CLIP-PyTorch![]() https://github.com/bubbliiiing/clip-pytorch具体源码可查看↑项目,本文仅做代码分析。
https://github.com/bubbliiiing/clip-pytorch具体源码可查看↑项目,本文仅做代码分析。

一、模型结构
模型的前向传递函数如下:
def forward(self, image, text):
# 编码器
image_features = self.encode_image(image) # 图像编码
text_features = self.encode_text(text) # 文本编码
# 归一化
image_features = image_features / image_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
text_features = text_features / text_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
# 矩阵混合
logit_scale = self.logit_scale.exp()
logits_per_image = logit_scale * image_features @ text_features.t()
logits_per_text = logits_per_image.t()
return logits_per_image, logits_per_text可见模型为双分支混合结构,可以分为三个部分:编码器、归一化和矩阵混合。与原文结构一致[AICG]连接万物的CLIP。在代码默认的情况下,图形编码器为ViT,文本编码器为Bert。
在完成特征提取后,通过矩阵混合计算来获取CLIP模型的图像-文本相似度。首先,logit_scale为缩放参数用于计算缩放比例,一般为,代码如下:
self.logit_scale = nn.Parameter(torch.ones([]) * np.log(1 / 0.07))随后进行矩阵乘法,image_features和text_features通过矩阵乘法@进行结合,同时text_features要进行转置,代码如下:
logits_per_image = logit_scale * image_features @ text_features.t()二、模型训练
2.1数据加载
由于CLIP为多模态模型,其数据集包同时包含文本和图像,故存储方式为Json字符串。使用dataloader加载之前需要解析Json文件,Json文件中的单条格式如下:
[
# 单条数据
{
"image": "flickr8k-images/2513260012_03d33305cf.jpg", # 图像文件路径
"caption": [
"A black dog is running after a white dog in the snow .", # 文本信息
"Black dog chasing brown dog through snow",
"Two dogs chase each other across the snowy ground .",
"Two dogs play together in the snow .",
"Two dogs running through a low lying body of water ."
]
},
]完成Json解析后,使用ClipDataset进行数据加载,其单个数据块的获取函数如下:
def __getitem__(self, index):
photo_name = self.image[index]
image_path = os.path.join(self.datasets_path, photo_name)
# 随机选择一条对应的文本
caption = self.text[np.random.choice(self.img2txt[index])]
# 加载图像
image = Image.open(image_path)
# 强制转换为RGB图像
image = cvtColor(image)
# 进行随机增强的方式
if self.autoaugment_flag:
image = self.AutoAugment(image, random=self.random)
else:
image = self.get_random_data(image, self.input_shape, random=self.random)
image = np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image, dtype='float32')), (2, 0, 1))
# 返回结果为图像和一句从对应的语料中随机抽取的文本
return image, caption2.2数据灌注
从2.1章的代码中获得参数后,图像和文本将会被输入模型,得到图像特征向量和文本特征向量,通过交叉熵损失函数将两个特征向量与实际值进行比对即可得到反向传播参数。
with autocast():
# 训练,得特征向量
logits_per_image, logits_per_text = model_train(images, texts)
# 将文本特征向量转换为目标标签
labels = torch.arange(len(logits_per_image)).long().to(images.device)
# 损失函数计算
loss_logits_per_image = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(logits_per_image, labels)
loss_logits_per_text = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(logits_per_text, labels)
loss = loss_logits_per_image + loss_logits_per_text
# 反向传播
scaler.scale(loss).backward()
scaler.step(optimizer)
scaler.update()三、模型预测
模型预测的前半部分和训练相同,但是预测时会将特征向量显化为文本:
logits_per_image, logits_per_text = self.net(images, texts)
probs = logits_per_image.softmax(dim=-1).cpu().numpy()四、数据流分析
使用本文第一张图进行预测,输入图像会被变形为224x224x3的torch向量
![]()
输入文本则会逐行输入

完成编码后,图像特征向量和文本特征向量都会变成512维的torch向量(文本会分四组)
![]()
完成相似度计算后得到的输出特征向量为:
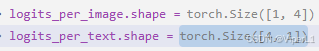
得到的输出结果为:
![]()
由结果Probs可见和图像最接近的是第一句话: The two children glided happily on the skateboard.
Tips.需要补齐部分依赖,同时会提示缺少bpe_simple_vocab_16e6,这是一个语料库,可以在
bpe_simple_vocab_16e6 下载,解压后放入model目录即可。


























 686
686

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








