ultralytics.Engine.Results
整体结构概述
Results 类及其相关组件主要包括以下几个核心类:
BaseTensor - 基础张量类,为其他结果类提供设备处理功能
Results - 主要的结果类,封装了检测、分割、姿态估计等任务的结果
Boxes - 处理边界框相关数据
Masks - 处理分割掩码相关数据
Keypoints - 处理关键点相关数据
Probs - 处理分类概率相关数据
OBB - 处理有向边界框相关数据
详细代码解析
BaseTensor 类
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license
"""
Ultralytics Results, Boxes and Masks classes for handling inference results.
Usage: See https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/predict/
"""
from copy import deepcopy
from functools import lru_cache
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import torch
from ultralytics.data.augment import LetterBox
from ultralytics.utils import LOGGER, SimpleClass, ops
from ultralytics.utils.checks import check_requirements
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator, colors, save_one_box
from ultralytics.utils.torch_utils import smart_inference_mode
class BaseTensor(SimpleClass):
"""
Base tensor class with additional methods for easy manipulation and device handling.
Attributes:
data (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): Prediction data such as bounding boxes, masks, or keypoints.
orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): Original shape of the image, typically in the format (height, width).
Methods:
cpu: Return a copy of the tensor stored in CPU memory.
numpy: Returns a copy of the tensor as a numpy array.
cuda: Moves the tensor to GPU memory, returning a new instance if necessary.
to: Return a copy of the tensor with the specified device and dtype.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
>>> orig_shape = (720, 1280)
>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape)
>>> cpu_tensor = base_tensor.cpu()
>>> numpy_array = base_tensor.numpy()
>>> gpu_tensor = base_tensor.cuda()
"""
def __init__(self, data, orig_shape) -> None:
"""
Initialize BaseTensor with prediction data and the original shape of the image.
Args:
data (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): Prediction data such as bounding boxes, masks, or keypoints.
orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): Original shape of the image in (height, width) format.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
>>> orig_shape = (720, 1280)
>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape)
"""
assert isinstance(data, (torch.Tensor, np.ndarray)), "data must be torch.Tensor or np.ndarray"
self.data = data
self.orig_shape = orig_shape
@property
def shape(self):
"""
Returns the shape of the underlying data tensor.
Returns:
(Tuple[int, ...]): The shape of the data tensor.
Examples:
>>> data = torch.rand(100, 4)
>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape=(720, 1280))
>>> print(base_tensor.shape)
(100, 4)
"""
return self.data.shape
def cpu(self):
"""
Returns a copy of the tensor stored in CPU memory.
Returns:
(BaseTensor): A new BaseTensor object with the data tensor moved to CPU memory.
Examples:
>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]).cuda()
>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape=(720, 1280))
>>> cpu_tensor = base_tensor.cpu()
>>> isinstance(cpu_tensor, BaseTensor)
True
>>> cpu_tensor.data.device
device(type='cpu')
"""
return self if isinstance(self.data, np.ndarray) else self.__class__(self.data.cpu(), self.orig_shape)
def numpy(self):
"""
Returns a copy of the tensor as a numpy array.
Returns:
(np.ndarray): A numpy array containing the same data as the original tensor.
Examples:
>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
>>> orig_shape = (720, 1280)
>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape)
>>> numpy_array = base_tensor.numpy()
>>> print(type(numpy_array))
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
"""
return self if isinstance(self.data, np.ndarray) else self.__class__(self.data.numpy(), self.orig_shape)
def cuda(self):
"""
Moves the tensor to GPU memory.
Returns:
(BaseTensor): A new BaseTensor instance with the data moved to GPU memory if it's not already a
numpy array, otherwise returns self.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> from ultralytics.engine.results import BaseTensor
>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape=(720, 1280))
>>> gpu_tensor = base_tensor.cuda()
>>> print(gpu_tensor.data.device)
cuda:0
"""
return self.__class__(torch.as_tensor(self.data).cuda(), self.orig_shape)
def to(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Return a copy of the tensor with the specified device and dtype.
Args:
*args (Any): Variable length argument list to be passed to torch.Tensor.to().
**kwargs (Any): Arbitrary keyword arguments to be passed to torch.Tensor.to().
Returns:
(BaseTensor): A new BaseTensor instance with the data moved to the specified device and/or dtype.
Examples:
>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(torch.randn(3, 4), orig_shape=(480, 640))
>>> cuda_tensor = base_tensor.to("cuda")
>>> float16_tensor = base_tensor.to(dtype=torch.float16)
"""
return self.__class__(torch.as_tensor(self.data).to(*args, **kwargs), self.orig_shape)
def __len__(self): # override len(results)
"""
Returns the length of the underlying data tensor.
Returns:
(int): The number of elements in the first dimension of the data tensor.
Examples:
>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape=(720, 1280))
>>> len(base_tensor)
2
"""
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
"""
Returns a new BaseTensor instance containing the specified indexed elements of the data tensor.
Args:
idx (int | List[int] | torch.Tensor): Index or indices to select from the data tensor.
Returns:
(BaseTensor): A new BaseTensor instance containing the indexed data.
Examples:
>>> data = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
>>> base_tensor = BaseTensor(data, orig_shape=(720, 1280))
>>> result = base_tensor[0] # Select the first row
>>> print(result.data)
tensor([1, 2, 3])
"""
return self.__class__(self.data[idx], self.orig_shape)
其实就是对底层添加一些方法,很直观。
其中有继承于SimpleClass,其实就是方便打印查看里面的属性和值的。
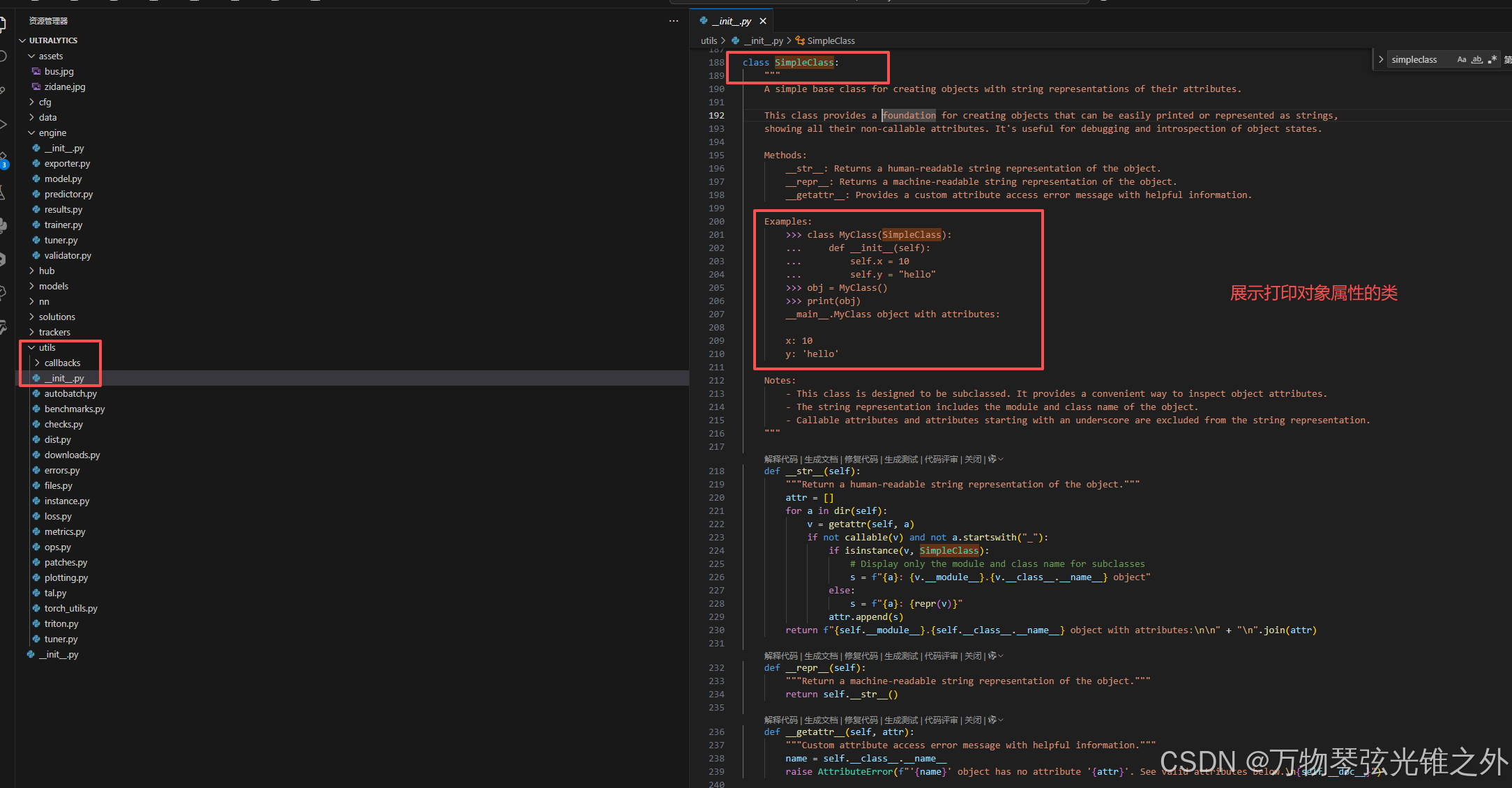
class Boxes(BaseTensor)
class Boxes(BaseTensor):
"""
A class for managing and manipulating detection boxes.
This class provides functionality for handling detection boxes, including their coordinates, confidence scores,
class labels, and optional tracking IDs. It supports various box formats and offers methods for easy manipulation
and conversion between different coordinate systems.
Attributes:
data (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The raw tensor containing detection boxes and associated data.
orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): The original image dimensions (height, width).
is_track (bool): Indicates whether tracking IDs are included in the box data.
xyxy (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Boxes in [x1, y1, x2, y2] format.
conf (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Confidence scores for each box.
cls (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Class labels for each box.
id (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Tracking IDs for each box (if available).
xywh (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Boxes in [x, y, width, height] format.
xyxyn (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Normalized [x1, y1, x2, y2] boxes relative to orig_shape.
xywhn (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Normalized [x, y, width, height] boxes relative to orig_shape.
Methods:
cpu(): Returns a copy of the object with all tensors on CPU memory.
numpy(): Returns a copy of the object with all tensors as numpy arrays.
cuda(): Returns a copy of the object with all tensors on GPU memory.
to(*args, **kwargs): Returns a copy of the object with tensors on specified device and dtype.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> boxes_data = torch.tensor([[100, 50, 150, 100, 0.9, 0], [200, 150, 300, 250, 0.8, 1]])
>>> orig_shape = (480, 640) # height, width
>>> boxes = Boxes(boxes_data, orig_shape)
>>> print(boxes.xyxy)
>>> print(boxes.conf)
>>> print(boxes.cls)
>>> print(boxes.xywhn)
"""
def __init__(self, boxes, orig_shape) -> None:
"""
Initialize the Boxes class with detection box data and the original image shape.
This class manages detection boxes, providing easy access and manipulation of box coordinates,
confidence scores, class identifiers, and optional tracking IDs. It supports multiple formats
for box coordinates, including both absolute and normalized forms.
Args:
boxes (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array with detection boxes of shape
(num_boxes, 6) or (num_boxes, 7). Columns should contain
[x1, y1, x2, y2, confidence, class, (optional) track_id].
orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): The original image shape as (height, width). Used for normalization.
Attributes:
data (torch.Tensor): The raw tensor containing detection boxes and their associated data.
orig_shape (Tuple[int, int]): The original image size, used for normalization.
is_track (bool): Indicates whether tracking IDs are included in the box data.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> boxes = torch.tensor([[100, 50, 150, 100, 0.9, 0]])
>>> orig_shape = (480, 640)
>>> detection_boxes = Boxes(boxes, orig_shape)
>>> print(detection_boxes.xyxy)
tensor([[100., 50., 150., 100.]])
"""
if boxes.ndim == 1:
boxes = boxes[None, :]
n = boxes.shape[-1]
assert n in {
6, 7}, f"expected 6 or 7 values but got {
n}" # xyxy, track_id, conf, cls
super().__init__(boxes, orig_shape)
self.is_track = n == 7
self.orig_shape = orig_shape
@property
def xyxy(self):
"""
Returns bounding boxes in [x1, y1, x2, y2] format.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array of shape (n, 4) containing bounding box
coordinates in [x1, y1, x2, y2] format, where n is the number of boxes.
Examples:
>>> results = model("image.jpg")
>>> boxes = results[0].boxes
>>> xyxy = boxes.xyxy
>>> print(xyxy)
"""
return self.data[:, :4]
@property
def conf(self):
"""
Returns the confidence scores for each detection box.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A 1D tensor or array containing confidence scores for each detection,
with shape (N,) where N is the number of detections.
Examples:
>>> boxes = Boxes(torch.tensor([[10, 20, 30, 40, 0.9, 0]]), orig_shape=(100, 100))
>>> conf_scores = boxes.conf
>>> print(conf_scores)
tensor([0.9000])
"""
return self.data[:, -2]
@property
def cls(self):
"""
Returns the class ID tensor representing category predictions for each bounding box.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array containing the class IDs for each detection box.
The shape is (N,), where N is the number of boxes.
Examples:
>>> results = model("image.jpg")
>>> boxes = results[0].boxes
>>> class_ids = boxes.cls
>>> print(class_ids) # tensor([0., 2., 1.])
"""
return self.data[:, -1]
@property
def id(self):
"""
Returns the tracking IDs for each detection box if available.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor | None): A tensor containing tracking IDs for each box if tracking is enabled,
otherwise None. Shape is (N,) where N is the number of boxes.
Examples:
>>> results = model.track("path/to/video.mp4")
>>> for result in results:
... boxes = result.boxes
... if boxes.is_track:
... track_ids = boxes.id
... print(f"Tracking IDs: {track_ids}")
... else:
... print("Tracking is not enabled for these boxes.")
Notes:
- This property is only available when tracking is enabled (i.e., when `is_track` is True).
- The tracking IDs are typically used to associate detections across multiple frames in video analysis.
"""
return self.data[:, -3] if self.is_track else None
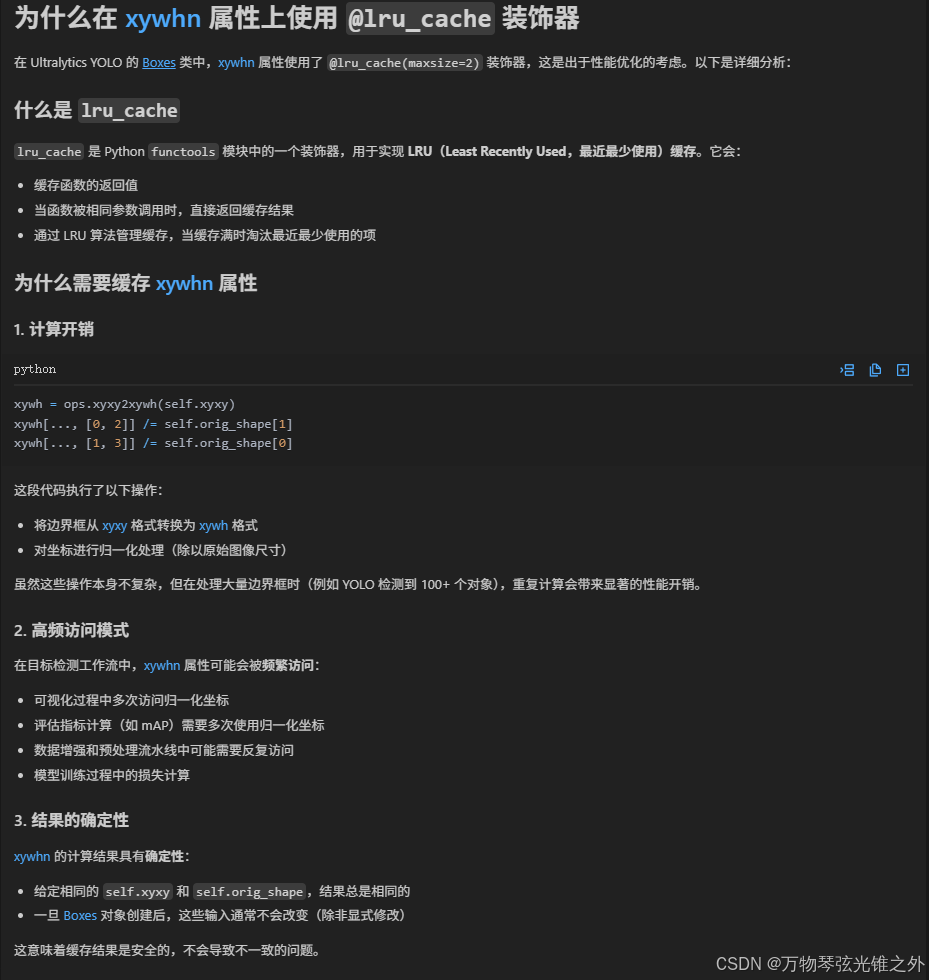
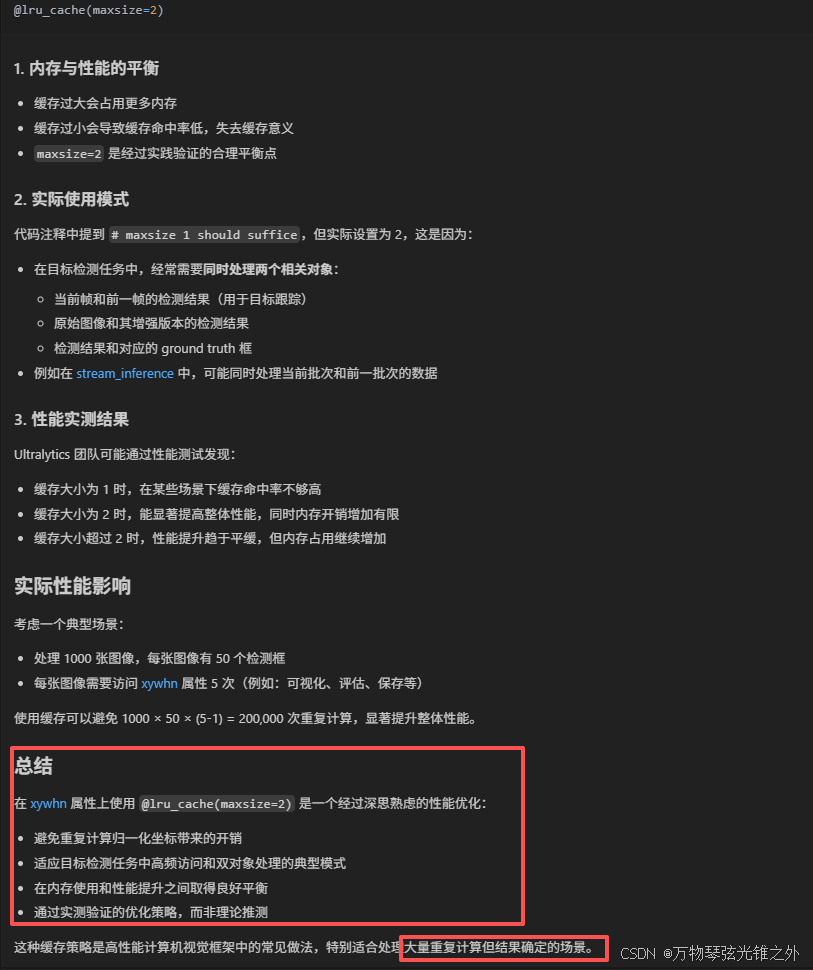
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=2) # maxsize 1 should suffice
def xywh(self):
"""
Convert bounding boxes from [x1, y1, x2, y2] format to [x, y, width, height] format.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Boxes in [x_center, y_center, width, height] format, where x_center, y_center are the coordinates of
the center point of the bounding box, width, height are the dimensions of the bounding box and the
shape of the returned tensor is (N, 4), where N is the number of boxes.
Examples:
>>> boxes = Boxes(torch.tensor([[100, 50, 150, 100], [200, 150, 300, 250]]), orig_shape=(480, 640))
>>> xywh = boxes.xywh
>>> print(xywh)
tensor([[100.0000, 50.0000, 50.0000, 50.0000],
[200.0000, 150.0000, 100.0000, 100.0000]])
"""
return ops.xyxy2xywh(self.xyxy)
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=2)
def xyxyn(self):
"""
Returns normalized bounding box coordinates relative to the original image size.
This property calculates and returns the bounding box coordinates in [x1, y1, x2, y2] format,
normalized to the range [0, 1] based on the original image dimensions.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Normalized bounding box coordinates with shape (N, 4), where N is
the number of boxes. Each row contains [x1, y1, x2, y2] values normalized to [0, 1].
Examples:
>>> boxes = Boxes(torch.tensor([[100, 50, 300, 400, 0.9, 0]]), orig_shape=(480, 640))
>>> normalized = boxes.xyxyn
>>> print(normalized)
tensor([[0.1562, 0.1042, 0.4688, 0.8333]])
"""
xyxy = self.xyxy.clone() if isinstance(self.xyxy, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(self.xyxy)
xyxy[..., [0, 2]] /= self.orig_shape[1]
xyxy[..., [1, 3]] /= self.orig_shape[0]
return xyxy
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=2)
def xywhn(self):
"""
Returns normalized bounding boxes in [x, y, width, height] format.
This property calculates and returns the normalized bounding box coordinates in the format
[x_center, y_center, width, height], where all values are relative to the original image dimensions.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Normalized bounding boxes with shape (N, 4), where N is the
number of boxes. Each row contains [x_center, y_center, width, height] values normalized
to [0, 1] based on the original image dimensions.
Examples:
>>> boxes = Boxes(torch.tensor([[100, 50, 150, 100, 0.9, 0]]), orig_shape=(480, 640))
>>> normalized = boxes.xywhn
>>> print(normalized)
tensor([[0.1953, 0.1562, 0.0781, 0.1042]])
"""
xywh = ops.xyxy2xywh(self.xyxy)
xywh[..., [0, 2]] /= self.orig_shape[1]
xywh[..., [1, 3]] /= self.orig_shape[0]
return xywh
@property 设置方法为属性
可以看到维度是:
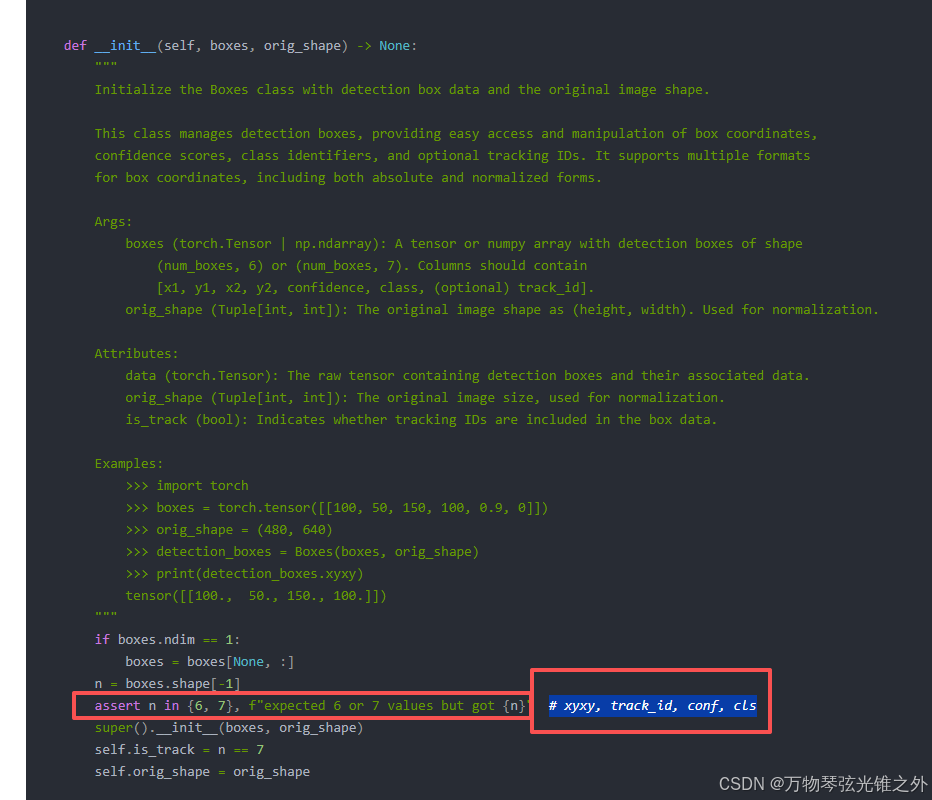
有track任务就是7维
不然就是6维度
这里为什么用 lru_cache??
class Probs(BaseTensors)
Probs 类继承自 BaseTensor,专门用于处理图像分类任务的输出概率。它提供了便捷的方法来访问最高概率类别及其置信度。
核心属性
data: 原始概率张量,包含每个类别的预测概率
top1: 最高概率类别的索引
top5: 前5个最高概率类别的索引列表
top1conf: 最高概率类别的置信度分数
top5conf: 前5个最高概率类别的置信度分数
class Probs(BaseTensor):
"""
A class for storing and manipulating classification probabilities.
This class extends BaseTensor and provides methods for accessing and manipulating
classification probabilities, including top-1 and top-5 predictions.
Attributes:
data (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The raw tensor or array containing classification probabilities.
orig_shape (tuple | None): The original image shape as (height, width). Not used in this class.
top1 (int): Index of the class with the highest probability.
top5 (List[int]): Indices of the top 5 classes by probability.
top1conf (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Confidence score of the top 1 class.
top5conf (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Confidence scores of the top 5 classes.
Methods:
cpu(): Returns a copy of the probabilities tensor on CPU memory.
numpy(): Returns a copy of the probabilities tensor as a numpy array.
cuda(): Returns a copy of the probabilities tensor on GPU memory.
to(*args, **kwargs): Returns a copy of the probabilities tensor with specified device and dtype.
Examples:
>>> probs = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.3, 0.6])
>>> p = Probs(probs)
>>> print(p.top1)
2
>>> print(p.top5)
[2, 1, 0]
>>> print(p.top1conf)
tensor(0.6000)
>>> print(p.top5conf)
tensor([0.6000, 0.3000, 0.1000])
"""
def __init__(self, probs, orig_shape=None) -> None:
"""
Initialize the Probs class with classification probabilities.
This class stores and manages classification probabilities, providing easy access to top predictions and their
confidences.
Args:
probs (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): A 1D tensor or array of classification probabilities.
orig_shape (tuple | None): The original image shape as (height, width). Not used in this class but kept for
consistency with other result classes.
Attributes:
data (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): The raw tensor or array containing classification probabilities.
top1 (int): Index of the top 1 class.
top5 (List[int]): Indices of the top 5 classes.
top1conf (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): Confidence of the top 1 class.
top5conf (torch.Tensor | np.ndarray): Confidences of the top 5 classes.
Examples:
>>> import torch
>>> probs = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.3, 0.2, 0.4])
>>> p = Probs(probs)
>>> print(p.top1)
3
>>> print(p.top1conf)
tensor(0.4000)
>>> print(p.top5)
[3, 1, 2, 0]
"""
super().__init__(probs, orig_shape)
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=1)
def top1(self):
"""
Returns the index of the class with the highest probability.
Returns:
(int): Index of the class with the highest probability.
Examples:
>>> probs = Probs(torch.tensor([0.1, 0.3, 0.6]))
>>> probs.top1
2
"""
return int(self.data.argmax())
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=1)
def top5(self):
"""
Returns the indices of the top 5 class probabilities.
Returns:
(List[int]): A list containing the indices of the top 5 class probabilities, sorted in descending order.
Examples:
>>> probs = Probs(torch.tensor([0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]))
>>> print(probs.top5)
[4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
"""
return (-self.data).argsort(0)[:5].tolist() # this way works with both torch and numpy.
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=1)
def top1conf(self):
"""
Returns the confidence score of the highest probability class.
This property retrieves the confidence score (probability) of the class with the highest predicted probability
from the classification results.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor containing the confidence score of the top 1 class.
Examples:
>>> results = model("image.jpg") # classify an image
>>> probs = results[0].probs # get classification probabilities
>>> top1_confidence = probs.top1conf # get confidence of top 1 class
>>> print(f"Top 1 class confidence: {top1_confidence.item():.4f}")
"""
return self.data[self.top1]
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=1)
def top5conf(self):
"""
Returns confidence scores for the top 5 classification predictions.
This property retrieves the confidence scores corresponding to the top 5 class probabilities
predicted by the model. It provides a quick way to access the most likely class predictions
along with their associated confidence levels.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or array containing the confidence scores for the
top 5 predicted classes, sorted in descending order of probability.
Examples:
>>> results = model("image.jpg")
>>> probs = results[0].probs
>>> top5_conf = probs.top5conf
>>> print(top5_conf) # Prints confidence scores for top 5 classes
"""
return self.data[self.top5]
举例子
# 假设我们有一个分类模型的输出概率
probs = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.3, 0.2, 0.4])
p = Probs(probs)
# 获取最高概率类别
print(p.top1) # 输出: 3
# 获取前5个类别(在此例中只有4个类别)
print(p.top5) # 输出: [3, 1, 2, 0]
# 获取最高概率的置信度
print(p.top1conf) # 输出: tensor(0.4000)
# 获取前5个类别的置信度
print(p.top5conf) # 输出: tensor([0.4000, 0.3000, 0.2000, 0.1000])
Masks
class Masks(BaseTensor):
"""
A class for storing and manipulating detection masks.
This class extends BaseTensor and provides functionality for handling segmentation masks,
including methods for converting between pixel and normalized coordinates.
Attributes:
data (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The raw tensor or array containing mask data.
orig_shape (tuple): Original image shape in (height, width) format.
xy (List[numpy.ndarray]): A list of segments in pixel coordinates.
xyn (List[numpy.ndarray]): A list of normalized segments.
Methods:
cpu(): Returns a copy of the Masks object with the mask tensor on CPU memory.
numpy(): Returns a copy of the Masks object with the mask tensor as a numpy array.
cuda(): Returns a copy of the Masks object with the mask tensor on GPU memory.
to(*args, **kwargs): Returns a copy of the Masks object with the mask tensor on specified device and dtype.
Examples:
>>> masks_data = torch.rand(1, 160, 160)
>>> orig_shape = (720, 1280)
>>> masks = Masks(masks_data, orig_shape)
>>> pixel_coords = masks.xy
>>> normalized_coords = masks.xyn
"""
def __init__(self, masks, orig_shape) -> None




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










