1.栈的简介
栈(stack)又名堆栈,它是一种运算受限的线性表。其限制是仅允许在表的一端进行插入和删除运算。这一端被称为栈顶,相对地,把另一端称为栈底。向一个栈插入新元素又称作进栈、入栈或压栈,它是把新元素放到栈顶元素的上面,使之成为新的栈顶元素;从一个栈删除元素又称作出栈或退栈,它是把栈顶元素删除掉,使其相邻的元素成为新的栈顶元素。(百度百科)
2.栈的种类
- 顺序栈
顺序栈即使用顺序表实现的栈。本博文中的顺序栈为顺序表的继承。关于顺序表请参见:《数据结构》期末提纲之顺序表 - 链栈
链栈即使用链表实现的栈。本博文中的链栈为链表的继承。关于链表请参见:《数据结构》期末提纲之链表
3.栈的基本操作
- 入栈
入栈,顾名思义,即讲数据存入栈中,通常以对线性表进行头插的方式实现。如图所示:(灵魂画师)
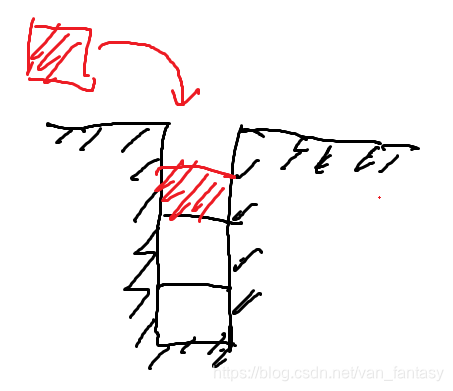
- 出栈
出栈即弹出栈顶元素,一班通过对线性表表头元素进行返回并删除来实现。如图所示:
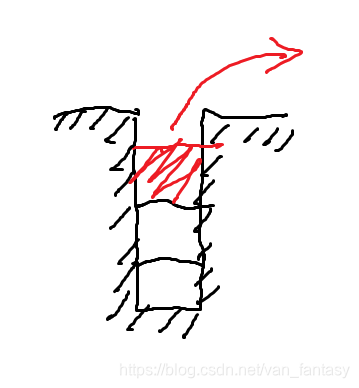
栈只能对栈顶元素进行操作,所以其操作种类较少。
4.顺序栈的C++实现
由于顺序栈使限定操作的顺序表,所以其为顺序表的私有继承,特此声明。顺序表实现不在本博文赘述。传送门
- 类型构造
template<class DataType>
class SeqStack : private SeqList<DataType> //顺序栈类,为顺序表的私有继承
{
public:
SeqStack(); //构造
~SeqStack(); //析构
void push(DataType x); //从栈顶添加元素
DataType top(); //访问栈顶
void pop(); //删除栈顶
int size(); //返回大小
void clr(); //清空栈
};
- 构造与析构
template<class DataType> //会对线性表进行自动构造与析构,此处无需另外的操作
SeqStack<DataType>::SeqStack()
{
cout << "SeqStack Constructed!" << endl;
}
template<class DataType>
SeqStack<DataType>::~SeqStack()
{
cout << "SeqStack Distructed!" << endl;
}
- 入栈
template<class DataType>
void SeqStack<DataType>::push(DataType x)
{
this->insert(this->len + 1,x); //这里是在尾部添加值,实际上头部也可以,只要注意操作都在同一端就行
}
- 访问栈顶元素
template<class DataType>
DataType SeqStack<DataType>::top()
{
return this->get(this->len); //注意这里仅仅只是访问,不会删除栈顶
}
- 删除栈顶
template<class DataType>
void SeqStack<DataType>::pop()
{
this->del_loc(this->len); //删除尾部即可
}
- 返回栈长
template<class DataType>
int SeqStack<DataType>::size()
{
return this->len; //直接返回顺序表长度即可
}
- 清空栈
template<class DataType>
void SeqStack<DataType>::clr()
{
this->clear(); //清空顺序表即可
}
- 调试函数
void SeqStack_debug()
{
SeqStack<int> s;
int sw;
cout << "SeqStack Options:\n1.Push data\n2.View the top data\n3.Pop the top data\n4.View the size of stack\n5.Clear the stack\n6.Print the stack while popping\n7.Exit" << endl;
while(cin >> sw)
{
if(sw == 1)
{
int x;
cout << "Please input the data: ";
cin >> x;
s.push(x);
}
else if (sw == 2)
{
cout << s.top() << endl;
}
else if (sw == 3)
{
s.pop();
}
else if (sw == 4)
{
cout << s.size() << endl;
}
else if (sw == 5)
{
s.clr();
}
else if (sw == 6)
{
while(s.size())
{
cout << s.top() << " ";
s.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
else
{
break;
}
cout << "SeqStack Options:\n1.Push data\n2.View the top data\n3.Pop the top data\n4.View the size of stack\n5.Clear the stack\n6.Print the stack while popping\n7.Exit" << endl;
}
}
5.链栈的C++实现
代码与顺序栈除类型名与取长度操作外几乎一模一样,此处直接贴代码不做过多解释。链栈基于链表实现,链表相关内容本博文不作赘述。 传送门
template<class DataType>
class LinkStack : private LinkList<DataType> //链式栈类,为链表的私有继承
{
public:
LinkStack(); //构造
~LinkStack(); //析构
void push(DataType x); //从栈顶添加元素
DataType top(); //访问栈顶
void pop(); //删除栈顶
int size(); //返回大小
void clr(); //清空栈
};
template<class DataType>
LinkStack<DataType>::LinkStack()
{
cout << "LinkStack Constructed!" << endl;
}
template<class DataType>
LinkStack<DataType>::~LinkStack()
{
cout << "LinkStack Distructed!" << endl;
}
template<class DataType>
void LinkStack<DataType>::push(DataType x)
{
this->insert(this->length() + 1,x);
}
template<class DataType>
DataType LinkStack<DataType>::top()
{
return this->get(this->length());
}
template<class DataType>
void LinkStack<DataType>::pop()
{
this->del_loc(this->length());
}
template<class DataType>
int LinkStack<DataType>::size()
{
return this->length();
}
template<class DataType>
void LinkStack<DataType>::clr()
{
this->clear();
}
void LinkStack_debug()
{
LinkStack<int> s;
int sw;
cout << "LinkStack Options:\n1.Push data\n2.View the top data\n3.Pop the top data\n4.View the size of stack\n5.Clear the stack\n6.Print the stack while popping\n7.Exit" << endl;
while(cin >> sw)
{
if(sw == 1)
{
int x;
cout << "Please input the data: ";
cin >> x;
s.push(x);
}
else if (sw == 2)
{
cout << s.top() << endl;
}
else if (sw == 3)
{
s.pop();
}
else if (sw == 4)
{
cout << s.size() << endl;
}
else if (sw == 5)
{
s.clr();
}
else if (sw == 6)
{
while(s.size())
{
cout << s.top() << " ";
s.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
else
{
break;
}
cout << "LinkStack Options:\n1.Push data\n2.View the top data\n3.Pop the top data\n4.View the size of stack\n5.Clear the stack\n6.Print the stack while popping\n7.Exit" << endl;
}
}
6.小结
栈是一种常用的数据结构,经常作为各种算法的工具,必须掌握。
总提纲:《数据结构》期末提纲小结





 本文详细介绍了栈的概念、种类,包括顺序栈和链栈,并提供了这两种栈在C++中的实现。栈的基本操作包括入栈和出栈,文章还包含了顺序栈和链栈的构造、访问栈顶元素、删除栈顶元素等功能的实现。栈作为一种重要的数据结构,对于理解和实现算法至关重要。
本文详细介绍了栈的概念、种类,包括顺序栈和链栈,并提供了这两种栈在C++中的实现。栈的基本操作包括入栈和出栈,文章还包含了顺序栈和链栈的构造、访问栈顶元素、删除栈顶元素等功能的实现。栈作为一种重要的数据结构,对于理解和实现算法至关重要。
















 160
160

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








