前言:希望在大量数据中进行的元素增加、删除、查找都在log(n)复杂度内完成,排序+二分查找显然不可以,因为新加入数据就要进行重新排序。而使用“平衡二叉树”数据结构存放数据就可以达到目的,在STL中体现为以下四种排序容器:multiset、set、multimap、map。
multimap
头文件#include<map>
multimap容器可以对里面的元素按照关键字排序,使用起来非常方便,其基本结构如下:
multimap<T1,T2> mpmultimap里面的元素都是以pair形式出现的,并且只能是两个成员变量,mp里的元素类型如下:
struct {
T1 first; //关键字
T2 second; //值
};multimap中的元素自动按照first进行排序,并可以按first进行查找。其默认从小到大进行排列,缺省排序规则如下:
return a.first<b.first; //为true则a排在b前面。
multimap元素插入操作:
struct Student
{
int id;
string name;
};
Student student[3]={{3,"Tom"},{1,"Jack"},{2,"Susan"}};
typedef multimap<int,string>Mul_Map;
Mul_Map mp;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
mp.insert(make_pair(student[i].id,student[i].name));
}
其中make_pair函数可生成形式pair的数对用以把元素加入multimap容器中。
multimap元素遍历操作:
for (Mul_Map::iterator p = mp.begin(); p!=mp.end(); p++)
{
cout<<&p<<" " << p->first << " " << p->second << endl;
}
cout <<&p<<" " <<&mp.end();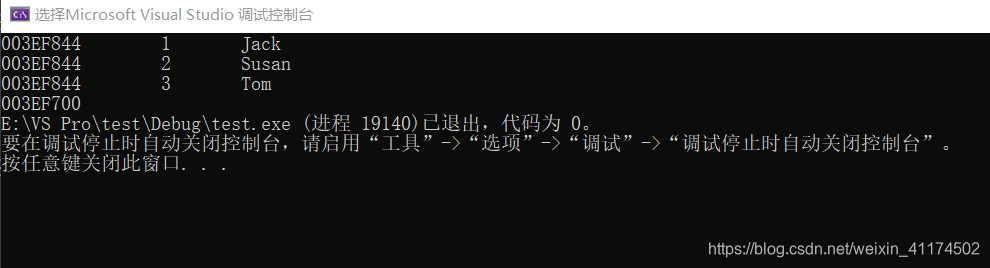
很神奇的就是迭代器p的地址一直都没变,
multimap元素删除操作:
//mp.clear();//元素全部清空
//mp.erase(mp.begin());//删除第一个元素
Mul_Map::iterator i=mp.find(2);//找到id为2的学生
mp.erase(i);//删除id=2的学生
map
和multimap相比,map的区别在于:
1.不能有关键字重复的元素
2.可以使用[],下标为关键字,返回值为first和关键字相同的元素的second值
3.插入元素可能失败
单词词频统计程序:
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
struct word
{
string wd;
int times;
};
struct Rule
{
bool operator()( const word& word1, const word& word2)const {
//const表示参数对象不会被修改,最后的const表明调用函数对象不会被修改!
if (word1.times != word2.times)
{
return word1.times > word2.times;//出现频率高的排在前面
}
else
{
return !word1.wd.compare(word2.wd);//字母顺序小的排在前面
}
}
};
int main() {
multiset<word, Rule>st;
map<string, int>mp;
string words[] = { "this","is","ok","this","plus","that","is","plus","plus" };
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
mp[words[i]]++;
}
for (map<string, int>::iterator i = mp.begin(); i != mp.end(); i++)
{
word tmp;
tmp.wd = i->first,tmp.times=i->second;
st.insert(tmp);
}
for (multiset<word,Rule>::iterator i = st.begin(); i !=st.end(); i++)
{
cout << i->wd << ":" << i->times << endl;
}
return 0;
}

























 3520
3520

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








