题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5394
大家最喜欢看到的东西:
WA:试试这组数据
Input
5
a 0
b 1
b 2
a 3
a 2Output
14RE(爆栈):看题目下面提示,手动加栈后记得用C++提交
RE(越界):看看有没有把根节点(没有字符)加入回文树
解题思路:
塞进回文树的每次都是一条从起点开始的链,每次我们都找当前还没有被加到回文树中的字符加入回文树之后在这条链上新产生的回文串总数。
①如何按照一条链一条链的顺序向回文树扔进未添加过的字符?
字典树DFS即可。
②如何正确扔进字符,使得求得是字典树当前这个点所在的链上新产生的回文串数量?
(eg.也就是下面这个图对于4这个节点,求节点14这个串的新产的生回文串,而不是节点1234这个串新产生的回文串。)
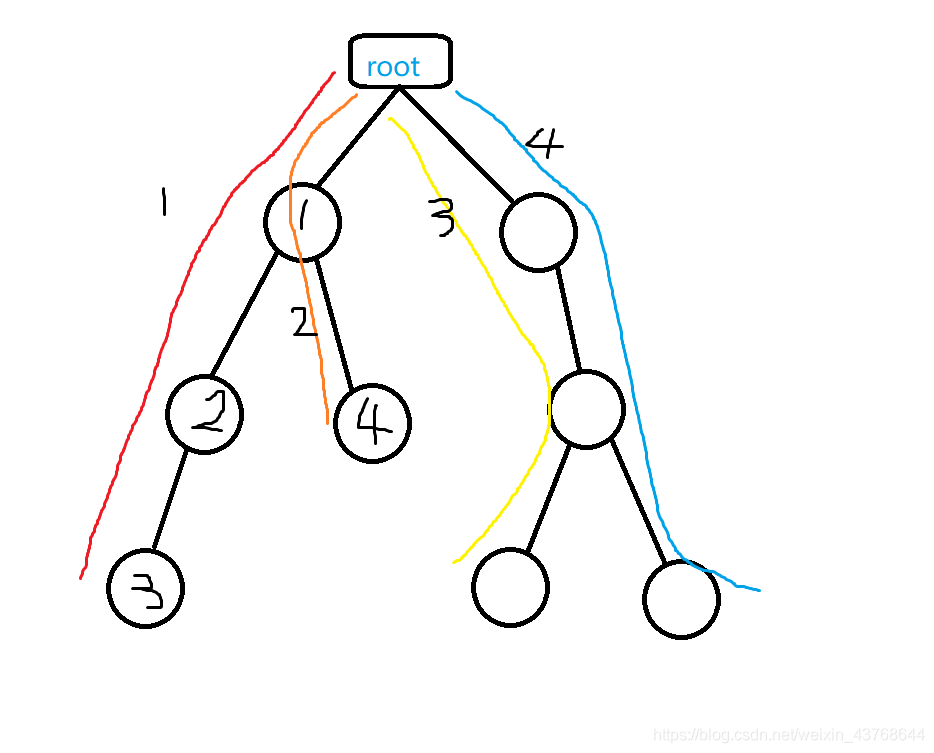
首先我们要知道
这两种情况在回文树里的不同是什么?
上一个加入字符所在回文串的节点的位置不同,而我们需要上一个加入的字符所在的最长回文串下标,来对此进行失配匹配过程。
上图用节点3所在最长回文串来给4失配匹配显然错误。
然后我们总结出了我们的问题
如何正确根据当前的字符获取当前字符父节点所在的回文串的下标?
我们在dfs的时候会一直搜到一条链的最底部,然后逐层返回直到上一个分枝点,开始另一条支线。作为分枝点肯定还在这条链上。那我们就维护这条链上每一个深度的节点的字符所在最长回文串的下标,在DFS字典树的时候记录深度,每次新加入字符都索引上一个深度的对应回文串位置即可。那就把原本回文树板子里用于记录上一个节点回文串位置的last,改成数组,然后每次新加入点的时候,就把当前这个点深度的last改成自己的就行。
③如何求得加进该字符新产生的字符串?
当前的贡献 = 当前加入字符所在回文串长度 + 当前字符的最长回文后缀的贡献
代码:(文件读入读出/读入数据后ctrl+Z看结果,板子网上各处搜刮来的嘿嘿)
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for (int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define for0(i,a,b) for (int i=a;i<b;i++)
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
#define debug(x) printf("----Line %s----\n",#x)
#define pt(x,y) printf("%s = %d\n",#x,y)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define df(x) ll x;scanf("%I64d",&x)
#define df2(x,y) ll x,y;scanf("%I64d %I64d",&x,&y)
#define mod 1000000007
#define duozu(T) int T;scanf("%d",&T);while (T--)
namespace FastI{
const int SIZE = 1 << 16;
char buf[SIZE], str[64];
int l = SIZE, r = SIZE;
int read(char *s) {
while (r) {
for (; l < r && buf[l] <= ' '; l++);
if (l < r) break;
l = 0, r = int(fread(buf, 1, SIZE, stdin));
}
int cur = 0;
while (r) {
for (; l < r && buf[l] > ' '; l++) s[cur++] = buf[l];
if (l < r) break;
l = 0, r = int(fread(buf, 1, SIZE, stdin));
}
s[cur] = '\0';
return cur;
}
template<typename type>
bool read(type &x, int len = 0, int cur = 0, bool flag = false) {
if (!(len = read(str))) return false;
if (str[cur] == '-') flag = true, cur++;
for (x = 0; cur < len; cur++) x = x * 10 + str[cur] - '0';
if (flag) x = -x;
return true;
}
template <typename type>
type read(int len = 0, int cur = 0, bool flag = false, type x = 0) {
if (!(len = read(str))) return false;
if (str[cur] == '-') flag = true, cur++;
for (x = 0; cur < len; cur++) x = x * 10 + str[cur] - '0';
return flag ? -x : x;
}
} using FastI::read;
const int N = 2e6+10;
const int maxn = 2e6+50;
const int ALP = 4;
ll ans = 0;
int sss[N];
//vector<int>v[N];
struct node
{
int to;
int last;
}edge[N];
int head[N],id;
void add(int u,int v){edge[id].to=v;edge[id].last = head[u];head[u]=id++;}
struct PAM{
int next[maxn][ALP];
int fail[maxn];
ll cnt[maxn]; //当前节点代表回文串对答案的贡献
int num[maxn];
int len[maxn];
int s[maxn]; // 存放添加的字符
int last[maxn];
int n; // 已添加字符个数
int p; // 节点个数
int newnode(int w){//新建一个节点,长度初始化为这个节点代表的回文串长度
for(int i=0;i<ALP;i++)
next[p][i] = 0;
cnt[p] = 0;
num[p] = 0;
len[p] = w;
return p++;
}
void init(){
p = 0;
newnode(0);
newnode(-1);
last[0] = 0;
n = 0;
s[n] = -1; // 开头放一个字符集中没有的字符,减少特判
fail[0] = 1;
}
int get_fail(int x){//找最长回文后缀,最好情况就是本身,最坏没有
while(s[n-len[x]-1] != s[n]) x = fail[x];
return x;
}
ll add(int dep,int c){
c -= 'a';
s[n=dep] = c;///关键
int cur = get_fail(last[n-1]);
if(!next[cur][c]){
int now = newnode(len[cur]+2);//len赋值在这
fail[now] = next[get_fail(fail[cur])][c];
next[cur][c] = now;
cnt[now]=cnt[fail[now]]+len[now];
}
last[n] = next[cur][c];///当前加入字符树中的节点位置
return cnt[last[n]];///返回当前回文总数
}
}pam;
void dfs(int dep,int Now)
{
for (int i=head[Now];i!=0;i=edge[i].last){
ll t = ans;
ans += pam.add(dep,sss[edge[i].to]);
dfs(dep+1,edge[i].to);
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
read(T);
while (T--){
pam.init();
id = 1;
ans = 0;
memset(head,0,sizeof head);
int n;
read(n);
char s[2];
int fa;
for1(i,1,n){
read(s);read(fa);
add(fa,i);
sss[i] = s[0];
}
dfs(1,0);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
这道题把回文树和字典树结合起来了。





 本文详细介绍了如何利用回文树解决HDU 5394问题,即在字典树中查找回文串总数。解题思路包括如何按照字典序遍历字符并正确构建回文树,以及如何计算每个节点加入后新产生的回文串数量。通过深度优先搜索和维护每个节点回文串位置的数组,可以有效地计算贡献值。
本文详细介绍了如何利用回文树解决HDU 5394问题,即在字典树中查找回文串总数。解题思路包括如何按照字典序遍历字符并正确构建回文树,以及如何计算每个节点加入后新产生的回文串数量。通过深度优先搜索和维护每个节点回文串位置的数组,可以有效地计算贡献值。
















 9万+
9万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








