“ Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs. ”
‣ dynamic connectivity
‣ quick find
‣ quick union
‣ improvements
‣ applications
1.Dynamic connectivity(动态连接)
Given a set of N objects.
- Union command: connect two objects.(Union-连通两个分量)
- Find/connected query: is there a path connecting the two objects?
给定n个对象,对这n个对象最基本的操作有两个:连接其中的两个对象,检测其中两个对象是否是连通的。
We assume "is connected to" is an equivalence relation:(连通分量特性)
- Reflexive: p is connected to p.
- Symmetric: if p is connected to q, then q is connected to p.
- Transitive: if p is connected to q and q is connected to r, then p is connected to r
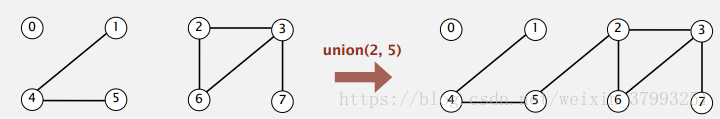
Goal:Design efficient data structure for union-find.
- The number of objects N can be huge.
- The number of operations M can be huge.
- Find queries and union commands may be intermixed
基于这样的数据结构的定义,以上的查找和合并的两个基本操作可以描述如下:
如果两个对象具有相同的id值,则两个对象连通,否则没有;对两个对象合并必须把其中一个对象所属的最大连通分支中所有对象的id值置为另一个对象所属的最大连通分支的统一id值,使得构成的新的最大连通分支里所有对象id值相同。
Problem:
How many connected components result after performing the following sequence of unionoperations on a set of 10
10 items?
1–2, 3–4, 5–6, 7–8, 7–9, 2–8, 0–5, 1–9
The connected components are {0,5,6}, {3,4}, and {1,2,7,8,9}.
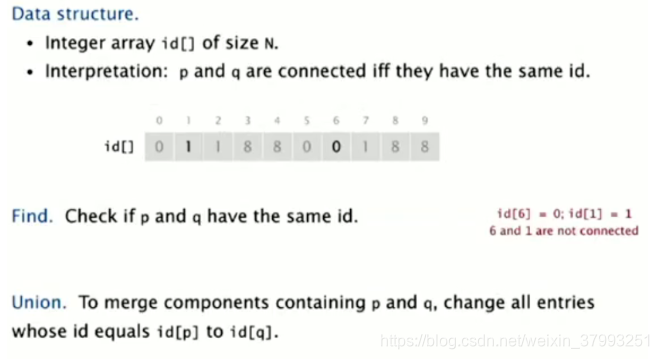
2. Quick find(快速查找)
| element | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| group number | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
For the first point(0,1), update the group number of element 0 and 1 to 0 or 1.(Union并操作)
| element | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| group number | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
Java:
public class QuickFindUF {
private int[] id; // id[i] = component identifier of i
/**
* Initializes an empty union–find data structure with {@code n} sites
* {@code 0} through {@code n-1}. Each site is initially in its own
* component.
* @param n the number of sites
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code n < 0}
*/
public QuickFindUF(int n) {
id = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
id[i] = i;
}
/**
* Returns true if the the two sites are in the same component.
*
* @param p the integer representing one site
* @param q the integer representing the other site
* @return {@code true} if the two sites {@code p} and {@code q} are in the same component;
* {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
*/
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return id[p] == id[q];
}
/**
* Merges the component containing site {@code p} with the
* the component containing site {@code q}.
*
* @param p the integer representing one site
* @param q the integer representing the other site
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
*/
public void union(int p, int q) {
int pID = id[p]; // needed for correctness
int qID = id[q]; // to reduce the number of array accesses
for(int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
// p and q are already in the same component
if (id[i] == pID) id[i] = qID ;
}
}
int pID = id[p]; // needed for correctness
int qID = id[q]; // to reduce the number of array accesses
for(int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
// p and q are already in the same component
if (id[i] == pID) id[i] = qID ;
}
}Python:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# 作者: Adward Wang
# 邮箱: JHWang0517@gmail.com
# 时间: 2018-06-11 16:13:22
# 描述: 佛性编程
id={}
def QuickFind(n):
for i in range(1,n+1):
id[i]=i
def connected(p,q):
return id[p] == id[q]
def unionid(p,q):
pID = id[p]
qID = id[q]
for i in range(0,n):
if(id[i] == pID):id[i] = qID
Constant time find.
| algorithm | initialize | union | find |
| quich-find | N | N | 1 |
Problem:
What is the maximum number of \verb#id[]#id[] array entries that can change (from one value to a different value) during one call to the union when using the quick-find data structure on n elements?
n-1
In the worst case, all of the entries except #id[q]#id[q] are changed from #id[p]#id[p] to #id[q]#id[q].
This doesn't work well on a huge dataset.
3. Quick union(快速合并)
Problem:Suppose that in a quick-union data structure on 10 elements that the \verb#id[]#id[] array is
| i | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| id[i] | 0 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
The root of 3 is 6: 3→5→2→6. Which are the roots of 33 and 77, respectively?
The root of 7 is 6: 7→1→9→5→2→6.
Union the root of 2 numbers.
Java:
public class QuickFindUF {
private int[] id; // id[i] = component identifier of i
public QuickUnionUF(int N) {
id = new int[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N ; i++) id[i] = i;
}
private int root(int i) {
while(i != id[i]) i = id[i];
reruen i;
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return root[p] == root[q];
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int i = root[p];
int j = root[q];
id[i] = j;
}
}
| algorithm | initialize | union | find |
| quick find | N | N | 1 |
| quickunion | N | N | N |
What is the maximum number of array accesses during a find operation when using the quick-union data structure on n elements? linear
4. Quick union improvements(优化)

Avoid putting large trees below.
Improvements1: Weighted quick-union demo
与Quick-Union随意地合并两个子树不同的是,改进的合并方法是有方向性的,将一个较小的子树的根合并到较大的子树的根上(较大的这个子树的根作为合并之后的树的根节点),这里较小的子树和较大的子树中的“较小”、“较大”的定义是广义的,可是是子树的规格(节点个数)、子树的高度(深度)或是某种的排序。这样的做法类似于维护一棵某种度量方向上的平衡树,保证树的形状不会像Quick-Union那样随机和不确定,使得复杂度变得可控(不可控是因为不确定导致的O(N))。
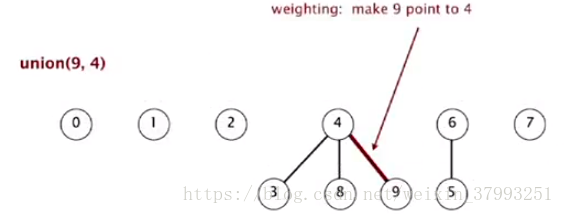

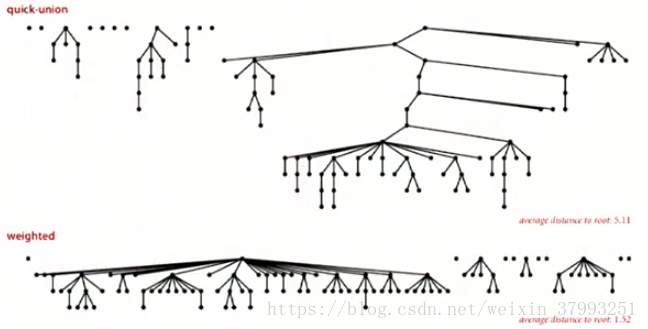
The depth of any node x is at most lg N.
| algorithm | initialize | union | connected |
| quick-find | N | N | 1 |
| quick-union | N | N | N |
| weighted QU | N | lg N | lg N |
Java:
public class WeightedQuickUnionUF {
private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i
private int[] size; // size[i] = number of sites in subtree rooted at i
private int count; // number of components
/**
* Initializes an empty union–find data structure with {@code n} sites
* {@code 0} through {@code n-1}. Each site is initially in its own
* component.
*
* @param n the number of sites
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code n < 0}
*/
public WeightedQuickUnionUF(int n) {
count = n;
parent = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
/**
* Returns the number of components.
*
* @return the number of components (between {@code 1} and {@code n})
*/
public int count() {
return count;
}
/**
* Returns the component identifier for the component containing site {@code p}.
*
* @param p the integer representing one object
* @return the component identifier for the component containing site {@code p}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= p < n}
*/
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
while (p != parent[p])
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
// validate that p is a valid index
private void validate(int p) {
int n = parent.length;
if (p < 0 || p >= n) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n-1));
}
}
/**
* Returns true if the the two sites are in the same component.
*
* @param p the integer representing one site
* @param q the integer representing the other site
* @return {@code true} if the two sites {@code p} and {@code q} are in the same component;
* {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
*/
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
/**
* Merges the component containing site {@code p} with the
* the component containing site {@code q}.
*
* @param p the integer representing one site
* @param q the integer representing the other site
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
*/
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
// make smaller root point to larger one
if (size[rootP] < size[rootQ]) {
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
size[rootQ] += size[rootP];
}
else {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
size[rootP] += size[rootQ];
}
count--;
}
/**
* Reads in a sequence of pairs of integers (between 0 and n-1) from standard input,
* where each integer represents some object;
* if the sites are in different components, merge the two components
* and print the pair to standard output.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = StdIn.readInt();
WeightedQuickUnionUF uf = new WeightedQuickUnionUF(n);
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt();
if (uf.connected(p, q)) continue;
uf.union(p, q);
StdOut.println(p + " " + q);
}
StdOut.println(uf.count() + " components");
}
}python:
class WeightedQuickUnionUF(BaseComp):
""" UNION FIND: Weighted Quick-union [lazy approach] to avoid tall trees."""
def __init__(self, N): # $ = N
"""Initialize union-find data structure w/N objects (0 to N-1)."""
super(WeightedQuickUnionUF, self).__init__("WeightedQuickUnionUF")
self.ID = range(N) # Set if of each object to itself.
# Keep track of SIZE(# objects in tree) of each tree rooted at i
self.SZ = [1]*N # Needed to determine which tree is smaller/bigger
def _root(self, i):
"""Chase parent pointers until reach root."""
d = 0 # Used for informative prints for educational purposes
while i != self.ID[i]: # depth of i array accesses
i = self.ID[i]
d += 1
return BaseComp.NtRoot(rootnode=i, depth=d)
def connected(self, p, q): # $ = lg N
"""Return if p and q are in the same connected component (i.e. have the same root)."""
return self._root(p).rootnode == self._root(q).rootnode # Runs depth of p & q array accesses
def union(self, p, q): # $ = lg N
"""Add connection between p and q."""
# Runs Depth of p and q array accesses...
p_root = self._root(p).rootnode
q_root = self._root(q).rootnode
if p_root == q_root:
return
# IMPROVEMENT #1: Modification to Quick-Union to make it weighted: 4:03
# Balance trees by linking root of smaller tree to root of larger tree
# Modified quick-union:
# * Link root of smaller tree to root of larger tree.
# * Update the SZ[] array.
# Each union involves changing only one array entry
if self.SZ[p_root] < self.SZ[q_root]: # Make ID[p_root] a child of q_root
self.ID[p_root] = q_root # link root of smaller tree(p_root) to root of larger tree(q_root)
self.SZ[q_root] += self.SZ[p_root] # Larger tree size increases
else: # Make ID[q_root] a child of p_root
self.ID[q_root] = p_root # link root of smaller tree(q_root) to root of larger tree(p_root)
self.SZ[p_root] += self.SZ[q_root]
def __str__(self):
"""Print the size vector as well as the ID vector."""
return '\n'.join([
super(WeightedQuickUnionUF, self).__str__(),
"siz: " + ' '.join('{SZ:>2}'.format(SZ=e) for e in self.SZ)])
Improvements2: Path compression
路径压缩,在计算某个节点的根节点时,直接将该节点以及由该节点指向根节点的路径中的节点的id值置为根节点的id值,即这条路径上的所有节点都以根节点作为父节点。
private int root(int i)
{
while(i != id[i])
{
id[i] = id[id[i]];//compression
i = id[i];
}
return i;
}Improvements2: Weighted quick-union with Path compression(amoritized analysis)
Proposition. [Hopcroft-Ulman, Tarjan] Starting from an empty data structure, any sequence of M union-find ops on N objects makes ≤ c ( N + M lg* N ) array accesses.
- Analysis can be improved to N + M α(M, N).
- The simple algorithm with fascinating mathematics
Nearly to linear running time.
Problem:
Suppose that the id[] array during the weighted quick-union (by size) algorithm is given as below. Which id[] entry changes when we apply the union operation to 3 and 6?
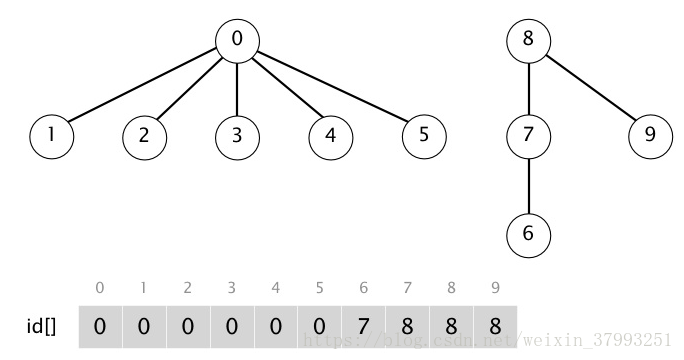
id[8] = 0
5. Applications
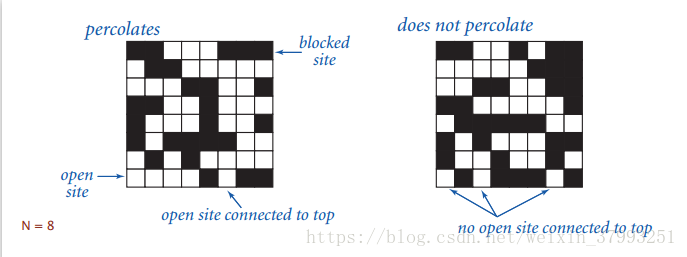
Percolation
A model for many physical systems:
- N-by-N grid of sites.
- Each site is open with probability p (or blocked with probability 1 – p).
- System percolates iff top and bottom are connected by open sites.
Monte Carlo simulation
- Initialize N-by-N whole grid to be blocked.
- Declare random sites open until top connected to the bottom.
- Vacancy percentage estimates p*.
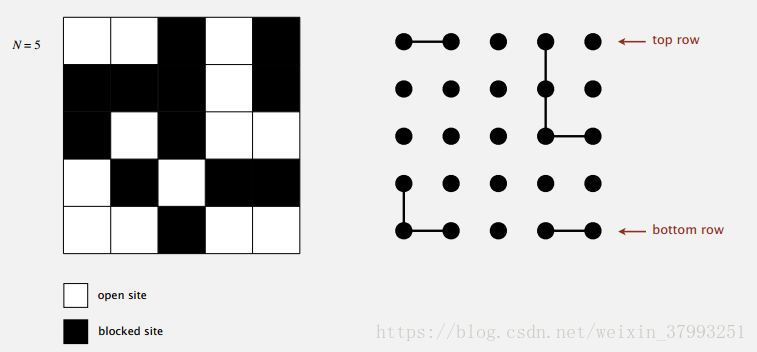
Dynamic connectivity solution to estimate percolation threshold
- Create an object for each site and name them 0 to N 2 – 1.
- Sites are in the same component if connected by open sites.
- Percolates iff any site on the bottom row is connected to site on the top row.
6. Summary









 本文详细介绍了并查集算法的基本概念及其两种实现方式——快速查找和快速合并,并讨论了它们的时间复杂度。针对快速合并算法的缺点,文章进一步提出了加权快速合并及路径压缩等优化方法,有效提高了算法效率。
本文详细介绍了并查集算法的基本概念及其两种实现方式——快速查找和快速合并,并讨论了它们的时间复杂度。针对快速合并算法的缺点,文章进一步提出了加权快速合并及路径压缩等优化方法,有效提高了算法效率。
















 2612
2612

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








