本人项目地址大全:Victor94-king/NLP__ManVictor: 优快云 of ManVictor
写在前面: 笔者更新不易,希望走过路过点个关注和赞,笔芯!!!
写在前面: 笔者更新不易,希望走过路过点个关注和赞,笔芯!!!
写在前面: 笔者更新不易,希望走过路过点个关注和赞,笔芯!!!
1. 概述
在当今快速发展的自然语言处理领域,大型语言模型(LLM)正发挥着越来越重要的作用。从自动翻译到文本生成,这些模型在许多应用场景中表现出了惊人的能力。然而,要确保这些模型能够在实际应用中表现稳定且高效,必须对其进行严谨的评估。这篇文章将详细探讨LLM评估指标的定义、方法和最佳实践,并提供相应的代码示例,帮助您构建强大的LLM评估流程。
2. LLM评估指标的定义与重要性
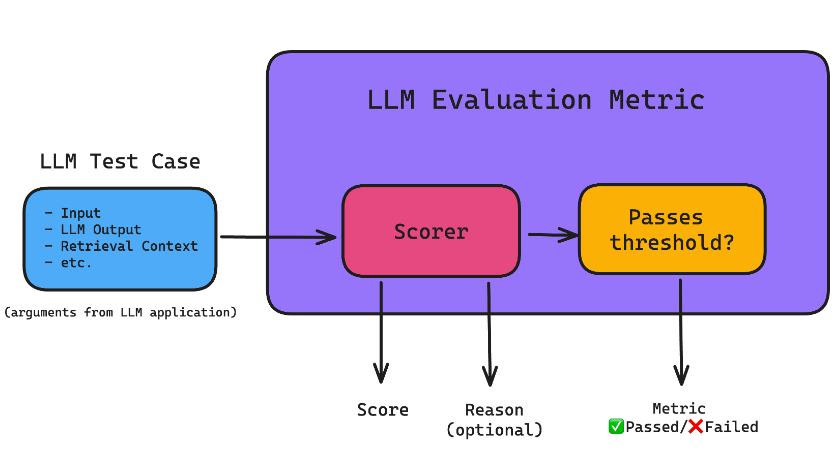
1) 什么是LLM评估指标?
LLM评估指标是用来量化和评估大型语言模型(LLM)输出质量的工具。它们根据一系列标准来评分模型的输出,确保模型在各种任务中表现良好。常见的评估指标包括答案相关性、正确性、幻觉检测、上下文相关性、责任指标以及任务特定指标。这些指标对于优化LLM的性能、识别潜在问题以及提升模型的实用性至关重要。
2) LLM评估的挑战
尽管LLM评估对于优化模型至关重要,但这一过程常常面临挑战。首先,LLM的输出可能具有高度的多样性和不确定性,使得评估变得复杂。此外,如何选择和实施合适的评估指标,以准确反映模型的实际性能,也是一大难题。因此,开发一个全面且有效的LLM评估框架是构建成功LLM应用的关键。
3. LLM评估指标的主要类别
1) 答案相关性
答案相关性是评估LLM是否能够有效回答用户问题的关键指标。它衡量模型输出是否能够准确、全面地回应输入信息。例如,在问答系统中,答案相关性指标会评估模型是否提供了有用的、与问题相关的回答。
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
import numpy as np
def compute_relevance_score(predicted_answer, reference_answer, model):
pred_embedding = model.encode(predicted_answer)
ref_embedding = model.encode(reference_answer)
score = cosine_similarity([pred_embedding], [ref_embedding])[0][0]
return score
# 示例
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
model = SentenceTransformer('paraphrase-MiniLM-L6-v2')
predicted_answer = "The capital of France is Paris."
reference_answer = "Paris is the capital city of France."
relevance_score = compute_relevance_score(predicted_answer, reference_answer, model)
print(f"Relevance Score: {relevance_score}")
2) 正确性
正确性指标用于验证LLM的输出是否符合事实。它可以通过比对模型生成的内容与已知的真实信息来计算。这对于确保模型在处理事实性问题时的准确性尤其重要。
import requests
def check_factual_accuracy(output_text, fact_checking_api_url):
response = requests.post(fact_checking_api_url, data={'text': output_text})
result = response.json()
return result['is_factual']
# 示例
fact_checking_api_url = "https://example.com/fact-check-api"
output_text = "The Earth revolves around the Sun."
is_factual = check_factual_accuracy(output_text, fact_checking_api_url)
print(f"Is Factual: {is_factual}")
3) 幻觉检测
幻觉指的是LLM生成虚假或不准确的信息。检测幻觉对于提高模型的可靠性和用户信任至关重要。幻觉检测可以通过人工审核或结合自动化工具来实现。
def detect_hallucination(output_text, known_facts):
hallucinations = [fact for fact in known_facts if fact not in output_text]
return len(hallucinations) > 0
# 示例
known_facts = ["The capital of France is Paris.", "Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius."]
output_text = "The capital of France is Berlin."
has_hallucination = detect_hallucination(output_text, known_facts)
print(f"Has Hallucination: {has_hallucination}")





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 1026
1026

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










