声明零长度数组是 GNU 对标准 C 的扩展,可以参考这里 Zero-Length 。若要在一个结体体中声明一个 0 长度数组则这个声明必须放在结构体的最后,如:
struct hci_dev_req {
uint16_t dev_id;
uint32_t dev_opt;
};
struct hci_dev_list_req {
uint16_t dev_num;
struct hci_dev_req dev_req[0]; /* hci_dev_req structures */
};这个0长度数组的声明是不占用所在结构体的大小的,如:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef unsigned short uint16_t;
typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
struct hci_dev_req {
uint16_t dev_id;
uint32_t dev_opt;
};
struct hci_dev_list_req {
uint16_t dev_num;
struct hci_dev_req dev_req[0]; /* hci_dev_req structures */
};
int main()
{
printf("sizeof struct hci_dev_req = %lu\n", sizeof(struct hci_dev_req));
printf("size of struct hci_dev_list_req = %lu\n", sizeof(struct hci_dev_list_req));
return 0;
}![]()
sizeof(hci_dev_list_req) 的大小只是计算了 uint16_t dev_num 的大小,因为默认是4字节对齐,所以这里sizeof 结果为 4。在上面的链接中有这样一句话:Flexible array members have incomplete type, and so the sizeof operator may not be applied. As a quirk of the original implementation of zero-length arrays, sizeof evaluates to zero。
那这样声明有什么好处呢?
A zero-length array can be useful as the last element of a structure that is really a header for a variable-length object。翻译:零长度数组可以用作结构的最后一个元素,该元素实际上是可变长度对象的头。它的好处就是用于可变长对象,那如果用指针代替是不是也可以实现可变长对象呢?我觉得是可以的,如可以这样声明:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef unsigned short uint16_t;
typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
struct hci_dev_req {
uint16_t dev_id;
uint32_t dev_opt;
};
struct hci_dev_list_req {
uint16_t dev_num;
struct hci_dev_req *dev_req; /* hci_dev_req structures */
};
int main()
{
printf("sizeof struct hci_dev_req = %lu\n", sizeof(struct hci_dev_req));
printf("size of struct hci_dev_list_req = %lu\n", sizeof(struct hci_dev_list_req));
return 0;
}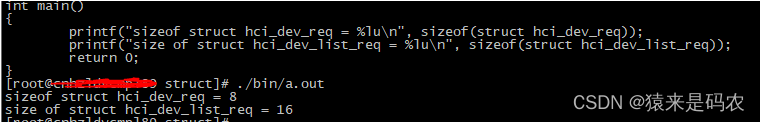
此时 sizeof(hci_dev_list_req) = 16,因为在64 位系统下一个指针占用 8 byte 大小,这里应该是按8 byte 对齐了,所以为16,如果设置成 4 byte 对齐,那应该为 12,如:
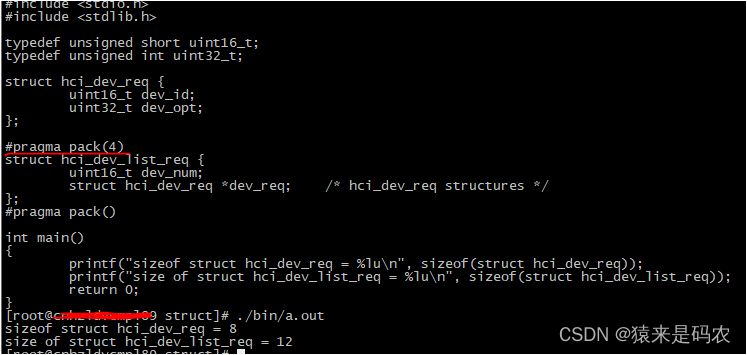
可以看到仅仅是换成了指针,数据结构的长度就增加了 12 byte。而且在实际使用的时候,这个指针可能指向的是 malloc 分配的内存空间,即:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef unsigned short uint16_t;
typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
struct hci_dev_req {
uint16_t dev_id;
uint32_t dev_opt;
};
#pragma pack(4)
struct hci_dev_list_req {
uint16_t dev_num;
struct hci_dev_req *dev_req; /* hci_dev_req structures */
};
#pragma pack()
int main()
{
printf("sizeof struct hci_dev_req = %lu\n", sizeof(struct hci_dev_req));
printf("size of struct hci_dev_list_req = %lu\n", sizeof(struct hci_dev_list_req));
int num = 16;//
struct hci_dev_list_req dl;
dl.dev_req = (struct hci_dev_req*)malloc(sizeof(struct hci_dev_req) * num);
/* do something*/
free(dl.dev_req);
return 0;
}使用malloc 或 new 分配的内存,你还必须进行手动释放,否则就会造成内存泄漏。那使用0长度数组的好处呢?看下面的代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma pack (1)
typedef struct private_data {
char tag[4];
int version;
char type;
char data[0];
}PrivateData;
#pragma pack ()
int main()
{
printf("sizeof PrivateData = %lu\n", sizeof(PrivateData)); // 9 bytes
/*这样申请内存后,sendBuf->data 就指向了 sendBuf+sizeof(PrivateData) 的位置,
* 即可以存放数据的内存的头了,这样做的好处是只需要释放一次 free(sendBuf) 即可。
*/
size_t totalMem = sizeof(PrivateData) + 256;
PrivateData *sendBuf = (PrivateData*)malloc(totalMem);
memset(sendBuf, 0, totalMem);
sendBuf->tag[0] = 'D';
sendBuf->tag[1] = 'H';
sendBuf->tag[2] = 'A';
sendBuf->tag[3] = 'V';
sendBuf->version = 0x10;
sendBuf->type = 0x11;
memcpy(sendBuf->data, "hello world", 11);
printf("sendBuf = %c, %c, %c, %c, data[0] = %s\n", sendBuf->tag[0], sendBuf->tag[1], sendBuf->tag[2], sendBuf->tag[3], sendBuf->data);
//这里只要释放sendBuf就可以
free(sendBuf);
return 0;
}![]()
使用0长度数组的好处就是实现了可变长对象,方便内存的申请和释放。
在 bluez 源码中就有这种用法,如下:
//有类型声明如下
struct hci_dev_req {
uint16_t dev_id;
uint32_t dev_opt;
};
struct hci_dev_list_req {
uint16_t dev_num;
struct hci_dev_req dev_req[0]; /* hci_dev_req structures */
};
static void print_dev_list(int ctl, int flags)
{
struct hci_dev_list_req *dl;
struct hci_dev_req *dr;
int i;
/* 申请了一大块内存 */
if (!(dl = malloc(HCI_MAX_DEV * sizeof(struct hci_dev_req) +
sizeof(uint16_t)))) {
perror("Can't allocate memory");
exit(1);
}
dl->dev_num = HCI_MAX_DEV;
dr = dl->dev_req;/* 这里指向了数据位置 */
if (ioctl(ctl, HCIGETDEVLIST, (void *) dl) < 0) {
perror("Can't get device list");
free(dl);
exit(1);
}
/* 这里操作实际的设备个数 */
for (i = 0; i< dl->dev_num; i++) {
di.dev_id = (dr+i)->dev_id;
if (ioctl(ctl, HCIGETDEVINFO, (void *) &di) < 0)
continue;
print_dev_info(ctl, &di);
}
free(dl);
}





 文章讨论了C语言中GNU扩展的零长度数组特性,它不占用结构体的大小,常用于表示可变长对象的头部。相比于使用指针,零长度数组可以简化内存管理和释放,避免内存泄漏。文中通过示例代码对比了两种方法的差异,并给出了在实际应用中的例子,如bluez源码中的用法。
文章讨论了C语言中GNU扩展的零长度数组特性,它不占用结构体的大小,常用于表示可变长对象的头部。相比于使用指针,零长度数组可以简化内存管理和释放,避免内存泄漏。文中通过示例代码对比了两种方法的差异,并给出了在实际应用中的例子,如bluez源码中的用法。
















 31
31

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








