给定一个字符串,找出不含有重复字符的最长子串的长度。
示例:
给定 "abcabcbb" ,没有重复字符的最长子串是 "abc" ,那么长度就是3。
给定 "bbbbb" ,最长的子串就是 "b" ,长度是1。
给定 "pwwkew" ,最长子串是 "wke" ,长度是3。请注意答案必须是一个子串,"pwke" 是 子序列 而不是子串。
首先什么是子串???
子串:串中任意个连续的字符串组成的子序列称为改串的子串。(百度百科-子串)
当然最容易想到的就是超级接地气的暴力检索,不停地遍历每一组数据用嵌套循环走起:
public static int Method1(String str)
{
int charLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.Length; i++)//每个遍历循环
for (int j = i + 1; j <= str.Length; j++)
if (CompareChar(str, i, j)) charLength = Math.Max(charLength, j - i);
return charLength;
}
public static bool CompareChar(string str, int start, int end)
{
HashSet<char> charHashSet = new HashSet<char>();
for (int i = start; i < end; i++)
{
char ch = str.ToCharArray()[i];
if (charHashSet.Contains(ch)) return false;//发现重复,返回false
charHashSet.Add(ch);
}
return true;//并没有发现重复,返回true
}就这么接地气,但是时间会过于复杂,同时里面还有大量已经计算过的数据重复进行的计算。下面是进行10000次的时间(测试数据:"bpjoyabkdvyofinuqhvgueyqxjkbjwyklhbmhewmzwbeeqyuxtdrabkxlwausyggghuplscnofrvvsptls")

这里用到了HashSet!!!具体用法(MSDN—HashSet用法),自己看一下好了。
由于速度慢所以只能进行优化,网上最多的优化算法就是 滑动窗口,就是声明俩个指针,一个指针负责读取后面char的数据扩大范围,里一个指针负责减少读取的范围。这样可以尽可能的减少重复判断数据。下面是官方的解释:
如果从索引 ii 到 j - 1j−1之间的子字符串 s_{ij}sij 已经被检查为没有重复字符。我们只需要检查 s[j]s[j] 对应的字符是否已经存在于子字符串 s_{ij}sij中。
要检查一个字符是否已经在子字符串中,我们可以检查整个子字符串,这将产生一个复杂度为 O(n^2)O(n2) 的算法,但我们可以做得更好。
通过使用 HashSet 作为滑动窗口,我们可以用 O(1)O(1) 的时间来完成对字符是否在当前的子字符串中的检查。
滑动窗口是数组/字符串问题中常用的抽象概念。 窗口通常是在数组/字符串中由开始和结束索引定义的一系列元素的集合,即 [i, j)[i,j)(左闭,右开)。而滑动窗口是可以将两个边界向某一方向“滑动”的窗口。例如,我们将 [i, j)[i,j)向右滑动 11 个元素,则它将变为 [i+1, j+1)[i+1,j+1)(左闭,右开)。
回到我们的问题,我们使用 HashSet 将字符存储在当前窗口 [i, j)[i,j)(最初 j = ij=i)中。 然后我们向右侧滑动索引 jj,如果它不在 HashSet 中,我们会继续滑动 jj。直到 s[j] 已经存在于 HashSet 中。此时,我们找到的没有重复字符的最长子字符串将会以索引 ii 开头。如果我们对所有的 i
i 这样做,就可以得到答案
c#的代码:
public static int Method2(String str)
{
HashSet<char> charHashSet = new HashSet<char>();
int i = 0, j = 0;
int charLength = 0;
char[] chars = str.ToCharArray();
while (i < str.Length && j < str.Length)//这里也可以换成双for循环
{
if (!charHashSet.Contains(chars[j]))//这里是j
{
charHashSet.Add(chars[j++]);//先添加j,然后j++,扩大范围
charLength = Math.Max(charLength, j - i);
}
else
{
charHashSet.Remove(chars[i++]);//减小范围
}
}
return charLength;
}同样10000次的时间(测试数据:"bpjoyabkdvyofinuqhvgueyqxjkbjwyklhbmhewmzwbeeqyuxtdrabkxlwausyggghuplscnofrvvsptls"):
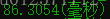
其实第二种算法还是有很明显优化空间的。就是我们在前面发现了已经存在的元素,可以跳过这个元素之前的区间。也就是说,如果 s[j]s[j] 在 [i, j)[i,j) 范围内有与 j'j′ 重复的字符,我们不需要逐渐增加 ii 。 我们可以直接跳过 [i,j′][i,j′] 范围内的所有元素,并将 ii 变为 j' + 1j′+1。
s[j]s[j] 在 [i, j)[i,j) 范围内有与 j'j′ 重复的字符,我们不需要逐渐增加 ii 。 我们可以直接跳过 [i,j′][i,j′] 范围内的所有元素,并将 ii 变为 j' + 1j′+1。对的,想想确实是那么回事,这样又可以减少很多判断,于是自己想到了Dic的使用:
public static int Method3(String str)
{
Dictionary<char, int> charDic = new Dictionary<char, int>();
int i = 0;
int startIndex = 0;
int charLength = 0;
char[] chars = str.ToCharArray();
while (i < str.Length)
{
if (!charDic.ContainsKey(chars[i]))
{
charDic.Add(chars[i], i);
charLength = Math.Max(charLength, i - startIndex + 1);
i++;
}
else
{
charDic.TryGetValue(chars[i], out startIndex);
i = ++startIndex;
charDic.Clear();//因为之前有重复的key,全部清除
}
}
return charLength;
}Dictionary<char, int>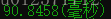
当然下面也可改成List<char> :
public static int Method4(String str)
{
List<char> charList = new List<char>();
int i = 0;
int startIndex = 0;
int charLength = 0;
char[] chars = str.ToCharArray();
while (i < str.Length)
{
if (charList.Contains(chars[i]))
{
for (int j = startIndex; j < i; j++)
{
if (chars[i].Equals(chars[j]))
{
startIndex = j + 1;
break;
}
}
}
charLength = Math.Max(charLength, i - startIndex + 1);
charList.Add(chars[i]);
i++;
}
return charLength;
}测试时间为:
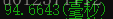
但是速度之路还远没有结束最后修改的代码:
public static int Method5(String str)
{
Dictionary<char, int> charList = new Dictionary<char, int>();
char[] chars = str.ToCharArray();
int startIndex = 0;
int charLength = 0;
int index;
for (int i = 0; i < str.Length; i++)
{
if (charList.ContainsKey(chars[i]))
{
charList.TryGetValue(chars[i], out index);
if (index >= startIndex)//实现剔除之前区间的作用
startIndex = index + 1;
charList.Remove(chars[i]);
}
charLength = Math.Max(charLength, i - startIndex + 1);
if (charLength >= str.Length - startIndex) return charLength;//其实后面的数据跟本就没有必要算了
charList.Add(chars[i], i);
}
return charLength;
}一个循环判断之前是否有存在存在的把startIndex进位
if (index >= startIndex)//实现剔除之前区间的作用
startIndex = index + 1;同时当:
if (charLength >= str.Length - startIndex) return charLength;//其实后面的数据跟本就没有必要算了最后时间测试:
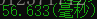


























 2414
2414

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








