分享一下我老师大神的人工智能教程!零基础,通俗易懂!http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/jiangjunshow
也欢迎大家转载本篇文章。分享知识,造福人民,实现我们中华民族伟大复兴!
引言
桥接模式就将要解决什么样的问题呢?我们具几个显示中的例子来加深理解
例子一
拿汽车在路上行驶的来说。即有轿车,又有公共汽车,它们都不但能在市区中的公路上行驶,也能在高速公路上行驶。这你会发现,对于不同的交通工具,行驶在不同的环境中,每个都作为一个需求,我们会有很多种可能的需求,
例子二
再比如说我们每天用的电脑,有各种牌子的,什么Dell,Hp,Acer,Lenovo,Apple,不同的电脑上还可以装不一样的操作系统,比如说Windows(WindowsXP,Windows7.Windows8),Linux(RedHat,Ubunto,LinuxMint,CentOS),MacOS等等,如果每台电脑配上一个操作系统,我么也会有很多的组合。如果我们每个需求都用一个单独的类来对应,很容易出现问题,我们知道在继承的时候基类和子类的耦合度是很高的
传统方式的缺点
小结
我们会发现,以前我们需求中的变动都是单维度的,也就是只有一个需求面在变动,而这次我们面临的时,几个不同的方向同时变动,每个变动,都会产生一个新的需求,我们需要去对应这些需求,以前那些模式都是不划算的,这时候桥接模式就出现了,用以应对这种多维度的需求变动
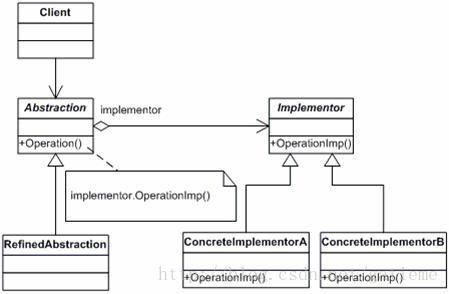
桥接模式概述
在软件系统中,某些类型由于自身的逻辑,它具有两个或多个维度的变化,那么如何应对这种“多维度的变化”?如何利用面向对象的技术来使得该类型能够轻松的沿着多个方向进行变化,而又不引入额外的复杂度?这就要使用Bridge模式。
意图:
GOF在提出桥梁模式的时候指出,桥梁模式的用意是"将抽象化(Abstraction)与实现化(Implementation)脱耦,使得二者可以独立地变化"。这句话有三个关键词,也就是抽象化、实现化和脱耦。
首先看操作系统的代码
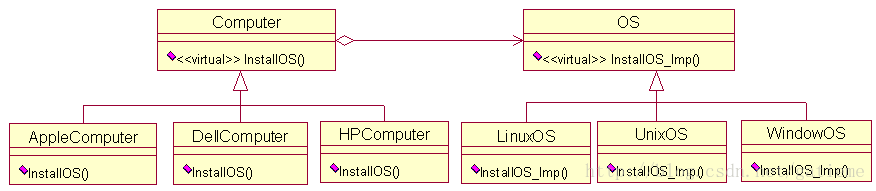
#ifndef __OS_H_INCLUDED__#define __OS_H_INCLUDED__// 操作系统class OS{public : virtual ~OS( ){ }; virtual void InstallOSImage( ) const = 0; // 安装操作系统};// WINDOWS操作系统class WindowsOS : public OS{public: virtual ~WindowsOS( ){ }; void InstallOSImage( ) const { std::cout <<"安装WINDOWS操作系统" <<std::endl; }};// LINUX操作系统class LinuxOS : public OS{public: virtual ~LinuxOS( ){ }; void InstallOSImage( ) const { std::cout <<"安装LINUX操作系统" <<std::endl; }};// MACOX操作系统class MacOS : public OS{public: virtual ~MacOS( ){ }; void InstallOSImage( ) const { std::cout <<"安装MACOS操作系统" <<std::endl; }};#endif // __OS_H_INCLUDED__下面看电脑的代码
在安装时候,传一个OS*类型的指针进来,从未指定安装某个操作系统
#ifndef __COMPUTER_H_INCLUDED__#define __COMPUTER_H_INCLUDED__#include "OS.h"// 计算机的基类class Computer{public : virtual ~Computer( ){ }; virtual void InstallOS(const OS *os) = 0; // 在计算机上安装操作系统};// 计算机的基类class DellComputer : public Computer{public : virtual ~DellComputer( ){ }; void InstallOS(const OS *os) // 在计算机上安装操作系统 { std::cout <<"我有台戴尔电脑..." <<std::endl; os->InstallOSImage( ); // 安装操作系统的镜像 std::cout <<std::endl; }};// 计算机的基类class AcerComputer : public Computer{public : virtual ~AcerComputer( ){ }; void InstallOS(const OS *os) // 在计算机上安装操作系统 { std::cout <<"我有台宏基电脑..." <<std::endl; os->InstallOSImage( ); // 安装操作系统的镜像 std::cout <<std::endl; }};// 计算机的基类class AppleComputer : public Computer{public : virtual ~AppleComputer( ){ }; void InstallOS(const OS *os) // 在计算机上安装操作系统 { std::cout <<"我有台苹果电脑..." <<std::endl; os->InstallOSImage( ); // 安装操作系统的镜像 std::cout <<std::endl; }};#endif // __COMPUTER_H_INCLUDED__下面看看主程序该怎么写
#include <iostream>#include "OS.h"#include "Computer.h"using namespace std;int main(){ OS *os = NULL; Computer *com = NULL; os = new WindowsOS( ); com = new DellComputer( ); com->InstallOS(os); // 在Dell笔记本上安装Windows操作系统 delete os; os = NULL; delete com; com = NULL; os = new LinuxOS( ); com = new AcerComputer( ); com->InstallOS(os); // 在宏基电脑上安装Linux操作系统 delete os; os = NULL; delete com; com = NULL; os = new MacOS( ); com = new AppleComputer( ); com->InstallOS(os); // 在苹果机上安装MacOs delete os; os = NULL; delete com; com = NULL; return 0;}附言-另外的实现方式(组合/聚合)
#include <iostream>//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 操作系统class OS{public : virtual ~OS( ){ }; virtual void InstallOSImage( ) const = 0; // 安装操作系统};// WINDOWS操作系统class WindowsOS : public OS{public: virtual ~WindowsOS( ){ }; void InstallOSImage( ) const { std::cout <<"安装WINDOWS操作系统" <<std::endl; }};// LINUX操作系统class LinuxOS : public OS{public: virtual ~LinuxOS( ){ }; void InstallOSImage( ) const { std::cout <<"安装LINUX操作系统" <<std::endl; }};// MACOX操作系统class MacOS : public OS{public: virtual ~MacOS( ){ }; void InstallOSImage( ) const { std::cout <<"安装MACOS操作系统" <<std::endl; }};//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 计算机的基类class Computer{public : Computer(OS *os) :m_os(os) { } virtual ~Computer( ) { }; virtual void InstallOS( ) = 0; // 在计算机上安装操作系统protected : OS *m_os; // 安装的操作系统};// 计算机的基类class DellComputer : public Computer{public : DellComputer(OS *os) :Computer(os) { } virtual ~DellComputer( ){ }; void InstallOS( ) // 在计算机上安装操作系统 { std::cout <<"This is a DELL computer..." <<std::endl; this->m_os->InstallOSImage( ); // 安装操作系统的镜像 std::cout <<std::endl; }};// 计算机的基类class AcerComputer : public Computer{public : AcerComputer(OS *os) :Computer(os) { } virtual ~AcerComputer( ) { } void InstallOS( ) // 在计算机上安装操作系统 { std::cout <<"This is a ACER computer..." <<std::endl; this->m_os->InstallOSImage( ); // 安装操作系统的镜像 std::cout <<std::endl; }};// 计算机的基类class AppleComputer : public Computer{public : AppleComputer(OS *os) :Computer(os) { } virtual ~AppleComputer( ){ }; void InstallOS( ) // 在计算机上安装操作系统 { std::cout <<"This is a APPLE computer..." <<std::endl; this->m_os->InstallOSImage( ); // 安装操作系统的镜像 std::cout <<std::endl; }};////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////int main(){ OS *os = NULL; Computer *com = NULL; os = new WindowsOS( ); com = new DellComputer(os); com->InstallOS( );// Dell上安装了Windows delete os; os = NULL; delete com; com = NULL; os = new LinuxOS( ); com = new AcerComputer(os); com->InstallOS( );// 宏基上装了个Linux delete os; os = NULL; delete com; com = NULL; os = new MacOS( ); com = new AppleComputer(os); // 苹果电脑上安装MACOS com->InstallOS( ); delete os; os = NULL; delete com; com = NULL; return 0;}给我老师的人工智能教程打call!http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/jiangjunshow

 桥接模式解析与实例
桥接模式解析与实例







 本文深入探讨桥接模式在解决多维度变化问题中的应用,通过汽车和电脑操作系统安装的实例,阐述如何通过桥接模式降低类结构复杂度,提高代码的可扩展性和维护性。
本文深入探讨桥接模式在解决多维度变化问题中的应用,通过汽车和电脑操作系统安装的实例,阐述如何通过桥接模式降低类结构复杂度,提高代码的可扩展性和维护性。
















 1169
1169

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








