文章目录
- 窗口分析函数
-
-
- 1. 分析函数
- 2. 聚合函数
- 3. 窗口函数
-
- 行列转换
-
-
- 1. 行转列
- 2. 列转行
-
- JSON处理
-
-
- 1. JSON对象
- 2. JSON数组
-
- Hive SQL
- Spark SQL
-
- 时间处理
窗口分析函数
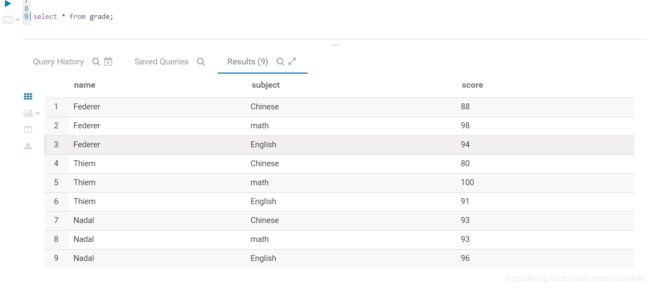
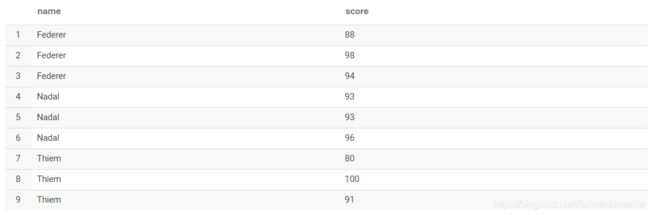
函数中用到的表数据如下图:
1. 分析函数
- row_number()
- rank()
- dense_rank()
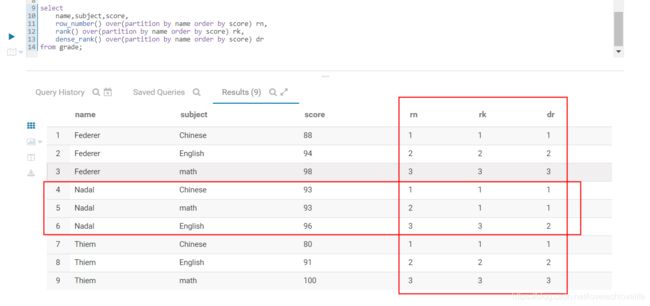
这3个函数通常用在组内排序中,但实现的效果却不相同,用法如下:
select
name,subject,score,
row_number() over(partition by name order by score) rn,
rank() over(partition by name order by score) rk,
dense_rank() over(partition by name order by score) dr
from grade;
排序之后编号对比, 如下图:
2. 聚合函数
- count()组内计数
- sum()组内求和
- avg()组内求平均值
- max()&min()组内求最大最小值
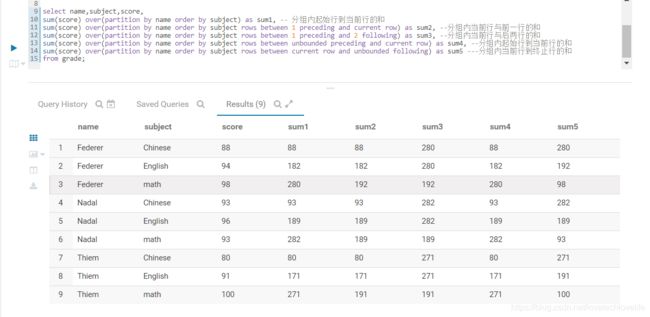
下面SQL以sum函数为例展示聚合函数的用法,其他函数的用法类似。
select
name,subject,score,
sum(score) over(partition by name order by subject) as sum1, -- 分组内起始行到当前行的和
sum(score) over(partition by name order by subject rows between 1 preceding and current row) as sum2, --分组内当前行与前一行的和
sum(score) over(partition by name order by subject rows between 1 preceding and 2 following) as sum3, --分组内当前行与后两行的和
sum(score) over(partition by name order by subject rows between unbounded preceding and current row) as sum4, --分组内起始行到当前行的和
sum(score) over(partition by name order by subject rows between current row and unbounded following) as sum5 ---分组内当前行到终止行的和
from grade;
计算结果如下图:
3. 窗口函数
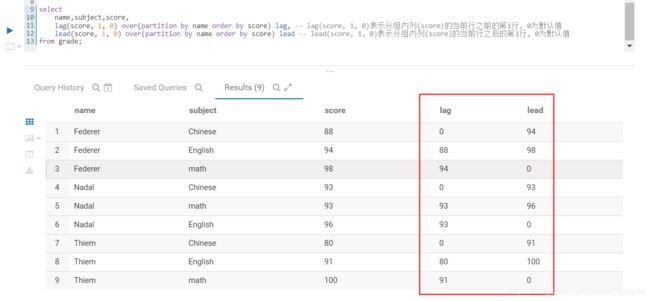
- lag(col, n, default) 表示分组内列(col)的当前行之前的第n行, default为默认值
- lead(col, n, default) 表示分组内列(col)的当前行之后的第n行, default为默认值
用法如下图:
select
name,subject,score,
lag(score, 1, 0) over(partition by name order by score) lag, -- lag(score, 1, 0)表示分组内列(score)的当前行之前的第1行, 0为默认值
lead(score, 1, 0) over(partition by name order by score) lead -- lead(score, 1, 0)表示分组内列(score)的当前行之后的第1行, 0为默认值
from grade;
结果如下图:
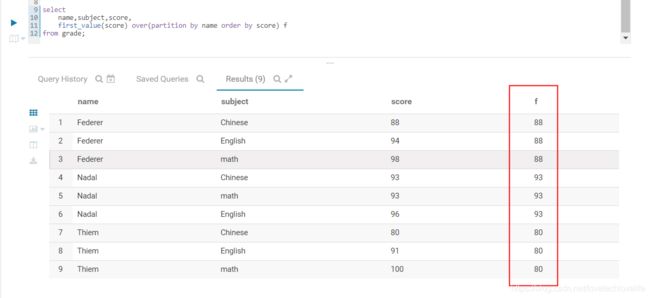
- first_value(col) 组内排序第一个值
- last_value(col) 组内排序最后一个值
用法如下图:
select
name,subject,score,
first_value(score) over(partition by name order by score) f
from grade;
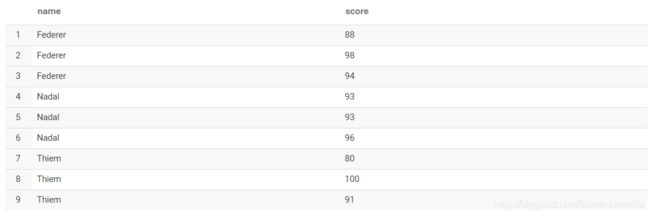
行列转换
1. 行转列
原始数据如下图:
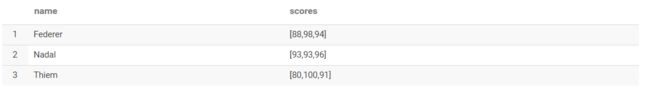
转换SQL:
select name, collect_list(score) from grade group by name;
结果:
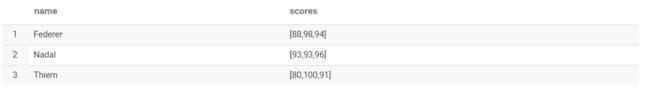
2. 列转行
原始数据:
转换SQL:
select name, score from grade lateral view explode (scores) tmp as score
结果:
JSON处理
1. JSON对象
JSON对象的处理可以用get_json_object()函数或json_tuple()函数。
字段field的值是一个JSONObject:{“status”:0,“version”:“v1.0”}
- get_json_object()
select get_json_object(field, "$.status"), get_json_object(field, "$.version") from db.table; - json_tuple()
如果需要获取多个key的值,建议用json_tuple函数,性能优于get_json_object()。select json.status, json.version from qjdods.cif_credit_report t lateral view json_tuple(report_value, 'status', 'version') json as status, version limit 1;
2. JSON数组
Hive SQL
Hive中的处理思路:
- 把JSON对象之间的逗号(,)替换成特殊字符,比如^*,因为之后要以这个特殊字符串来切分
- 替换掉中括号([]),为空
- 以步骤1中的特殊字符串切分处理后的JSON数组
- 结合 lateral view explode()函数,使得JSON数组转成多行JSON对象
select
id, json
from db.table
lateral view explode(
split(
regexp_replace(regexp_replace(json_array, "},", "}^*^*"), "\\[|\\]", ""), "\\^\\*\\^\\*"
)
) t as json
Spark SQL
使用Hive SQL处理JSON数组有一个弊端,如果JSON数组里面有嵌套数组的时候,单纯的替换掉中括号得出的结果就是错误的。而Spark SQL提供了一个内建函数substring_index(str: Column, delim: String, count: Int),这个函数可以从指定的索引位置,并指定指定分隔符来切分字符串,这样就可以实现只替换JSON数组中的首尾中括号。当然,在Hive SQL也可以自己写一个UDF来实现这个功能。
实现代码如下:
//Json数组行转列
def explodeFunc(spark: SparkSession, df: Dataset[Row]): Dataset[Row] = {
import spark.implicits._
df.select($"user_id",
explode(
split(
substring_index(
substring_index(
regexp_replace($"json_array", "},", "}^*^*"),
"[", -1),
"]", 1),
"\\^\\*\\^\\*"
)
).as("json")
)
}
时间处理
- 获取当前时间,并格式化(yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss)
from_unixtime(unix_timestamp(), 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')








 本文详细介绍了窗口分析函数(row_number(), rank(), dense_rank())、聚合函数(如sum(), avg())及时间处理在HiveSQL和SparkSQL中的实践,包括行转列和列转行操作,以及如何处理JSON对象和数组。
本文详细介绍了窗口分析函数(row_number(), rank(), dense_rank())、聚合函数(如sum(), avg())及时间处理在HiveSQL和SparkSQL中的实践,包括行转列和列转行操作,以及如何处理JSON对象和数组。
















 1073
1073

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








