_literals
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("./MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
with tf.Graph().as_default():
output_graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
output_graph_path = './models/expert-graph.pb'
with open(output_graph_path, 'rb') as f:
output_graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
_ = tf.import_graph_def(output_graph_def, name="")
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
input = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name("input:0")
output = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name("output:0")
img1 = cv2.imread(r'H:\CPPProjects\TFDemo\x64\Release\mnist\01.PNG',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
img1 = cv2.resize(img1,(28,28),) # 为图片重新指定尺寸
# print(img1)
img1=(img1-0)/255.0
img1=img1.reshape((-1,28*28))
print(type(img1),img1.shape,"\n")
print(mnist.test.images.shape,type(mnist.test.images))
# y_conv_2 = sess.run(output, feed_dict={input:mnist.test.images})
y_conv_2 = sess.run(output, feed_dict={input:img1})
#tf.convert_to_tensor()
with tf.Session() as sess2:
data_numpy =int((tf.argmax(y_conv_2, 1)).eval())# tf2:data_numpy = data_tensor.numpy()
print("result:",data_numpy)
以上训练和推理部分代码参考:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/guvcolie/article/details/77478973
如果没有意外的话,以上Python推理的结果应该和以下C推理的结果是完全一致的,因为调用同样的模型和底层tf1.15 api!
以下是c部分代码,当然部分使用了C++,毋庸置疑的是api部分是完全的C
PS:对于冻结的pb模型,编译(CPP)与训练(Python)版本TensorFlow版本需保持一致或相差不是很大,但是如果是1.x和2.x这样的跨度很有可能会推理失败(划重点)
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include "tensorflow/c/c_api.h"
#include "tensorflow/c/tf_attrtype.h"
#include "tensorflow/c/tf_datatype.h"
#include "tensorflow/c/tf_status.h"
#include "tensorflow/c/tf_tensor.h"
#include "tensorflow/c/eager/c_api.h"
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/dnn.hpp>
#pragma warning (disable: 4996)
using namespace std;
using namespace tensorflow;
//C++中argmin和argmax的实现- https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/theonegis/article/details/83036074
template<class ForwardIterator>
inline size_t argmin(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last)
{
return std::distance(first, std::min_element(first, last));
}
template<class ForwardIterator>
inline size_t argmax(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last)
{
return std::distance(first, std::max_element(first, last));
}
//https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1583407
TF_Tensor* CreateTensor(TF_DataType data_type, const std::int64_t* dims, std::size_t num_dims, const void* data, std::size_t len)
{
if (dims == nullptr || data == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
TF_Tensor* tensor = TF_AllocateTensor(data_type, dims, static_cast<int>(num_dims), len);
if (tensor == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
void* tensor_data = TF_TensorData(tensor);
if (tensor_data == nullptr)
{
TF_DeleteTensor(tensor);
return nullptr;
}
std::memcpy(TF_TensorData(tensor), data, (std::min)(len, TF_TensorByteSize(tensor)));
return tensor;
}
TF_Tensor* Mat2Tensor(cv::Mat img, TF_DataType data_type,int tagHeight,int tagWidth,int channel)
{
const std::vector<std::int64_t>input_dims = { 1, tagHeight, tagWidth, channel };
unsigned long long data_size = 1;
switch (data_type)
{
case TF_FLOAT:
data_size = sizeof(std::float_t);
break;
case TF_UINT8:
data_size = sizeof(std::uint8_t);
break;
case TF_UINT32:
data_size = sizeof(std::uint32_t);
break;
case TF_DOUBLE:
data_size = sizeof(std::double_t);
break;
default:
data_size = sizeof(std::float_t);
break;
}
for (auto i : input_dims)
{
data_size *= i;//bytes size
}
cv::resize(img, img, cv::Size(tagWidth, tagHeight));
cvtColor(img, img, (1== channel)?cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY:cv::COLOR_RGB2BGR);
//img = (img - 0) / 255.0f;
//mnist部分测试代码,其他dim需要自行填充数据
size_t length = tagHeight * tagWidth;
float* data = new float[length];
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; ++i)
{
data[i] = img.data[i] / 255.0f;//归一化
}
//PS:这里的(n,h,w,c)的n,也就是批大小TF会自动扩展一维无需手动扩增,这个和NCNN里面是一致的,需要注意一下!
TF_Tensor* image_input = CreateTensor(data_type, input_dims.data(), input_dims.size(), data, data_size);
return image_input;
}
//int main(int argc, char** argv)
//{
// printf("tf version:%s\n", TF_Version());
//
// return 0;
//}
TF_Buffer* read_file(const char* file);
void free_buffer(void* data, size_t length) {
free(data);
}
TF_Buffer* read_file(const char* file) {
FILE* f = fopen(file, "rb");
fseek(f, 0, SEEK_END);
long fsize = ftell(f);
fseek(f, 0, SEEK_SET); //same as rewind(f);
void* data = malloc(fsize);
fread(data, fsize, 1, f);
fclose(f);
TF_Buffer* buf = TF_NewBuffer();
buf->data = data;
buf->length = fsize;
buf->data_deallocator = free_buffer;
return buf;
}
void NoOpDeallocator(void* data, size_t a, void* b) {}
//https://github.com/AmirulOm/tensorflow_capi_sample/blob/master/main.c
// 加载的pb文件必须为已经冻结的!
int main()
{
//********* Read model
//TF_Graph* Graph = TF_NewGraph();
//TF_Status* Status = TF_NewStatus();
TF_Buffer* graph_def = read_file("expert-graph.pb");
TF_Graph* graph = TF_NewGraph();
// Import graph_def into graph
TF_Status* status = TF_NewStatus();
TF_ImportGraphDefOptions* opts = TF_NewImportGraphDefOptions();
TF_GraphImportGraphDef(graph, graph_def, opts, status);
TF_DeleteImportGraphDefOptions(opts);
if (TF_GetCode(status) != TF_OK) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Unable to import graph %s", TF_Message(status));
return 1;
}
fprintf(stdout, "Successfully imported graph");
TF_SessionOptions* SessionOpts = TF_NewSessionOptions();
//TF_Buffer* RunOpts = NULL;
//const char* saved_model_dir = "H:\\PYTHON\\xiufu\\model\\";
//const char* tags = "serve"; // default model serving tag; can change in future
//int ntags = 1;
//TF_Session* Session = TF_LoadSessionFromSavedModel(SessionOpts, RunOpts, saved_model_dir, &tags, ntags, Graph, NULL, Status);
TF_Session* Session = TF_NewSession(graph, SessionOpts, status);
if (TF_GetCode(status) == TF_OK)
{
printf("TF_LoadSessionFromSavedModel OK\n");
}
else
{
printf("%s", TF_Message(status));
}
//****** Get input tensor
//TODO : need to use saved_model_cli to read saved_model arch
int NumInputs = 1;
TF_Output* Input = (TF_Output*)malloc(sizeof(TF_Output) * NumInputs);
//x不用写input:0 虽然不知道为什么?y亦是如此
TF_Output t0 = { TF_GraphOperationByName(graph, "input"), 0 };
if (t0.oper == NULL)
printf("ERROR: Failed TF_GraphOperationByName input\n");
else
printf("TF_GraphOperationByName input is OK\n");
Input[0] = t0;
//********* Get Output tensor
int NumOutputs = 1;
TF_Output* Output = (TF_Output*)malloc(sizeof(TF_Output) * NumOutputs);
TF_Output t2 = { TF_GraphOperationByName(graph, "output"), 0 };
if (t2.oper == NULL)
printf("ERROR: Failed TF_GraphOperationByName output\n");
else
printf("TF_GraphOperationByName output is OK\n");
Output[0] = t2;
//********* Allocate data for inputs & outputs
TF_Tensor** InputValues = (TF_Tensor**)malloc(sizeof(TF_Tensor*) * NumInputs);
TF_Tensor** OutputValues = (TF_Tensor**)malloc(sizeof(TF_Tensor*) * NumOutputs);
//这里图片我们用OpenCV读取8的灰度图片
TF_Tensor* float_tensor = Mat2Tensor(cv::imread("./mnist/temp/demo.PNG"), TF_FLOAT,28,28,1);//TF_NewTensor(TF_FLOAT, dims, ndims, data, ndata, &NoOpDeallocator, 0);
if (float_tensor != NULL)
{
printf("TF_NewTensor is OK\n");
}
else
printf("ERROR: Failed TF_NewTensor\n");
InputValues[0] = float_tensor;
// //Run the Session
TF_SessionRun(Session, NULL, Input, InputValues, NumInputs, Output, OutputValues, NumOutputs, NULL, 0, NULL, status);
if (TF_GetCode(status) == TF_OK)
{
printf("Session is OK\n");
}
else
{
printf("%s", TF_Message(status));
}
// //Free memory
TF_DeleteGraph(graph);
TF_DeleteSession(Session,status);
TF_DeleteSessionOptions(SessionOpts);
TF_DeleteStatus(status);
void* buff = TF_TensorData(OutputValues[0]);
float* offsets = (float*)buff;
printf("Result Tensor :\n");
std::vector<float>result_list;
result_list.resize(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
//printf("%f,%d\n", offsets[i],(i));
result_list[i] = offsets[i];
}
size_t maxIndex = argmax(result_list.begin(), result_list.end());
std::cout <<"------------------->result:"<< maxIndex << '\n';
printf("----end----");
getchar();
return 0;
}
C部分代码参考自:
https://liuxiaofei.com.cn/blog/tensorflow-c-api%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0%E5%8D%B7%E7%A7%AF%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97/
https://github.com/AmirulOm/tensorflow_capi_sample/blob/master/main.c
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1583407 (Opencv Mat转Tensor)

如果你跟着做,结果是如下,说明你大获成功,贺电!

对上面的代码稍微更改一下,改成GAN模型, 输入为三通道BGR图片,输出也为图片,
关键代码:
//https://stackoverflow.com/questions/63389018/how-to-convert-tf-tensor-to-opencv-mat-in-c
cv::Mat testInputImage(out_h, out_w, CV_8UC3, TF_TensorData(*OutputValues));
cv::imwrite("./assets/mRGBAImg.png", testInputImage);
这里的OutputValues就是Tensor的地址,最后我们可以做更多有趣的事情,比如自动p图(deepfill,自行Google),当然这个我们也可以用Pytorch的项目,Git上一大堆,Torch的话,我们可以用官方提供的libTorch(官方提供C++DLL,非常厚道,为你点赞!)或用腾讯的NCNN转化为可以跨平台的项目,目前Pytorch已经支持AMD ROCm(竞品为NVIDIA Cuda)的显卡加速推理
不用老黄的显卡依然可以炼丹!
以下是效果图:

使用这个我们甚至可以做漫画自动翻译,这项工作我框架已经做好了,就等最后合并项目了,敬请期待!
这里还有TensorFlow C++ API推理的代码,仅供参考, 但是那个dll编译需要Bazel和MSYS2就非常麻烦了:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/dageda1991/article/details/79721333
有谁有编译好的CPP dll希望能分享一波
新发现!一个使用TensorFlow C API Wrap到CPP到项目CppFlow:https://github.com/serizba/cppflow,基本和我的思路一致,只是把C反封装为cpp,也就是套娃的套娃!
我现在已经是完全的翻译腔了(跑路…)
PS:Ads时间,大家可以加群一起探讨一下各种深度学习或者图形框架,集思广益,群号:558174476(游戏与人工智能生命体)
























 659
659

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








