视图
定义:本身不存放数据,只存放sql查询语句(好处:自动更新数据;提高效率;节省存放设备空间)。是一张临时的表,客户端与数据库断开连接后遍消失了。
如何创建视图?
create view 视图名称(<视图列名1>,<视图列名2>···)
as
<select 查询语句>l
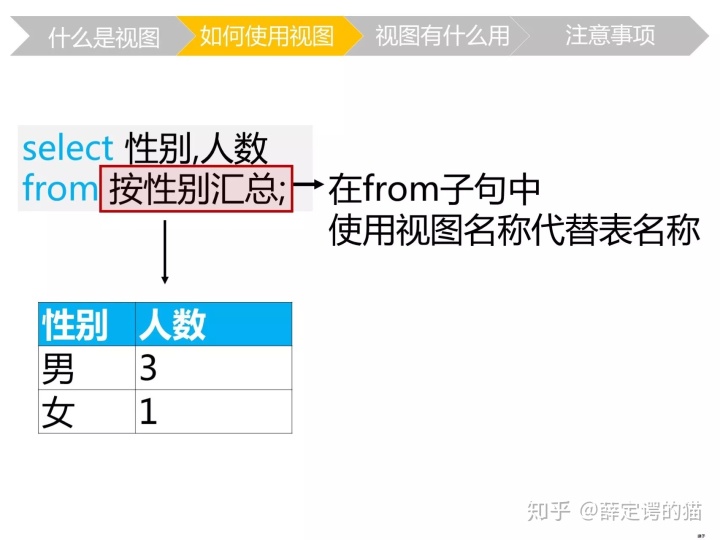
举个栗子:create view 按性别汇总(性别,人数)
as
select 性别,count(*)
from student
group by 性别;如何创建视图
子查询

例题:找出每个课程里成绩最低的学号
第一步:查找出每门课程的最低成绩有哪些值
select 课程号,min(成绩)
from score
group by 课程号;第二步:在成绩表里查找这些值对应的学号
select 学号,成绩
from score
where 成绩 in (80,60,80);最终sql:
select 学号,成绩
from score
where 成绩 in (
select min(成绩)
from score
group by 课程号
);题目:哪些学生的成绩比课程0002的全部成绩里的任意一个高呢?(any)
select 学号,成绩
from score
where 成绩 > any(
select 成绩
from score
where 课程号 = '0002'
);
第一步:查找出课程0002的全部成绩 select 成绩
from score
where 课程号 = '0002';
第二步:比任意一个高any(子查询)select 学号,成绩
from score
where 成绩 > any(子查询);标量子查询:只返回一个值。(通常是where语句中无法使用聚合函数的情况下使用标量子查询),所以可以和比较运算符、between···and···等一起使用。

任何单一值的地方都可以使用标量子查询。
举例:select 学号, 成绩, (select avg(成绩) from score) as 平均成绩
from score;
关联子查询
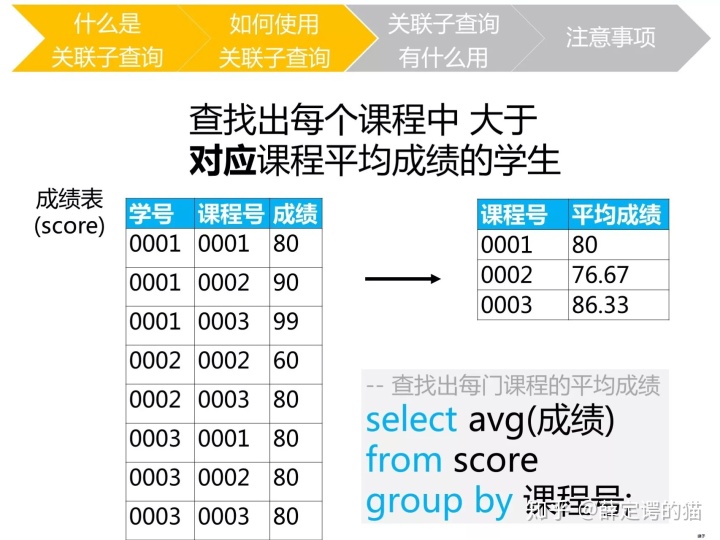
说白了关联子查询就是想按组进行筛选数据的时候使用,如想看看每个课程中大于平均成绩的学生;选取出各商品种类中高于该商品种类的平均销售单价的商品。
这里举个《sql基础教程》p169的例子:
--按照商品种类计算平均价格
select avg(sale_price)
from Product
group by product_type;但是,如果我们使用标量子查询的方法,直接把上述select语句中使用到where子句中的话,会发生错误。
--发生错误的子查询
select product_id, product_name, sale_price
from Product
where sale_price > (select avg(sale_price)
from Product
group by product_type);出错原因:在where子句中使用子查询时,该子查询的结果必须是单一的。
但是,如果以商品种类分组为单位,对销售单价和平均单价进行比较,除此之外似乎也没什么其他方法了。到底咋办?
→关联子查询
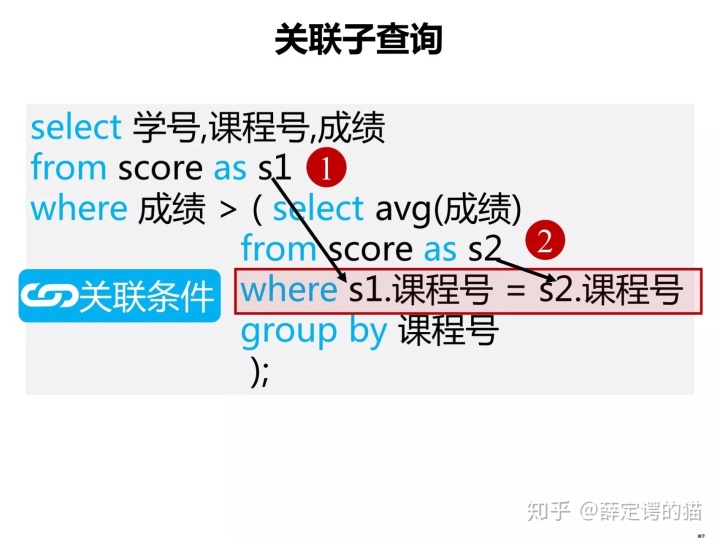
--通过关联子查询按照商品种类对平均销售单价进行比较
select product_type, product_name, sale_price
from Product as p1
where sale_price > (select avg(sale_price)
from Product as p2
where p1.product_type = p2.product_type
group by product_type);这里起到关键作用的就是在子查询中添加的where子句的条件。该条件的意思就是,在同一商品种类中对各商品的销售单价和平均单价进行比较。
这是由于作为比较对象的都是同一张product表,因此为了进行区分,分别使用了P1和P2两个别名。在使用关联子查询时,需要在表所对应的列名前加上表的别名,如p1.product_type
在细分的组内进行比较时,需要使用关联子查询







 博客介绍了SQL查询的相关技巧,包括视图的定义、创建方法,其能自动更新数据、提高效率等;还讲解了子查询,通过例题展示查找每门课程最低成绩对应学号的方法;介绍了标量子查询,可在单一值处使用;最后阐述关联子查询,用于按组筛选数据。
博客介绍了SQL查询的相关技巧,包括视图的定义、创建方法,其能自动更新数据、提高效率等;还讲解了子查询,通过例题展示查找每门课程最低成绩对应学号的方法;介绍了标量子查询,可在单一值处使用;最后阐述关联子查询,用于按组筛选数据。
















 1689
1689

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








