data模块
- overview布局
-
- \_\_init__.py
- annotator.py
- augment.py
-
- `class BaseTransform`
- `class Compose`
- `class BaseMixTransform`
- `class Mosaic`
- `class MixUp`
- `RandomPerspective`
- `class RandomHSV`
- `class RandomFlip`
- `class LetterBox`
- `class CopyPaste`
- `class Albumtation`
- `class Format `
- `class `
- `v8_transforms`
- `classify_transforms`
- `class ClassifyLetterBox`
- `class CenterCrop`
- `class ToTensor`
- base.py
- bulid.py
- dataset.py
- 未完待续
overview布局
从上往下解析
__init__.py
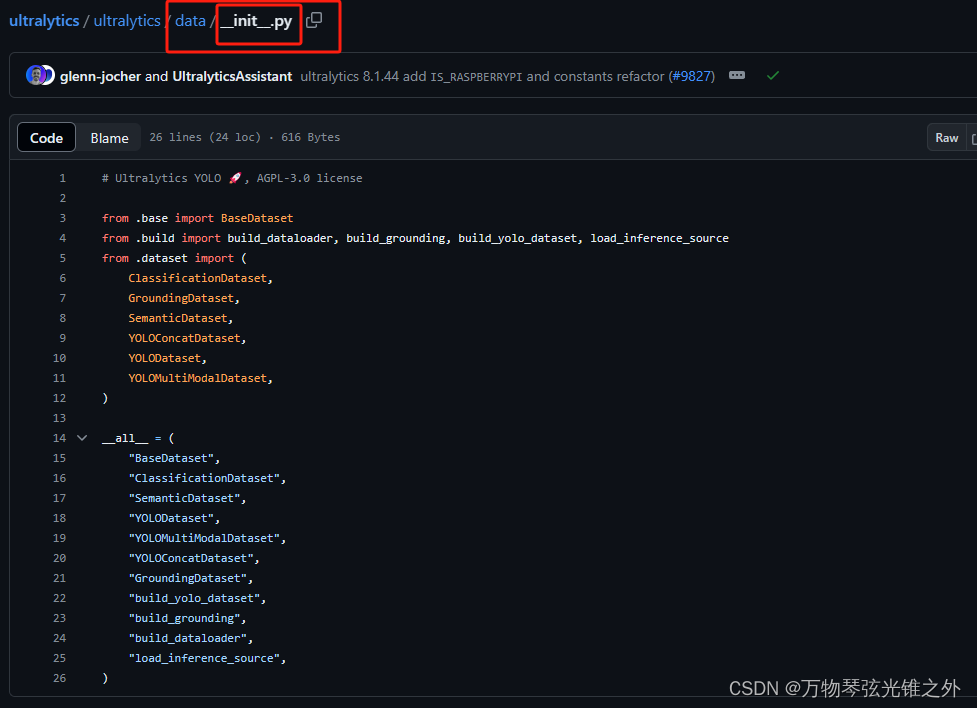
from .base import BaseDataset
__init__.py 文件在 Python 中扮演着重要的角色,它是 Python 包结构的一部分。
当一个目录包含 __init__.py 文件时,Python 会将这个目录视为一个包,允许你导入其中的模块和类。这个文件的目的是告诉 Python 解释器,目录内的内容是一个可导入的模块集合,也就是一个包。
在这个特定的例子中,__init__.py 文件是 ultralytics 库(假设是 ultralytics 包)的一部分,它导出了 base.py、build.py 和 dataset.py 中的一些关键类和函数。通过这种方式,用户可以直接从 ultralytics 包中导入这些导出的类和函数,而不需要知道它们在哪个具体的模块里。
例如,用户可以这样导入和使用这些类和函数:
from ultralytics import BaseDataset, YOLODataset, build_yolo_dataset
dataset = BaseDataset()
yolo_dataset = YOLODataset()
dataloader = build_yolo_dataset(dataset)
这种组织方式提高了代码的可读性和可维护性,因为用户只需要记住在包级别上可用的接口,而不是每个单独模块的细节。同时,__init__.py 也可以用来执行一些初始化逻辑,比如设置配置、注册自定义类型等。
__all__
annotator.py
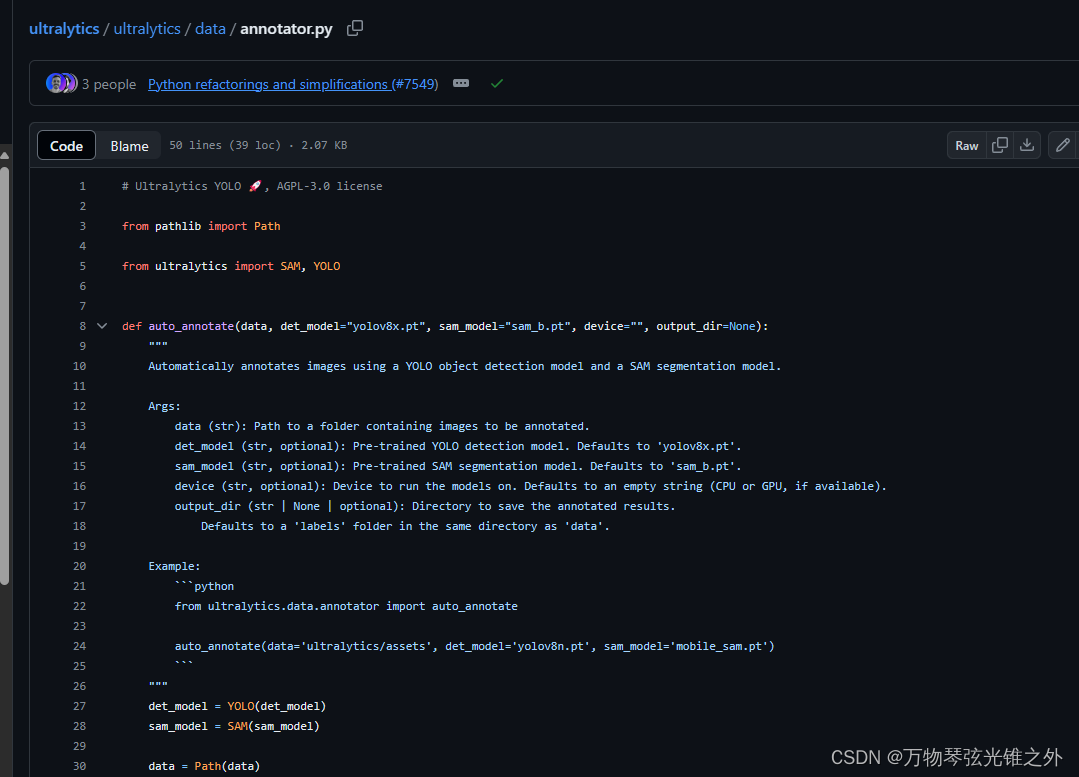
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
from pathlib import Path
from ultralytics import SAM, YOLO
def auto_annotate(data, det_model="yolov8x.pt", sam_model="sam_b.pt", device="", output_dir=None):
"""
Automatically annotates images using a YOLO object detection model and a SAM segmentation model.
Args:
data (str): Path to a folder containing images to be annotated.
det_model (str, optional): Pre-trained YOLO detection model. Defaults to 'yolov8x.pt'.
sam_model (str, optional): Pre-trained SAM segmentation model. Defaults to 'sam_b.pt'.
device (str, optional): Device to run the models on. Defaults to an empty string (CPU or GPU, if available).
output_dir (str | None | optional): Directory to save the annotated results.
Defaults to a 'labels' folder in the same directory as 'data'.
Example:
```python
from ultralytics.data.annotator import auto_annotate
auto_annotate(data='ultralytics/assets', det_model='yolov8n.pt', sam_model='mobile_sam.pt')
```
"""
det_model = YOLO(det_model)
sam_model = SAM(sam_model)
data = Path(data)
if not output_dir:
output_dir = data.parent / f"{
data.stem}_auto_annotate_labels"
Path(output_dir).mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
det_results = det_model(data, stream=True, device=device)
for result in det_results:
class_ids = result.boxes.cls.int().tolist() # noqa
if len(class_ids):
boxes = result.boxes.xyxy # Boxes object for bbox outputs
sam_results = sam_model(result.orig_img, bboxes=boxes, verbose=False, save=False, device=device)
segments = sam_results[0].masks.xyn # noqa
with open(f"{
Path(output_dir) / Path(result.path).stem}.txt", "w") as f:
for i in range(len(segments)):
s = segments[i]
if len(s) == 0:
continue
segment = map(str, segments[i].reshape(-1).tolist())
f.write(f"{
class_ids[i]} " + " ".join(segment) + "\n")

augment.py
数据增强
class BaseTransform
# TODO: we might need a BaseTransform to make all these augments be compatible with both classification and semantic
class BaseTransform:
"""
Base class for image transformations.
This is a generic transformation class that can be extended for specific image processing needs.
The class is designed to be compatible with both classification and semantic segmentation tasks.
Methods:
__init__: Initializes the BaseTransform object.
apply_image: Applies image transformation to labels.
apply_instances: Applies transformations to object instances in labels.
apply_semantic: Applies semantic segmentation to an image.
__call__: Applies all label transformations to an image, instances, and semantic masks.
"""
def __init__(self) -> None:
"""Initializes the BaseTransform object."""
pass
def apply_image(self, labels):
"""Applies image transformations to labels."""
pass
def apply_instances(self, labels):
"""Applies transformations to object instances in labels."""
pass
def apply_semantic(self, labels):
"""Applies semantic segmentation to an image."""
pass
def __call__(self, labels):
"""Applies all label transformations to an image, instances, and semantic masks."""
self.apply_image(labels)
self.apply_instances(labels)
self.apply_semantic(labels)

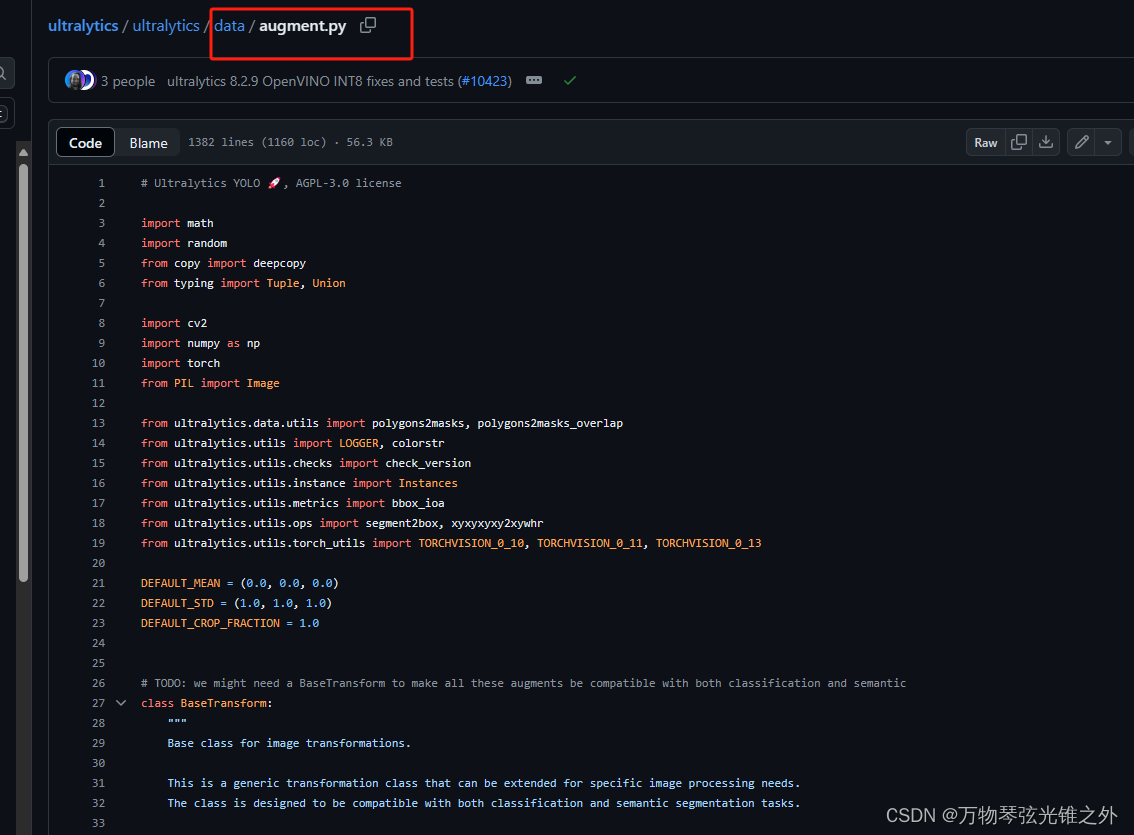
class Compose
class Compose:
"""Class for composing multiple image transformations."""
def __init__(self, transforms):
"""Initializes the Compose object with a list of transforms."""
self.transforms = transforms if isinstance(transforms, list) else [transforms]
def __call__(self, data):
"""Applies a series of transformations to input data."""
for t in self.transforms:
data = t(data)
return data
def append(self, transform):
"""Appends a new transform to the existing list of transforms."""
self.transforms.append(transform)
def insert(self, index, transform):
"""Inserts a new transform to the existing list of transforms."""
self.transforms.insert(index, transform)
def __getitem__(self, index: Union[list, int]) -> "Compose":
"""Retrieve a specific transform or a set of transforms using indexing."""
assert isinstance(index, (int, list)), f"The indices should be either list or int type but got {
type(index)}"
index = [index] if isinstance(index, int) else index
return Compose([self.transforms[i] for i in index])
def __setitem__(self, index: Union[list, int], value: Union[list, int]) -> None:
"""Retrieve a specific transform or a set of transforms using indexing."""
assert isinstance(index, (int, list)), f"The indices should be either list or int type but got {
type(index)}"
if isinstance(index, list):
assert isinstance(
value, list
), f"The indices should be the same type as values, but got {
type(index)} and {
type(value)}"
if isinstance(index, int):
index, value = [index], [value]
for i, v in zip(index, value):
assert i < len(self.transforms), f"list index {
i} out of range {
len(self.transforms)}."
self.transforms[i] = v
def tolist(self):
"""Converts the list of transforms to a standard Python list."""
return self.transforms
def __repr__(self):
"""Returns a string representation of the object."""
return f"{
self.__class__.__name__}({
', '.join([f'{
t}' for t in self.transforms])})"
class BaseMixTransform
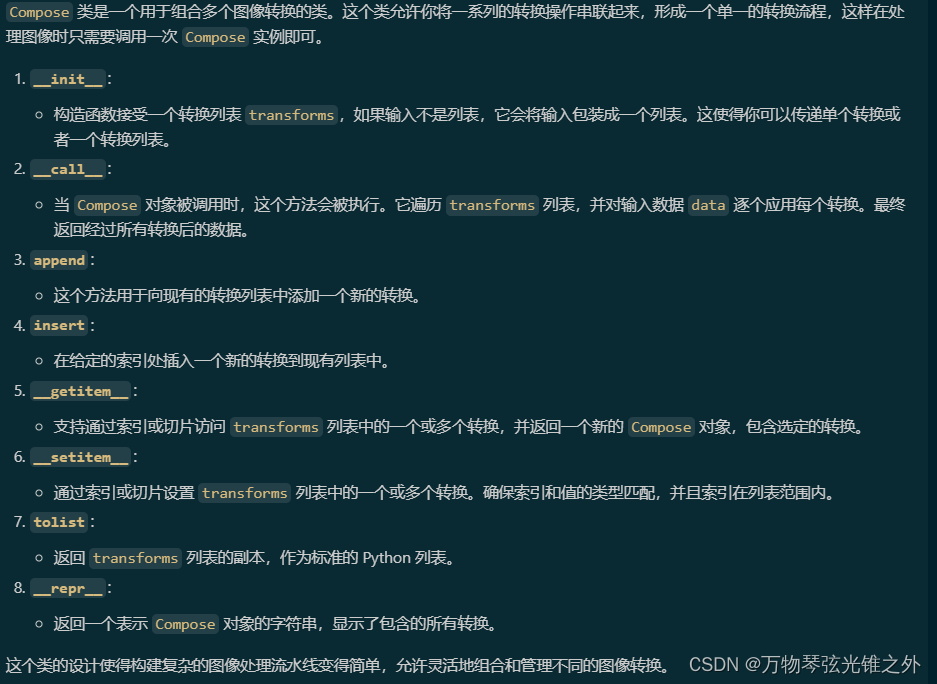
class BaseMixTransform:
"""
Class for base mix (MixUp/Mosaic) transformations.
This implementation is from mmyolo.
"""
def __init__(self, dataset, pre_transform=None, p=0.0) -> None:
"""Initializes the BaseMixTransform object with dataset, pre_transform, and probability."""
self.dataset = dataset
self.pre_transform = pre_transform
self.p = p
def __call__(self, labels):
"""Applies pre-processing transforms and mixup/mosaic transforms to labels data."""
if random.uniform(0, 1) > self.p:
return labels
# Get index of one or three other images
indexes = self.get_indexes()
if isinstance(indexes, int):
indexes = [indexes]
# Get images information will be used for Mosaic or MixUp
mix_labels = [self.dataset.get_image_and_label(i) for i in indexes]
if self.pre_transform is not None:
for i, data in enumerate(mix_labels):
mix_labels[i] = self.pre_transform(data)
labels["mix_labels"] = mix_labels
# Update cls and texts
labels = self._update_label_text(labels)
# Mosaic or MixUp
labels = self._mix_transform(labels)
labels.pop("mix_labels", None)
return labels
def _mix_transform(self, labels):
"""Applies MixUp or Mosaic augmentation to the label dictionary."""
raise NotImplementedError
def get_indexes(self):
"""Gets a list of shuffled indexes for mosaic augmentation."""
raise NotImplementedError
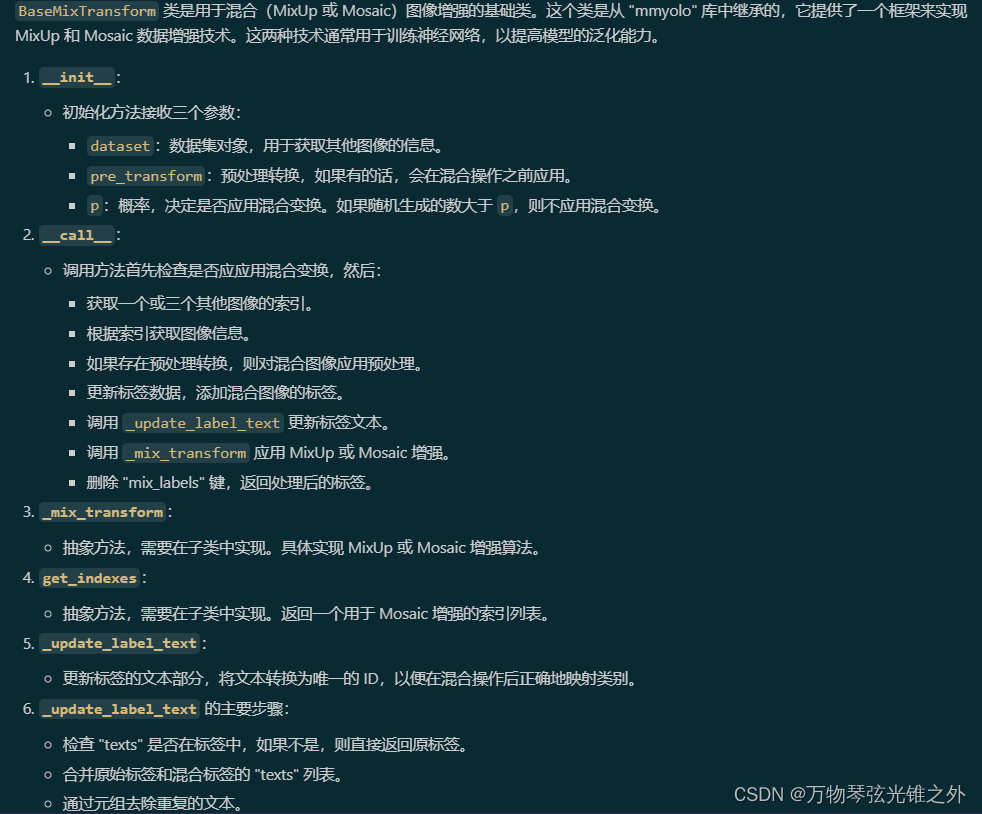
def _update_label_text(self, labels):
"""Update label text."""
if "texts" not in labels:
return labels
mix_texts = sum([labels["texts"]] + [x["texts"] for x in labels["mix_labels"]], [])
mix_texts = list({
tuple(x) for x in mix_texts})
text2id = {
text: i for i, text in enumerate(mix_texts)}
for label in [labels] + labels["mix_labels"]:
for i, cls in enumerate(label["cls"].squeeze(-1).tolist()):
text = label["texts"][int(cls)]
label["cls"][i] = text2id[tuple(text)]
label["texts"] = mix_texts
return labels
class Mosaic
class Mosaic(BaseMixTransform):
"""
Mosaic augmentation.
This class performs mosaic augmentation by combining multiple (4 or 9) images into a single mosaic image.
The augmentation is applied to a dataset with a given probability.
Attributes:
dataset: The dataset on which the mosaic augmentation is applied.
imgsz (int, optional): Image size (height and width) after mosaic pipeline of a single image. Default to 640.
p (float, optional): Probability of applying the mosaic augmentation. Must be in the range 0-1. Default to 1.0.
n (int, optional): The grid size, either 4 (for 2x2) or 9 (for 3x3).
"""
def __init__(self, dataset, imgsz=640, p=1.0, n=4):
"""Initializes the object with a dataset, image size, probability, and border."""
assert 0 <= p <= 1.0, f"The probability should be in range [0, 1], but got {
p}."
assert n in {
4, 9}, "grid must be equal to 4 or 9."
super().__init__(dataset=dataset, p=p)
self.dataset = dataset
self.imgsz = imgsz
self.border = (-imgsz // 2, -imgsz // 2) # width, height
self.n = n
def get_indexes(self, buffer=True):
"""Return a list of random indexes from the dataset."""
if buffer: # select images from buffer
return random.choices(list(self.dataset.buffer), k=self.n - 1)
else: # select any images
return [random.randint(0, len(self.dataset) - 1) for _ in range(self.n - 1)]
def _mix_transform(self, labels):
"""Apply mixup transformation to the input image and labels."""
assert labels.get("rect_shape", None) is None, "rect and mosaic are mutually exclusive."
assert len(labels.get("mix_labels", [])), "There are no other images for mosaic augment."
return (
self._mosaic3(labels) if self.n == 3 else self._mosaic4(labels) if self.n == 4 else self._mosaic9(labels)
) # This code is modified for mosaic3 method.
def _mosaic3(self, labels):
"""Create a 1x3 image mosaic."""
mosaic_labels = []
s = self.imgsz
for i in range(3):
labels_patch = labels if i == 0 else labels["mix_labels"][i - 1]
# Load image
img = labels_patch["img"]
h, w = labels_patch.pop("resized_shape")
# Place img in img3
if i == 0: # center
img3 = np.full((s * 3, s * 3, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 3 tiles
h0, w0 = h, w
c = s, s, s + w, s + h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (base) coordinates
elif i == 1: # right
c = s + w0, s, s + w0 + w, s + h
elif i == 2: # left
c = s - w, s + h0 - h, s, s + h0
padw, padh = c[:2]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = (max(x, 0) for x in c) # allocate coords
img3[y1:y2, x1:x2] = img[y1 - padh :, x1 - padw :] # img3[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
# hp, wp = h, w # height, width previous for next iteration
# Labels assuming imgsz*2 mosaic size
labels_patch = self._update_labels(labels_patch, padw + self.border[0], padh + self.border[1])
mosaic_labels.append(labels_patch)
final_labels = self._cat_labels(mosaic_labels)
final_labels["img"] = img3[-self.border[0] : self.border[0], -self.border[1] : self.border[1]]
return final_labels
def _mosaic4(self, labels):
"""Create a 2x2 image mosaic."""
mosaic_labels = []
s = self.imgsz
yc, xc = (int(random.uniform(-x, 2 * s + x)) for x in self.border) # mosaic center x, y
for i in range(4):
labels_patch = labels if i == 0 else labels["mix_labels"][i - 1]
# Load image
img = labels_patch["img"]
h, w = labels_patch.pop("resized_shape")
# Place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image)
elif i == 1: # top right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, w, min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
padw = x1a - x1b
padh = y1a - y1b
labels_patch = self._update_labels(labels_patch, padw, padh)
mosaic_labels.append(labels_patch)
final_labels = self._cat_labels(mosaic_labels)
final_labels["img"] = img4
return final_labels
def _mosaic9(self, labels):
"""Create a 3x3 image mosaic."""
mosaic_labels = []
s = self.imgsz
hp, wp = -1, -1 # height, width previous
for i in range(9):
labels_patch = labels if i == 0 else labels["mix_labels"][i - 1]
# Load image
img = labels_patch["img"]
h, w = labels_patch.pop("resized_shape")
# Place img in img9
if i == 0: # center
img9 = np.full((s * 3, s * 3, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
h0, w0 = h, w
c = s, s, s + w, s + h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (base) coordinates
elif i == 1: # top
c = s, s - h, s + w, s
elif i == 2: # top right
c = s + wp, s - h, s + wp + w, s
elif i == 3: # right
c = s + w0, s, s + w0 + w, s + h
elif i == 4: # bottom right
c = s + w0, s + hp, s + w0 + w, s + hp + h
elif i == 5: # bottom
c = s + w0 - w, s + h0, s + w0, s + h0 + h
elif i == 6: # bottom left
c = s + w0 - wp - w, s + h0, s + w0 - wp, s + h0 + h
elif i == 7: # left
c = s - w, s + h0 - h, s, s + h0
elif i == 8: # top left
c = s - w, s + h0 - hp - h, s, s + h0 - hp
padw, padh = c[:2]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = (max(x, 0) for x in c) # allocate coords
# Image
img9[y1:y2, x1:x2] = img[y1 - padh :, x1 - padw :] # img9[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
hp, wp = h, w # height, width previous for next iteration
# Labels assuming imgsz*2 mosaic size
labels_patch = self._update_labels(labels_patch, padw + self.border[0], padh + self.border[1])
mosaic_labels.append(labels_patch)
final_labels = self._cat_labels(mosaic_labels)
final_labels["img"] = img9[-self.border[0] : self.border[0], -self.border[1] : self.border[1]]
return final_labels
@staticmethod
def _update_labels(labels, padw, padh):
"""Update labels."""
nh, nw = labels["img"].shape[:2]
labels["instances"].convert_bbox(format="xyxy")
labels["instances"].denormalize(nw, nh)
labels["instances"].add_padding(padw, padh)
return labels
def _cat_labels(self, mosaic_labels):
"""Return labels with mosaic border instances clipped."""
if len(mosaic_labels) == 0:
return {
}
cls = []
instances = []
imgsz = self.imgsz * 2 # mosaic imgsz
for labels in mosaic_labels:
cls.append(labels["cls"])
instances.append(labels["instances"])
# Final labels
final_labels = {
"im_file": mosaic_labels[0]["im_file"],
"ori_shape": mosaic_labels[0]["ori_shape"],
"resized_shape": (imgsz, imgsz),
"cls": np.concatenate(cls, 0),
"instances": Instances.concatenate(instances, axis=0),
"mosaic_border": self.border,
}
final_labels["instances"].clip(imgsz, imgsz)
good = final_labels["instances"].remove_zero_area_boxes()
final_labels["cls"] = final_labels["cls"][good]
if "texts" in mosaic_labels[0]:
final_labels["texts"] = mosaic_labels[0]["texts"]
return final_labels

具体介绍一下_mosaic3
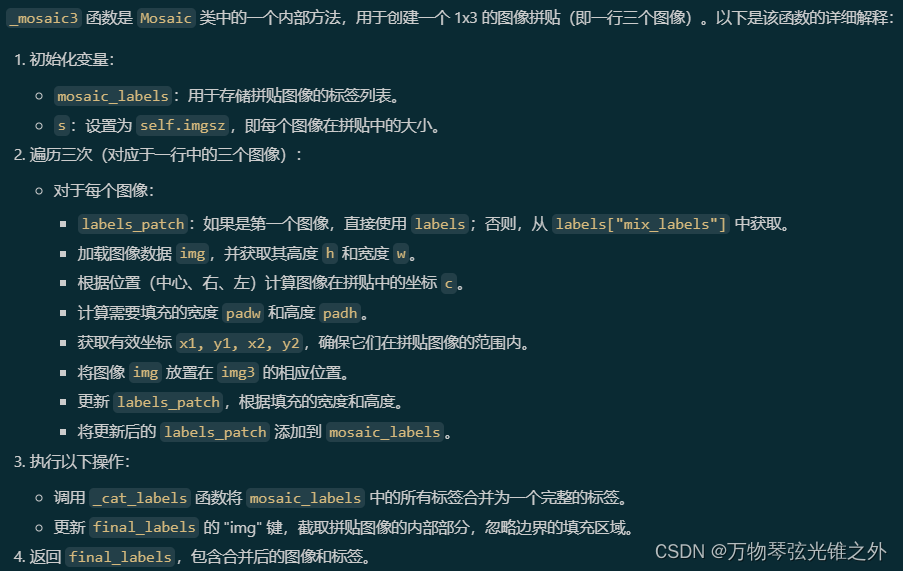
静态方法更新label
# 静态方法,用于更新单个图像的标签
@staticmethod
def _update_labels(labels, padw, padh):
# 获取图像的高度和宽度
nh, nw = labels["img"].shape[:2]
# 将实例(boxes)转换为xyxy格式
labels["instances"].convert_bbox(format="xyxy")
# 反标准化实例坐标,基于图像的实际尺寸
labels["instances"].denormalize(nw, nh)
# 添加填充到实例坐标
labels["instances"].add_padding(padw, padh)
# 返回更新后的标签
return labels
# 静态方法,用于将多个图像的标签组合成一个拼贴图像的标签
@staticmethod
def _cat_labels(mosaic_labels):
# 检查输入列表是否为空
if len(mosaic_labels) == 0:
return {
}
# 初始化类别列表和实例列表
cls = []
instances = []
# 拼贴图像的大小是原始图像大小的两倍
imgsz = self.imgsz * 2
# 遍历每个图像的标签
for labels in mosaic_labels:
# 收集类别
cls.append(labels["cls"])
# 收集实例
instances.append(labels["instances"])
# 创建最终的标签字典
final_labels = {
"im_file": mosaic_labels[0]["im_file"], # 图像的文件名
"ori_shape": mosaic_labels[0]["ori_shape"], # 图像的原始形状
"resized_shape": (imgsz, imgsz), # 拼贴图像的尺寸
"cls": np.concatenate(cls, 0), # 合并所有图像的类别
"instances": Instances.concatenate(instances, axis=0), # 合并所有图像的实例
"mosaic_border": self.border, # 拼贴图像的边框信息
}
# 裁剪超出拼贴图像边界的实例
final_labels["instances"].clip(imgsz, imgsz)
# 移除面积为零的实例
good = final_labels["instances"].remove_zero_area_boxes()
# 根据有效的实例更新类别
final_labels["cls"] = final_labels["cls"][good]
# 如果原始标签中有"texts"字段,将其添加到最终标签中
if "texts" in mosaic_labels[0]:
final_labels["texts"] = mosaic_labels[0]["texts"]
# 返回组合后的标签
return final_labels
class MixUp
class MixUp(BaseMixTransform):
"""Class for applying MixUp augmentation to the dataset."""
def __init__(self, dataset, pre_transform=None, p=0.0) -> None:
"""初始化MixUp对象,传入数据集、预处理变换和应用MixUp的概率。
参数:
- dataset: 数据集对象
- pre_transform: 可选的预处理变换
- p: 应用MixUp的概率,默认为0.0,表示默认不应用MixUp
"""
super().__init__(dataset=dataset, pre_transform=pre_transform, p=p)
def get_indexes(self):
"""从数据集中随机获取一个索引。
返回:
- 一个随机生成的整数索引,范围在0到数据集长度减1之间。
"""
return random.randint(0, len(self.dataset) - 1)
def _mix_transform(self, labels):
"""根据https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.09412.pdf中的描述应用MixUp数据增强。
参数:
- labels: 包含图像和对应标签的字典,如{'img': 图像, 'instances': 实例, 'cls': 类别}
返回:
- 应用MixUp后的混合标签字典。
"""
# 生成MixUp的混合比例,这里使用alpha=beta=32.0
r = np.random.beta(32.0, 32.0)
# 获取第二个图像及其标签
labels2 = labels["mix_labels"][0]
# 混合两个图像
mixed_img = (labels["img"] * r + labels2["img"] * (1 - r)).astype(np.uint8)
# 混合两个实例(如边界框)
mixed_instances = Instances.concatenate([labels["instances"], labels2["instances"]], axis=0)
# 混合两个类别
mixed_cls = np.concatenate([labels["cls"], labels2["cls"]], 0)
# 返回混合后的标签字典
return {
"img": mixed_img, "instances": mixed_instances, "cls": mixed_cls}
RandomPerspective
class RandomPerspective:
"""
Implements random perspective and affine transformations on images and corresponding bounding boxes, segments, and
keypoints. These transformations include rotation, translation, scaling, and shearing. The class also offers the
option to apply these transformations conditionally with a specified probability.
Attributes:
degrees (float): Degree range for random rotations.
translate (float): Fraction of total width and height for random translation.
scale (float): Scaling factor interval, e.g., a scale factor of 0.1 allows a resize between 90%-110%.
shear (float): Shear intensity (angle in degrees).
perspective (float): Perspective distortion factor.
border (tuple): Tuple specifying mosaic border.
pre_transform (callable): A function/transform to apply to the image before starting the random transformation.
Methods:
affine_transform(img, border): Applies a series of affine transformations to the image.
apply_bboxes(bboxes, M): Transforms bounding boxes using the calculated affine matrix.
apply_segments(segments, M): Transforms segments and generates new bounding boxes.
apply_keypoints(keypoints, M): Transforms keypoints.
__call__(labels): Main method to apply transformations to both images and their corresponding annotations.
box_candidates(box1, box2): Filters out bounding boxes that don't meet certain criteria post-transformation.
"""
def __init__(
self, degrees=0.0, translate=0.1, scale=0.5, shear=0.0, perspective=0.0, border=(0, 0), pre_transform=None
):
"""Initializes RandomPerspective object with transformation parameters."""
self.degrees = degrees
self.translate = translate
self.scale = scale
self.shear = shear
self.perspective = perspective
self.border = border # mosaic border
self.pre_transform = pre_transform
def affine_transform(self, img, border):
"""
Applies a sequence of affine transformations centered around the image center.
Args:
img (ndarray): Input image.
border (tuple): Border dimensions.
Returns:
img (ndarray): Transformed image.
M (ndarray): Transformation matrix.
s (float): Scale factor.
"""
# Center
C 




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 3339
3339

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










