注:本文为 “MLPPP ” 相关合辑。
英文引文,机翻未校。
略作重排,未整理去重。
如有内容异常,请看原文。
What is MLPPP?
MLPPP
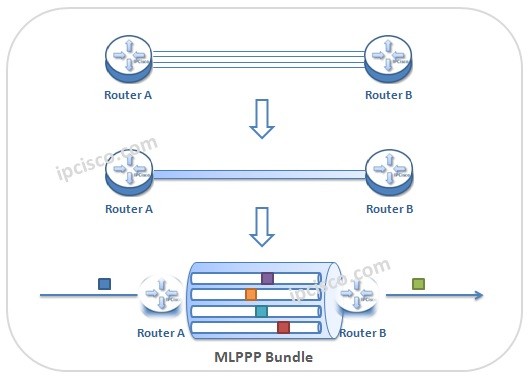
MLPPP (Multilink Point-to-Point Protocol) is the protocol that bundles multiple serial WAN links into one Logical Bundle. As a name, PPP Multilink, MLP and MP are also used for MLPPP (Multilink Point-to-Point Protocol). Here, we will learn the theoretical parts.
MLPPP(多链路点对点协议) 是一种将多个串行广域网链路捆绑成一个逻辑链路的协议。PPP Multilink、MLP 和 MP 也是 MLPPP(多链路点对点协议) 的别称。在这里,我们将学习其理论部分。
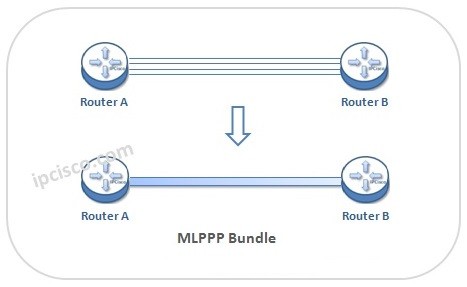
There can be multiple PPP serial links between two nodes. With MLPPP, these links are bundled and become a single logical link.
在两个节点之间可以有 多个 PPP 串行链路。通过 MLPPP,这些链路被捆绑成一个单一的逻辑链路。
PPP Multilink Load Balancing
PPP 多链路负载均衡
In PPP Multilink, Load Balancing is used between the member links of the Logical Link. The traffic is shared between each link of these links. Load Balancing is used with fragmentation in MLPPP.
在 PPP 多链路 中,负载均衡 用于逻辑链路的成员链路之间。流量在这些链路的每条链路之间共享。在 MLPPP 中,负载均衡与分片功能一起使用。
PPP Multilink Fault Tolerance
PPP 多链路容错
MLPPP provides Fault Tolerance with multiple links to the same destination. If one of the links between the nodes fails, the link stays up and the communication continues. With this mechanism, MLPPP also provides redundancy between links.
MLPPP 通过提供到同一目的地的多条链路来实现 容错功能。如果节点之间的某条链路失败,链路仍然保持连接状态,通信继续进行。通过这种机制,MLPPP 还提供了链路之间的 冗余。
Easiness in Layer 3
第 3 层配置的简便性
The Layer 3 configuration, IP configurations and Routing Protocol configurations are done on the Logical interface of PPP Multilink. So, MLPPP provides also a Layer 3 configuration easiness.
PPP 多链路 的逻辑接口上完成第 3 层配置、IP 配置以及路由协议配置。因此,MLPPP 还提供了第 3 层配置的便利性。
MLPPP Fragmentation
MLPPP 分片
In MLPPP (PPP Multilink), packet fragmentation is also supported besides load balancing. With packet fragmentation, the packets that are fragmented are sent at the same time in different members of the Logical Bundle.
在 MLPPP(PPP 多链路) 中,除了负载均衡之外,还支持 数据包分片。通过数据包分片,分片后的数据包会同时通过逻辑捆绑的不同成员链路发送。

Here, if the coming packet has MLPPP Header, it is fragmented and sequenced and at the other end it is reassembled. If it is not, the packet is not sequenced and sent only as first come first sent.
如果传入的数据包带有 MLPPP 头,则会对其进行分片和排序,然后在另一端重新组装。如果没有,则数据包不会排序,而是按照先到先发送的方式发送。
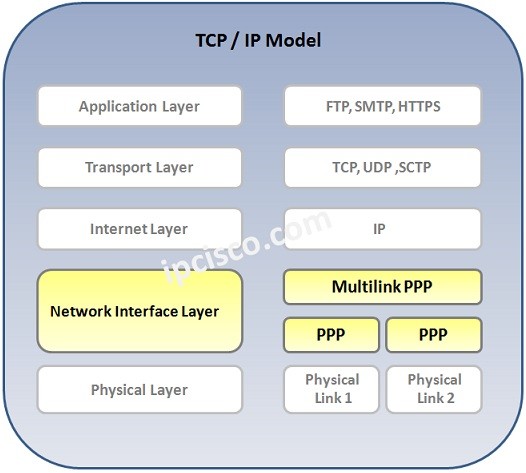
MLPPP in TCP/IP Model
MLPPP 在 TCP/IP 模型中的位置
In TCP/IP Model, PPP Multilink works in the Network Interface Layer like PPP. But it is above the PPP in the hierarchy.
在 TCP/IP 模型中,PPP 多链路 与 PPP 一样工作在网络接口层,但它在层次结构中位于 PPP 之上。
Multilink PPP: One Big Virtual WAN Pipe
多链路 PPP:一个大型虚拟广域网管道
Webmaster
by George E. author)
on September 1, 1999
Network management is a little like alchemy: take a dash or two of ISDN, add some frame relay, throw in a couple of routers, mix them all together, and somehow, some way, the result is bandwidth gold.
网络管理有点像炼金术:加入一些 ISDN,添加一些帧中继,再加入几个路由器,将它们混合在一起,不知何故,最终得到了带宽的黄金。
Of course, the formula for creating fully interoperable networks is much more complicated. Fortunately, network managers do have access to some tools that can make bandwidth magic a little easier to perform. Two of the most important elements in the technology bag of tricks are the point-to-point protocol (PPP) and its follow-up, the multilink point-to-point protocol (MLPPP).
当然,创建完全互操作网络的公式要复杂得多。幸运的是,网络管理员确实可以使用一些工具来使带宽魔法更容易实现。技术工具包中最重要的两个元素是点对点协议 (PPP) 及其后续的多链路点对点协议 (MLPPP)。
PPP, a product of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), is the de facto WAN link protocol for connecting clients and servers and for interconnecting routers to form enterprise networks. PPP’s main advantage is that unlike other protocols which operate at the data link layer, PPP achieves interoperability between devices by negotiating different configuration options, including link quality, link authentication and network protocols.
PPP 是互联网工程任务组 (IETF) 的产品,是连接客户端和服务器以及互连路由器以形成企业网络的实际广域网链路协议。PPP 的主要优势在于,与其他在数据链路层运行的协议不同,PPP 通过协商不同的配置选项(包括链路质量、链路认证和网络协议)来实现设备之间的互操作性。
Over the years, the IETF has made some significant changes to PPP. But as its name states, PPP is intended for simple point-to-point connections. Now that the enterprise network infrastructure is moving rapidly to digital switched services such as ISDN, frame relay and ATM, PPP is in need of even more changes.
多年来,IETF 对 PPP 做出了一些重大更改。但正如其名称所示,PPP 旨在用于简单的点对点连接。如今,企业网络基础设施正迅速转向数字交换服务(如 ISDN、帧中继和 ATM),PPP 需要更多的更改。
Enter MLPPP, known in IETF circles as RFC (Request for Comment) 1717. MLPPP takes advantage of the ability of switched WAN services to open multiple virtual connections between devices to give users extra bandwidth as needed. With MLPPP, routers and other access devices can combine multiple PPP links connected to various WAN services into one logical data pipe.
于是出现了 MLPPP,在 IETF 中被称为 RFC(征求意见)1717。MLPPP 利用了交换式广域网服务在设备之间打开多个虚拟连接的能力,以按需为用户提供额外的带宽。借助 MLPPP,路由器和其他接入设备可以将连接到各种广域网服务的多个 PPP 链路组合成一个逻辑数据管道。
The IETF formally approved the MLPPP specification last November. Makers of ISDN routers and access devices have already started using MLPPP to bundle 64Kbps ISDN B channels to deliver more bandwidth. MLPPP also allows network managers aggregate WAN circuits of different types without requiring major configuration changes to existing router Internet works.
IETF 于去年 11 月正式批准了 MLPPP 规范。ISDN 路由器和接入设备的制造商已经开始使用 MLPPP 来捆绑 64Kbps 的 ISDN B 信道以提供更多的带宽。MLPPP 还允许网络管理员在无需对现有路由器互联网进行重大配置更改的情况下聚合不同类型的广域网电路。
Because MLPPP works over any switched WAN service, it has a wide range of potential uses (see “PPP Plus”). Network managers could deploy MLPPP-equipped devices to create a technology-independent enterprise framework in which the actual WAN services linking two devices would be invisible to end users. Under this model, WAN devices would negotiate bandwidth rules between two directly connected peers, using whatever type of service was available. New digital WAN services such as ATM (asynchronous transfer mode) could be added to the network mix as needed, without making the existing network infrastructure obsolete.
由于 MLPPP 可以在任何交换式广域网服务上工作,因此它具有广泛的应用潜力(参见“PPP 加强版”)。网络管理员可以部署配备 MLPPP 的设备,创建一个技术独立的企业框架,在该框架中,连接两台设备的实际广域网服务对最终用户来说是不可见的。在这种模式下,广域网设备会在两个直接连接的对等方之间协商带宽规则,使用任何可用的服务类型。根据需要,可以将新的数字广域网服务(如 ATM,即异步传输模式)添加到网络组合中,而不会使现有的网络基础设施过时。
The ABCs of PPP
Although it is usually considered a single entity, PPP is actually a group of protocols that together provide an extensive set of network connectivity services. The PPP suite is based on four key design principles: negotiation of configuration options, multi-protocol support, protocol extendibility and WAN service independence.
尽管 PPP 通常被视为一个单一实体,但实际上它是一组提供广泛网络连接服务的协议。PPP 协议套件基于四个关键设计原则:配置选项的协商、多协议支持、协议可扩展性和广域网服务独立性。
在这里,“ABCs” 是一个常用的英语短语,意思是“基础知识”或“基本要素”,类似于我们说的“入门知识”或“基础部分”。因此,“The ABCs of PPP” 可以理解为“PPP 的基础知识”或“PPP 的基本原理”。
这一部分主要介绍了 PPP 的四个关键设计原则,这些原则是理解 PPP 协议的基础。具体来说,这些原则包括:
Negotiation of configuration options(配置选项的协商)
PPP 能够在两个直接连接的终端系统之间协商各种配置选项,如数据封装格式、数据包大小、链路质量和认证方式等。这使得 PPP 能够适应不同的网络环境和设备需求。Multi-protocol support(多协议支持)
PPP 支持多种网络层协议,如 IP、Novell IPX、AppleTalk 等。这意味着 PPP 可以在不同的网络环境中工作,而不仅仅局限于某一种协议。Protocol extendibility(协议可扩展性)
PPP 可以通过扩展来支持新的功能和特性。例如,通过额外的 RFC(Request for Comments,征求意见)文档,PPP 可以增加数据认证服务、加密功能以及压缩算法等。WAN service independence(广域网服务独立性)
PPP 不依赖于特定的广域网服务,它可以运行在多种广域网技术上,如 ISDN、帧中继、X.25 等。这使得 PPP 具有很强的通用性和适应性。
这些原则共同构成了 PPP 协议的核心特性,使得 PPP 成为一种广泛使用的网络协议。通过理解这些基础知识,读者可以更好地理解 PPP 在网络通信中的作用和优势。
Negotiation of configuration options: This refers to PPP’s ability to establish throughput requirements between two directly connected end systems. In an enterprise network, end systems often differ in terms of buffer requirements, packet-size limits and network protocol-support lists. The physical link that interconnects any two end systems could vary from a low-speed analog line to a high-speed digital connection with varying degrees of line quality.
配置选项的协商:这指的是 PPP 在两个直接连接的终端系统之间建立吞吐量需求的能力。在企业网络中,终端系统通常在缓冲区需求、数据包大小限制和网络协议支持列表方面存在差异。连接任意两个终端系统的物理链路可以从低速模拟线路到具有不同线路质量的高速数字连接不等。
To cope with all these possibilities, PPP has a suite of standard default settings to handle all common configurations. To establish a link, two communicating devices attempt to use these default settings to find a common ground. Each end of the PPP link describes its capabilities and requirements; the settings are negotiated between the two sides for each option at the link level. These options include data encapsulation formats, packet sizes, link quality and authentication.
为了应对所有这些可能性,PPP 有一套标准的默认设置,用于处理所有常见配置。为了建立链路,两个通信设备会尝试使用这些默认设置来找到共同点。PPP 链路的每一端都会描述其能力和需求;链路层的每一选项都会在双方之间进行协商。这些选项包括数据封装格式、数据包大小、链路质量和认证。
The protocol that negotiates all these options is known as the link control protocol (LCP). The protocol that negotiates the network protocols to be multiplexed over a PPP link is called the network control protocol (NCP); there can be many NCP data streams over a single PPP link. Although PPP’s configuration negotiation options also allow end systems to set link peer authentication (a security function) and data compression options, PPP does not dictate the actual algorithms used for security or compression. For security, PPP defines PAP (password authentication protocol) and CHAP (challenge handshake authentication protocol) as common standard authentication methods that may be negotiated, but it also lets users add new authentication algorithms. The same holds true for compression.
协商所有这些选项的协议称为链路控制协议 (LCP)。协商将在 PPP 链路上复用的网络协议的协议称为网络控制协议 (NCP);在单个 PPP 链路上可以有多个 NCP 数据流。尽管 PPP 的配置协商选项还允许终端系统设置链路对等方认证(一种安全功能)和数据压缩选项,但 PPP 并不规定用于安全或压缩的实际算法。对于安全,PPP 定义了 PAP(密码认证协议)和 CHAP(挑战握手认证协议)作为可以协商的通用标准认证方法,但它也允许用户添加新的认证算法。对于压缩也是如此。
Multi-protocol support: PPP’s ability to handle multiple network-layer protocols was one of the chief reasons it became a de facto standard. Unlike the serial IP protocol (SLIP), the IETF routing protocol that handles only IP datagrams, PPP works with a range of packet formats including IP, Novell IPX, AppleTalk, DECnet, XNS, Banyan Vines and OSI. Each network-layer protocol is separately configured by the appropriate NCP.
多协议支持:PPP 处理多种网络层协议的能力是其成为事实标准的主要原因之一。与仅处理 IP 数据报的 IETF 路由协议串行 IP 协议 (SLIP) 不同,PPP 支持包括 IP、Novell IPX、AppleTalk、DECnet、XNS、Banyan Vines 和 OSI 在内的多种数据包格式。每种网络层协议都由相应的 NCP 单独配置。
Protocol extendibility: Over the years, the IETF extended PPP through a number of additional RFCs that define features like common data authentication services and encryption capabilities for security and compression algorithms. For example, with many WAN technologies, compression algorithms are chosen according to the quality of the link. Different technologies use different compression schemes, introducing multiple layers of compression and decompression into the network. Running PPP compression at the NCP level removes these considerations and uses fewer system resources.
协议可扩展性:多年来,IETF 通过许多额外的 RFC 对 PPP 进行了扩展,定义了诸如通用数据认证服务和安全及压缩算法的加密功能等特性。例如,在许多广域网技术中,根据链路的质量选择压缩算法。不同的技术使用不同的压缩方案,从而在网络中引入了多层压缩和解压缩。在 NCP 级别运行 PPP 压缩可以消除这些考虑因素,并使用更少的系统资源。
WAN service independence: The initial version of PPP was built expressly to run over HDLC (high-level data link control) networks. Since then, the IETF has added RFCs that enable PPP to work with every major WAN service now in use including ISDN, frame relay, X.25, Sonet and synchronous/asynchronous HDLC framing.
广域网服务独立性:PPP 的最初版本是专门为在 HDLC(高级数据链路控制)网络上运行而设计的。从那时起,IETF 增加了 RFC,使 PPP 能够与目前正在使用的每一种主要广域网服务一起工作,包括 ISDN、帧中继、X.25、Sonet 以及同步/异步 HDLC 帧。
The Need for MLPPP
MLPPP 的需求
For all its strengths, PPP has one inherent limitation when it comes to network deployment: it is designed to handle only one physical link at a time. MLPPP does away with this restriction. MLPPP is a higher-level data link protocol that sits between PPP and the network protocol layer. It accommodates one or more PPP links, with each PPP link representing either a separate physical WAN connection or a channel in a multichannel switched service, such as ISDN or frame relay.
尽管 PPP 有许多优点,但在网络部署方面存在一个固有限制:它被设计为一次只能处理一个物理链路。MLPPP 消除了这一限制。MLPPP 是一种位于 PPP 和网络协议层之间的高级数据链路协议。它可以容纳一个或多个 PPP 链路,每个 PPP 链路代表一个单独的物理广域网连接或一个多信道交换服务(如 ISDN 或帧中继)中的一个信道。
MLPPP’s ability to combine multiple lower-speed links into a single, higher-speed data path is often referred to as WAN-independent or packet-based inverse multiplexing (see “WAN Independence” below). Packet-based inverse muxing isn’t new; for instance, ISDN vendors have been offering ways to combine multiple ISDN 64Kbps B channels for some time. But up to now, these solutions have been proprietary: vendor and technology-specific. MLPPP embodies a standard approach that cuts across vendor and WAN technology lines.
MLPPP 将多个低速链路组合成一条高速数据路径的能力通常被称为广域网独立或基于数据包的反向复用(参见下面的“广域网独立性”)。基于数据包的反向复用并非新事物;例如,ISDN 供应商早就提供了一些将多个 ISDN 64Kbps B 信道组合在一起的方法。但到目前为止,这些解决方案都是专有的:特定于供应商和技术。MLPPP 体现了一种跨越供应商和广域网技术领域的标准方法。
MLPPP negotiates configuration options the same way as conventional PPP. However, during the negotiation process, one router or access device indicates to the other communicating device that it is willing to combine multiple connections and treat them as a single physical pipe. It does this by sending along a multilink option message as part of its initial LCP option negotiation.
MLPPP 以与传统 PPP 相同的方式协商配置选项。然而,在协商过程中,一个路由器或接入设备会向另一个通信设备表明,它愿意将多个连接组合在一起,并将它们视为一个物理管道。它通过在初始 LCP 选项协商中发送一个多链路选项消息来实现这一点。
Once a multilink session is successfully opened, MLPPP at the sending side receives network protocol data units (PDUs) from higher-layer protocols or applications. It then fragments those PDUs into smaller packets, adds an MLPPP header to each fragment and sends them over the available PPP links (see Figure 1). On the receiving end, the MLPPP software takes the fragmented packets from the different links, puts them in their correct order based on their MLPPP headers and reconverts them to their original network-layer PDUs.
一旦成功打开一个多链路会话,发送端的 MLPPP 会从更高层的协议或应用程序接收网络协议数据单元(PDUs)。然后,它将这些 PDUs 分片成更小的数据包,在每个分片上添加一个 MLPPP 头,并将它们发送到可用的 PPP 链路上(参见图 1)。在接收端,MLPPP 软件会从不同的链路上获取分片的数据包,根据它们的 MLPPP 头将它们按正确的顺序排列,并将它们重新转换为原始的网络层 PDUs。
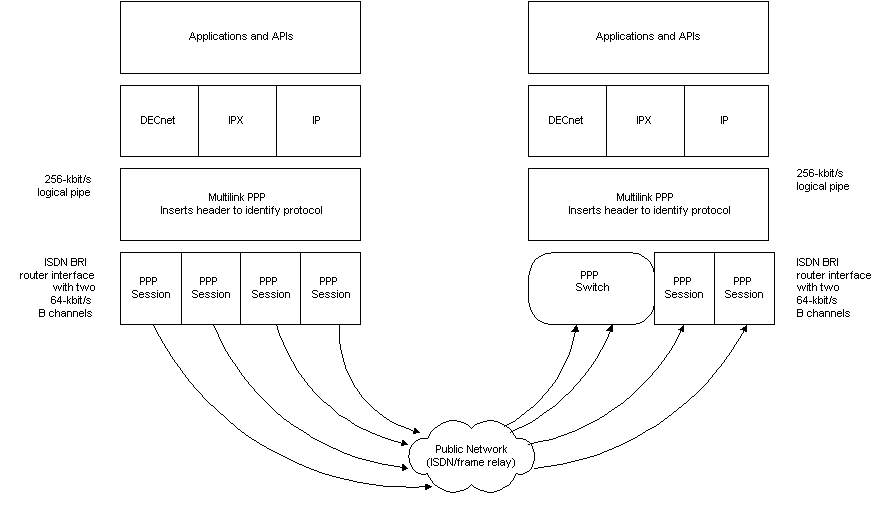
Figure 1. The Multiprotocol Link
图 1. 多协议链路
MLPPP is independent of the actual physical links and the WAN services that run over them. This means MLPPP traffic can traverse a mix of physical and logical connections from multiple WAN services—a frame relay virtual circuit, multiple ISDN channels and an X.25 connection, for example. MLPPP functions as a logical link layer that dynamically adds or removes links between two communicating devices as bandwidth needs change. The MLPPP standard does not dictate how traffic is balanced over these member PPP links, leaving network managers free to determine how to use the available links or channels.
MLPPP 与实际的物理链路和在其上运行的广域网服务无关。这意味着 MLPPP 流量可以跨越多个广域网服务的物理和逻辑连接的混合体——例如帧中继虚拟电路、多个 ISDN 信道和 X.25 连接。MLPPP 作为一个逻辑链路层,根据带宽需求的变化动态地在两个通信设备之间添加或删除链路。MLPPP 标准并不规定流量如何在这些成员 PPP 链路之间进行平衡,从而让网络管理员自由决定如何使用可用的链路或信道。
MLPPP’s ability to combine separate PPP links into one logical data pipe is one of the most important features of the protocol. It allows additional WAN bandwidth or new WAN services to be added as needed without disrupting the existing WAN infrastructure. With MLPPP, different WAN services such as ISDN, frame relay and ATM can be used together. For instance, a network manager can establish a frame relay connection to serve as the primary link between a central site and a branch office, with ISDN serving as an adjunct when bandwidth demand rises (see Figure 2).
将单独的 PPP 链路组合成一个逻辑数据管道是该协议最重要的特性之一。它允许根据需要添加额外的广域网带宽或新的广域网服务,而不会干扰现有的广域网基础设施。通过 MLPPP,不同的广域网服务(如 ISDN、帧中继和 ATM)可以一起使用。例如,网络管理员可以建立一个帧中继连接,作为中心站点和分支机构之间的主要链路,当带宽需求增加时,ISDN 作为辅助链路(参见图 2)。
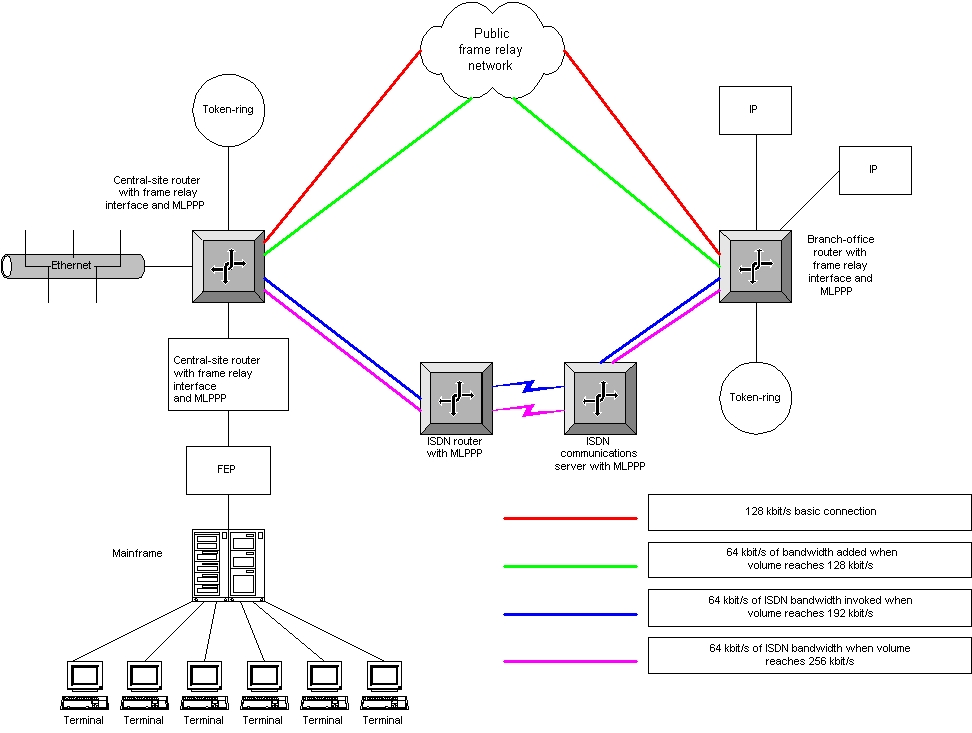
Figure 2. Many Circuits, One Pipe
图 2. 多电路,一根管道
Through the dynamic addition and deletion of PPP links, MLPPP enables dynamic bandwidth allocation, or “rubber bandwidth”, between two peer systems. During the LCP option negotiation, all PPP links in an MLPPP group identify themselves as belonging to the same group or bundle. To add a new link or WAN service to the bundle, all that’s required is attaching the appropriate MLPPP group identifier to the link. Likewise, when a member PPP link is terminated, it is automatically removed from its parent MLPPP bundle by eliminating the identifier.
通过动态添加和删除 PPP 链路,MLPPP 实现了两个对等系统之间的动态带宽分配,或称为“弹性带宽”。在 LCP 选项协商期间,MLPPP 组中的所有 PPP 链路都将自己标识为属于同一个组或捆绑包。要将新的链路或广域网服务添加到捆绑包中,只需将适当的 MLPPP 组标识符附加到链路上即可。同样,当成员 PPP 链路终止时,通过删除标识符,它将自动从其父 MLPPP 捆绑包中移除。
PPP is WAN service-independent, so the member links of an MLPPP bundle can be associated with either permanent virtual circuits (PVCs), which have fixed end points, or switched virtual circuits (SVCs), which are dialed up on demand.
PPP 与广域网服务无关,因此 MLPPP 捆绑包的成员链路可以与具有固定端点的永久虚拟电路(PVC)或按需拨号的交换虚拟电路(SVC)相关联。
MLPPP’s ability to create different groups of WAN links produces some intriguing possibilities for network managers. For instance, they could use MLPPP to segregate traffic according to the network-layer protocol. This approach would enable network managers to separate expedited control messages from normal data traffic or to queue data into separate MLPPP bundles based on application-specific requirements.
MLPPP 创建不同广域网链路组的能力为网络管理员带来了一些有趣的可能性。例如,他们可以使用 MLPPP 根据网络层协议对流量进行分隔。这种方法将使网络管理员能够将紧急控制消息与正常数据流量分开,或者根据特定应用程序的要求将数据排队到不同的 MLPPP 捆绑包中。
Here’s an example of how MLPPP’s segregated packet queueing works. Suppose a central site is connected to a remote site via two 64Kbps frame-relay links and two ISDN basic-rate interface (BRI) connections. Two types of traffic traverse these links: IP traffic from UNIX operations and DECnet traffic from a Digital Equipment Corporation VAX network. If the frame relay and ISDN channels are treated as one MLPPP bundle, both traffic types have access to the full bandwidth of the link at any given time.
以下是一个关于 MLPPP 的分隔数据包排队如何工作的例子。假设一个中心站点通过两条 64Kbps 的帧中继链路和两条 ISDN 基本速率接口(BRI)连接与一个远程站点相连。这两种链路上传输着两种类型的流量:来自 UNIX 操作的 IP 流量和来自 Digital Equipment Corporation VAX 网络的 DECnet 流量。如果将帧中继和 ISDN 信道视为一个 MLPPP 捆绑包,那么这两种流量类型在任何给定时间都可以访问链路的全部带宽。
The single-pipe approach makes for easier network management, but it could create problems if one traffic type starts dominating the pipe. In this example, if the UNIX IP traffic started bursting beyond 60 percent of the overall link rate, it would begin to eat into bandwidth available for DECnet, slowing performance for users on the VAX network.
单一管道方法使网络管理更加容易,但如果一种流量类型开始主导管道,它可能会引发问题。在这个例子中,如果 UNIX IP 流量开始超过整个链路速率的 60%,它将开始占用 DECnet 可用的带宽,从而降低 VAX 网络上用户的性能。
With MLPPP, this problem can be avoided. The network manager can not only combine various physical interfaces to create one large pipe, but also allocate channels within that virtual pipe. For instance, the network manager can create two 128-kbit/s MLPPP bundles, each consisting of a single ISDN B channel and a 64Kbps frame-relay link. Those bundles could then be dedicated to each type of traffic.
通过 MLPPP,可以避免这个问题。网络管理员不仅可以将各种物理接口组合在一起创建一个大管道,还可以在该虚拟管道内分配信道。例如,网络管理员可以创建两个 128 kbit/s 的 MLPPP 捆绑包,每个捆绑包由一个 ISDN B 信道和一个 64Kbps 的帧中继链路组成。然后,这些捆绑包可以专门用于每种类型的流量。
Spoofing
伪装
One big problem with using routers for switched WAN services isn’t activating a link, but shutting it down when data transfer is done. Most LAN protocols and client-server applications are chatty, carrying on almost incessant messaging to synchronize routing databases and maintain client-server sessions.
使用路由器进行交换式广域网服务的一个大问题是,问题不在于激活链路,而在于数据传输完成后关闭链路。大多数局域网协议和客户端 - 服务器应用程序都很“健谈”,几乎不停地发送消息以同步路由数据库并维持客户端 - 服务器会话。
Left unchecked, these processes can keep an ISDN link up indefinitely without passing a single byte of application data. Needless to say, all this uptime quickly adds up, especially where charges are based on call duration. Considering that more than 35 percent of WAN costs are related to line costs, the ability to control activation and deactivation of member links in an MLPPP group is crucial.
如果不对这些过程加以控制,它们可以在没有传递任何应用程序数据的情况下无限期地保持 ISDN 链路处于激活状态。不用说,所有这些在线时间很快就会累积起来,特别是在按通话时长计费的情况下。鉴于超过 35% 的广域网成本与线路成本有关,控制 MLPPP 组中成员链路的激活和去激活的能力至关重要。
MLPPP offers two solutions: usage thresholds and spoofing. In the usage threshold scheme, once a circuit becomes idle or the traffic it carries falls below a level predefined by the network manager, MLPPP will automatically remove that circuit from its bundle until demand rises. The problem with the usage threshold approach is that it can be difficult to define threshold levels effectively in bursty environments using chatty protocols. For example, in Novell IPX environments, it can be difficult to gauge the requirements of SAP (service advertising protocol) and RIP (router information protocol) messages.
MLPPP 提供了两种解决方案:使用阈值和伪装。在使用阈值方案中,一旦电路处于空闲状态或其所承载的流量低于网络管理员预定义的水平,MLPPP 将自动将该电路从其捆绑包中移除,直到需求增加为止。使用阈值方法的问题在于,在使用健谈协议的突发环境中,很难有效定义阈值水平。例如,在 Novell IPX 环境中,很难衡量 SAP(服务广告协议)和 RIP(路由器信息协议)消息的要求。
Spoofing helps address this problem. It is a technique used by routers to filter network traffic. Spoofing keeps unnecessary traffic like session keep-alive messages from traversing the WAN link. Rather than sending these messages over the WAN, the router acts as a proxy and responds to them locally. Once the router takes over the polling and responses for the application, the WAN link can be shut down until it is truly needed.
伪装有助于解决这个问题。这是一种由路由器用来过滤网络流量的技术。伪装可以防止像会话保持消息这样的不必要的流量通过广域网链路。路由器不会将这些消息发送到广域网,而是充当代理并在本地进行响应。一旦路由器接管了应用程序的轮询和响应,广域网链路就可以关闭,直到真正需要时为止。
WAN Magic
广域网魔法
MLPPP’s WAN service independence means users and network managers can be insulated from network service changes. As new WAN services, such as frame relay and ATM become available, MLPPP can be used to incorporate them into logical bundles. To routers, MLPPP looks like a data link protocol; the router doesn’t have to deal with the complexity of the various physical connections and switched circuits that MLPPP draws together in its logical pipes. This helps reduce router reconfiguration costs, since a new router interface isn’t required when a new WAN service is added.
MLPPP 的广域网服务独立性意味着用户和网络管理员可以免受网络服务变更的影响。随着诸如帧中继和 ATM 等新的广域网服务的出现,MLPPP 可以将它们纳入逻辑捆绑包中。对于路由器来说,MLPPP 看起来就像一种数据链路协议;路由器无需处理 MLPPP 在其逻辑管道中整合的各种物理连接和交换电路的复杂性。这有助于降低路由器重新配置的成本,因为在添加新的广域网服务时无需新的路由器接口。
To network managers, the difference between adding a new circuit or virtual circuit to an MLPPP bundle and adding a router interface is significant. Adding a circuit to a preexisting MLPPP logical pipe is transparent to the network, particularly in switched environments like ISDN, frame relay or ATM. It simply adds bandwidth to the pipe; no additional interfaces or path information is required. In contrast, any change to a physical router interface triggers an update to the routing table of every router involved in the change. In environments where circuits are frequently activated and deactivated, this could generate excessive amounts of network topology changes and much extra work for network managers.
对于网络管理员来说,在 MLPPP 捆绑包中添加新的电路或虚拟电路与添加路由器接口之间的差异是显著的。在预先存在的 MLPPP 逻辑管道中添加电路对网络是透明的,特别是在像 ISDN、帧中继或 ATM 这样的交换环境中。它只是为管道增加了带宽;不需要额外的接口或路径信息。相比之下,对物理路由器接口的任何更改都会触发涉及更改的每个路由器的路由表更新。在电路频繁激活和去激活的环境中,这可能会产生大量的网络拓扑变更以及网络管理员的额外工作。
Not only can MLPPP save network managers time and effort, but it also offers an important tactical tool for network designers. It can be used to simplify fault management and build redundancy into the network at low cost.
MLPPP 不仅可以为网络管理员节省时间和精力,还可以为网络设计人员提供一个重要的战术工具。它可以用于简化故障管理,并以低成本在网络中构建冗余。
Keeping Up with ATM
跟上 ATM 的步伐
Along with making use of WAN services already in place, MLPPP is positioned to work with technologies just making it to the real world. The most prominent of these technologies is ATM.
除了利用现有的广域网服务外,MLPPP 还准备与刚刚进入现实世界的技术一起工作。其中最突出的技术是 ATM。
ATM SVCs can be activated and deactivated on demand, much like ISDN circuits. ATM circuits can be included in an MLPPP circuit group as more bandwidth is required. Bundling will become especially useful if lower-speed ATM ports (T1 or T3) become widely deployed.
ATM SVC 可以按需激活和去激活,就像 ISDN 电路一样。随着对更多带宽的需求增加,可以将 ATM 电路纳入 MLPPP 电路组。如果低速 ATM 端口(T1 或 T3)得到广泛应用,捆绑将变得特别有用。
In the long run, as ATM takes over the enterprise network backbone, things could get more complicated. ISDN, frame relay and ATM will dominate the WAN landscape, with ISDN and frame relay functioning as a feeder technology and ATM serving as the enterprise backbone aggregating ISDN and frame-relay circuits over faster pipes. An ATM pipe at Sonet OC3 speed (155Mbps) can aggregate more than 2,400 64Kbps ISDN B channels.
从长远来看,随着 ATM 接管企业网络骨干,事情可能会变得更加复杂。ISDN、帧中继和 ATM 将主导广域网领域,其中 ISDN 和帧中继作为馈线技术,ATM 作为企业骨干,通过更快的管道聚合 ISDN 和帧中继电路。一个速度为 Sonet OC3(155Mbps)的 ATM 管道可以聚合超过 2400 个 64Kbps 的 ISDN B 信道。
That is a large amount of bandwidth by today’s standards, but thanks to the rise of LAN switching and high-speed LANs, aggregate throughput requirements for the LAN will escalate at an even more rapid rate, reaching tens of gigabits per second in the next few years. To reduce the disparity between the LAN and WAN worlds, network managers will need to aggregate B channels and frame-relay circuits. Inverse multiplexing using MLPPP offers a flexible way to do this.
按照当今的标准,这是一个很大的带宽量,但由于局域网交换和高速局域网的兴起,局域网的聚合吞吐量需求将以更快的速度增长,在未来几年内将达到每秒数十吉比特。为了减少局域网和广域网之间的差异,网络管理员需要聚合 B 信道和帧中继电路。使用 MLPPP 的反向复用提供了一种灵活的方法来实现这一点。
PPP Plus
PPP 加强版
MLPPP delivers some key functions to help network managers build multi-protocol enterprise networks. Here are some of MLPPP’s strongest selling points:
MLPPP 提供了一些关键功能,帮助网络管理员构建多协议企业网络。以下是 MLPPP 最有力的一些卖点:
Mix-and-match WANs: With MLPPP, net managers can configure multiple physical links and virtual circuits as one logical pipe, using different WAN service types (ISDN, frame relay, X.25 and ATM) in the process.
混合匹配广域网:通过 MLPPP,网络管理员可以将多个物理链路和虚拟电路配置为一个逻辑管道,在此过程中使用不同类型的广域网服务(ISDN、帧中继、X.25 和 ATM)。
Bandwidth on demand: Circuits can be activated and added automatically to a logical pipe when more bandwidth is needed, or if one of the links in the logical pipe fails.
按需带宽:当需要更多带宽时,或者逻辑管道中的某个链路出现故障时,电路可以自动激活并添加到逻辑管道中。
Big protocol tent: MLPPP handles routing for all major network- and transport-layer protocols, including IP, IPX, Netbios, DECnet and SNA.
大协议阵营:MLPPP 处理所有主要的网络层和传输层协议(包括 IP、IPX、Netbios、DECnet 和 SNA)的路由。
Network negotiation: MLPPP has inherited PPP’s ability to negotiate configuration options between communicating devices. This means two end systems can set the terms of transmission without requiring manual intervention.
网络协商:MLPPP 继承了 PPP 在通信设备之间协商配置选项的能力。这意味着两个终端系统可以在不需要人工干预的情况下设定传输条件。
No traffic, no link: MLPPP uses LAN protocol spoofing to keep unnecessary network traffic, such as session keep-alive packets, from traversing the WAN.
无流量,无链路:MLPPP 使用局域网协议伪装来防止不必要的网络流量(如会话保持数据包)通过广域网。
WAN Independence
广域网独立性
The two basic types of inverse multiplexing are circuit-based and packet-based. Under the circuit-based scheme, a data stream is sliced into equal portions, regardless of its contents, with each portion transmitted over a different available circuit. With circuit-based inverse muxing, synchronization of traffic streams is generally handled by hardware.
反向复用的两种基本类型是基于电路的和基于数据包的。在基于电路的方案中,数据流被切分成相等的部分,不管其内容如何,每个部分都在不同的可用电路上传输。在基于电路的反向复用中,通常由硬件处理流量流的同步。
Packet-based inverse multiplexing is a software-based process. In this scheme, packets are distributed among available circuits according to rules or policies that govern allocation of traffic across circuits. These rules can include segregation according to protocol or percentage-based prioritization. The multilink point-to-point protocol (MLPPP) uses packet-based inverse multiplexing.
基于数据包的反向复用是一种基于软件的过程。在这种方案中,根据管理流量在电路之间分配的规则或策略,将数据包分配到可用的电路中。这些规则可以包括按协议分隔或基于百分比的优先级划分。多链路点对点协议(MLPPP)使用基于数据包的反向复用。
One key difference between the two approaches is that packet-based inverse multiplexing schemes can handle multiple circuit types, while circuit-based schemes cannot. With MLPPP, for example, a synchronous 56Kbps X.25 link can be bundled together with a 64Kbps ISDN B channel to create a single logical pipe offering 120Kbps of bandwidth. This bundling ability extends to the full range of available WAN services, including dial-up analog lines, switched 56Kbps services, frame-relay connections and T1 or T3 services.
这两种方法的一个关键区别是,基于数据包的反向复用方案可以处理多种电路类型,而基于电路的方案则不能。例如,通过 MLPPP,可以将一个同步的 56Kbps X.25 链路与一个 64Kbps 的 ISDN B 信道捆绑在一起,创建一个提供 120Kbps 带宽的单一逻辑管道。这种捆绑能力涵盖了所有可用的广域网服务,包括拨号模拟线路、交换的 56Kbps 服务、帧中继连接以及 T1 或 T3 服务。
Another difference is that packet-based inverse multiplexing is seamless to the destination router or end system. In the case of MLPPP, the flow of data appears consistent by means of software synchronization of MLPPP fragments. In contrast, circuit-based inverse muxing requires the receiving device to stop data flow until all bonded channels are characterized for latency. This is the only means by which the hardware-based solution can ensure data is received in the correct order.
另一个区别是,基于数据包的反向复用对目标路由器或终端系统来说是无缝的。在 MLPPP 的情况下,通过 MLPPP 片段的软件同步,数据流看起来是一致的。相比之下,基于电路的反向复用要求接收设备在所有绑定的信道被延迟特性描述之前停止数据流。这是基于硬件的解决方案确保数据按正确顺序接收的唯一方法。
Except for applications that require constant bit rate transmission or have strict requirements on circuit latency, software-based solutions are generally regarded as superior because they add considerable value and flexibility to the basic inverse muxing function. In the case of MLPPP, users are able to combine different WAN connections while taking advantage of PPP’s configuration negotiation and multi-protocol routing support.
除了对电路延迟有严格要求或需要恒定比特率传输的应用程序外,基于软件的解决方案通常被认为是优越的,因为它们为基本的反向复用功能增加了相当大的价值和灵活性。在 MLPPP 的情况下,用户可以在利用 PPP 的配置协商和多协议路由支持的同时,将不同的广域网连接组合在一起。
George E. Conant is a cofounder of Xyplex Inc. (Littleton, Mass.), a maker of internetworking products.
via:
-
What is MLPPP? | PPP Multilink | MLPP Bundle ⋆ IPCisco
https://ipcisco.com/lesson/what-is-mlppp/ -
MLPPP Configuration on Cisco Packet Tracer ⋆ IpCisco
https://ipcisco.com/lesson/mlppp-configuration-on-cisco-packet-tracer/ -
Multilink PPP: One Big Virtual WAN Pipe | Linux Journal
https://www.linuxjournal.com/article/3149 -
Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation Services Router Software Configuration Guide - Configuring MLPPP [Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation Services Routers] - Cisco
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/asr_901/Configuration/Guide/b_asr901-scg/b_asr901-scg_chapter_011100.html





















 897
897

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








