文章目录
一、代码调试
首先是训练阶段,右击属性中,选择调试,将命令参数的第一个参数设为 train
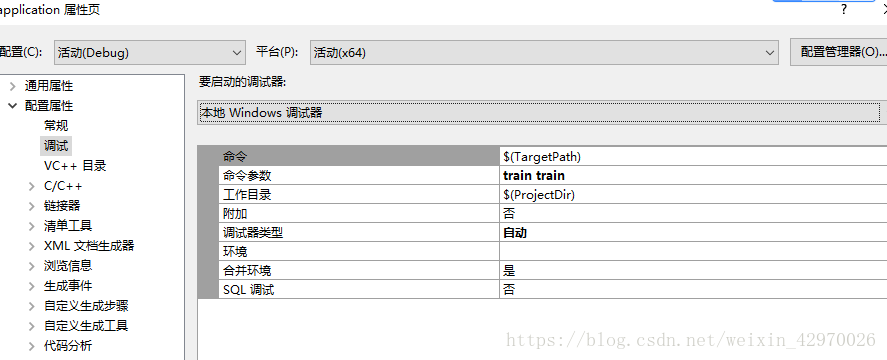
运行 main 函数,报错,
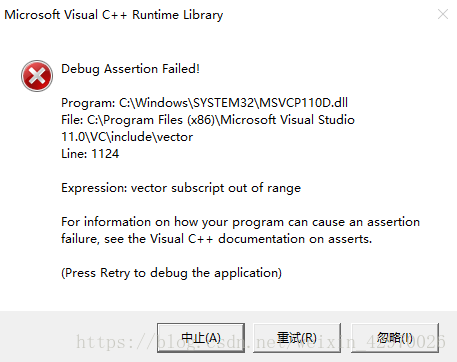
发现 argc 的值为 0,如图:
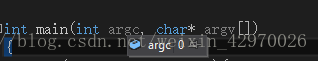
正常的值应该为 3,如图:
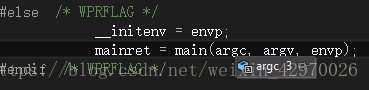
因为现在是训练阶段,所以从 train 函数开始找错误
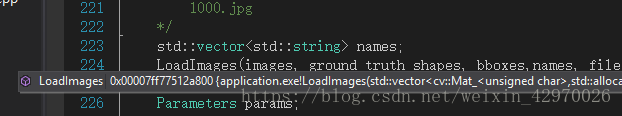
果然 LoadImage 失败了,按 F12,跳转到 LoadImage() 函数,发现提供的图片路径与所需要的图片路径不符
提供的图片路径为:
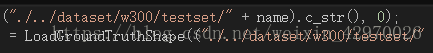
而所需要的图片路径为

将路径改为正确路径:
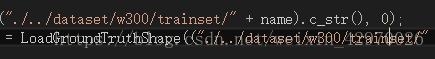
再次运行,运行成功
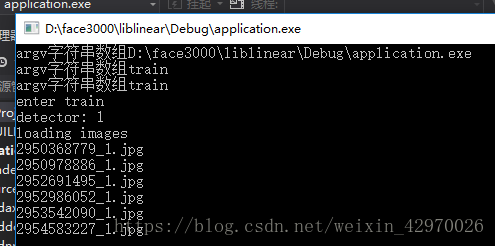
二、train
void Train(const char* ModelName){
std::vector<cv::Mat_<uchar> > images;
std::vector<cv::Mat_<double> > ground_truth_shapes;
std::vector<BoundingBox> bboxes;
std::string file_names = "./../dataset/w300/train_test_jpgs.txt";
// train_jpgs.txt contains all the paths for each image, one image per line
// for example: in Linux you can use ls *.jpg > train_jpgs.txt to get the paths
// the file looks like as below
/*
1.jpg
2.jpg
3.jpg
...
1000.jpg
*/
std::vector<std::string> names;
//加载图片并检测人脸
LoadImages(images, ground_truth_shapes, bboxes,names, file_names);
Parameters params;
params.local_features_num_ = 300;
params.landmarks_num_per_face_ = 68;
params.regressor_stages_ = 2;
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.4);
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.3);
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.2);
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.1);
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.08);
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.05);
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.05);
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.05);
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.05);
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.05);
params.local_radius_by_stage_.push_back(0.05);
params.tree_depth_ = 5;
params.trees_num_per_forest_ = 8;
params.initial_guess_ = 5;//扩充数据集的参数,即将每张图片扩充为几张图片
//计算所有加载的训练图片的平均脸
params.mean_shape_ = GetMeanShape(ground_truth_shapes, bboxes);
CascadeRegressor cas_reg;
//开始训练
cas_reg.Train(images, ground_truth_shapes, bboxes, params);
cas_reg.SaveCascadeRegressor(ModelName);
return;
}
1.加载图片并检测人脸
//加载图片
void LoadImages(std::vector<cv::Mat_<uchar> >& images,
std::vector<cv::Mat_<double> >& ground_truth_shapes,
//const std::vector<cv::Mat_<double> >& current_shapes,
std::vector<BoundingBox>& bboxes,
std::vector<std::string>& names,
std::string file_names){
std::string fn_haar = "./../haarcascade_frontalface_alt2.xml";
cv::CascadeClassifier haar_cascade;
bool yes = haar_cascade.load(fn_haar);
std::cout << "detector: " << yes << std::endl;
std::cout << "loading images\n";
std::ifstream fin;
fin.open(file_names.c_str(), std::ifstream::in);
// train_jpgs.txt contains all the paths for each image, one image per line
// for example: in Linux you can use ls *.jpg > train_jpgs.txt to get the paths
// the file looks like as below
/*
1.jpg
2.jpg
3.jpg
...
1000.jpg
*/
std::string name;
int count = 0;//初始化从图片中检测到的符合要求的人脸数量
//std::cout << name << std::endl;
while (fin >> name){
//读取图片
std::cout << "reading file: " << name << std::endl;
//std::cout << name << std::endl;
std::string pts = name.substr(0, name.length() - 3) + "pts";
//将读取的图片存入image
cv::Mat_<uchar> image = cv::imread(("./../dataset/w300/trainset/" + name).c_str(), 0);
//std::cout<<"image.size"<<image.size()<<std::endl;输出image.size(),发现每张image的尺寸都不一样
//获取加载图片的ground_truth_shape
cv::Mat_<double> ground_truth_shape = LoadGroundTruthShape(("./../dataset/w300/trainset/" + pts).c_str());
std::vector<cv::Rect> faces;
//检测图片中的多个人脸框
haar_cascade.detectMultiScale(image, faces, 1.1, 2, 0, cv::Size(30, 30));
//std::cout<<"after"<<faces.size()<<std::endl;face.size()大小不一,有的为1,有的为4
//遍历检测每个人脸框,如果人脸框包含ground_truth_shape,则count++
for (int i = 0; i < faces.size(); i++){
cv::Rect faceRec = faces[i];
if (ShapeInRect(ground_truth_shape, faceRec)){
// check if the detected face rectangle is in the ground_truth_shape
images.push_back(image);
names.push_back(pts);
ground_truth_shapes.push_back(ground_truth_shape);
BoundingBox bbox;
bbox.start_x = faceRec.x;
bbox.start_y = faceRec.y;
bbox.width = faceRec.width;
bbox.height = faceRec.height;
bbox.center_x = bbox.start_x + bbox.width / 2.0;
bbox.center_y = bbox.start_y + bbox.height / 2.0;
bboxes.push_back(bbox);
count++;//从图片中检测到的符合要求的人脸数量
if (count%100 == 0){
std::cout << count << " images loaded\n";
}
break;
}
}
}
//std::cout<<"加载图片数量"<<count<<std::endl;
std::cout << "get " << bboxes.size() << " faces\n";
fin.close();
}
2.计算所有加载的训练图片的平均脸
// get the mean shape, 每个landmark的坐标点范围为[-1, 1]x[-1, 1]
//计算平均脸
cv::Mat_<double> GetMeanShape(const std::vector<cv::Mat_<double> >& all_shapes,
const std::vector<BoundingBox>& all_bboxes) {
//通常选择第一个人脸模型作为对齐标准
cv::Mat_<double> mean_shape = cv::Mat::zeros(all_shapes[0].rows, 2, CV_32FC1);
for (int i = 0; i < all_shapes.size(); i++)
{
////将人脸模型坐标归一化到[-1.1]
mean_shape += ProjectShape(all_shapes[i], all_bboxes[i]);
}
mean_shape = 1.0 / all_shapes.size()*mean_shape;
//std::cout<<"训练图片的平均脸"<<mean_shape<<std::endl;
return mean_shape;
}
3.开始训练
3.1扩充数据集
//扩充数据集
std::cout << "augment data sets" << std::endl;
cv::RNG random_generator(current_time);
for (int i = 0; i < images_.size(); i++){
//params_.initial_guess_ 决定将每张图片扩充为几张图片
for (int j = 0; j < params_.initial_guess_; j++)
{
int index = 0;
do {
//在0到图片数范围内随机产生index,且index服从均匀分布
index = random_generator.uniform(0, images_.size());
}while(index == i);//index!=i的时候就跳出循环,即随机产生一个不等于i的index,然后用产生的这张图片的形状作为第i张图片的初始化形状
//push_back的作用是在在vector尾部加入一个数据
augmented_images_index.push_back(i);
augmented_ground_truth_shapes.push_back(ground_truth_shapes_[i]);
augmented_bboxes.push_back(bboxes_[i]);
//取出随机产生图片的真实形状,通过相应处理后作为第i张图片的初始形状
cv::Mat_<double> temp = ground_truth_shapes_[index];
temp = ProjectShape(temp, bboxes_[index]);
temp = ReProjection(temp, bboxes_[i]);
augmented_current_shapes.push_back(temp);
}
augmented_images_index.push_back(i);
augmented_ground_truth_shapes.push_back(ground_truth_shapes_[i]);
augmented_bboxes.push_back(bboxes_[i]);
//将之前计算的平均脸作为第i张图片原始的初始化形状
augmented_current_shapes.push_back(ReProjection(params_.mean_shape_, bboxes_[i]));
}
std::cout << "augmented size: " << augmented_current_shapes.size() << std::endl;
3.2 计算回归目标即真实形状增量
// calculate the regression targets
std::cout << "calculate regression targets" << std::endl;
#pragma omp parallel for
//计算每个人脸的真实形状增量
for (int i = 0; i < augmented_current_shapes.size(); i++){
regression_targets[i] = ProjectShape(augmented_ground_truth_shapes[i], augmented_bboxes[i])
- ProjectShape(augmented_current_shapes[i], augmented_bboxes[i]);
cv::Mat_<double> rotation;
double scale;
//计算平均形状与各初始化形状之间的相似变换,即rotations和scales
getSimilarityTransform(params_.mean_shape_, ProjectShape(augmented_current_shapes[i], augmented_bboxes[i]), rotation, scale);
cv::transpose(rotation, rotation);
//根据rotations和scales得到统一坐标的真实形状增量
regression_targets[i] = scale * regression_targets[i] * rotation;
getSimilarityTransform(ProjectShape(augmented_current_shapes[i], augmented_bboxes[i]), params_.mean_shape_, rotation, scale);
rotations_[i] = rotation;
scales_[i] = scale;
}
3.3 各阶段随机森林的训练
随机选取 300 对像素点
在各 landmark 半径区域内随机选取 300 对像素点,并计算它们之间的差值,叫做 pixel_difference_features,即像素差特征点。
//在半径范围内随机选取local_features_num_对像素点a和b
for (int i = 0; i < local_features_num_; i++){
double x, y;
do{
x = rd.uniform(-local_radius_, local_radius_);
y = rd.uniform(-local_radius_, local_radius_);
} while (x*x + y*y > local_radius_*local_radius_);
cv::Point2f a(x, y);
do{
x = rd.uniform(-local_radius_, local_radius_);
y = rd.uniform(-local_radius_, local_radius_);
} while (x*x + y*y > local_radius_*local_radius_);
cv::Point2f b(x, y);
local_position_[i] = FeatureLocations(a, b);
}
//计算刚刚选取的像素对的差值
//std::cout << "get pixel differences" << std::endl;
cv::Mat_<int> pixel_differences(local_features_num_, augmented_images_index.size()); // matrix: features*images
for (int i = 0; i < augmented_images_index.size(); i++){
cv::Mat_<double> rotation = rotations[i];
double scale = scales[i];
//getSimilarityTransform(ProjectShape(augmented_current_shapes[i], augmented_bboxes[i]),mean_shape_, rotation, scale);
//将选取的像素点对坐标与平均脸坐标对齐,并计算像素点对之间的像素差值
for (int j = 0; j < local_features_num_; j++){
FeatureLocations pos = local_position_[j];
double delta_x = rotation(0, 0)*pos.start.x + rotation(0, 1)*pos.start.y;
double delta_y = rotation(1, 0)*pos.start.x + rotation(1, 1)*pos.start.y;
delta_x = scale*delta_x*augmented_bboxes[i].width / 2.0;
delta_y = scale*delta_y*augmented_bboxes[i].height / 2.0;
int real_x = delta_x + augmented_current_shapes[i](landmark_index_, 0);
int real_y = delta_y + augmented_current_shapes[i](landmark_index_, 1);
real_x = std::max(0, std::min(real_x, images[augmented_images_index[i]].cols - 1)); // which cols
real_y = std::max(0, std::min(real_y, images[augmented_images_index[i]].rows - 1)); // which rows
int tmp = (int)images[augmented_images_index[i]](real_y, real_x); //real_y at first
delta_x = rotation(0, 0)*pos.end.x + rotation(0, 1)*pos.end.y;
delta_y = rotation(1, 0)*pos.end.x + rotation(1, 1)*pos.end.y;
delta_x = scale*delta_x*augmented_bboxes[i].width / 2.0;
delta_y = scale*delta_y*augmented_bboxes[i].height / 2.0;
real_x = delta_x + augmented_current_shapes[i](landmark_index_, 0);
real_y = delta_y + augmented_current_shapes[i](landmark_index_, 1);
real_x = std::max(0, std::min(real_x, images[augmented_images_index[i]].cols - 1)); // which cols
real_y = std::max(0, std::min(real_y, images[augmented_images_index[i]].rows - 1)); // which rows
pixel_differences(j, i) = tmp - (int)images[augmented_images_index[i]](real_y, real_x);
}
}
随机森林数据集重构,相当于有放回抽取
// train Random Forest
// construct each tree in the forest
//随机森林数据集的重构,相当于有放回抽取
double overlap = 0.4;
int step = floor(((double)augmented_images_index.size())*overlap / (trees_num_per_forest_ - 1));
trees_.clear();
all_leaf_nodes_ = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < trees_num_per_forest_; i++){
int start_index = i*step;
int end_index = augmented_images_index.size() - (trees_num_per_forest_ - i - 1)*step;

树的构建

随机产生临时阈值
// random generate threshold
std::vector<int> data;
data.reserve(images_indexes.size());
for (int i = 0; i < images_indexes.size(); i++){
//将新划分的数据集(100张)中所有的图片的某个landmark的300对像素点差值存入data
data.push_back(pixel_differences(j, images_indexes[i]));
}
std::sort(data.begin(), data.end());//排序
//用于选取阈值的临时索引
int tmp_index = floor((float)(images_indexes.size()*(0.5 + 0.9*(rd.uniform(0.0, 1.0) - 0.5))));
//根据临时索引从data中选取对应值作为临时阈值
int tmp_threshold = data[tmp_index];
根据临时阈值对重构后的数据集进行划分
若小于临时阈值,则被临时划分到左子树,并取出该图片的真实形状增量,反之则被划分到右子树。
for (int i = 0; i < images_indexes.size(); i++){
int index = images_indexes[i];
//小于随机产生的阈值则被划分到左边
if (pixel_differences(j, index) < tmp_threshold){
tmp_left_indexes.push_back(index);
// do with regression target
double value = regression_targets_->at(index)(landmark_index_, 0);
Ex_2_lc += pow(value, 2);
Ex_lc += value;
value = regression_targets_->at(index)(landmark_index_, 1);
Ey_2_lc += pow(value, 2);
Ey_lc += value;
}
//如果大于阈值就被划分到右边
else{
tmp_right_indexes.push_back(index);
double value = regression_targets_->at(index)(landmark_index_, 0);
Ex_2_rc += pow(value, 2);
Ex_rc += value;
value = regression_targets_->at(index)(landmark_index_, 1);
Ey_2_rc += pow(value, 2);
Ey_rc += value;
}
}
计算方差,选择使得方差减小最大的像素差值点作为真正的分裂节点
if (tmp_left_indexes.size() == 0){
var_lc = 0.0;
} else{
//计算方差,DX=EX^2-(EX)^2
var_lc = Ex_2_lc / tmp_left_indexes.size() - pow(Ex_lc / tmp_left_indexes.size(), 2)
+ Ey_2_lc / tmp_left_indexes.size() - pow(Ey_lc / tmp_left_indexes.size(), 2);
}
if (tmp_right_indexes.size() == 0){
var_rc = 0.0;
} else{
var_rc = Ex_2_rc / tmp_right_indexes.size() - pow(Ex_rc / tmp_right_indexes.size(), 2)
+ Ey_2_rc / tmp_right_indexes.size() - pow(Ey_rc / tmp_right_indexes.size(), 2);
}
var_red = -var_lc*tmp_left_indexes.size() - var_rc*tmp_right_indexes.size();
//选取使得方差减小最大的像素差值点作为分裂节点
if (var_red > var){
var = var_red;
threshold = tmp_threshold;
feature_index = j;
left_indexes = tmp_left_indexes;
right_indexes = tmp_right_indexes;
}
}
}
对上一过程进行递归
//递归构造树
node->left_child_ = BuildTree(selected_indexes, pixel_differences, left_indexes, current_depth + 1);
node->right_child_ = BuildTree(selected_indexes, pixel_differences, right_indexes, current_depth + 1);
构建树的完整代码
//树的构建
Node* RandomForest::BuildTree(std::set<int>& selected_indexes, cv::Mat_<int>& pixel_differences, std::vector<int>& images_indexes, int current_depth){
//std::cout<<"images_index.size:"<<images_indexes.size()<<std::endl;
if (images_indexes.size() > 0){ // the node may not split under some cases
Node* node = new Node();
node->depth_ = current_depth;
node->samples_ = images_indexes.size();
std::vector<int> left_indexes, right_indexes;
if (current_depth == tree_depth_){ // the node reaches max depth
node->is_leaf_ = true;
node->leaf_identity = all_leaf_nodes_;
all_leaf_nodes_++;
return node;
}
//寻找分裂节点
int ret = FindSplitFeature(node, selected_indexes, pixel_differences, images_indexes, left_indexes, right_indexes);
// actually it won't enter the if block, when the random function is good enough
//当前数据集已不可划分,是一个包含所有数据的叶子节点
if (ret == 1){ // the current node contain all sample when reaches max variance reduction, it is leaf node
node->is_leaf_ = true;
node->leaf_identity = all_leaf_nodes_;
all_leaf_nodes_++;
return node;
}
//if (current_depth + 1 < tree_depth_){
//递归构造树
node->left_child_ = BuildTree(selected_indexes, pixel_differences, left_indexes, current_depth + 1);
node->right_child_ = BuildTree(selected_indexes, pixel_differences, right_indexes, current_depth + 1);
//}
return node;
}
else{ // this case is not possible in this data structure
return NULL;
}
}
3.4 获取每层的全局二值特征点
std::cout << "Get Global Binary Features" << std::endl;
struct feature_node **global_binary_features;
global_binary_features = new struct feature_node* [augmented_current_shapes.size()];
//初始化每张图片的全局二值特征
for(int i = 0; i < augmented_current_shapes.size(); ++i){
global_binary_features[i] = new feature_node[params_.trees_num_per_forest_*params_.landmarks_num_per_face_+1];
}
int num_feature = 0;//初始化全局二值特征点的数量
for (int i=0; i < params_.landmarks_num_per_face_; ++i){
num_feature += rd_forests_[i].all_leaf_nodes_;//每个landmark所对应的随机森林的所有叶子节点数量之和
}
#pragma omp parallel for
//遍历每张图片
for (int i = 0; i < augmented_current_shapes.size(); ++i){
int index = 1;
int ind = 0;
const cv::Mat_<double>& rotation = rotations_[i];
const double scale = scales_[i];
const cv::Mat_<uchar>& image = images[augmented_images_index[i]];
const BoundingBox& bbox = augmented_bboxes[i];
const cv::Mat_<double>& current_shape = augmented_current_shapes[i];
//每个landmark
for (int j = 0; j < params_.landmarks_num_per_face_; ++j){
//随机森林里的每棵树
for (int k = 0; k < params_.trees_num_per_forest_; ++k){
Node* node = rd_forests_[j].trees_[k];
//如果这个节点不是叶子结点的话就判断它下一步的走向
while (!node->is_leaf_){
FeatureLocations& pos = node->feature_locations_;
double delta_x = rotation(0, 0)*pos.start.x + rotation(0, 1)*pos.start.y;
double delta_y = rotation(1, 0)*pos.start.x + rotation(1, 1)*pos.start.y;
delta_x = scale*delta_x*bbox.width / 2.0;
delta_y = scale*delta_y*bbox.height / 2.0;
int real_x = delta_x + current_shape(j, 0);
int real_y = delta_y + current_shape(j, 1);
real_x = std::max(0, std::min(real_x, image.cols - 1)); // which cols
real_y = std::max(0, std::min(real_y, image.rows - 1)); // which rows
int tmp = (int)image(real_y, real_x); //real_y at first
delta_x = rotation(0, 0)*pos.end.x + rotation(0, 1)*pos.end.y;
delta_y = rotation(1, 0)*pos.end.x + rotation(1, 1)*pos.end.y;
delta_x = scale*delta_x*bbox.width / 2.0;
delta_y = scale*delta_y*bbox.height / 2.0;
real_x = delta_x + current_shape(j, 0);
real_y = delta_y + current_shape(j, 1);
real_x = std::max(0, std::min(real_x, image.cols - 1)); // which cols
real_y = std::max(0, std::min(real_y, image.rows - 1)); // which rows
//小于阈值就到左边
if ((tmp - (int)image(real_y, real_x)) < node->threshold_){
node = node->left_child_;// go left
}
//否则在右边
else{
node = node->right_child_;// go right
}
}
global_binary_features[i][ind].index = index + node->leaf_identity;//rd_forests_[j].GetBinaryFeatureIndex(k, images[augmented_images_index[i]], augmented_bboxes[i], augmented_current_shapes[i], rotations_[i], scales_[i]);
global_binary_features[i][ind].value = 1.0;
ind++;
// std::cout<< global_binary_features[i][ind].index << " ";
}
index += rd_forests_[j].all_leaf_nodes_;
}
if (i%2000 == 0 && i > 0){
std::cout << "extracted " << i << " images" << std::endl;
}
global_binary_features[i][params_.trees_num_per_forest_*params_.landmarks_num_per_face_].index = -1;
global_binary_features[i][params_.trees_num_per_forest_*params_.landmarks_num_per_face_].value = -1.0;
}
3.5 全局回归并预测回归目标
//每一层的全局回归
std::cout << "Global Regression of stage " << stage_ << std::endl;
linear_model_x_.resize(params_.landmarks_num_per_face_);
linear_model_y_.resize(params_.landmarks_num_per_face_);
double** targets = new double*[params_.landmarks_num_per_face_];
for (int i = 0; i < params_.landmarks_num_per_face_; ++i){
targets[i] = new double[augmented_current_shapes.size()];
}
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < params_.landmarks_num_per_face_; ++i){
if(i%10==0)
std::cout << "regress landmark " << i << std::endl;
for(int j = 0; j< augmented_current_shapes.size();j++){
//获取每张图片每个landmark的回归目标的横坐标
targets[i][j] = regression_targets[j](i, 0);
}
prob->y = targets[i];
check_parameter(prob, regression_params);
//回归模型,就是那个求W的公式的具体实现
struct model* regression_model = train(prob, regression_params);
//横坐标的线性模型
linear_model_x_[i] = regression_model;
for(int j = 0; j < augmented_current_shapes.size(); j++){
//获取每张图片每个landmark的回归目标的纵坐标
targets[i][j] = regression_targets[j](i, 1);
}
prob->y = targets[i];
check_parameter(prob, regression_params);
regression_model = train(prob, regression_params);
//纵坐标的线性模型
linear_model_y_[i] = regression_model;
}
for (int i = 0; i < params_.landmarks_num_per_face_; ++i){
delete[] targets[i];// = new double[augmented_current_shapes.size()];
}
delete[] targets;
//预测回归目标
std::cout << "predict regression targets" << std::endl;
std::vector<cv::Mat_<double> > predict_regression_targets;
predict_regression_targets.resize(augmented_current_shapes.size());
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < augmented_current_shapes.size(); i++){
cv::Mat_<double> a(params_.landmarks_num_per_face_, 2, 0.0);
for (int j = 0; j < params_.landmarks_num_per_face_; j++){
//预测横坐标增量
a(j, 0) = predict(linear_model_x_[j], global_binary_features[i]);
//预测纵坐标增量
a(j, 1) = predict(linear_model_y_[j], global_binary_features[i]);
}
cv::Mat_<double> rot;
cv::transpose(rotations_[i], rot);
//与平均脸坐标统一的预测形状增量
predict_regression_targets[i] = scales_[i] * a * rot;
if (i%2000 == 0 && i > 0){
std::cout << "predict " << i << " images" << std::endl;
}
}
std::cout << "\n";
训练终于完成了,接下来就级联回归器保存起来以便测试时调用

三、test
void Test(const char* ModelName, const char* name){
CascadeRegressor cas_load;
cas_load.LoadCascadeRegressor(ModelName);
TestImage(name, cas_load);
return;
}
void Test(const char* ModelName){
CascadeRegressor cas_load;
cas_load.LoadCascadeRegressor(ModelName);//加载训练阶段得到的级联回归器
std::vector<cv::Mat_<uchar> > images;//待测试图片
std::vector<cv::Mat_<double> > ground_truth_shapes;//待测试图片的真实形状
std::vector<BoundingBox> bboxes;//人脸框
std::vector<std::string> names;//测试图片名
std::string file_names = "./../dataset/w300/test_jpgs.txt";//存放测试图片名的文件名
LoadImages(images, ground_truth_shapes, bboxes,names, file_names);//加载测试图片
// struct timeval t1, t2;
// gettimeofday(&t1, NULL);
string str = ModelName;
double mean_error = 0;//初始化mean_error
std::vector<cv::Mat_<double> > regression_shapes;//定义回归得到的形状
std::ofstream fout;
fout.open((str + "_result.txt").c_str(), std::fstream::out);
for (int i = 0; i < images.size(); i++){
//将平均形状在全局坐标下重建作为初始回归形状
cv::Mat_<double> current_shape = ReProjection(cas_load.params_.mean_shape_, bboxes[i]);
//通过级联回归器得到的预测形状
cv::Mat_<double> res = cas_load.Predict(images[i], current_shape, bboxes[i]);//, ground_truth_shapes[i]);
regression_shapes.push_back(res);
//计算预测人脸形状与真实人脸形状之间的误差
double err = CalculateError(ground_truth_shapes[i], res);
cout << "error: " << err << std::endl;
fout << i << " " << err << endl;
//计算平均误差
mean_error = mean_error + err;
}
cout << "mean_error is : " << mean_error <<" "<< mean_error / images.size() << endl;
fout << "regression error is : " << mean_error / images.size() << endl;
//遍历每张图片
for (int i = 0; i < names.size(); i++)
{
cv::Mat_<double> tmp_mat = cv::Mat::zeros(68, 2, CV_64F);
string file_name ="./data/"+ names[i];
tmp_mat = regression_shapes[i];
fout.open(file_name, std::fstream::out);
//对于每张图片的每个landmark,将其回归形状的横纵坐标输出到文件中
for (int i = 0; i < 68; i++){
fout << tmp_mat(i, 0) << " " << tmp_mat(i, 1) << std::endl;
cout << tmp_mat(i, 0) << " " << tmp_mat(i, 1) << std::endl;
}
fout.close();
}
fout.close();
// gettimeofday(&t2, NULL);
// double time_full = t2.tv_sec - t1.tv_sec + (t2.tv_usec - t1.tv_usec)/1000000.0;
// cout << "time full: " << time_full << " : " << time_full/images.size() << endl;
return;
}
四、开始测试
测试之前需要先把图片加载路径修改一下,如图:
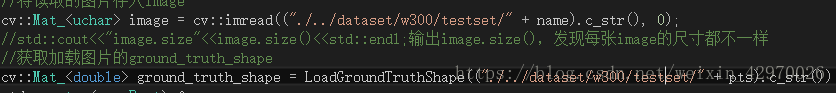
测试开始
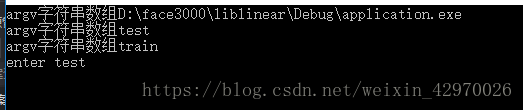
测试结果
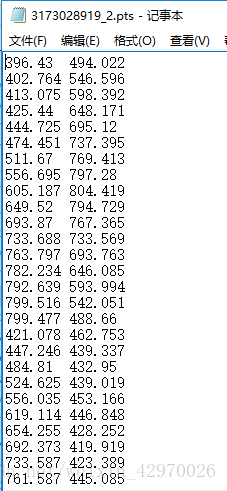
返回的是 68 个 landmark 的坐标,用记事本打开如图所示:
























 279
279

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








