Collection是一个接口 ,继承了Iterable接口 。
Iterable 接口中主要有iterator 方法用于循环,和foreach 方法。
Collection 按分类可以分为List 和Set两个子接口。
List:有序,可重复。
Set : 无序, 不可重复。
为什么说List是有序可重复呢?List的子类有如下几个Arraylist LinkedList Vector . 其中Arraylist和Vector都是有Object[] 数组组成的。他们的区别是Vector是线程安全的ArrayList不是线程安全的。可以看一下如下代码(以ArrayList为例):
transient Object[] elementData;
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e; //这里是重点,我们添加元素的时候把元素直接往数组后面添加,并且实现size的长度增加。因为数组中的元素是可以重复的,而且每次都是放在数组的末尾,我们可以根据数组下标查询。所以也是有序的。
return true;
}
同理在Vector中。不同的就是synchnized.这个关键字,是一个同步方法。
public synchronizedboolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
而在LinkedList中则是以Link链表的形式来。每次增加元素的话就是把元素往Node节点拼接,Node节点主要包含三部分。prev , element value , next . 添加Element的时候就是把上一个节点的next指向新加入到指点。所以也是有序的,可重复的。
private static class Node {
E item;
Node next;
Node prev;
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
总结 LinkedList ArrayList Vector:
LinkedList:因为添加删除只要改变节点的前后关系,所以在添加删除的操作会很快。但是没有提供下标查询,我们如果想查找某一个节点的值,就必须找到前一个节点或者后一个节点,然后依次类推,找到Link的头或者尾。所以查询起来比较慢
ArrayList: 因为Object[]数组可以根据下标来查询,所以查询速度很快。但是如果往数组中添加某一个元素,那么这个元素之后的元素下标都得+1.反之删除元素的话,下标就是-1.
Vector: 因为Vector中的大多数方法都是加了synchronized.所以是线程安全的,相对于Arraylist效率会下降很多,所以现在几乎都不推荐使用Vector.
接下来,我们说一说为什么Set是无序的。
因为Set的两个子类HashSet和TreeSet.两个子类
HashSet:
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
因为HashMap中的key是不可以重复的,所以我们往HashSet中添加到元素也是不可重复的。
具体HashMap的实现可以参考这个。http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/vking_wang/article/details/14166593
http://www.importnew.com/18633.html.
简单的说HashMap的实现原理就是数组加链表。
// 存储时:
int hash = key.hashCode(); // 这个hashCode方法这里不详述,只要理解每个key的hash是一个固定的int值
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
Entry[index] = value;
HashMap中其实是存放着一个键值对的形式。 所以没差存储一组对象的时候,会先对key取hash code并且取余。决定了key放在哪个数组中哪个位置。
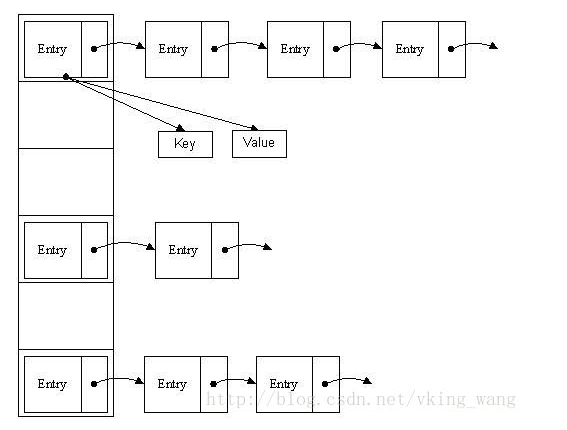
但是以上以上如果hash code取余数还是在数组同一个位置的话,我们就会遍历这个数组中的entry。如果发现添加进来的键值对的key已经存在,则覆盖掉老的值。如果不存在则加添到键值对链表的末尾。其中HashMap的key可以为null. 可以参考以下代码。
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value); //null总是放在数组的第一个链表中
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//遍历链表
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//如果key在链表中已存在,则替换为新value
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry(hash, key, value, e); //参数e, 是Entry.next
//如果size超过threshold,则扩充table大小。再散列
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}




 本文详细解析了Java集合框架中List和Set的区别,包括它们的子类ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector及HashSet的特点与实现方式。
本文详细解析了Java集合框架中List和Set的区别,包括它们的子类ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector及HashSet的特点与实现方式。
















 171万+
171万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








