前言
本文记录的是linux之线程一些程序
一、线程所涉及到的函数
线程:
pthread_create ( 创建线程 )
头文件:
#include <pthread.h>
定义函数:
//int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, NULL, void *(*start_routine) (void *), NULL);
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
参数分析:
thread --> 线程id号的地址
attr --> 线程属性,一般设置为NULL
start_routine --> 回调函数
arg -->回调函数的参数,一般设置为NULL
返回值:
若成功则返回 0,
否则返回-1, 错误原因存于 errno 中.
编译的时候要加: -pthread
二、例子
1.例题1
题目:
功能:创建线程,主线程和子线程分别打印进程id和各自线程id
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void* Thread_Func(void* arg);
void Print_Id(char* s);
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t new_tid; //定义新线程的id
int num = pthread_create(&new_tid, NULL, Thread_Func, "new thread"); //创建新线程
if(0 != num) {
printf("create new thread fail!\n");
perror("thread errno");
return -1;
}
Print_Id("main thread");
sleep(2);
return 0;
}
//回调函数
void* Thread_Func(void* arg) {
Print_Id((char*)arg);
return (void*)0;
}
//打印ID
void Print_Id(char* s) {
pid_t pid;
pthread_t tid;
pid = getpid(); //获取进程的ID
tid = pthread_self(); //获取线程的ID
printf("%s process id是 %ld, thread id是:%ld\n", s, pid, tid);
return ;
结果显示:
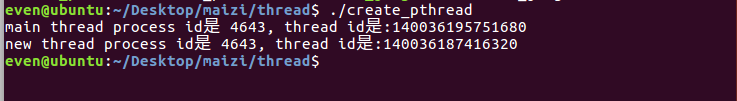
注意:必须要在主线程末尾添加睡眠,不然,主线程会直接结束,进程也就会结束,导致子线程没有被执行。
2.例题2
题目:功能:子线程打印结构体的成员变量值
代码如下:
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct student{
int age;
char name[20];
int id;
}stu, *STU;
void* Thread_Func(void* arg);
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int *val;
stu stu1;
stu1.age = 20;
strcpy(stu1.name, "kangzhanming");
stu1.id = 1001;
pthread_t new_tid;
int num = pthread_create(&new_tid, NULL, Thread_Func, (void*)(&stu1) );//创建新线程
if(0 != num) {
printf("create new thread fail!\n");
perror("thread errno");
return -1;
}
int i;
printf("main thread has %d args\n", argc);
for(i = 0; i < argc; i++) {
printf("main thread args is %s\n", argv[i]);
}
pthread_exit(val);
}
void* Thread_Func(void* arg) {
sleep(1);
printf("student age is %d, name is %s, id is %d\n", ((STU)arg)->age, ((STU)arg)->name, ((STU)arg)->id);
return (void*)0;
结果显示:
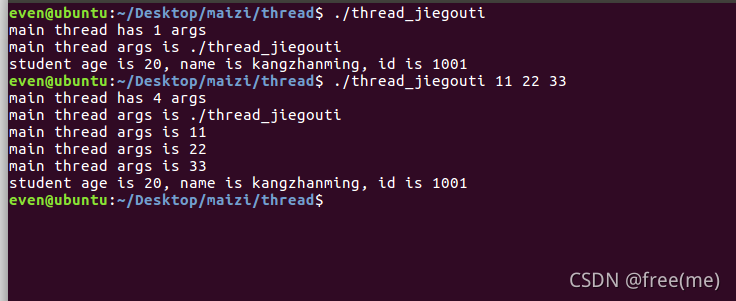





 本文详细介绍了Linux中线程的创建过程,涉及`pthread_create`函数及其参数,并通过两个实例演示了如何在主线程和子线程中打印进程ID和线程ID,以及如何在子线程中操作结构体变量。务必关注主线程睡眠的重要性。
本文详细介绍了Linux中线程的创建过程,涉及`pthread_create`函数及其参数,并通过两个实例演示了如何在主线程和子线程中打印进程ID和线程ID,以及如何在子线程中操作结构体变量。务必关注主线程睡眠的重要性。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










