继续看看roudi的代码:
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) noexcept
{
using iox::roudi::IceOryxRouDiApp;
iox::config::CmdLineParserConfigFileOption cmdLineParser;
auto cmdLineArgs = cmdLineParser.parse(argc, argv);
if (cmdLineArgs.has_error())
{
IOX_LOG(Fatal, "Unable to parse command line arguments!");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (!cmdLineArgs.value().run)
{
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
iox::config::TomlRouDiConfigFileProvider configFileProvider(cmdLineArgs.value());
auto config = configFileProvider.parse();
if (config.has_error())
{
auto errorStringIndex = static_cast<uint64_t>(config.error());
IOX_LOG(Fatal,
"Couldn't parse config file. Error: "
<< iox::roudi::ROUDI_CONFIG_FILE_PARSE_ERROR_STRINGS[errorStringIndex]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
IceOryxRouDiApp roudi(config.value()); (1)
return roudi.run(); (2)
}toml解析完成后,从(1)开始使用解析后的内存池配置参数创建共享内存。IceOryxRouDiApp的构造函数如下:
IceOryxRouDiApp::IceOryxRouDiApp(const IceoryxConfig& config) noexcept
: RouDiApp(config)
{
}调用其父类的构造函数:
RouDiApp::RouDiApp(const IceoryxConfig& config) noexcept
: m_run(checkAndOptimizeConfig(config))
, m_config(config)
{
// be silent if not running
if (m_run)
{
iox::log::Logger::setLogLevel(m_config.logLevel);
auto& roudiConfig = static_cast<config::RouDiConfig&>(m_config);
IOX_LOG(Trace, "RouDi config is:");
IOX_LOG(Trace, " Domain ID = " << static_cast<DomainId::value_type>(roudiConfig.domainId));
IOX_LOG(Trace,
" Unique RouDi ID = " << static_cast<roudi::UniqueRouDiId::value_type>(roudiConfig.uniqueRouDiId));
IOX_LOG(Trace, " Monitoring Mode = " << roudiConfig.monitoringMode);
IOX_LOG(Trace, " Shares Address Space With Applications = " << roudiConfig.sharesAddressSpaceWithApplications);
IOX_LOG(Trace, " Process Termination Delay = " << roudiConfig.processTerminationDelay);
IOX_LOG(Trace, " Process Kill Delay = " << roudiConfig.processKillDelay);
IOX_LOG(Trace, " Compatibility Check Level = " << roudiConfig.compatibilityCheckLevel);
IOX_LOG(Trace, " Introspection Chunk Count = " << roudiConfig.introspectionChunkCount);
IOX_LOG(Trace, " Discovery Chunk Count = " << roudiConfig.discoveryChunkCount);
}
}简单检查配置参数是否为空,将配置参数赋值给成员变量。
(2)中的代码如下:
uint8_t IceOryxRouDiApp::run() noexcept
{
if (m_run)
{
static optional<IceOryxRouDiComponents> m_rouDiComponents;
auto componentsScopeGuard = makeScopedStatic(m_rouDiComponents, m_config); (1)
static optional<RouDi> roudi;
auto roudiScopeGuard = makeScopedStatic(
roudi, m_rouDiComponents.value().rouDiMemoryManager, m_rouDiComponents.value().portManager, m_config);
iox::waitForTerminationRequest();
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}(1)中的makeScopedStatic的作用为使用RAII机制,确保对象销毁时有正确的析构行为。这行代码可以简单理解为使用参数m_config构造IceOryxRouDiComponents对象:
IceOryxRouDiComponents::IceOryxRouDiComponents(const IceoryxConfig& config) noexcept
: rouDiMemoryManager(config) (1)
, portManager([&]() -> IceOryxRouDiMemoryManager* {
// this temporary object will create a roudi IPC channel
// and close it immediatelly
// if there was an outdated roudi IPC channel, it will be cleaned up
// if there is an outdated IPC channel, the start of the apps will be terminated
runtime::IpcInterfaceBase::cleanupOutdatedIpcChannel(roudi::IPC_CHANNEL_ROUDI_NAME); (2)
rouDiMemoryManager.createAndAnnounceMemory().or_else([](RouDiMemoryManagerError error) {
IOX_LOG(Fatal, "Could not create SharedMemory! Error: " << error);
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::ROUDI_COMPONENTS__SHARED_MEMORY_UNAVAILABLE);
}); (3)
return &rouDiMemoryManager;
}())
{
}先看(1)的实现:
IceOryxRouDiMemoryManager::IceOryxRouDiMemoryManager(const IceoryxConfig& config) noexcept
: m_fileLock(std::move(
FileLockBuilder()
.name(concatenate(iceoryxResourcePrefix(config.domainId, ResourceType::ICEORYX_DEFINED), ROUDI_LOCK_NAME))
.permission(iox::perms::owner_read | iox::perms::owner_write)
.create()
.or_else([](auto& error) {
if (error == FileLockError::LOCKED_BY_OTHER_PROCESS)
{
IOX_LOG(Fatal, "Could not acquire lock, is RouDi still running?");
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::ICEORYX_ROUDI_MEMORY_MANAGER__ROUDI_STILL_RUNNING);
}
else
{
IOX_LOG(Fatal, "Error occurred while acquiring file lock named " << ROUDI_LOCK_NAME);
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::ICEORYX_ROUDI_MEMORY_MANAGER__COULD_NOT_ACQUIRE_FILE_LOCK);
}
})
.value()))
, m_portPoolBlock(config.uniqueRouDiId)
, m_defaultMemory(config)
{
m_defaultMemory.m_managementShm.addMemoryBlock(&m_portPoolBlock).or_else([](auto) {
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::ICEORYX_ROUDI_MEMORY_MANAGER__FAILED_TO_ADD_PORTPOOL_MEMORY_BLOCK);
});
m_memoryManager.addMemoryProvider(&m_defaultMemory.m_managementShm).or_else([](auto) {
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::ICEORYX_ROUDI_MEMORY_MANAGER__FAILED_TO_ADD_MANAGEMENT_MEMORY_BLOCK);
});
}这段代码的主要作用可以总结为一个项目经理(m_managementShm)需要负责为五个总监( m_introspectionMemPoolBlock、m_discoveryMemPoolBlock、heartbeatPoolBlock、m_segmentManagerBlock、m_portPoolBlock,排名有先后)创建一段共享内存并划分地址范围(请参考读一读冰羚代码(3)Roudi共享内存创建的关键数据结构-优快云博客):
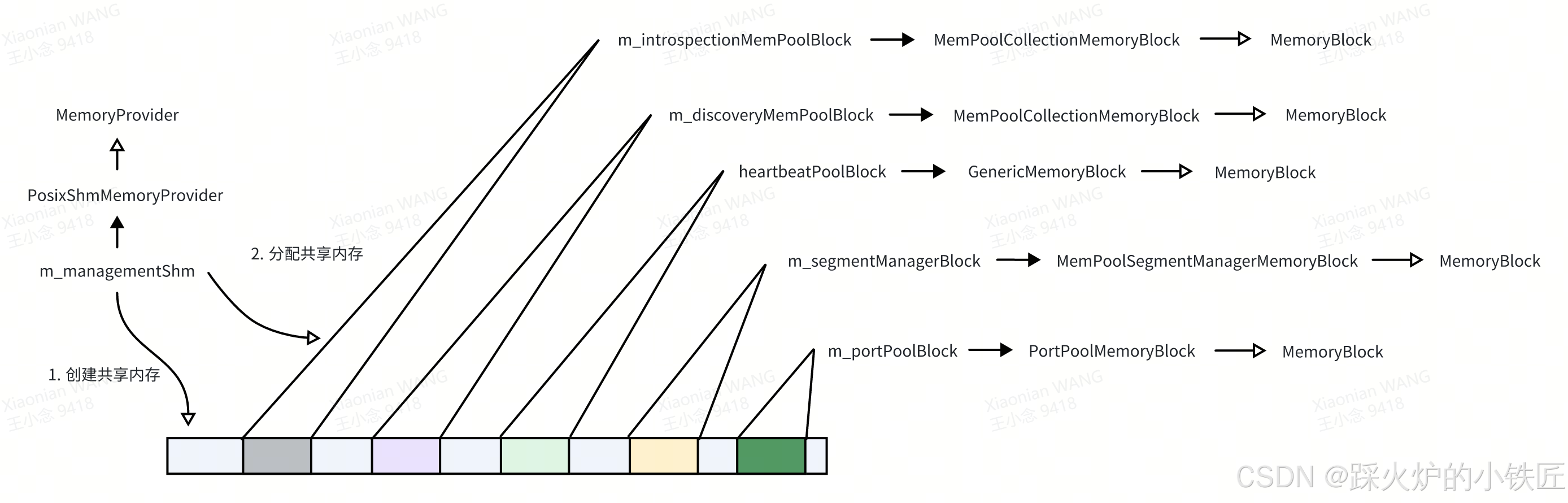
图1 项目经理m_managementShm管理的各MemoryBlock
几个划分给总监(MemoryBlock)的共享内存段的作用如下:
| m_introspectionMemPoolBlock | 创建冰羚运行时状况监控相关的数据结构 |
| m_discoveryMemPoolBlock | 创建冰羚服务发现相关的数据结构 |
| heartbeatPoolBlock | 创建各进程与Roudi进程维持心跳相关的数据结构 |
| m_segmentManagerBlock | 创建数据共享内存块相关的数据结构,其上的数据结构也用来创建数据共享内存 |
| m_portPoolBlock | 创建各进程相互通信相关的数据结构 |
接着看下面的代码:
IceOryxRouDiComponents::IceOryxRouDiComponents(const IceoryxConfig& config) noexcept
: rouDiMemoryManager(config) (1)
, portManager([&]() -> IceOryxRouDiMemoryManager* {
// this temporary object will create a roudi IPC channel
// and close it immediatelly
// if there was an outdated roudi IPC channel, it will be cleaned up
// if there is an outdated IPC channel, the start of the apps will be terminated
runtime::IpcInterfaceBase::cleanupOutdatedIpcChannel(roudi::IPC_CHANNEL_ROUDI_NAME); (2)
rouDiMemoryManager.createAndAnnounceMemory().or_else([](RouDiMemoryManagerError error) {
IOX_LOG(Fatal, "Could not create SharedMemory! Error: " << error);
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::ROUDI_COMPONENTS__SHARED_MEMORY_UNAVAILABLE);
}); (3)
return &rouDiMemoryManager;
}())
{
}(2)清理socket资源,防止之前Roudi进程异常终止或已有Roudi进程占用该socket。Roudi进程通过socket连接将共享内存上建立的相关数据结构地址传给通信参与进程(如数据发布者进程、数据订阅者进程等)。
(3)中被调用函数的名称简单明了,作用为创建共享内存并划好MemoryBlock们的地址范围,告诉它们:内存分配完毕,请自行决定怎么使用。
expected<void, RouDiMemoryManagerError> IceOryxRouDiMemoryManager::createAndAnnounceMemory() noexcept
{
auto result = m_memoryManager.createAndAnnounceMemory();
m_defaultMemory.heartbeatPoolBlock.emplace();
auto portPool = m_portPoolBlock.portPool();
if (result.has_value() && portPool.has_value())
{
m_portPool.emplace(*portPool.value());
}
return result;
}IceOryxRouDiMemoryManager::createAndAnnounceMemory()调用RouDiMemoryManager::createAndAnnounceMemory():
expected<void, RouDiMemoryManagerError> RouDiMemoryManager::createAndAnnounceMemory() noexcept
{
if (m_memoryProvider.empty())
{
return err(RouDiMemoryManagerError::NO_MEMORY_PROVIDER_PRESENT);
}
for (auto memoryProvider : m_memoryProvider)
{
auto result = memoryProvider->create(); (1)
if (result.has_error())
{
IOX_LOG(
Error,
"Could not create memory: MemoryProviderError = " << MemoryProvider::getErrorString(result.error()));
return err(RouDiMemoryManagerError::MEMORY_CREATION_FAILED);
}
}
for (auto memoryProvider : m_memoryProvider)
{
memoryProvider->announceMemoryAvailable(); (2)
}
return ok();
}原来RouDiMemoryManager会管理多个项目经理(MemoryProvider),通过(1)(2)看出,最终内存的创建和分配还是要交给各项目经理完成。通过之前的代码分析,RouDiMemoryManager目前只管理一个项目经理,即m_managementShm(PosixShmMemoryProvider),参考如下代码中的(1):
IceOryxRouDiMemoryManager::IceOryxRouDiMemoryManager(const IceoryxConfig& config) noexcept
: m_fileLock(std::move(
FileLockBuilder()
.name(concatenate(iceoryxResourcePrefix(config.domainId, ResourceType::ICEORYX_DEFINED), ROUDI_LOCK_NAME))
.permission(iox::perms::owner_read | iox::perms::owner_write)
.create()
.or_else([](auto& error) {
if (error == FileLockError::LOCKED_BY_OTHER_PROCESS)
{
IOX_LOG(Fatal, "Could not acquire lock, is RouDi still running?");
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::ICEORYX_ROUDI_MEMORY_MANAGER__ROUDI_STILL_RUNNING);
}
else
{
IOX_LOG(Fatal, "Error occurred while acquiring file lock named " << ROUDI_LOCK_NAME);
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::ICEORYX_ROUDI_MEMORY_MANAGER__COULD_NOT_ACQUIRE_FILE_LOCK);
}
})
.value()))
, m_portPoolBlock(config.uniqueRouDiId)
, m_defaultMemory(config)
{
m_defaultMemory.m_managementShm.addMemoryBlock(&m_portPoolBlock).or_else([](auto) {
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::ICEORYX_ROUDI_MEMORY_MANAGER__FAILED_TO_ADD_PORTPOOL_MEMORY_BLOCK);
});
m_memoryManager.addMemoryProvider(&m_defaultMemory.m_managementShm).or_else([](auto) {
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::ICEORYX_ROUDI_MEMORY_MANAGER__FAILED_TO_ADD_MANAGEMENT_MEMORY_BLOCK);
}); (1)
}现在只需分析m_managementShm的create()和announceMemoryAvailable()实现即可。
m_managementShm的类型为PosixShmMemoryProvider,create()接口继承自其基类MemoryProvider:
expected<void, MemoryProviderError> MemoryProvider::create() noexcept
{
if (m_memoryBlocks.empty())
{
return err(MemoryProviderError::NO_MEMORY_BLOCKS_PRESENT);
}
if (isAvailable())
{
return err(MemoryProviderError::MEMORY_ALREADY_CREATED);
}
uint64_t totalSize = 0u;
uint64_t maxAlignment = 1;
for (auto* memoryBlock : m_memoryBlocks) (1)
{
auto alignment = memoryBlock->alignment();
if (alignment > maxAlignment)
{
maxAlignment = alignment;
}
// just in case the memory block doesn't calculate its size as multiple of the alignment
// this shouldn't be necessary, but also doesn't harm
auto size = align(memoryBlock->size(), alignment);
totalSize = align(totalSize, alignment) + size;
}
auto memoryResult = createMemory(totalSize, maxAlignment); (2)
if (memoryResult.has_error())
{
return err(memoryResult.error());
}
m_memory = memoryResult.value();
m_size = totalSize;
auto maybeSegmentId = UntypedRelativePointer::registerPtr(m_memory, m_size); (3)
if (!maybeSegmentId.has_value())
{
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::MEMORY_PROVIDER__INSUFFICIENT_SEGMENT_IDS);
}
m_segmentId = maybeSegmentId.value();
IOX_LOG(Debug,
"Registered memory segment " << iox::log::hex(m_memory) << " with size " << m_size << " to id "
<< m_segmentId);
iox::BumpAllocator allocator(m_memory, m_size); (4)
for (auto* memoryBlock : m_memoryBlocks)
{
auto allocationResult = allocator.allocate(memoryBlock->size(), memoryBlock->alignment());
if (allocationResult.has_error())
{
return err(MemoryProviderError::MEMORY_ALLOCATION_FAILED);
}
memoryBlock->m_memory = allocationResult.value(); (5)
}
return ok();
}(1)中的循环统计各个总监们(MemoryBlock)对内存大小即地址对齐(alignment)的要求,计算总的内存大小及对齐需求。alignment就是将数值调整到某数的整数倍。在64位计算机上,通常alignment为8字节,以使bus的”运输量“达到最高效率。在冰羚中根据aligenment调整起始地址和数据结构长度的分配是很常见的操作
(2)调用子类(这里是PosixShmMemoryProvider)的createMemory实现建立共享内存映射
(3)计算该共享内存段的segment id,至关重要。请参考冰羚杂谈(二)建设云盘和怎样找到云盘-优快云博客
(4)初始化BumpAllocator,至关重要。请参考冰羚杂谈(一)在哪存放金子-优快云博客
(5)利用BumpAllocator的内存分配结构,给各个总监们(MemoryBlock)划分起始地址
PosixShmMemoryProvider中createMemory的实现如下:
expected<void*, MemoryProviderError> PosixShmMemoryProvider::createMemory(const uint64_t size,
const uint64_t alignment) noexcept
{
if (alignment > detail::pageSize())
{
return err(MemoryProviderError::MEMORY_ALIGNMENT_EXCEEDS_PAGE_SIZE);
}
if (!PosixSharedMemoryObjectBuilder()
.name(concatenate(iceoryxResourcePrefix(m_domainId, ResourceType::ICEORYX_DEFINED), m_shmName))
.memorySizeInBytes(size)
.accessMode(m_accessMode)
.openMode(m_openMode)
.permissions(SHM_MEMORY_PERMISSIONS)
.create() (1)
.and_then([this](auto& sharedMemoryObject) { m_shmObject.emplace(std::move(sharedMemoryObject)); }))
{
return err(MemoryProviderError::MEMORY_CREATION_FAILED);
}
auto baseAddress = m_shmObject->getBaseAddress(); (2)
if (baseAddress == nullptr)
{
return err(MemoryProviderError::MEMORY_CREATION_FAILED);
}
return ok(baseAddress);
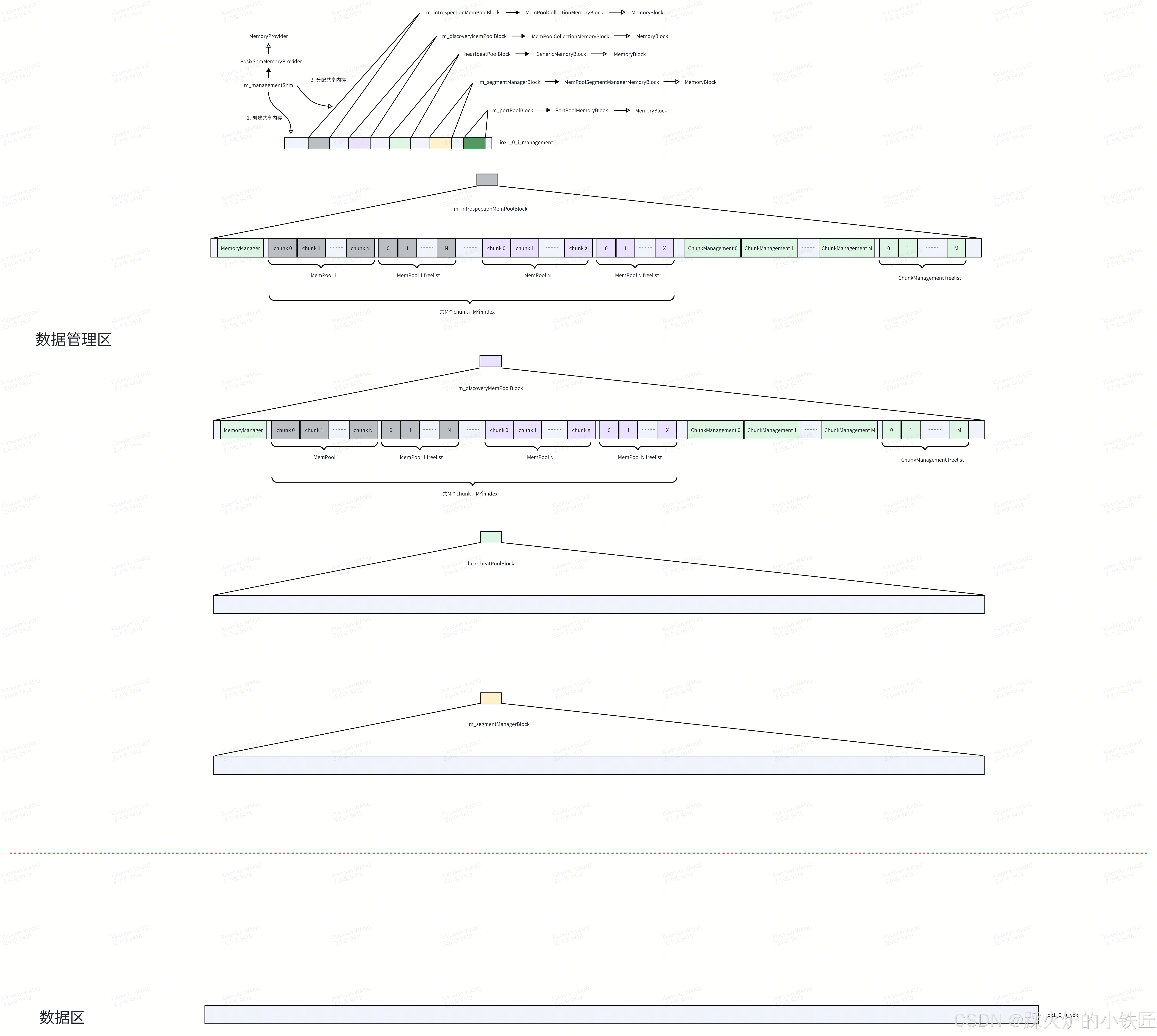
}(1)使用mmap建立共享内存(以linux系统为例),这段代码执行完后,会建立如下的数据管理共享内存:

(2)返回共享内存的起始地址
PosixShmMemoryProvider::create执行完后,系统的建立的共享内存如下:
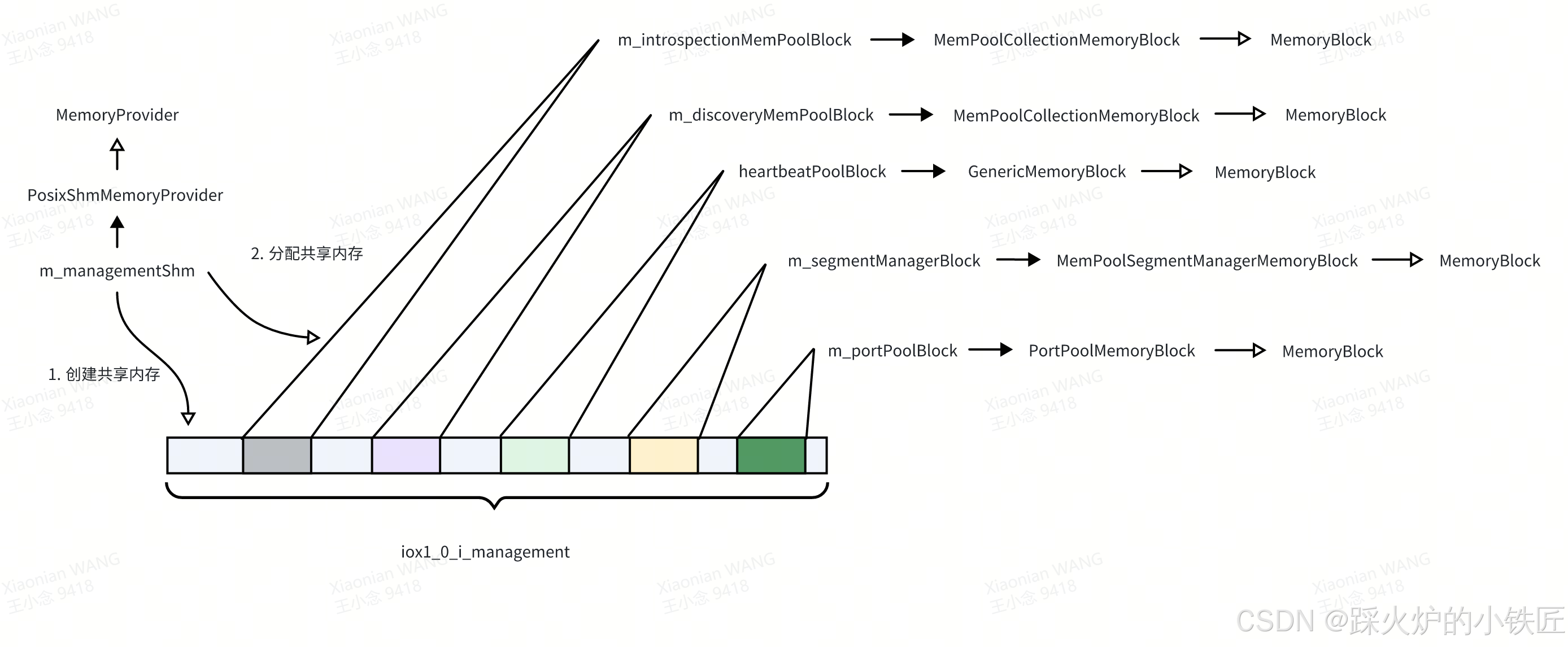
数据管理共享内存映射完成,各个总监们(MemoryBlock)获取了自己的势力范围(共享内存的起始地址,大小)。
接下来看m_managementShm(PosixShmMemoryProvider)的announceMemoryAvailable()实现,该接口继承其基类MemoryProvider:
void MemoryProvider::announceMemoryAvailable() noexcept
{
if (!m_memoryAvailableAnnounced)
{
for (auto memoryBlock : m_memoryBlocks) (1)
{
memoryBlock->onMemoryAvailable(memoryBlock->m_memory); (2)
}
m_memoryAvailableAnnounced = true;
}
}(1)表明项目经理(MemoryProvider)想让各个总监们(MemoryBlock)自行决定在自己的地盘上做点什么事情
(2)各个总监们(MemoryBlock)需要先拿到各自地盘的起始地址,看来是要在地盘上搞基建,建立一些数据结构了
总监们包括m_introspectionMemPoolBlock、m_discoveryMemPoolBlock、heartbeatPoolBlock、m_segmentManagerBlock、m_portPoolBlock。逐个看下各自onMemoryAvailable的实现。
1. m_introspectionMemPoolBlock的类型为MemPoolCollectionMemoryBlock:
void MemPoolCollectionMemoryBlock::onMemoryAvailable(not_null<void*> memory) noexcept
{
BumpAllocator allocator(memory, size());
auto* memoryManager = allocator.allocate(sizeof(mepoo::MemoryManager), alignof(mepoo::MemoryManager))
.expect("There should be enough memory for the 'MemoryManager'"); (1)
m_memoryManager = new (memoryManager) mepoo::MemoryManager;
m_memoryManager->configureMemoryManager(m_memPoolConfig, allocator, allocator); (2)
}(1)首先使用BumpAllocator分配了MemoryManager的地址:
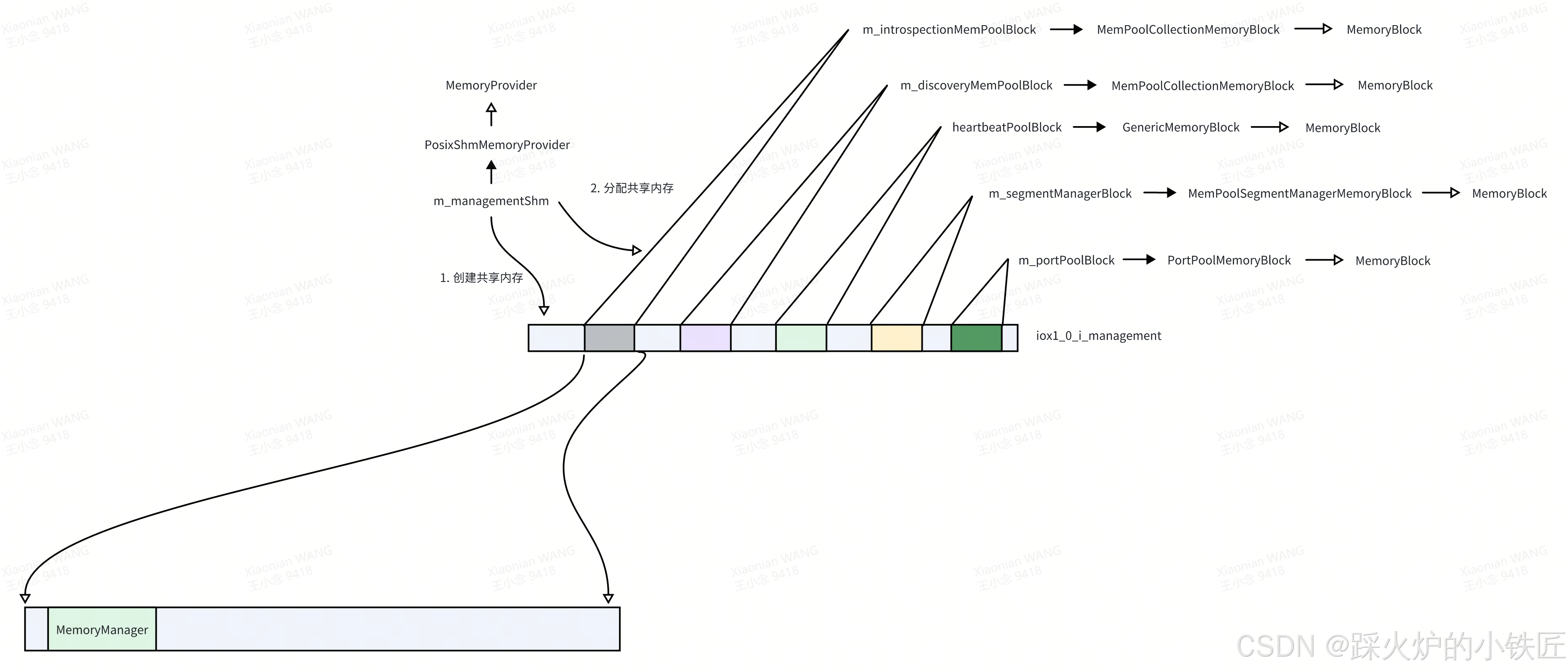
(2)继续使用同一个BumpAllocator分配不同数据结构的地址:
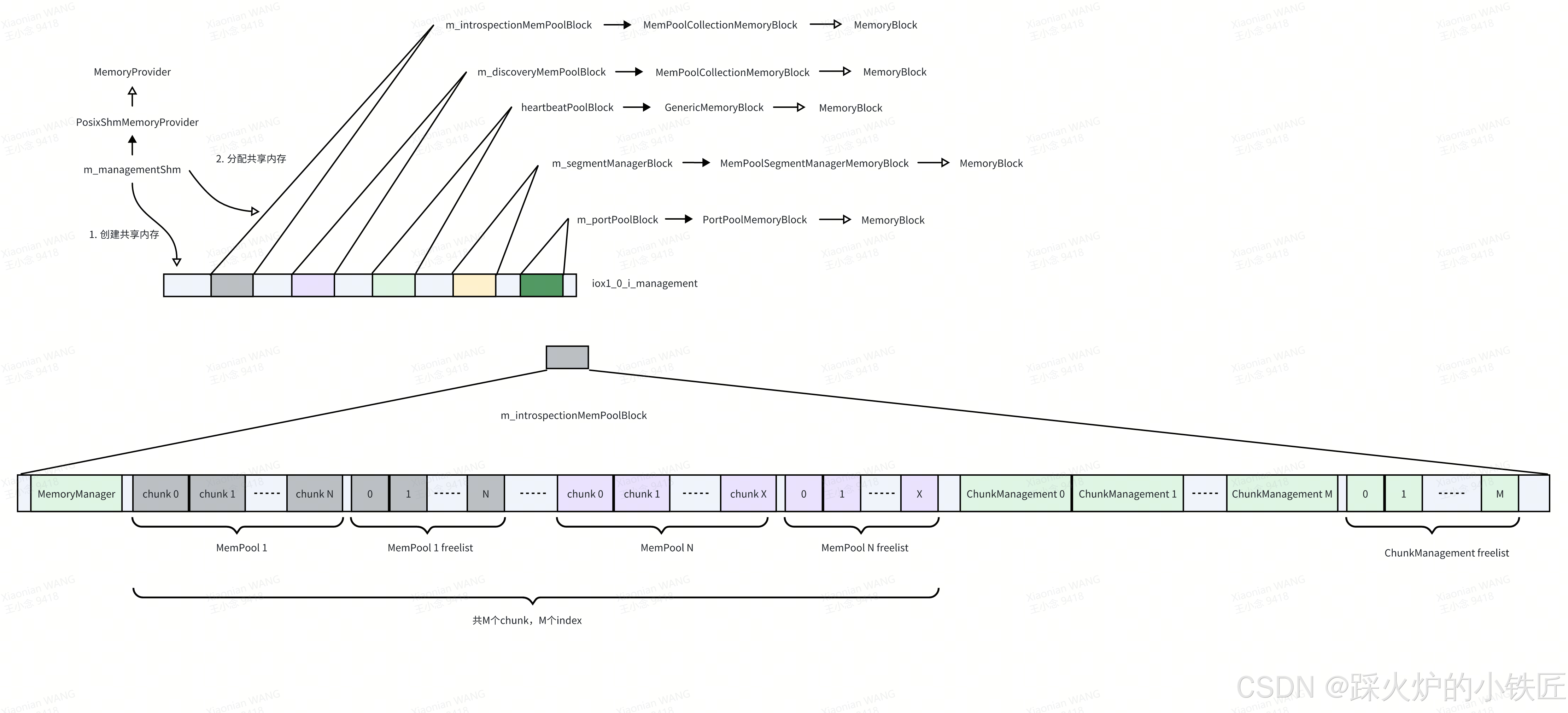
void MemoryManager::configureMemoryManager(const MePooConfig& mePooConfig,
BumpAllocator& managementAllocator,
BumpAllocator& chunkMemoryAllocator) noexcept
{
for (auto entry : mePooConfig.m_mempoolConfig)
{
addMemPool(managementAllocator, chunkMemoryAllocator, entry.m_size, entry.m_chunkCount);
}
generateChunkManagementPool(managementAllocator);
}上述代码执行完后,共享内存的布局如下:
2. m_discoveryMemPoolBlock的类型也为MemPoolCollectionMemoryBlock,onMemoryAvailable的实现和m_introspectionMemPoolBlock一样,函数执行完后共享内存的布局如下:
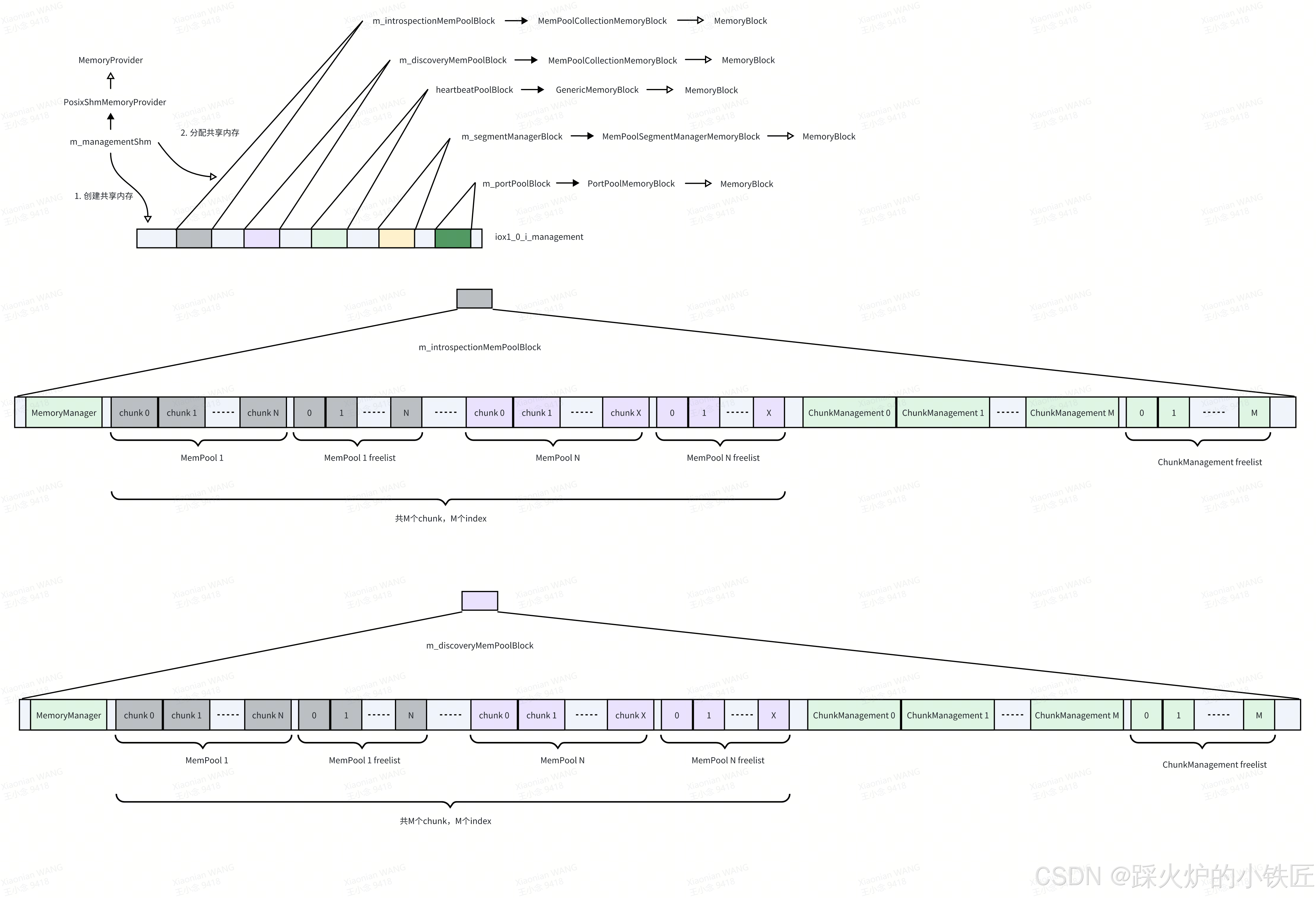
3. heartbeatPoolBlock的类型为GenericMemoryBlock<HeartbeatPool>,GenericMemoryBlock<HeartbeatPool>中没有覆盖基类的onMemoryAvailable接口,而基类的onMemoryAvailable没有做任何事情:
void MemoryBlock::onMemoryAvailable(not_null<void*> memory [[maybe_unused]]) noexcept
{
// nothing to do in the default implementation
}执行完该函数后内存布局如下:
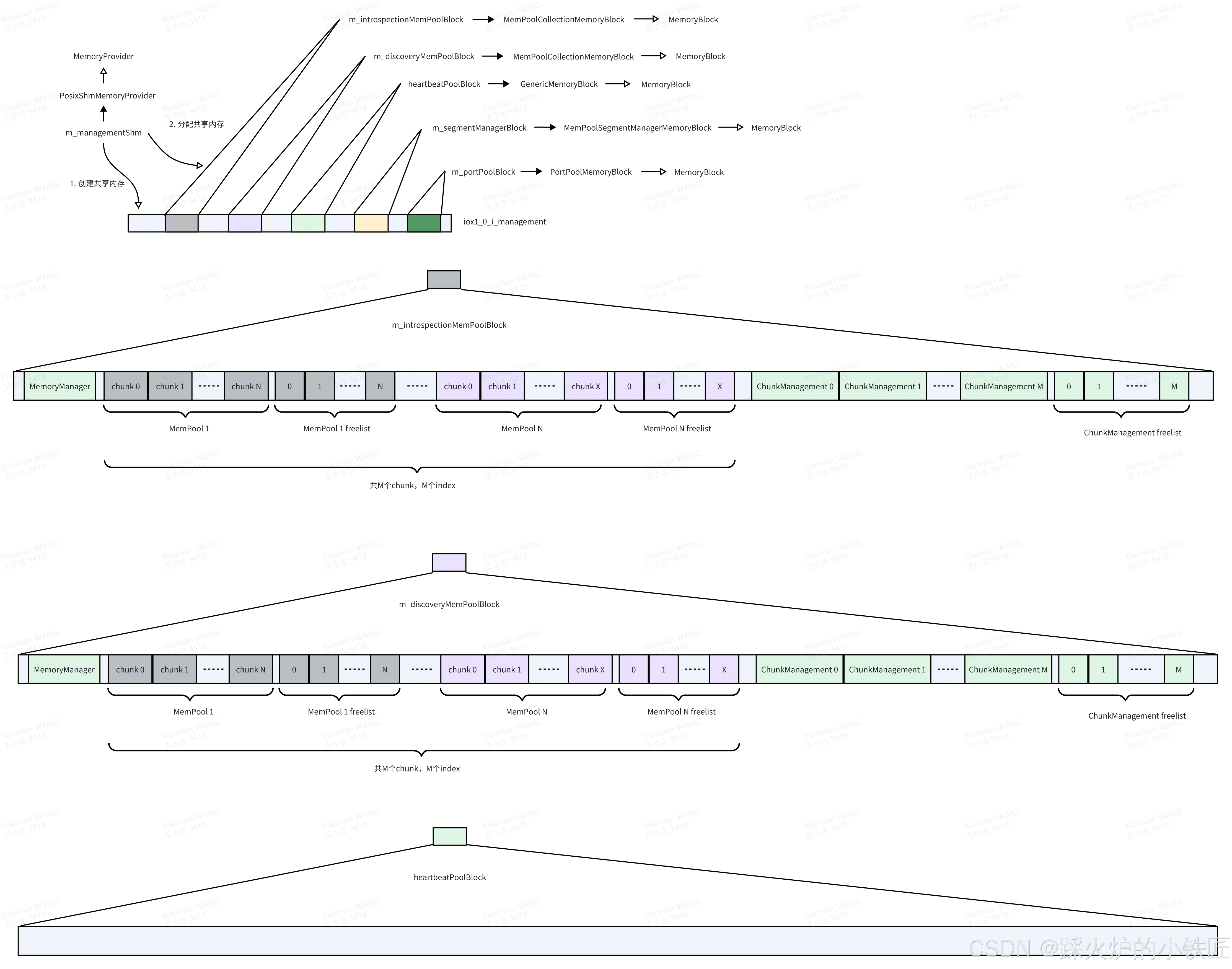
4. m_segmentManagerBlock的类型为MemPoolSegmentManagerMemoryBlock,其onMemoryAvailable的实现如下:
void MemPoolSegmentManagerMemoryBlock::onMemoryAvailable(not_null<void*> memory) noexcept
{
BumpAllocator allocator(memory, size());
auto* segmentManager = allocator.allocate(sizeof(mepoo::SegmentManager<>), alignof(mepoo::SegmentManager<>))
.expect("There should be enough memory for the 'SegmentManager'");
m_segmentManager = new (segmentManager) mepoo::SegmentManager<>(m_segmentConfig, m_domainId, &allocator);
}首先初始化BumpAllocator,然后从m_segmentManagerBlock的起始地址开始为SegmentManager分配地址空间,然后在该内存上继续使用同一个BumpAllocator构造SegmentManager对象。看看SegmentManager对象是怎么构造的:
template <typename SegmentType>
inline SegmentManager<SegmentType>::SegmentManager(const SegmentConfig& segmentConfig,
const DomainId domainId,
BumpAllocator* managementAllocator) noexcept
: m_managementAllocator(managementAllocator)
{
if (segmentConfig.m_sharedMemorySegments.capacity() > m_segmentContainer.capacity())
{
IOX_LOG(Fatal,
"Trying to add " << segmentConfig.m_sharedMemorySegments.capacity()
<< " segments while the 'SegmentManager' can manage only "
<< m_segmentContainer.capacity());
IOX_PANIC("Too many segments");
}
for (const auto& segmentEntry : segmentConfig.m_sharedMemorySegments) (1)
{
createSegment(segmentEntry, domainId);
}
}(1)中其实只包含一个segment,即使用hard code的默认内存池配置,请参考读一读冰羚代码(2)Roudi配置文件解析-优快云博客
createSegment的实现如下:
template <typename SegmentType>
inline void SegmentManager<SegmentType>::createSegment(const SegmentConfig::SegmentEntry& segmentEntry,
const DomainId domainId) noexcept
{
auto readerGroup = PosixGroup(segmentEntry.m_readerGroup);
auto writerGroup = PosixGroup(segmentEntry.m_writerGroup);
m_segmentContainer.emplace_back(segmentEntry.m_mempoolConfig,
domainId,
*m_managementAllocator,
readerGroup,
writerGroup,
segmentEntry.m_memoryInfo);
}m_segmentContainer的类型为vector<SegmentType, MAX_SHM_SEGMENTS>,而SegmentType默认为MePooSegment:
template <typename SegmentType = MePooSegment<>>
class SegmentManager
{
};看一下MePooSegment的构造函数:
template <typename SharedMemoryObjectType, typename MemoryManagerType>
inline MePooSegment<SharedMemoryObjectType, MemoryManagerType>::MePooSegment(
const MePooConfig& mempoolConfig,
const DomainId domainId,
BumpAllocator& managementAllocator,
const PosixGroup& readerGroup,
const PosixGroup& writerGroup,
const iox::mepoo::MemoryInfo& memoryInfo) noexcept
: m_readerGroup(readerGroup)
, m_writerGroup(writerGroup)
, m_memoryInfo(memoryInfo)
, m_sharedMemoryObject(createSharedMemoryObject(mempoolConfig, domainId, writerGroup)) (1)
{
using namespace detail;
PosixAcl acl;
if (!(readerGroup == writerGroup))
{
acl.addGroupPermission(PosixAcl::Permission::READ, readerGroup.getName());
}
acl.addGroupPermission(PosixAcl::Permission::READWRITE, writerGroup.getName()); (2)
acl.addPermissionEntry(PosixAcl::Category::USER, PosixAcl::Permission::READWRITE);
acl.addPermissionEntry(PosixAcl::Category::GROUP, PosixAcl::Permission::READWRITE);
acl.addPermissionEntry(PosixAcl::Category::OTHERS, PosixAcl::Permission::NONE);
if (!acl.writePermissionsToFile(m_sharedMemoryObject.getFileHandle()))
{
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::MEPOO__SEGMENT_COULD_NOT_APPLY_POSIX_RIGHTS_TO_SHARED_MEMORY);
}
BumpAllocator allocator(m_sharedMemoryObject.getBaseAddress(),
m_sharedMemoryObject.get_size().expect("Failed to get SHM size.")); (3)
m_memoryManager.configureMemoryManager(mempoolConfig, managementAllocator, allocator); (4)
}(1)创建数据区共享内存,即数据发布者进程将数据放置在该内存,数据订阅者进程从该内存取出数据,执行完该代码后,可以看到新的共享内存:
![]()
新的共享内存分为两个部分,即数据管理区和数据区:
(2)使用linux的acl机制对共享内存数据区进行更细粒度的权限控制,请参考linux ACL权限控制之用户权限控制程序设计-优快云博客和linux ACL权限控制之组权限控制程序设计-优快云博客
(3)使用数据区的地址初始化一个新的BumpAllocator,这个地方要特别注意,虽然和MemPoolCollectionMemoryBlock一样,最终会调用 m_memoryManager.configureMemoryManager,但MemPoolCollectionMemoryBlock中第二个和第三个参数是同一个BumpAllocator对象,MemPoolSegmentManagerMemoryBlock是不同的BumpAllocator对象,一个BumpAllocator对象用来在数据管理区分配地址,另外一个BumpAllocator对象用来在数据区分配地址
SegmentManager构造完成后,新的内存布局如下:
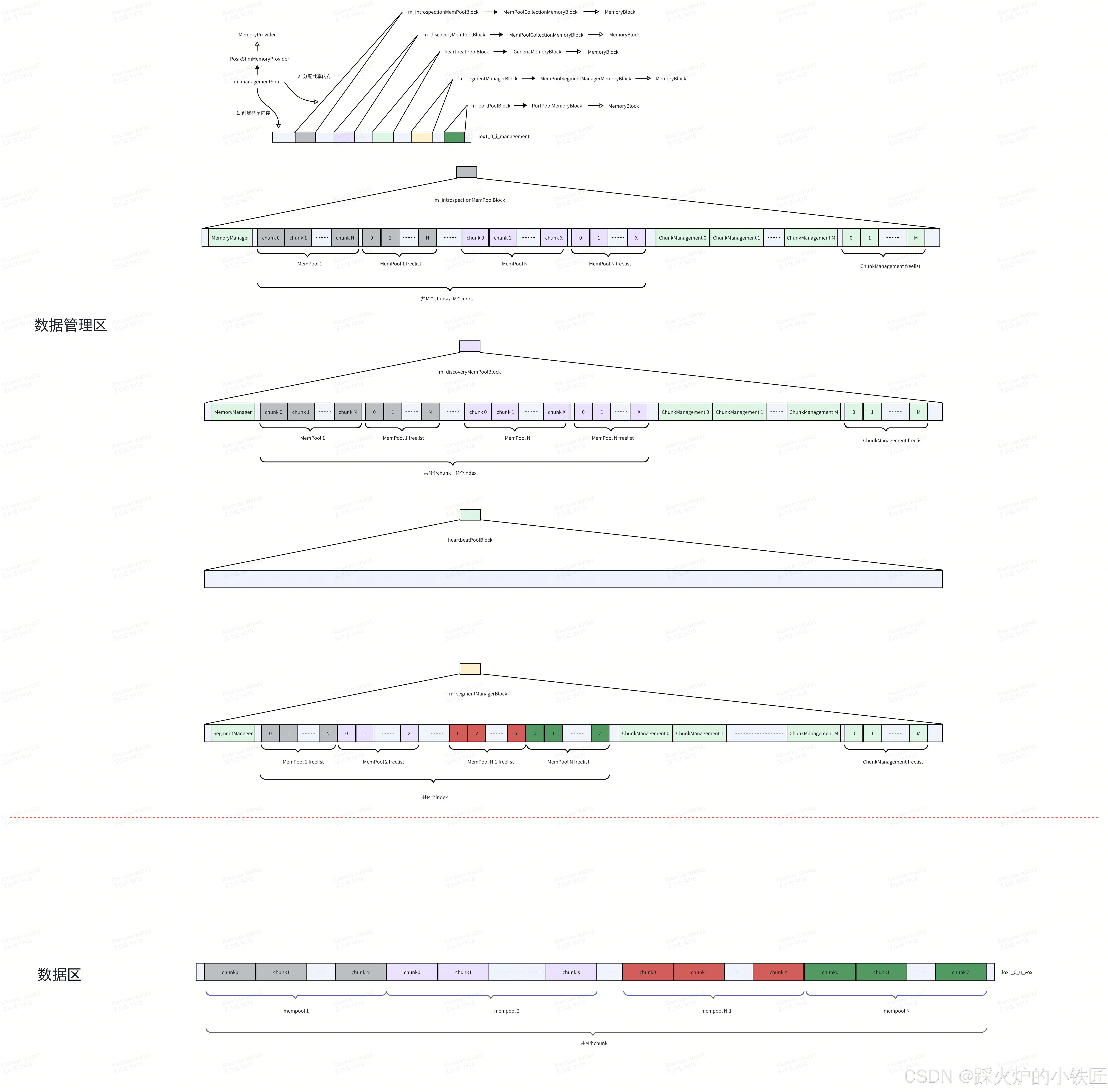
值得注意的是,m_segmentManagerBlock和数据区是一一对应的:
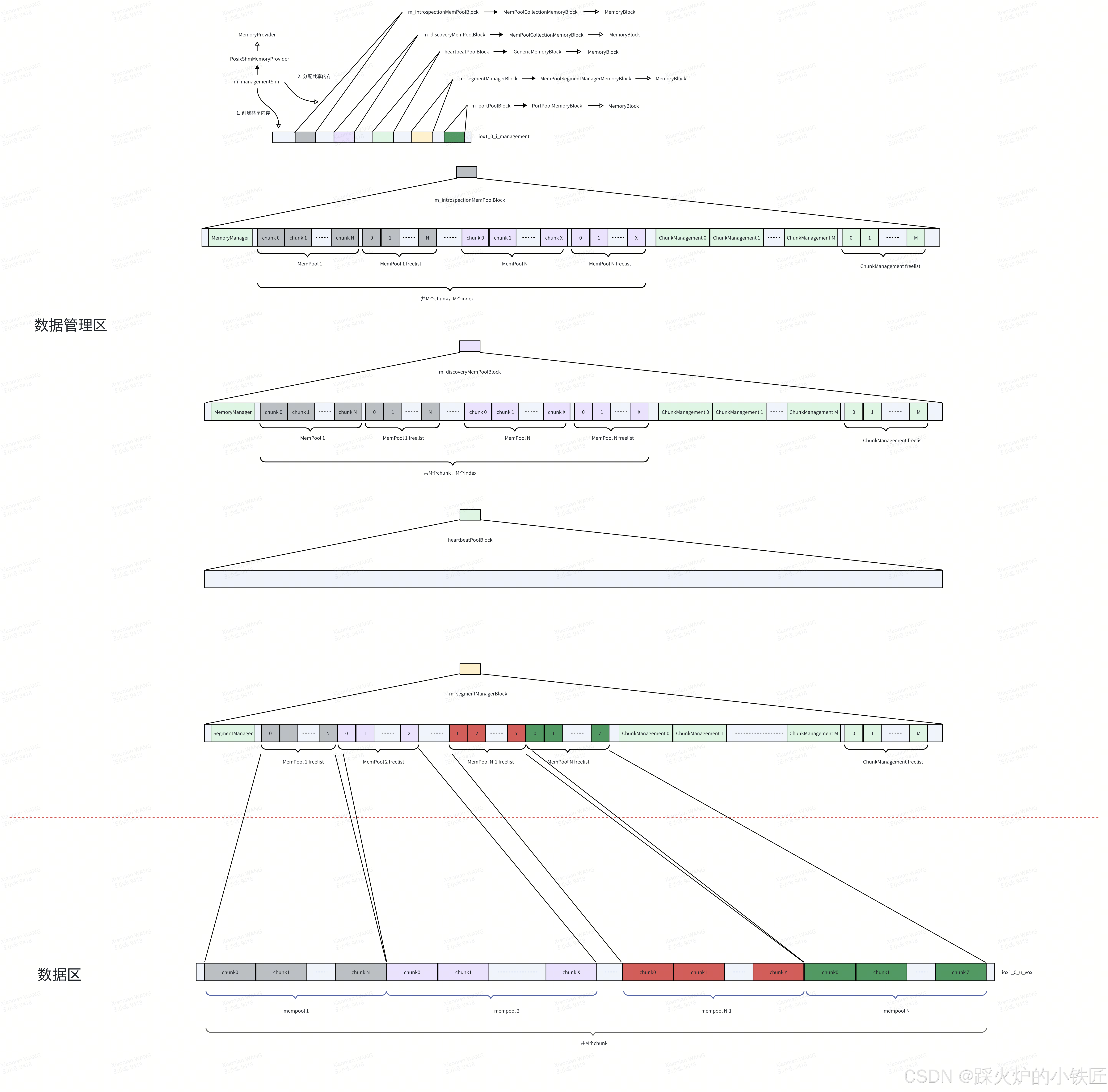
根据freelist寻找空闲的chunk和ChunkManagement,使用ChunkManagement管理chunk。
5. m_portPoolBlock的类型为PortPoolMemoryBlock,onMemoryAvailable的实现如下:
void PortPoolMemoryBlock::onMemoryAvailable(not_null<void*> memory) noexcept
{
m_portPoolData = new (memory) PortPoolData{m_uniqueRouDiId};
}基于起始内存构造一个PortPoolData的对象,现在的内存布局如下:
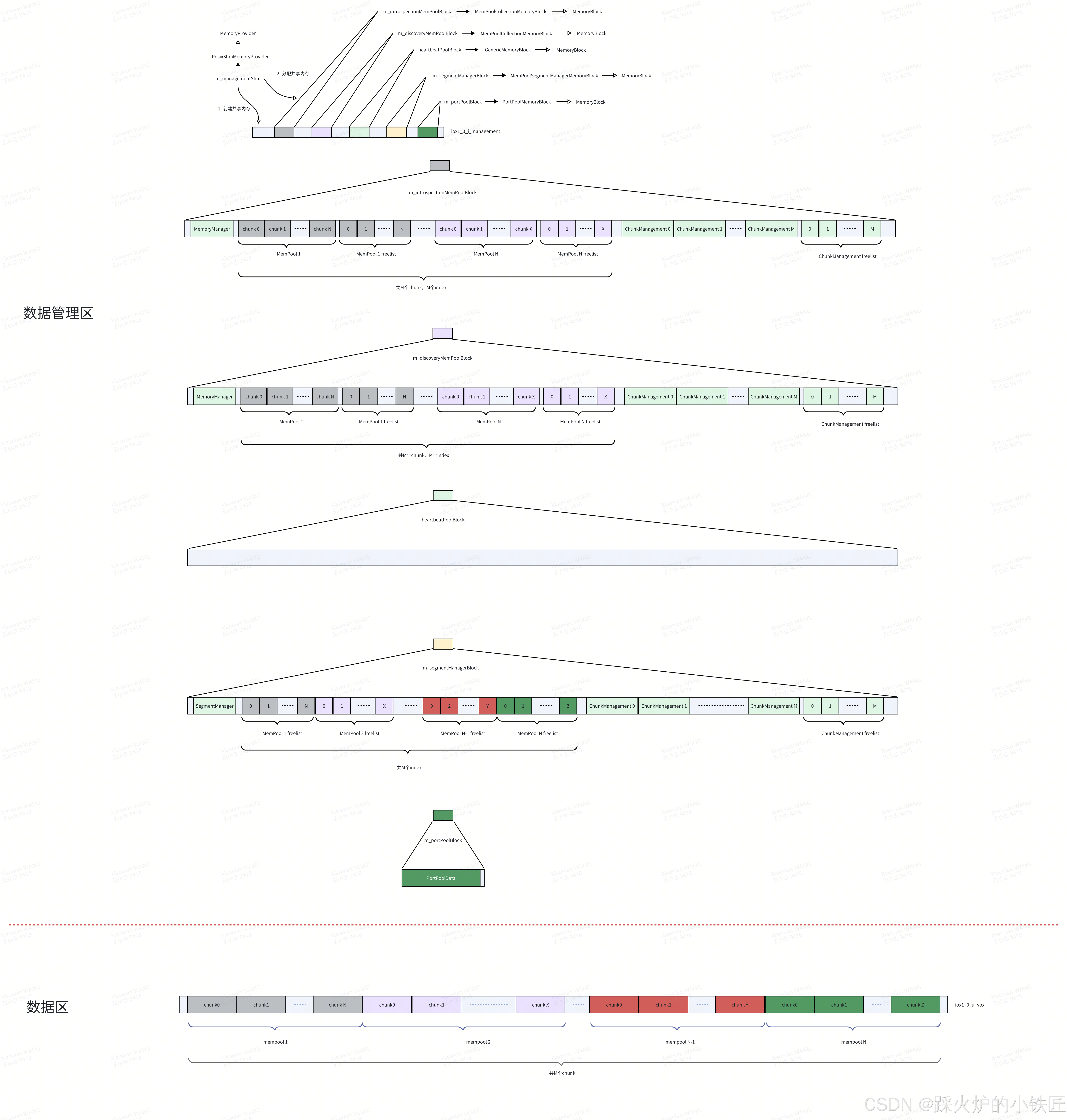
貌似heartbeatPoolBlock尚未建立任何数据结构,再接着往下看代码:
expected<void, RouDiMemoryManagerError> IceOryxRouDiMemoryManager::createAndAnnounceMemory() noexcept
{
auto result = m_memoryManager.createAndAnnounceMemory();
m_defaultMemory.heartbeatPoolBlock.emplace(); (1)
auto portPool = m_portPoolBlock.portPool();
if (result.has_value() && portPool.has_value())
{
m_portPool.emplace(*portPool.value());
}
return result;
}(1)中会调用emplace函数:
template <typename T>
template <typename... Targs>
optional<T*> GenericMemoryBlock<T>::emplace(Targs&&... args) noexcept
{
destroy();
auto rawMemory = this->memory();
if (rawMemory.has_value())
{
m_value = new (*rawMemory) T(std::forward<Targs>(args)...);
}
return value();
}在heartbeatPoolBlock的起始位置构造T对象,而T为HeartbeatPool,最后的内存布局如下:
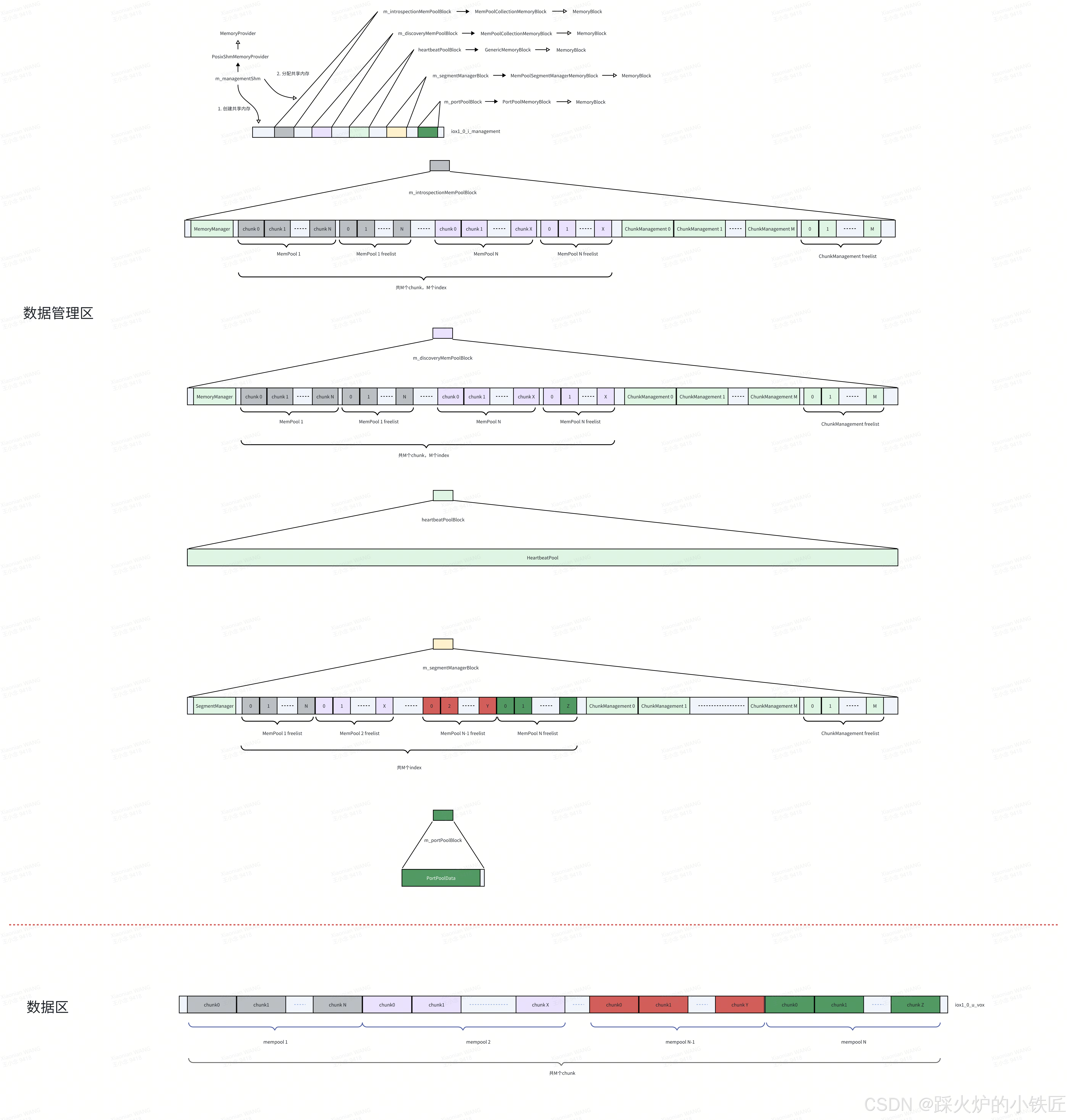
至此,两段共享内存及之上的数据结构创建完成。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








