生成式AI的大火让我这个搞RL的弱鸡研究生也不得不来学习CV了(别问,问就是RL找不到工作)
先上效果吧,代码在博客最后(只是一个学习的临时Demo,没有采用条件生成)
可以隐约地看出的确有那么点意思了,可能是调参的问题吧,也可能是数据集太小了,效果不是很好。

大致原理:
- 其实也还是基于隐变量的生成模型那一套(如:VAE),加噪过程对应的是Encoder,降噪过程对应的是Decoder。
- 整体目标是最大化数据的对数似然 logPθ(X)≥Eq(x1:T∣x0)logp(x0:T)q(x1:T∣x0){logP_{\theta}(X)}\geq{E_{q({x_{1:T}|{x_{0}}})}log \frac{p(x_{0:T})}{q(x_{1:T}|x_{0})}}logPθ(X)≥Eq(x1:T∣x0)logq(x1:T∣x0)p(x0:T),qqq是加噪过程,ppp是降噪过程。
- 预测模型(UNet)所预测的是 ttt 时刻的噪声,说白了本质上和VAE一样,都是用神经网络去近似隐变量(噪声)的后验分布(详细原理去看变分推断)。
训练
第一种,最大化对数似然的变分下界(variational lower-bound “VLB”):
出自论文:Luo C. Understanding diffusion models: A unified perspective[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.11970, 2022.
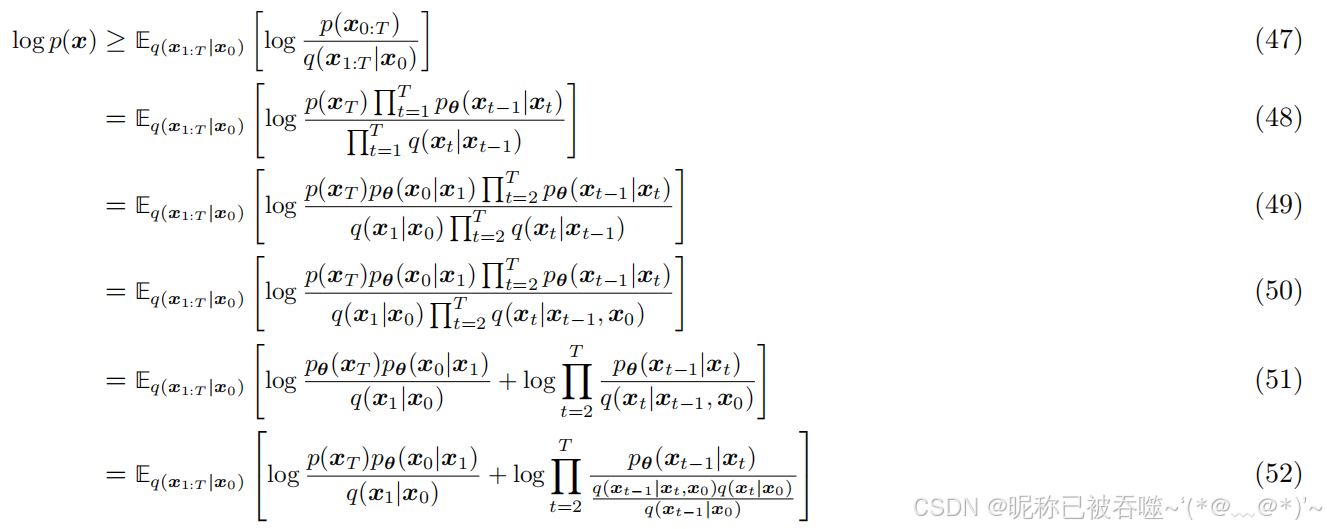
上述过程还是变分推断那一套,这个损失函数不是很常用,因为实现起来太麻烦了,不过有的代码里还是有的,比如在DiT的Meta官方实现代码里(使用该损失函数可以学习到后验分布的方差)(https://github.com/facebookresearch/DiT/blob/main/diffusion/gaussian_diffusion.py#L682)
第二种,也是最简单,最常用,最广为人知晓的
出自论文:Ho J, Jain A, Abbeel P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2020, 33: 6840-6851.
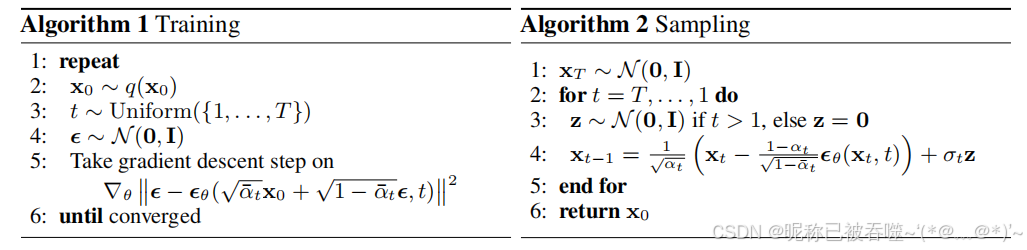
该方法其实是上面第一种方法的近似(运用了高斯分布和指数函数的之间关系),不过这种近似会导致丢失后验分布的方差信息,在论文中给出了方差 σt\sigma_{t}σt 的上界和下界 σt2=βt\sigma_{t}^{2}=\beta_{t}σt2=βt, σt2=1−α‾t−11−α‾tβt\sigma_{t}^{2}=\frac{1-\overline{\alpha}_{t-1}}{1-\overline{\alpha}_{t}}\beta_{t}σt2=1−αt1−αt−1βt,实际实现中选其中一个作为方差即可(论文中说二者的效果其实差不多…)。
近似过程如下,想看就看吧,反正我是懒得看了,知道个原因就差不多得了(手动滑稽)
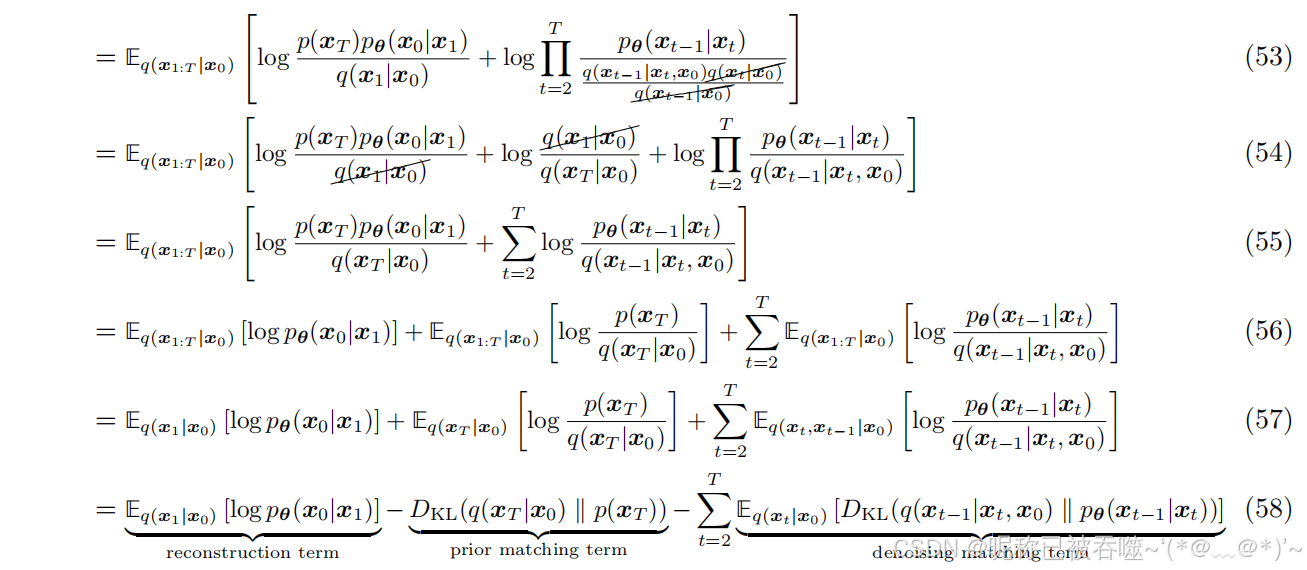
衔接(58)式中的最后一项进行化简,得到 qqq 分布的均值μq(xt,x0)\mu_{q}(x_{t},x_{0})μq(xt,x0),回到式(58)中,最小化qqq和ppp的KL散度可以等价于最小化两个分布均值的二范数(这个技巧在VAE中也有)。将加噪过程的公式 xt=α‾tx0+1−α‾tϵx_{t}=\sqrt{\overline{\alpha}_{t}}x_{0}+\sqrt{1-\overline{\alpha}_{t}}\epsilonxt=αtx0+1−αtϵ 代入就可以得到最终损失函数(Training的第5行)。

出自论文:Luo C. Understanding diffusion models: A unified perspective[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.11970, 2022.
代码分为三部分:main.py、scheduler.py 和 UNet.py
"UNet.py"
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class TimestepEmbedder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, frequency_embedding_size=1024):
super().__init__()
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(frequency_embedding_size, hidden_size, bias=True),
nn.SiLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias=True),
)
self.frequency_embedding_size = frequency_embedding_size
@staticmethod
def timestep_embedding(t, dim, max_period=10000):
half = dim // 2
freqs = torch.exp(
-math.log(max_period) * torch.arange(start=0, end=half, dtype=torch.float32) / half
).to(device=t.device)
args = t[:, None].float() * freqs[None]
embedding = torch.cat([torch.cos(args), torch.sin(args)], dim=-1)
if dim % 2:
embedding = torch.cat([embedding, torch.zeros_like(embedding[:, :1])], dim=-1)
return embedding
def forward(self, t):
t_freq = self.timestep_embedding(t, self.frequency_embedding_size)
t_emb = self.mlp(t_freq)
return t_emb
class AttentionBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, num_groups=32):
super().__init__()
self.channels = channels
self.norm = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=num_groups, num_channels=channels)
self.qkv = nn.Conv2d(channels, 3 * channels, 1)
self.output = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, 1)
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
q, k, v = torch.split(self.qkv(self.norm(x)), self.channels, dim=1)
q = q.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(B, H * W, C)
k = k.view(B, C, H * W)
v = v.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(B, H * W, C)
dot_products = torch.bmm(q, k) * (C ** (-0.5))
assert dot_products.shape == (B, H * W, H * W)
attention = torch.softmax(dot_products, dim=-1)
out = torch.bmm(attention, v)
assert out.shape == (B, H * W, C)
out = out.view(B, H, W, C).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
return F.selu(self.output(out) + x)
class DownsampleResBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1, num_groups=32, use_attention=False):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.norm1 = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=num_groups, num_channels=out_channels)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)
self.norm2 = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=num_groups, num_channels=out_channels)
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=num_groups, num_channels=out_channels)
) if stride != 1 or in_channels != out_channels else nn.Identity()
self.attention = AttentionBlock(out_channels, num_groups=num_groups) if use_attention else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x, c=None):
x = x + c if c is not None else x
out = F.selu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
out = self.norm2(self.conv2(out))
out += self.shortcut(x)
out = F.selu(out)
out = self.attention(out)
return out
class UpsampleResBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1, num_groups=32, use_attention=False):
super().__init__()
self.dconv1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=2 + stride, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.norm1 = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=num_groups, num_channels=out_channels)
self.dconv2 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)
self.norm2 = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=num_groups, num_channels=out_channels)
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=2 + stride, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=num_groups, num_channels=out_channels)
) if stride != 1 or in_channels != out_channels else nn.Identity()
self.attention = AttentionBlock(out_channels, num_groups=num_groups) if use_attention else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x, c=None):
x = x + c if c is not None else x
out = F.selu(self.norm1(self.dconv1(x)))
out = self.norm2(self.dconv2(out))
out += self.shortcut(x)
out = F.selu(out)
out = self.attention(out)
return out
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
block_channels=[64, 128, 256, 512, 1024],
use_attention=[False, False, False, False, True],
num_groups=32,
):
super().__init__()
assert len(block_channels) == len(use_attention)
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, block_channels[0], kernel_size=1, bias=False)
downsample = []
upsample = []
for i in range(len(block_channels) - 1):
layer = nn.ModuleDict()
layer["t_embedder1"] = TimestepEmbedder(block_channels[i])
layer["t_embedder2"] = TimestepEmbedder(block_channels[i])
layer["blocks"] = nn.ModuleList([
DownsampleResBlock(
block_channels[i],
block_channels[i],
stride=1,
num_groups=num_groups,
use_attention=use_attention[i]
),
DownsampleResBlock(
block_channels[i],
block_channels[i+1],
stride=2,
num_groups=num_groups,
use_attention=use_attention[i+1]
)
])
downsample.append(layer)
self.downsample = nn.ModuleList(downsample)
for j in reversed(range(1, len(block_channels))):
layer = nn.ModuleDict()
layer["t_embedder1"] = TimestepEmbedder(block_channels[j])
layer["t_embedder2"] = TimestepEmbedder(2 * block_channels[j-1])
layer["blocks"] = nn.ModuleList([
UpsampleResBlock(
block_channels[j],
block_channels[j-1],
stride=2,
num_groups=num_groups,
use_attention=use_attention[j]
),
UpsampleResBlock(
2 * block_channels[j-1],
block_channels[j-1],
stride=1,
num_groups=num_groups,
use_attention=use_attention[j-1]
)
])
upsample.append(layer)
self.upsample = nn.ModuleList(upsample)
self.output = nn.Conv2d(block_channels[0], out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x, t):
x = self.conv(x)
skip_features = []
for d_layer in self.downsample:
t_emb1 = d_layer["t_embedder1"](t).unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1)
x = d_layer["blocks"][0](x, t_emb1)
skip_features.append(x)
t_emb2 = d_layer["t_embedder2"](t).unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1)
x = d_layer["blocks"][1](x, t_emb2)
skip_features.reverse()
for i, up_layer in enumerate(self.upsample):
t_emb1 = up_layer["t_embedder1"](t).unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1)
x = up_layer["blocks"][0](x, t_emb1)
t_emb2 = up_layer["t_embedder2"](t).unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1)
x = torch.cat([x, skip_features[i]], dim=1)
x = up_layer["blocks"][1](x, t_emb2)
x = self.output(x)
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
device = "mps"
batch_size = 3
model = UNet(in_channels=3, out_channels=3).to(device)
x = torch.rand((batch_size, 3, 32, 32)).to(device)
t = torch.randint(low=0, high=1000, size=(batch_size,)).to(device)
y = model(x, t)
print(y.shape)
"scheduler.py"
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
def extract_into_tensor(arr, timesteps, broadcast_shape):
res = torch.from_numpy(arr).to(torch.float32).to(device=timesteps.device)[timesteps]
while len(res.shape) < len(broadcast_shape):
res = res[..., None]
return res + torch.zeros(broadcast_shape, device=timesteps.device)
class Scheduler:
def __init__(self, denoise_model, denoise_steps, beta_start=1e-4, beta_end=2e-2):
self.model = denoise_model
betas = np.array(
np.linspace(beta_start, beta_end, denoise_steps),
dtype=np.float64
)
self.denoise_steps = denoise_steps
assert len(betas.shape) == 1, "betas must be 1-D"
assert (betas > 0).all() and (betas <= 1).all()
alphas = 1.0 - betas
self.sqrt_alphas = np.sqrt(alphas)
self.one_minus_alphas = 1.0 - alphas
self.alphas_cumprod = np.cumprod(alphas, axis=0)
self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod = np.sqrt(self.alphas_cumprod)
self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod = np.sqrt(1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod)
self.alphas_cumprod_prev = np.append(1.0, self.alphas_cumprod[:-1])
def gaussian_q_sample(self, x0, t, noise):
return (
extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod, t, x0.shape) * x0
+ extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x0.shape) * noise
)
def training_losses(self, x, t):
noise = torch.randn_like(x)
x_t = self.gaussian_q_sample(x, t, noise)
predict_noise = self.model(x_t, t)
return F.mse_loss(predict_noise, noise)
@torch.no_grad()
def gaussian_p_sample(self, x_t, t):
t_mask = (t != 0).float().view(-1, *([1] * (len(x_t.shape) - 1)))
z = torch.randn_like(x_t) * t_mask
predict_noise = self.model(x_t, t)
x = x_t - (
extract_into_tensor(self.one_minus_alphas, t, x_t.shape)
* predict_noise
/ extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x_t.shape)
)
x = x / extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_alphas, t, x_t.shape)
sigma = torch.sqrt(
extract_into_tensor(self.one_minus_alphas, t, x_t.shape)
* (1.0 - extract_into_tensor(self.alphas_cumprod_prev, t, x_t.shape))
/ (1.0 - extract_into_tensor(self.alphas_cumprod, t, x_t.shape))
)
x = x + sigma * z
return x
@torch.no_grad()
def sample(self, x_shape, device):
xs = []
x = torch.randn(*x_shape, device=device)
for t in reversed(range(0, self.denoise_steps)):
t = torch.tensor([t], device=device).repeat(x_shape[0])
x = self.gaussian_p_sample(x, t)
xs.append(x.detach().cpu().numpy())
return xs
"main.py"
import torch
import numpy as np
from torch import nn, optim
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scheduler import Scheduler
from UNet import UNet
if __name__ == '__main__':
device = torch.device("mps")
batch_size = 512
lr = 2e-5
epochs = 2000
denoise_steps = 250
train_dataset = datasets.CIFAR10(
root='./data', train=True, download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=0.5, std=0.5, inplace=True)
])
)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
model = UNet(
in_channels=3,
out_channels=3,
block_channels=[64, 128, 256],
use_attention=[False, False, False],
).to(device)
optimizer = optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
scheduler = Scheduler(model, denoise_steps)
model.train()
for epoch in range(epochs):
print('*' * 40)
train_loss = []
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader, 1):
x, _ = data
x = Variable(x).to(device)
t = torch.randint(low=0, high=denoise_steps, size=(x.shape[0],)).to(device)
training_loss = scheduler.training_losses(x, t)
optimizer.zero_grad()
training_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_loss.append(training_loss.item())
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "unet-cifar10.pth")
print('Finish {} Loss: {:.6f}'.format(epoch + 1, np.mean(train_loss)))
model.eval()
xs = np.array(scheduler.sample((16, 3, 32, 32), device))
step_25 = xs[24]
step_50 = xs[49]
step_75 = xs[74]
step_100 = xs[99]
step_125 = xs[124]
step_150 = xs[149]
step_175 = xs[174]
step_200 = xs[199]
step_225 = xs[224]
step_250 = xs[-1]
x = np.concatenate([step_25, step_50, step_75, step_100, step_125,
step_150, step_175, step_200, step_225, step_250], axis=-1)
x = x.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
x = x.reshape(-1, 32 * 10, 3).clip(-1, 1)
x = (x + 1) / 2
x = x.astype(np.float32)
plt.imsave('result1.png', x)





















 1112
1112

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








