前序:花了好几天才把带你飞系列的KMP专题(地址:https://vjudge.net/contest/246969#overview搞定,刷了很多题,发现KMP可以用来解决这几类问题:
①单个字符串匹配问题(s1在s2中匹配):这个用strstr(const char* big, const char* small)函数也可以,这个函数返回small在big函数中首次出现的地址,没有出现就返回NULL。区别在于:
1️⃣如果只是求s1是否在s2中出现过的话,建议可以用strstr函数,这个函数的复杂度还是可以接受的(如果数据量达到1e6就还是老老实实用kmp,用这个函数会TLE,例如A题),如果实在不行,再换用kmp模板吧。当然strstr只能适用字符数组,若是数字就直接上kmp吧,当然,强行把数字用字符存也不是不可以,QAQ。
2️⃣如果求s1在s2中出现了几次(分为可重叠与不可重叠),就只能用kmp了。
3️⃣如果求s1在s2首次出现的下标,用kmp可以直接返回下标,而strstr函数貌似也可以,不过由于返回的是地址,需要转化一下。
附上kmp求以上问题的kmp_pre的各种变形
int KMP_Count(char s[], char p[]){
kmp_pre();
cnt = 0;
int i,j;
i = j = 0;
int n = strlen(s);
int m = strlen(p);
while(i < n){
while(j != -1 && s[i] != p[j]) j = nextt[j];
++i; ++j;
if(j >= m){
cnt++; //记录p在s中出现的个数
j = nextt[j]; //p在s中可以覆盖、重叠,例如s=abababa p=aba,最后cnt=3
//j = 0; //p在s中不可以覆盖、重叠,例如s=abababa p=aba,最后cnt=2
//return 1; //返回存在
//return i-m+1; //返回p首次在s中出现的下标
}
}
return cnt; //返回出现次数
//return 0; //返回不存在
// return -1; //p首次在s中出现的下标为-1,表示s中没有p
}
②字符串循环节问题(nextt数组的运用一):感觉kmp最牛的地方就是nextt数组了,nextt数组又称前缀数组(或许叫做最长前后缀数组更加合适),先看张图哈:
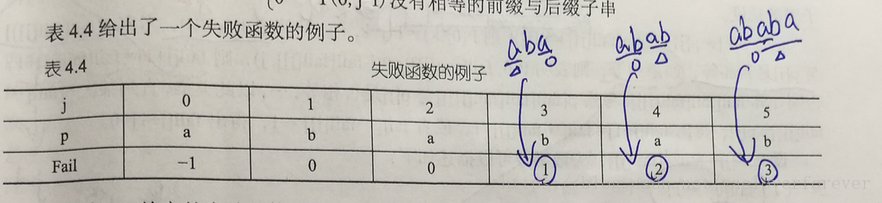
可以看出nextt[i]其实就是字符串s[0~(i-1)]的前后缀的最大相等长度。需要注意的是nextt[0]=-1,nextt[0]=0是不变的,至于原因,结合nextt的定义不难理解。还有就是上图中,其实nextt[6]=4,可以发现4就是字符串ababab的前后缀的最大相等长度,而6(字符串长度)-4=2即为循环节的长度。所以循环节的长度公式为:l = len-nextt[len],其中len为字符串的长度。这里也要分两种情况
1️⃣len%l == 0:就是字符串的长度是循环节的整数倍,有一种比较特殊的情况就是l == len这种类型的伪循环,例如abcde,它的循环节就是它本身,等于说并没有循环。而常见的是类似于abcbac这种(len = 6, l = 3)。有时候还会求周期个数(循环节个数):num = len/i;
2️⃣len%l != 0,就是字符串不是循环节的整数倍,没有循环到底,例如abcabcab(注意这里的nextt[8]=5(abcab),所以l = 8-5=3),
8%3==2 != 0,就是说最后一个循环节没有循环到底,只有2个(ab),要补上l-len%l=1个。
故涉及到循环节的问题,只要考虑三组类型:abcabc,abcabcab,abcdef就可以避免考虑不全的情况了。
③前后缀问题(nextt数组的应用二):
1️⃣nextt数组的定义见②,就是前后缀的最大相等长度,通过一个while循环,不断迭代,直到nextt[i]为0,可以求出字符串所有的前后缀相等的长度。例如,ababcababababcabab,最长的相等长度为nextt[18]=9(ababcabab),然后nextt[9]=4(abab),nextt[4]=2(ab), nextt[2]=0。注意,括号的字符串既可以理解为前缀,也可以理解为原字符串的前后缀的组合(由于之前前后缀的匹配带来的关系)。
2️⃣扩展kmp:扩展kmp中用到了两个数组:nextt和ext,其中nextt[i]数组的定义是:p[i.....(m-1)]与p[0....(m-1)]的最长公共前缀,也就是p串从i开始后面的字符串p1与整个p串的最长公共前缀。注意与kmp算法中的nextt数组的区别:kmp算法中的nextt[i]表示的是字符串p[0...(i-1)]这个字符串的最大相等前后缀的长度。举个栗子:abaabb。在kmp算法中,nextt的值除了nextt[0]=-1外,其余都为0。而在扩展kmp中,nextt[3]=2,因为nextt[3]表示的是字符串p1[3...5](即abb)与p(即abaabb)的最大公共前缀的长度,也就是2。
它的nextt[i]=m可以理解为p字符串前面m个字符在后面的第i个位置又出现了。 不难理解:nextt[0]总是等于m。
ext[i]数组:定义是s[i....(n-1)]与p[0....(m-1)]的最大公共前缀。也就是主串s的从i开始的后面的字符串s1与模式串p的最长公共前缀。当ext[i]=m时,也就是s1==p,说明p串在s串的第i个位置出现了,也就是kmp中的匹配成功,所以说扩展kmp是kmp的一种扩展。
ps:扩展kmp其实求得的是两个字符串的最大前缀,不过可以转化为两个字符串的最大相等前后缀长度(没错,就是上面kmp算法的nextt的应用)。具体就是加一个判断当if(ext[i]==n-i) 此时s[i....(n-1)]字符串就是s串的后缀,并且和p串的长度为ext[i]的前缀相等。
3️⃣环形串(可以从不同的下标开始形成n个串)性质:
①就是环形串的n个串的个数都一样,特别的,当原串是类似于abcabc这种“满循环串”时,每个串的个数就等于(len/循环节),也就是周期个数,而串的种类就等于一个循环节的长度。
②涉及到环串,还有一个经常用到的处理方式,就是倍增一次,将s串变成s+s,这样就不用取余什么的操作了。(这题没用到)
题意:
给你字符串s和p,问你p在s串中首次出现的下标,若没有出现,则返回-1。
思路:裸单个字符串匹配问题(s1在s2中匹配,①1️⃣类型),一开始直接用kmp写得,刚刚试了一下,TLE了,这题数据量1e6,T也是意料之中,所以数据量很大时,还是老老实实敲kmp板子吧。
AC代码(kmp板子):
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define Fin freopen("in.txt","r",stdin)
#define Fout freopen("out.txt","w",stdout)
#define Case(T) int T;for(scanf("%d",&T);T--;)
#define fo(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i < b; ++i)
#define fd(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i >= b; --i)
#define me(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define fi(a,n,val) fill(a,a+n,val);
#define Scand(n) scanf("%d",&n);
#define Scans(s) scanf("%s",s);
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a,ll b) { return b ? gcd(b,a%b): a; }
const int maxn = 1e6 + 500;
const int INF = 0xffffff;
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
#endif // ONLINE_JUDGE
int n,m;
int s[maxn], p[maxn];
int nextt[maxn];
void kmp_pre(){
int i,j;
j = nextt[0] = -1;
i = 0;
while(i < m){
while (j != -1 && p[i] != p[j]) j = nextt[j];
nextt[++i] = ++j;
}
}
int kmp(){
kmp_pre();
int i,j;
i = j = 0;
while (i < n) {
while (j != -1 && s[i] != p[j]) j = nextt[j];
++i; ++j;
if(j >= m){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
// Fin;
#endif // ONLINE_JUDGE
Case(T){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
fo(i,0,n)
Scand(s[i]);
fo(i,0,m)
Scand(p[i]);
me(nextt,0);
int ans = kmp();
if(ans != -1)
printf("%d\n",ans-m+1);
else
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
TLE代码(用的strstr函数):
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define Fin freopen("in.txt","r",stdin)
#define Fout freopen("out.txt","w",stdout)
#define Case(T) int T;for(scanf("%d",&T);T--;)
#define fo(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i < b; ++i)
#define fd(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i >= b; --i)
#define me(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define fi(a,n,val) fill(a,a+n,val);
#define Scand(n) scanf("%d",&n);
#define Scans(s) scanf("%s",s);
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a,ll b) { return b ? gcd(b,a%b): a; }
const int maxn = 1e6 + 500;
const int INF = 0xffffff;
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
#endif // ONLINE_JUDGE
int n,m;
int s[maxn], p[maxn];
int nextt[maxn];
void kmp_pre(){
int i,j;
j = nextt[0] = -1;
i = 0;
while(i < m){
while (j != -1 && p[i] != p[j]) j = nextt[j];
nextt[++i] = ++j;
}
}
int kmp(){
kmp_pre();
int i,j;
i = j = 0;
while (i < n) {
while (j != -1 && s[i] != p[j]) j = nextt[j];
++i; ++j;
if(j >= m){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
//Fin;
#endif // ONLINE_JUDGE
Case(T){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
fo(i,0,n)
Scand(s[i]);
fo(i,0,m)
Scand(p[i]);
char ss[maxn];
char pp[maxn];
fo(i, 0, n){
ss[i] = s[i]+'1'-1;
}
fo(i, 0, m){
pp[i] = p[i]+'1'-1;
}
char* ans = strstr(ss, pp);
if(ans == NULL)
cout << -1 << endl;
else
cout << distance(ss, ans)+1 << endl; //利用distance函数根据地址求距离
}
return 0;
}题意:
给你两个字符串s和p,问你s中有多少个p(可重叠)?
思路:裸的kmp板子(①2️⃣类型)。
代码:
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define Fin freopen("in.txt","r",stdin)
#define Fout freopen("out.txt","w",stdout)
#define Case(T) int T;for(scanf("%d",&T);T--;)
#define fo(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i < b; ++i)
#define fd(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i >= b; --i)
#define me(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define fi(a,n,val) fill(a,a+n,val);
#define Scand(n) scanf("%d",&n);
#define Scans(s) scanf("%s",s);
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a,ll b) { return b ? gcd(b,a%b): a; }
const int maxn = 1e6 + 5;
const int INF = 0xffffff;
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
#endif // ONLINE_JUDGE
char s[maxn],p[maxn];
int n,m;
int nextt[maxn];
void kmp_pre(){
int i,j;
j = nextt[0] = -1;
i = 0;
while (i < m) {
while (j != -1 && p[i] != p[j]) {
j = nextt[j];
}
nextt[++i] = ++j;
}
}
int kmp(){
kmp_pre();
int i,j;
i = j = 0;
int cnt = 0;
while (i < n) {
while (j != -1 && s[i] != p[j]) {
j = nextt[j];
}
++i; ++j;
if(j >= m){
cnt++;
j = nextt[j];
}
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
//Fin;
#endif // ONLINE_JUDGE
Case(T){
scanf("%s",p); scanf("%s",s);
n = strlen(s); m = strlen(p);
int ans = kmp();
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
题意:
给你两个字符串s和p,问你s中有多少个p(不可重叠)?
思路:裸的kmp板子(①2️⃣类型)。
代码:
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define Fin freopen("in.txt","r",stdin)
#define Fout freopen("out.txt","w",stdout)
#define Case(T) int T;for(scanf("%d",&T);T--;)
#define fo(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i < b; ++i)
#define fd(i,a,b) for(int i = a; i >= b; --i)
#define me(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define fi(a,n,val) fill(a,a+n,val);
#define Scand(n) scanf("%d",&n);
#define Scans(s) scanf("%s",s);
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a,ll b) { return b ? gcd(b,a%b): a; }
const int maxn = 10000 + 5;
const int INF = 0xffffff;
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
#endif // ONLINE_JUDGE
char s[maxn],p[maxn];
int n,




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1117
1117

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








