根据读一读冰羚代码(4)Roudi共享内存的建立过程-优快云博客的介绍,Roudi进程建立了两段共享内存并在管理区共享内存之上搞了很多基建。既然是共享内存,Roudi建立的两段内存肯定要被别的进程共享(比如数据的发布者进程和订阅者进程),进程们怎样才能顺利找到共享内存上已经构造好的数据结构呢?比如下面这张图:
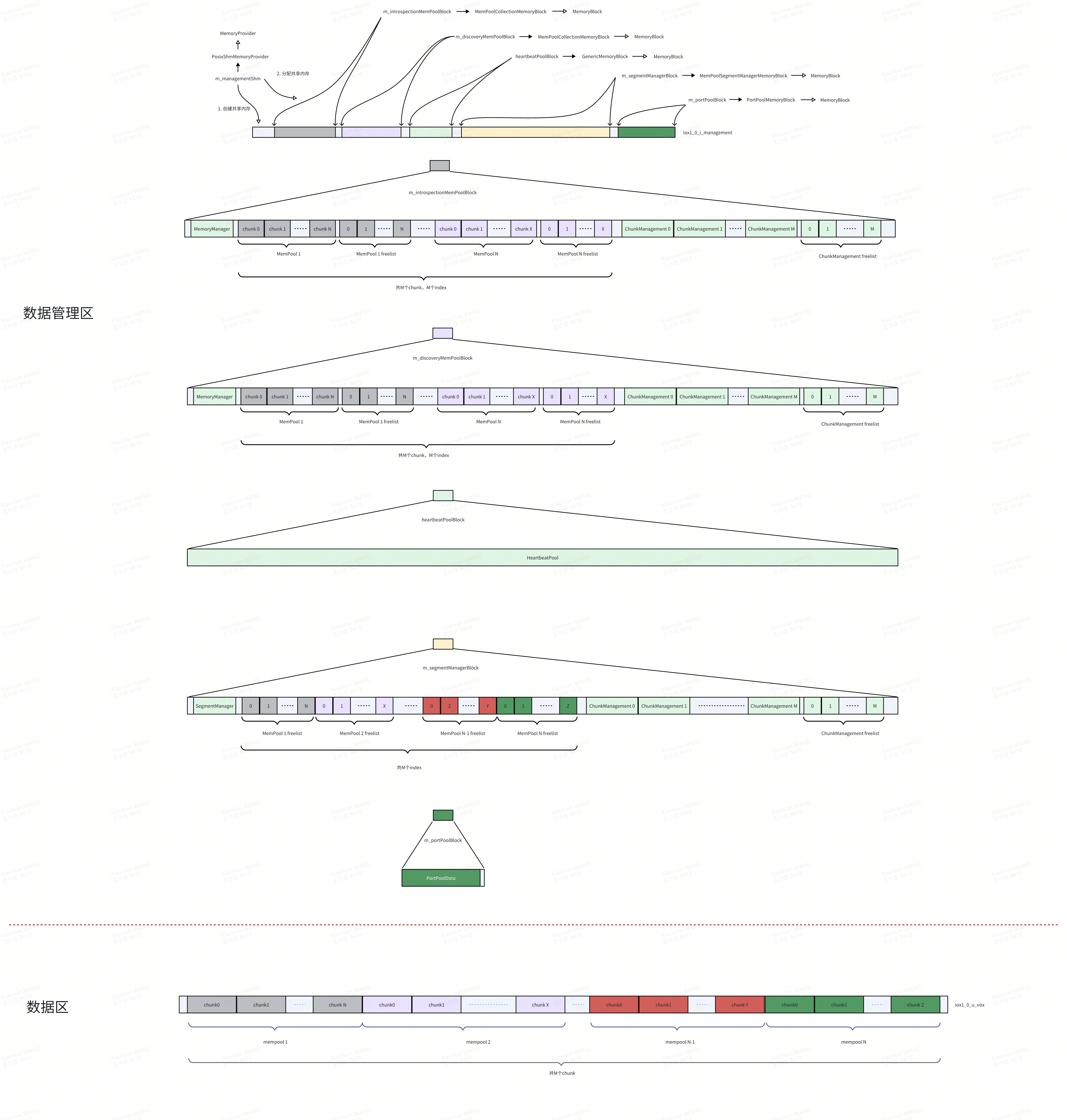
在m_segmentManagerBlock中构造了SegmentManager,发布者进程和订阅者进程需要拿到这个对象并借助这个对象找到可以存数据和取数据的内存区。
在冰羚杂谈(二)建设云盘和怎样找到云盘-优快云博客中提到,基于linux的共享内存映射理论,直接将共享内存上的Roudi进程中数据结构的地址传给其它进程是行不通的,但可以传递数据结构的segment id及offset,方便其它进程准确找到相关数据结构。那么,segment id及offset又通过什么方式传递给其它进程呢?
答案是socket,步骤如下:
- Roudi进程先建立一个server端的socket ,监听各进程的socket连接,假设socket的名称为R
- 发布者进程A建立socket R,作为client与Roudi进程中的server建立连接。发布者进程A也需建立一个自己专属的server端的socket P,Roudi进程建立 client端的socket P并与发布者进程A中的server建立连接
- 订阅者进B建立socket R,作为client与Roudi进程中的server建立连接。订阅者进程B也需建立一个自己专属的server端的socket S,Roudi进程建立 client端的socket S并与订阅者进程B中的server建立连接
示意图大概是这个样子:
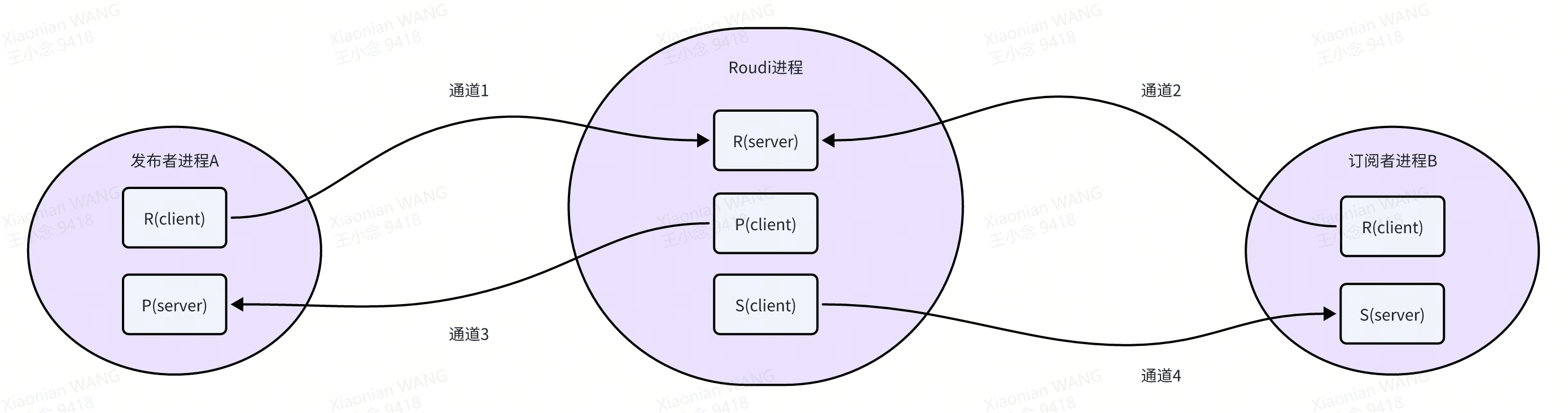
发布者进程A通过通道1向Roudi进程请求数据,Roudi进程通过通道3向发布者进程A返回响应数据。
订阅者进程B通过通道2向Roudi进程请求数据,Roudi进程通过通道4向订阅者进程B返回响应数据。
下面通过代码梳理一下以上socket的建立及数据的获取过程。
1 Roudi进程的socket创建
Roudi进程的main函数会调用RouDi的构造函数构造Roudi对象,构造函数最终会调用startProcessRuntimeMessagesThread():
void RouDi::startProcessRuntimeMessagesThread() noexcept
{
m_handleRuntimeMessageThread =
std::thread(&RouDi::processRuntimeMessages,
this,
runtime::IpcInterfaceCreator::create(
IPC_CHANNEL_ROUDI_NAME, m_roudiConfig.domainId, ResourceType::ICEORYX_DEFINED)
.expect("Creating IPC channel for request to RouDi"));
}创建一个线程运行RouDi::processRuntimeMessages成员函数,函数的参数由IpcInterfaceCreator::create返回:
expected<IpcInterfaceCreator, IpcInterfaceCreatorError> IpcInterfaceCreator::create(const RuntimeName_t& runtimeName,
const DomainId domainId,
const ResourceType resourceType,
const uint64_t maxMessages,
const uint64_t messageSize) noexcept
{
auto interfaceName = ipcChannelNameToInterfaceName(runtimeName, domainId, resourceType); (1)
auto fileLock =
FileLockBuilder().name(interfaceName).permission(iox::perms::owner_read | iox::perms::owner_write).create(); (2)
if (fileLock.has_error())
{
switch (fileLock.error())
{
case FileLockError::LOCKED_BY_OTHER_PROCESS:
return err(IpcInterfaceCreatorError::INTERFACE_IN_USE);
default:
return err(IpcInterfaceCreatorError::OBTAINING_LOCK_FAILED);
}
}
// remove outdated IPC channel, e.g. because of no proper termination of the process
cleanupOutdatedIpcChannel(interfaceName); (3)
return ok(IpcInterfaceCreator{
std::move(fileLock.value()), runtimeName, domainId, resourceType, maxMessages, messageSize}); (4)
}(1)中获取socket R的名字,名字为iox1_0_i_roudi,socket文件的全路径为/tmp/iox1_0_i_roudi
(2)建立文件锁文件/tmp/iox1_0_i_roudi.lock,该文件锁只有当Roudi进程退出时才会释放(通过RAII机制在FileLock对象的析构函数释放文件锁)。该文件锁用来竞争Roudi进程的创建,系统中只允许有一个Roudi进程运行
(3)清理socket /tmp/iox1_0_i_roudi,防止之前的Roudi进程异常终止没有及时关闭该socket
(4)调用IpcInterfaceCreator的构造函数:
IpcInterfaceCreator::IpcInterfaceCreator(FileLock&& fileLock,
const RuntimeName_t& runtimeName,
const DomainId domainId,
const ResourceType resourceType,
const uint64_t maxMessages,
const uint64_t messageSize) noexcept
: IpcInterfaceBase(runtimeName, domainId, resourceType, maxMessages, messageSize)
, m_fileLock(std::move(fileLock))
{
openIpcChannel(PosixIpcChannelSide::SERVER); (1)
}(1)建立server的socket iox1_0_i_roudi:
template <typename IpcChannelType>
bool IpcInterface<IpcChannelType>::openIpcChannel(const PosixIpcChannelSide channelSide) noexcept
{
m_channelSide = channelSide;
using IpcChannelBuilder_t = typename IpcChannelType::Builder_t; (1)
IpcChannelBuilder_t()
.name(m_interfaceName)
.channelSide(m_channelSide)
.maxMsgSize(m_maxMessageSize)
.maxMsgNumber(m_maxMessages)
.create()
.and_then([this](auto& ipcChannel) { this->m_ipcChannel.emplace(std::move(ipcChannel)); })
.or_else([this](auto& err) {
if (this->m_channelSide == PosixIpcChannelSide::SERVER)
{
IOX_LOG(Error,
"Unable to create ipc channel '" << this->m_interfaceName
<< "'. Error code: " << static_cast<uint8_t>(err));
}
else
{
// the client opens the channel and tries to do this in a loop when the channel is not available,
// therefore resulting in a wall of error messages on the console which leads to missing the important
// one that roudi is not running if this would be LogLevel::Error instead of LogLevel::Trace
IOX_LOG(Trace,
"Unable to open ipc channel '" << this->m_interfaceName
<< "'. Error code: " << static_cast<uint8_t>(err));
}
});
return isInitialized();
}先看下(1)中IpcChannelBuilder_t的实际类型:
class IpcInterfaceCreator : public IpcInterfaceBase
{
};
using IpcInterfaceBase = IpcInterface<platform::IoxIpcChannelType>;
#if defined(_WIN32)
using IoxIpcChannelType = iox::NamedPipe;
#elif defined(__FREERTOS__)
using IoxIpcChannelType = iox::NamedPipe;
#else
using IoxIpcChannelType = iox::UnixDomainSocket;
#endif
} // namespace platform
class UnixDomainSocket
{
public:
using Builder_t = UnixDomainSocketBuilder;
};linux平台上IpcChannelBuilder_t的实际类型为UnixDomainSocketBuilder,UnixDomainSocketBuilder::create()实际创建socket,此时的socket为/tmp/iox1_0_i_roudi,类型为server。IpcInterface<IpcChannelType>::openIpcChannel执行完成后,socket /tmp/iox1_0_i_roudi server端创建完成:

socket建立好,Roudi进程会创建一个接收socket消息的线程,线程的入口函数为:
void RouDi::processRuntimeMessages(runtime::IpcInterfaceCreator&& roudiIpcInterface) noexcept
{
auto roudiIpc = std::move(roudiIpcInterface);
setThreadName("IPC-msg-process");
IOX_LOG(Info, "Resource prefix: " << IOX_DEFAULT_RESOURCE_PREFIX);
IOX_LOG(Info, "Domain ID: " << static_cast<DomainId::value_type>(m_roudiConfig.domainId));
IOX_LOG(Info, "RouDi is ready for clients");
fflush(stdout); // explicitly flush 'stdout' for 'launch_testing'
while (m_runHandleRuntimeMessageThread)
{
// read RouDi's IPC channel
runtime::IpcMessage message;
if (roudiIpc.timedReceive(m_runtimeMessagesThreadTimeout, message)) (1)
{
auto cmd = runtime::stringToIpcMessageType(message.getElementAtIndex(0).c_str());
RuntimeName_t runtimeName{into<lossy<RuntimeName_t>>(message.getElementAtIndex(1))};
processMessage(message, cmd, runtimeName); (2)
}
}
}循环(1)接收消息,(2)处理消息
2 数据发布者进程的socket创建
以demo程序iceoryx_examples/waitset/ice_waitset_publisher.cpp的实现为例:
void sending()
{
iox::runtime::PoshRuntime::initRuntime("iox-cpp-publisher-waitset"); (1)
iox::popo::Publisher<CounterTopic> myPublisher({"Radar", "FrontLeft", "Counter"});
for (uint32_t counter = 0U; !iox::hasTerminationRequested(); ++counter)
{
myPublisher.publishCopyOf(CounterTopic{counter})
.and_then([&] { std::cout << "Sending: " << counter << std::endl; })
.or_else([&](auto) { std::cout << "Failed sending: " << counter << std::endl; });
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1000));
}
}
PoshRuntime& PoshRuntime::initRuntime(const RuntimeName_t& name) noexcept
{
return getInstance(make_optional<const RuntimeName_t*>(&name));
}
PoshRuntime& PoshRuntime::getInstance(optional<const RuntimeName_t*> name) noexcept
{
return getRuntimeFactory()(name);
}
PoshRuntime::factory_t& PoshRuntime::getRuntimeFactory() noexcept
{
static factory_t runtimeFactory = PoshRuntimeImpl::defaultRuntimeFactory;
return runtimeFactory;
}
PoshRuntime& PoshRuntime::defaultRuntimeFactory(optional<const RuntimeName_t*> name) noexcept
{
// Manual construction and destruction of the PoshRuntimeImpl, inspired by
// the nifty counter idiom.
static typename std::aligned_storage<sizeof(PoshRuntimeImpl), alignof(PoshRuntimeImpl)>::type buf;
// This is the primary lifetime participant. It ensures that, even if getLifetimeParticipant()
// is never called, the runtime has the same lifetime as a regular static variable.
static ScopeGuard staticLifetimeParticipant = [](auto name) {
new (&buf) PoshRuntimeImpl(name); (2)
poshRuntimeNeedsManualDestruction() = true;
return getLifetimeParticipant();
}(name);
return reinterpret_cast<PoshRuntimeImpl&>(buf);
}
(1)初始化运行时,最终在(2)中构造了PoshRuntimeImpl对象:
PoshRuntimeImpl::PoshRuntimeImpl(optional<const RuntimeName_t*> name,
const DomainId domainId,
const RuntimeLocation location) noexcept
: PoshRuntimeImpl(name, [&name, &domainId, &location] {
auto runtimeInterfaceResult =
IpcRuntimeInterface::create(*name.value(), domainId, runtime::PROCESS_WAITING_FOR_ROUDI_TIMEOUT);
}此时name的值为iox-cpp-publisher-waitset,这也是发布者进程中需要创建的socket server的名称。
IpcRuntimeInterface::create的实现:
expected<IpcRuntimeInterface, IpcRuntimeInterfaceError> IpcRuntimeInterface::create(
const RuntimeName_t& runtimeName, const DomainId domainId, const units::Duration roudiWaitingTimeout) noexcept
{
if (runtimeName.empty())
{
IOX_LOG(Debug, "The runtime name must not be empty!");
return err(IpcRuntimeInterfaceError::CANNOT_CREATE_APPLICATION_CHANNEL);
}
MgmtShmCharacteristics mgmtShmCharacteristics;
auto roudiIpcInterface = IpcInterfaceUser(roudi::IPC_CHANNEL_ROUDI_NAME, domainId, ResourceType::ICEORYX_DEFINED); (1)
auto appIpcInterface = IpcInterfaceCreator::create(runtimeName, domainId, ResourceType::USER_DEFINED); (2)
}(1)创建 client socket iox1_0_i_roudi,与Roudi进程的server socket建立连接
(2)创建server socket iox-cpp-publisher-waitset
IpcInterfaceCreator与IpcInterfaceUser均继承自IpcInterfaceBase,IpcInterfaceBase可以认为是socket相关操作的封装类。上述代码执行完后,系统的冰羚相关的socket如下:

接着看IpcRuntimeInterface::create中的状态机:
int64_t transmissionTimestamp{0};
auto regState = RegState::WAIT_FOR_ROUDI;
auto oldRegState = RegState::WAIT_FOR_ROUDI;
do
{
oldRegState = regState;
if (!roudiIpcInterface.isInitialized() || !roudiIpcInterface.ipcChannelMapsToFile())
{
IOX_LOG(Debug, "reopen RouDi's IPC channel!");
roudiIpcInterface.reopen();
regState = RegState::WAIT_FOR_ROUDI;
}
switch (regState)
{
case RegState::WAIT_FOR_ROUDI: (1)
{
waitForRoudi(roudiIpcInterface, timer);
if (roudiIpcInterface.isInitialized())
{
regState = RegState::SEND_REGISTER_REQUEST;
}
break;
}
case RegState::SEND_REGISTER_REQUEST: (2)
{
using namespace units;
using namespace std::chrono;
auto timestamp = duration_cast<microseconds>(system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count();
while (transmissionTimestamp == timestamp)
{
timestamp = duration_cast<microseconds>(system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count();
}
transmissionTimestamp = timestamp;
// send IpcMessageType::REG to RouDi
IpcMessage sendBuffer;
int pid = getpid();
IOX_ENFORCE(pid >= 0, "'getpid' must always return a positive number");
sendBuffer << IpcMessageTypeToString(IpcMessageType::REG) << runtimeName << convert::toString(pid)
<< convert::toString(PosixUser::getUserOfCurrentProcess().getID())
<< convert::toString(transmissionTimestamp)
<< static_cast<Serialization>(version::VersionInfo::getCurrentVersion()).toString();
bool successfullySent = roudiIpcInterface.timedSend(sendBuffer, 100_ms); (3)
if (successfullySent)
{
regState = RegState::WAIT_FOR_REGISTER_ACK;
}
else
{
regState = RegState::WAIT_FOR_ROUDI;
}
break;
}
case RegState::WAIT_FOR_REGISTER_ACK: (4)
if (waitForRegAck(transmissionTimestamp, *appIpcInterface, mgmtShmCharacteristics) == RegAckResult::SUCCESS)
{
regState = RegState::FINISHED;
}
else if (!timer.hasExpired())
{
regState = RegState::WAIT_FOR_ROUDI;
}
break;
case RegState::FINISHED:
// nothing to do, move along
break;
}
} while ((!timer.hasExpired() || regState != oldRegState) && regState != RegState::FINISHED);
(1)如果Roudi进程不存在,会等待Roudi进程创建完成
(2)如果Roudi进程存在,则通过socket iox1_0_i_roudi向Roudi进程发送注册消息,此时sendBuffer的内容为”1,iox-cpp-publisher-waitset,636271,1000,1744199487877171,1:22:951:41:018:REPRODUCIBLE-BUILD12:f3ccf20ab53d,“,各字段的含义如下:
| 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 消息类型 |
| iox-cpp-publisher-waitset | 发布者进程自定义名称,同时也是socket名称 |
| 636271 | 发布者进程的PID |
| 1000 | 发布者进程的USER ID |
| 1744199487877171 | 发布者进程请求数据时的时间戳 |
| 1:22:951:41:018:REPRODUCIBLE-BUILD12:f3ccf20ab53d | 冰羚版本号 |
回过头来看Roudi进程中的消息解析:
void RouDi::processMessage(const runtime::IpcMessage& message,
const iox::runtime::IpcMessageType& cmd,
const RuntimeName_t& runtimeName) noexcept
{
if (runtimeName.empty())
{
IOX_LOG(Error, "Got message with empty runtime name!");
return;
}
for (const auto s : platform::IOX_PATH_SEPARATORS)
{
const char separator[2]{s};
if (runtimeName.find(separator).has_value())
{
IOX_LOG(Error, "Got message with a runtime name with invalid characters: \"" << runtimeName << "\"!");
return;
}
}
switch (cmd)
{
case runtime::IpcMessageType::REG: (1)
{
if (message.getNumberOfElements() != 6)
{
IOX_LOG(Error,
"Wrong number of parameters for \"IpcMessageType::REG\" from \"" << runtimeName << "\"received!");
}
else
{
uint32_t pid{0U};
iox_uid_t userId{0};
int64_t transmissionTimestamp{0};
version::VersionInfo versionInfo = parseRegisterMessage(message, pid, userId, transmissionTimestamp);
registerProcess(runtimeName, (2)
pid,
PosixUser{userId},
transmissionTimestamp,
getUniqueSessionIdForProcess(),
versionInfo);
}
break;
}
}(1)中判断message类别(此时为IpcMessageType::REG)
(2)解析发布者进程的请求数据,向Roudi注册发布者进程的相关信息:
void RouDi::registerProcess(const RuntimeName_t& name,
const uint32_t pid,
const PosixUser user,
const int64_t transmissionTimestamp,
const uint64_t sessionId,
const version::VersionInfo& versionInfo) noexcept
{
bool monitorProcess = (m_roudiConfig.monitoringMode == roudi::MonitoringMode::ON
&& !m_roudiConfig.sharesAddressSpaceWithApplications);
IOX_DISCARD_RESULT(
m_prcMgr->registerProcess(name, pid, user, monitorProcess, transmissionTimestamp, sessionId, versionInfo));
}
bool ProcessManager::registerProcess(const RuntimeName_t& name,
const uint32_t pid,
const PosixUser user,
const bool isMonitored,
const int64_t transmissionTimestamp,
const uint64_t sessionId,
const version::VersionInfo& versionInfo) noexcept
{
bool returnValue{false};
findProcess(name)
.and_then([&](auto& process) {
// process is already in list (i.e. registered)
// depending on the mode we clean up the process resources and register it again
// if it is monitored, we reject the registration and wait for automatic cleanup
// otherwise we remove the process ourselves and register it again
if (process->isMonitored())
{
IOX_LOG(Warn, "Received register request, but termination of " << name << " not detected yet");
}
// process exists, we expect that the existing process crashed
IOX_LOG(Warn,
"Application '" << name
<< "' is still registered but it seems it has been terminated without RouDi "
"recognizing it. Re-registering application");
// remove the existing process and add the new process afterwards, we do not send ack to new process
constexpr TerminationFeedback TERMINATION_FEEDBACK{TerminationFeedback::DO_NOT_SEND_ACK_TO_PROCESS};
if (!this->searchForProcessAndRemoveIt(name, TERMINATION_FEEDBACK))
{
IOX_LOG(Warn, "Application " << name << " could not be removed");
return;
}
else
{
// try registration again, should succeed since removal was successful
returnValue =
this->addProcess(name, pid, user, isMonitored, transmissionTimestamp, sessionId, versionInfo);
}
})
.or_else([&]() {
// process does not exist in list and can be added
returnValue = this->addProcess(name, pid, user, isMonitored, transmissionTimestamp, sessionId, versionInfo); (1)
});
return returnValue;
}在(1)中调用ProcessManager::addProcess:
bool ProcessManager::addProcess(const RuntimeName_t& name,
const uint32_t pid,
const PosixUser& user,
const bool isMonitored,
const int64_t transmissionTimestamp,
const uint64_t sessionId,
const version::VersionInfo& versionInfo) noexcept
{
m_processList.emplace_back(name, m_domainId, pid, user, heartbeatPoolIndex, sessionId);
}
ProcessList_t m_processList;
class ProcessManager : public ProcessManagerInterface
{
public:
using ProcessList_t = iox::list<Process, MAX_PROCESS_NUMBER>;
};构造Process对象:
Process::Process(const RuntimeName_t& name,
const DomainId domainId,
const uint32_t pid,
const PosixUser& user,
const HeartbeatPoolIndexType heartbeatPoolIndex,
const uint64_t sessionId) noexcept
: m_pid(pid)
, m_ipcChannel(name, domainId, ResourceType::USER_DEFINED) (1)
, m_heartbeatPoolIndex(heartbeatPoolIndex)
, m_user(user)
, m_sessionId(sessionId)
{
}(1)中熟悉的IpcInterfaceUser m_ipcChannel又来了:
IpcInterfaceUser::IpcInterfaceUser(const RuntimeName_t& name,
const DomainId domainId,
const ResourceType resourceType,
const uint64_t maxMessages,
const uint64_t messageSize) noexcept
: IpcInterfaceBase(name, domainId, resourceType, maxMessages, messageSize)
{
openIpcChannel(PosixIpcChannelSide::CLIENT);
}Roudi进程的socket iox-cpp-publisher-waitset 作为client与发布者进程的server socket iox-cpp-publisher-waitset连接,返回发布者进程的请求相应数据。
继续看bool ProcessManager::addProcess:
bool ProcessManager::addProcess(const RuntimeName_t& name,
const uint32_t pid,
const PosixUser& user,
const bool isMonitored,
const int64_t transmissionTimestamp,
const uint64_t sessionId,
const version::VersionInfo& versionInfo) noexcept
{
// send REG_ACK and BaseAddrString
runtime::IpcMessage sendBuffer;
auto segmentManagerOffset = UntypedRelativePointer::getOffset(segment_id_t{m_mgmtSegmentId}, m_segmentManager);
sendBuffer << runtime::IpcMessageTypeToString(runtime::IpcMessageType::REG_ACK)
<< m_roudiMemoryInterface.mgmtMemoryProvider()->size() << segmentManagerOffset << transmissionTimestamp
<< m_mgmtSegmentId << heartbeatOffset;
m_processList.back().sendViaIpcChannel(sendBuffer);
}将SegmentManager对象所属的segment ID及offset通过刚刚建立的socket 连接m_ipcChannel返回给调用者进程,此时消息的类型为runtime::IpcMessageType::REG_ACK,sendBuffer的值为”2,34696160,11141448,1744250533142238,1,18446744073709551615,“,各字段的含义如下:
| 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 2 | 消息类型 |
| 34696160 | 共享内存管理区大小 |
| 11141448 | SegmentManager对象的偏移量 |
| 1744250533142238 | 发布者进程请求数据时的时间戳 |
| 1 | 共享内存管理区的segment ID |
| 18446744073709551615 | 发布者进程对应的 Heartbeat对象的偏移量 |
在发布者进程会收到这条消息(”2,34696160,11141448,1744250533142238,1,18446744073709551615,“)并解析:
IpcRuntimeInterface::RegAckResult
IpcRuntimeInterface::waitForRegAck(int64_t transmissionTimestamp,
IpcInterfaceCreator& appIpcInterface,
MgmtShmCharacteristics& mgmtShmCharacteristics) noexcept
{
// wait for the register ack from the RouDi daemon. If we receive another response we do a retry
constexpr size_t MAX_RETRY_COUNT = 3;
size_t retryCounter = 0;
while (retryCounter++ < MAX_RETRY_COUNT)
{
using namespace units::duration_literals;
IpcMessage receiveBuffer;
// wait for IpcMessageType::REG_ACK from RouDi for 1 seconds
if (appIpcInterface.timedReceive(1_s, receiveBuffer))
{
IOX_LOG(Info, "get Roudi message: " << receiveBuffer.getMessage());
std::string cmd = receiveBuffer.getElementAtIndex(0U);
if (stringToIpcMessageType(cmd.c_str()) == IpcMessageType::REG_ACK) (1)
{
constexpr uint32_t REGISTER_ACK_PARAMETERS = 6U;
if (receiveBuffer.getNumberOfElements() != REGISTER_ACK_PARAMETERS)
{
IOX_REPORT_FATAL(PoshError::IPC_INTERFACE__REG_ACK_INVALIG_NUMBER_OF_PARAMS);
}
// read out the shared memory base address and save it
UntypedRelativePointer::offset_t segmentManagerOffset{UntypedRelativePointer::NULL_POINTER_OFFSET};
UntypedRelativePointer::offset_t heartbeatOffset{UntypedRelativePointer::NULL_POINTER_OFFSET};
int64_t receivedTimestamp{0U};
auto topic_size_result =
iox::convert::from_string<uint64_t>(receiveBuffer.getElementAtIndex(1U).c_str());
auto segment_manager_offset_result =
iox::convert::from_string<uint64_t>(receiveBuffer.getElementAtIndex(2U).c_str());
auto recv_timestamp_result =
iox::convert::from_string<int64_t>(receiveBuffer.getElementAtIndex(3U).c_str());
auto segment_id_result =
iox::convert::from_string<uint64_t>(receiveBuffer.getElementAtIndex(4U).c_str());
auto heartbeat_offset_result =
iox::convert::from_string<uint64_t>(receiveBuffer.getElementAtIndex(5U).c_str());
// validate conversion results
if (!topic_size_result.has_value() || !segment_manager_offset_result.has_value()
|| !recv_timestamp_result.has_value() || !segment_id_result.has_value()
|| !heartbeat_offset_result.has_value())
{
return RegAckResult::MALFORMED_RESPONSE;
}
// assign conversion results
mgmtShmCharacteristics.shmTopicSize = topic_size_result.value();
mgmtShmCharacteristics.segmentId = segment_id_result.value();
segmentManagerOffset = segment_manager_offset_result.value();
receivedTimestamp = recv_timestamp_result.value();
heartbeatOffset = heartbeat_offset_result.value();
mgmtShmCharacteristics.segmentManagerAddressOffset = segmentManagerOffset;
if (heartbeatOffset != UntypedRelativePointer::NULL_POINTER_OFFSET)
{
mgmtShmCharacteristics.heartbeatAddressOffset = heartbeatOffset;
}
if (transmissionTimestamp == receivedTimestamp)
{
return RegAckResult::SUCCESS;
}
else
{
IOX_LOG(Warn, "Received a REG_ACK with an outdated timestamp!");
}
}
else
{
IOX_LOG(Error, "Wrong response received " << receiveBuffer.getMessage());
}
}
}
return RegAckResult::TIMEOUT;
}(1)解析Roudi进程返回的消息请求相应,得到SegmentManager对象的segment ID及offset。
3 数据订阅者进程的socket创建
以demo程序iceoryx_examples/waitset/ice_waitset_basic.cpp的实现为例,基本流程和数据发布者进程的socket创建过程一样。
最终,系统冰羚相关的socket如下:


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








