声明
来源于莫烦Python:Classification 分类学习
分类问题的通俗理解
分类和回归在于输出变量的类型上。通俗来讲,连续变量预测,如预测房价问题,属于回归问题; 离散变量预测,如把东西分成几类,属于分类问题。
代码
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# number 1 to 10 data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None,):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1,)
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b,)
return outputs
def compute_accuracy(v_xs, v_ys):
global prediction
y_pre = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: v_xs})
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_pre,1), tf.argmax(v_ys,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
result = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={xs: v_xs, ys: v_ys})
return result
# define placeholder for inputs to network
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # 28x28
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
# add output layer
prediction = add_layer(xs, 784, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.softmax)
# the error between prediction and real data
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(ys * tf.log(prediction),
reduction_indices=[1])) # loss
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
sess = tf.Session()
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
for i in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) # 分批进行学习,时间短,效果不一定比整套的差
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: batch_xs, ys: batch_ys})
if i % 50 == 0:
print(compute_accuracy(
mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels))
代码释义
1. MNIST 数据
首先准备数据(MNIST库)
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)
MNIST库是手写体数字库,差不多是这样子的
数据中包含55000张训练图片,每张图片的分辨率是28×28,所以我们的训练网络输入应该是28×28=784个像素数据。
搭建网络
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # 28x28
每张图片都表示一个数字,所以我们的输出是数字0到9,共10类。
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
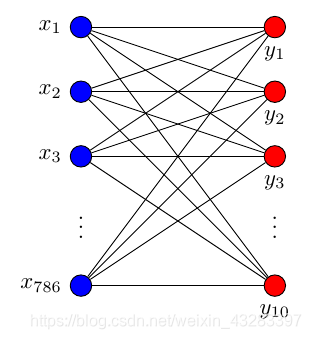
调用add_layer函数搭建一个最简单的训练网络结构,只有输入层和输出层。
prediction = add_layer(xs, 784, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.softmax)
其中输入数据是784个特征,输出数据是10个特征,激励采用softmax函数,网络结构图是这样子的
2. Cross entropy loss
loss函数(即最优化目标函数)选用交叉熵函数。交叉熵用来衡量预测值和真实值的相似程度,如果完全相同,它们的交叉熵等于零。
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(ys * tf.log(prediction),
reduction_indices=[1])) # loss
train方法(最优化算法)采用梯度下降法。
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
sess = tf.Session()
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
3. 训练
现在开始train,每次只取100张图片,免得数据太多训练太慢。
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: batch_xs, ys: batch_ys})
每训练50次输出一下预测精度
if i % 50 == 0:
print(compute_accuracy(
mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels))
输出结果如下:
0.1615
0.665
0.7495
0.7905
0.808
0.8262
0.8359
0.8432
0.8486
0.8538
0.8579
0.8592
0.8619
0.8613
0.8645
0.8658
0.8702
0.8719
0.8734
0.8754







 使用TensorFlow搭建神经网络,实现对手写数字的分类识别,通过MNIST数据集进行训练和测试,展示分类准确率的提升过程。
使用TensorFlow搭建神经网络,实现对手写数字的分类识别,通过MNIST数据集进行训练和测试,展示分类准确率的提升过程。

















 636
636

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








