In linear algebra, a symmetric n × n real matrix M is said to be positive definite if zTMz is positive for every non-zero columnvector z of n real numbers. Here zT denotes thetranspose of z.
- The real symmetric matrix
-
-
-
is positive definite since for any non-zero column vector
z with entries
a,
b and
c, we have
-
- This result is a sum of squares, and therefore non-negative; and is zero only if a = b = c = 0, that is, when z is zero.
- The real symmetric matrix
-
-
-
is not positive definite. If z is the vector
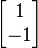 , one has
, one has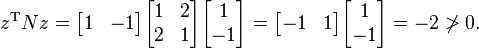
More generally, an n × n Hermitian matrix M is said to be positive definite if z*Mz is real and positive for all non-zero complex vectors z. Here z* denotes the conjugate transpose of z.
-
摘自:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Positive_semidefinite_matrix




 本文介绍了线性代数中正定矩阵的概念,详细解释了实对称矩阵和埃尔米特矩阵成为正定矩阵的条件,并通过具体的例子展示了如何判断一个矩阵是否为正定矩阵。
本文介绍了线性代数中正定矩阵的概念,详细解释了实对称矩阵和埃尔米特矩阵成为正定矩阵的条件,并通过具体的例子展示了如何判断一个矩阵是否为正定矩阵。
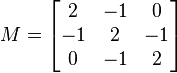

















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








