1.main方法包含TreeMap排序1,TreeMap排序2,HashMap排序,List排序,List排序,List排序
package com.tao.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Sort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TreeMap排序1
Map treeMap = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
// 升序排序
return o1.compareTo(o2);
}
});
treeMap.put("c", "ccccc");
treeMap.put("a", "aaaaa");
treeMap.put("b", "bbbbb");
treeMap.put("d", "ddddd");
// 排序后输出
for (String key : treeMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println("Key=" + key + ", Value=" + treeMap.get(key));
}
// TreeMap排序2
Map treeMap2 = new TreeMap();
treeMap2.put("d", 3);
treeMap2.put("b", 4);
treeMap2.put("a", 7);
treeMap2.put("c", 1);
// 转换成list
List> treeList = new ArrayList>(treeMap2.entrySet());
Collections.sort(treeList, new Comparator>() {
// 升序排序
public int compare(Entry o1, Entry o2) {
return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}
});
// 排序后输出
for (Map.Entry m : treeList) {
System.out.println("Key=" + m.getKey() + ", Value=" + m.getValue());
}
// HashMap排序
Map hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("c", 3);
hashMap.put("a", 2);
hashMap.put("b", 1);
hashMap.put("d", 4);
List> hashList = new ArrayList>(hashMap.entrySet());
Collections.sort(hashList, new Comparator>() {
// 升序排序
public int compare(Entry o1, Entry o2) {
return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}
});
// 排序后输出
for (Map.Entry m : hashList) {
System.out.println("Key=" + m.getKey() + ", Value=" + m.getValue());
}
// List排序
List nums = new ArrayList();
nums.add(3);
nums.add(5);
nums.add(2);
nums.add(1);
// 升序排序(默认)
Collections.sort(nums);
// 排序后输出
System.out.println(nums);
// List排序
List users = new ArrayList();
users.add(new User(2, "jack"));
users.add(new User(1, "tom"));
users.add(new User(3, "keck"));
users.add(new User(4, "tao"));
// id升序排序
Collections.sort(users);
// 排序后输出
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user.getId() + "," + user.getName());
}
// List排序
List> listMap = new ArrayList>();
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("age", 20);
map.put("sex", 1);
listMap.add(map);
Map map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put("age", 29);
map2.put("sex", 2);
listMap.add(map2);
Map map3 = new HashMap<>();
map3.put("age", 35);
map3.put("sex", 1);
listMap.add(map3);
// 按照map值排序
Collections.sort(listMap, new Comparator>() {
@Override
public int compare(Map o1, Map o2) {
return o1.get("age").compareTo(o2.get("age"));// age升序排序
}
});
// 排序后输出
for (Map m : listMap) {
System.out.println(m);
}
}
}
2.List排序的User.java类:
package com.tao.test;
public class User implements Comparable{
private int id;
private String name;
public User(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(User o) {
return this.id - o.getId();//id升序排序
}
}
3.运行截图
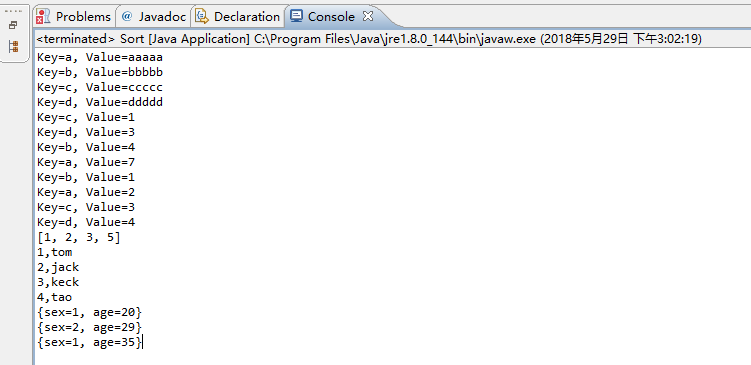







 本文展示了如何使用Java的Collections.sort方法对TreeMap、HashMap的键值对以及自定义对象列表进行排序。示例包括了升序排序以及根据特定字段排序Map和自定义对象List。
本文展示了如何使用Java的Collections.sort方法对TreeMap、HashMap的键值对以及自定义对象列表进行排序。示例包括了升序排序以及根据特定字段排序Map和自定义对象List。
















 857
857

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








