K近邻分类法(KNN)
KNN是分类方法中最简单且常用的一种,它的思想是假如一个样本在特征空间中的k个最相似(即特征空间中最邻近)的样本中的大多数属于某一个类别,则该样本也应该属于这个类别,其中K通常是不大于20的整数。KNN算法中,所选择的邻居都是已经正确分类的对象。该方法在定类决策上只依据最邻近的一个或者几个样本的类别来决定待分样本所属的类别。
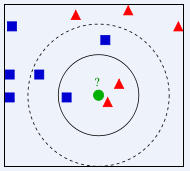
如图,对类别未知的绿色圆点进行类别划分,那它应该属于红色三角形还是蓝色正方形?如果K=3,由于红色三角形所占比例为2/3,绿色圆将被赋予红色三角形那个类,如果K=5,由于蓝色四方形比例为3/5,绿色圆被赋予蓝色四方形类。可以看出K的取值很大程度影响算法结果。
课本上给出了一个简单二维点分类的示例,创建两个不同的二维点集,用Pickle模块保存:
创建并保存点集:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from numpy.random import randn
import pickle
from pylab import *
# create sample data of 2D points
n = 200
# two normal distributions
class_1 = 0.6 * randn(n,2)
class_2 = 1.2 * randn(n,2) + array([5,1])
labels = hstack((ones(n),-ones(n)))
# save with Pickle
#with open('points_normal.pkl', 'w') as f:
with open('points_normal_test.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(class_1,f)
pickle.dump(class_2,f)
pickle.dump(labels,f)
# normal distribution and ring around it
print ("save OK!")
class_1 = 0.6 * randn(n,2)
r = 0.8 * randn(n,1) + 5
angle = 2*pi * randn(n,1)
class_2 = hstack((r*cos(angle),r*sin(angle)))
labels = hstack((ones(n),-ones(n)))
# save with Pickle
#with open('points_ring.pkl', 'w') as f:
with open('points_ring_test.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(class_1,f)
pickle.dump(class_2,f)
pickle.dump(labels,f)
print ("save OK!")
载入点集与测试分类可视化:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pickle
from pylab import *
from PCV.classifiers import knn
from PCV.tools import imtools
pklist=['points_normal.pkl','points_ring.pkl']
figure()
# load 2D points using Pickle
for i, pklfile







 本文介绍了Python中使用KNN算法和Dense SIFT(D-SIFT)进行手势识别的方法。KNN算法通过选择最近邻进行分类,其效果受K值影响。D-SIFT在图像上进行密集采样,用于提取特征。实验结果显示,KNN结合D-SIFT能实现较高的手势分类准确率,但分辨率和数据集大小对结果有显著影响。
本文介绍了Python中使用KNN算法和Dense SIFT(D-SIFT)进行手势识别的方法。KNN算法通过选择最近邻进行分类,其效果受K值影响。D-SIFT在图像上进行密集采样,用于提取特征。实验结果显示,KNN结合D-SIFT能实现较高的手势分类准确率,但分辨率和数据集大小对结果有显著影响。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








