1. Arbotix
1.1 添加配置文件
# 该文件是控制器配置,一个机器人模型可能有多个控制器,比如: 底盘、机械臂、夹持器(机械手)....
# 因此,根 name 是 controller
controllers: {
# 单控制器设置
base_controller: {
#类型: 差速控制器
type: diff_controller,
#参考坐标
base_frame_id: base_footprint,
#两个轮子之间的间距
base_width: 0.2,
#控制频率
ticks_meter: 2000,
#PID控制参数,使机器人车轮快速达到预期速度
Kp: 12,
Kd: 12,
Ki: 0,
Ko: 50,
#加速限制
accel_limit: 1.0
}
}
放在config里,建一个yaml文件

差速控制器:通过两个轮子速度差实现各种动作
参考坐标系:一般是根坐标系
1.2 launch文件编写
在以往基础上增加这些
<node pkg="arbotix_python" type="arbotix_driver" name="driver" output="screen">
<rosparam command="load" file="$(find urdf1_rviz)/config/control.yaml"/>
<param name="sim" value="true"/>
</node>
WARRING:把bashrc文件的IP地址换成本地的
订阅运动话题
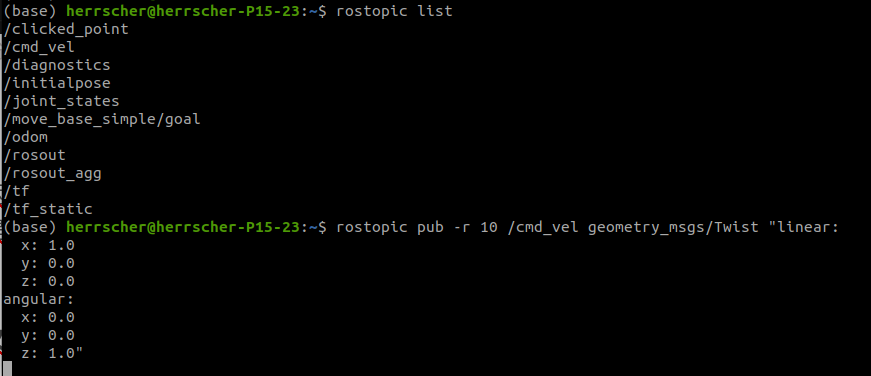
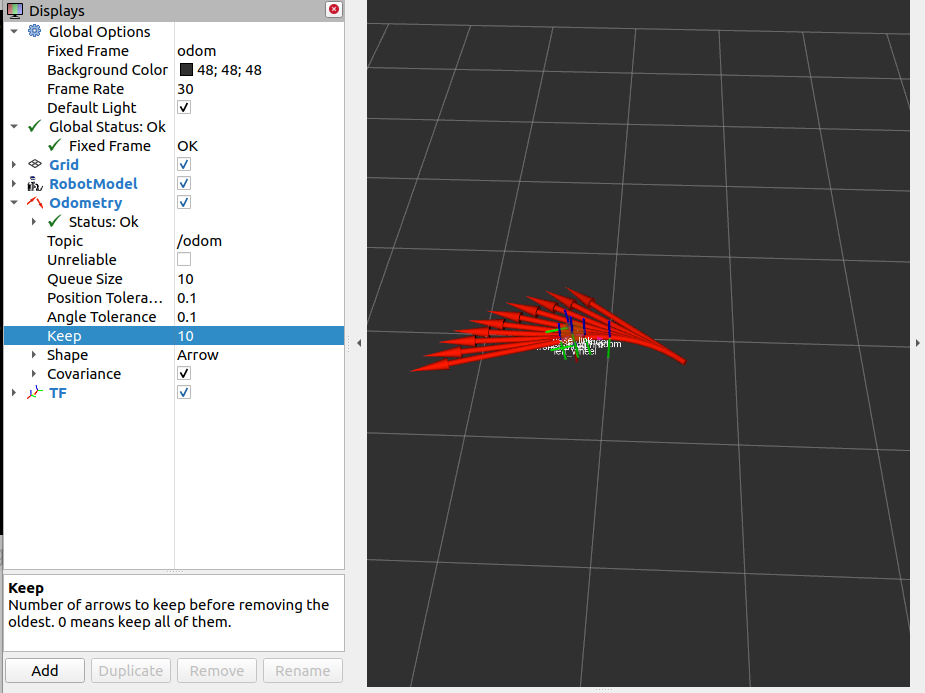
参考坐标系换成odom(初始位置)
2. gazebo
2.1 URDF集成gazebo
src下新建有文件夹urdf的目录,依赖:
urdf xacro gazebo_ros gazebo_ros_control gazebo_plugins

编码如下:
<robot name="car">
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="0.5 0.4 0.3"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
<material name="color">
<color rgba="0.5 0.5 0.4 0.5" />
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<box size="0.5 0.4 0.3"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
</collision>
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
<mass value="2"/>
<inertia ixx="1.0" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0" iyy="0.0" iyz="1.0" izz="1.0"/>
</inertial>
</link>
<gazebo reference="base_link">
<material>Gazebo/Blue</material>
</gazebo>
</robot>
代码详解
collision(设置碰撞模型)
collision里的是碰撞模型,一般情况下和Robot保持一致
inertial(惯性设置)
origin:质量坐标系
masss:质量 单位:kg
inertial:惯性矩阵 单位:kg·m²

一般要用到的惯性矩阵
球体:
<!-- Macro for inertia matrix -->
<xacro:macro name="sphere_inertial_matrix" params="m r">
<inertial>
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${2*m*r*r/5}" ixy="0" ixz="0"
iyy="${2*m*r*r/5}" iyz="0"
izz="${2*m*r*r/5}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
圆柱:
<xacro:macro name="cylinder_inertial_matrix" params="m r h">
<inertial>
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${m*(3*r*r+h*h)/12}" ixy = "0" ixz = "0"
iyy="${m*(3*r*r+h*h)/12}" iyz = "0"
izz="${m*r*r/2}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
立方体:
<xacro:macro name="Box_inertial_matrix" params="m l w h">
<inertial>
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${m*(h*h + l*l)/12}" ixy = "0" ixz = "0"
iyy="${m*(w*w + l*l)/12}" iyz= "0"
izz="${m*(w*w + h*h)/12}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
gazebo

注意:仿真环境中没有透明度的说法,所以这里颜色必须重新设置(注意大小写)
2.2 launch文件编写
<launch>
<param name="robot_description" textfile="$(find urdf_gazebo)/urdf/demo1.urdf" />
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch"/> //启动gazebo
<node pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" name="spawn_model" args="-urdf -model car_demo -param robot_description" />//载入模型
</launch>
2.3 加载地图
新建worlds文件夹,将地图资源导入
launch修改如下
<launch>
<param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro $(find urdf_gazebo)/urdf/demo2.urdf.xacro" />
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="$(find urdf_gazebo)/worlds/box_house.world" />
</include>
<node pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" name="spawn_model" args="-urdf -model my_car -param robot_description" />
</launch>
3.roscontrol
3.1 运动控制
在urdf下新建gazebo文件夹,新建文件:
<robot name="my_car_move" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<!-- 传动实现:用于连接控制器与关节 -->
<xacro:macro name="joint_trans" params="joint_name">
<!-- Transmission is important to link the joints and the controller -->
<transmission name="${joint_name}_trans">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type>
<joint name="${joint_name}">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
</joint>
<actuator name="${joint_name}_motor">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
<mechanicalReduction>1</mechanicalReduction>
</actuator>
</transmission>
</xacro:macro>
<!-- 每一个驱动轮都需要配置传动装置 -->
<xacro:joint_trans joint_name="left_wheel2base_link" />
<xacro:joint_trans joint_name="right_wheel2base_link" />
<!-- 控制器 -->
<gazebo>
<plugin name="differential_drive_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_diff_drive.so">
<rosDebugLevel>Debug</rosDebugLevel>
<publishWheelTF>true</publishWheelTF>
<robotNamespace>/</robotNamespace>
<publishTf>1</publishTf>
<publishWheelJointState>true</publishWheelJointState>
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
<updateRate>100.0</updateRate>
<legacyMode>true</legacyMode>
<leftJoint>left_wheel2base_link</leftJoint> <!-- 左轮 -->
<rightJoint>right_wheel2base_link</rightJoint> <!-- 右轮 -->
<wheelSeparation>${base_link_radius * 2}</wheelSeparation> <!-- 车轮间距 -->
<wheelDiameter>${wheel_radius * 2}</wheelDiameter> <!-- 车轮直径 -->
<broadcastTF>1</broadcastTF>
<wheelTorque>30</wheelTorque>
<wheelAcceleration>1.8</wheelAcceleration>
<commandTopic>cmd_vel</commandTopic> <!-- 运动控制话题 -->
<odometryFrame>odom</odometryFrame>
<odometryTopic>odom</odometryTopic> <!-- 里程计话题 -->
<robotBaseFrame>base_footprint</robotBaseFrame> <!-- 根坐标系 -->
</plugin>
</gazebo>
</robot>
结合标签将内容修改为正确的
将文件集成
<xacro:include filename="gazebo/move.xacro"/>
3.2 里程计使用
复用之前的rviz
<launch>
<node name="rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" args="-d $(find urdf1_rviz)/config/show_car.rviz"/>
<node name="joint_state_publisher" pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher"/>
<node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher"/>
</launch>
启动gazebo后启动rviz
配置如下
启动键盘控制

里程计会显示小车的路径
3.3 雷达仿真
和运动控制差不多,先新建雷达的xacro,复制文件如下
<robot name="my_sensors" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<!-- 雷达 -->
<gazebo reference="laser">
<sensor type="ray" name="rplidar">
<pose>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
<visualize>true</visualize>
<update_rate>5.5</update_rate>
<ray>
<scan>
<horizontal>
<samples>360</samples>
<resolution>1</resolution>
<min_angle>-3</min_angle>
<max_angle>3</max_angle>
</horizontal>
</scan>
<range>
<min>0.10</min>
<max>30.0</max>
<resolution>0.01</resolution>
</range>
<noise>
<type>gaussian</type>
<mean>0.0</mean>
<stddev>0.01</stddev>
</noise>
</ray>
<plugin name="gazebo_rplidar" filename="libgazebo_ros_laser.so">
<topicName>/scan</topicName>
<frameName>laser</frameName>
</plugin>
</sensor>
</gazebo>
</robot>
启动后效果如图
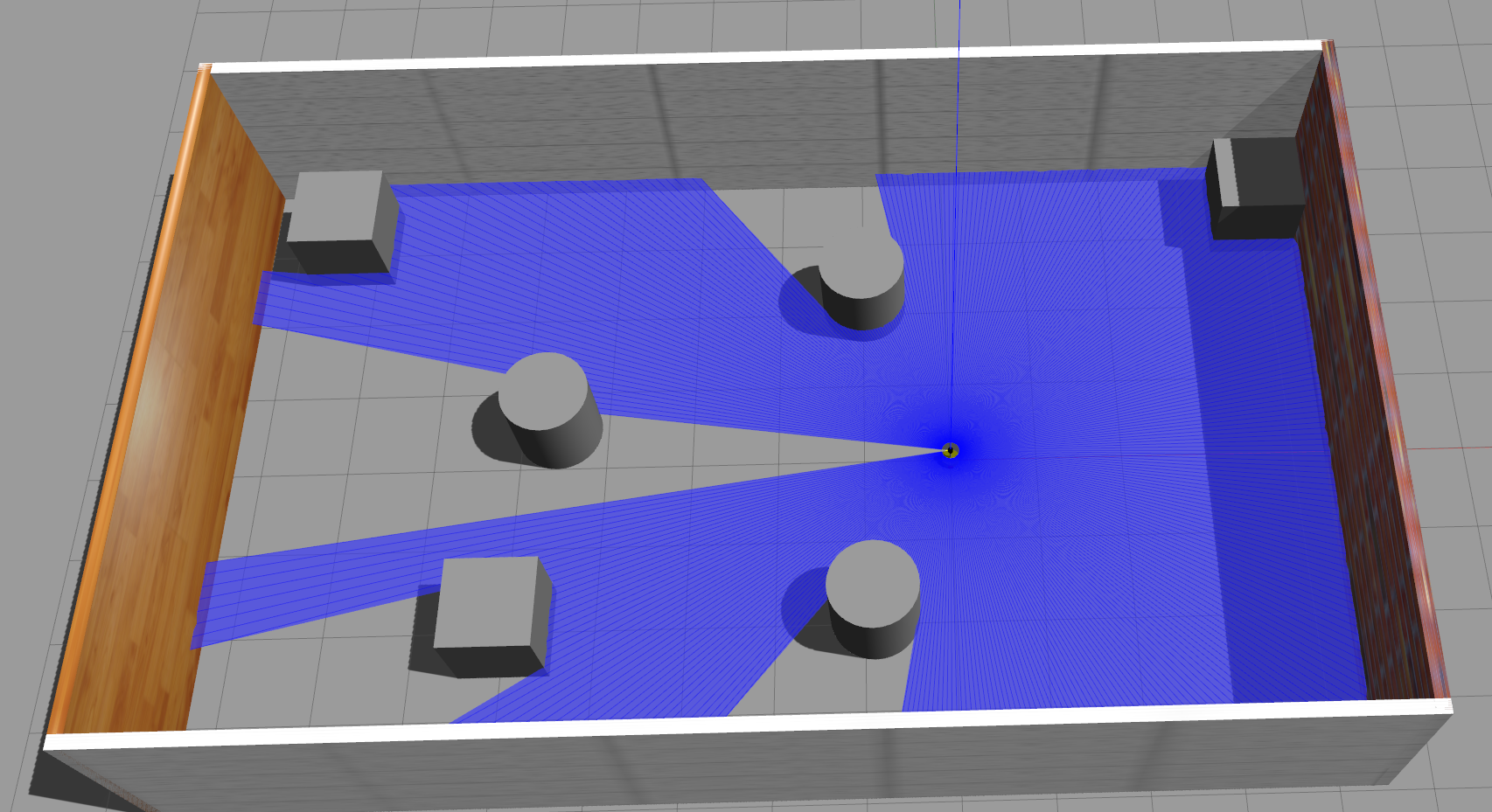
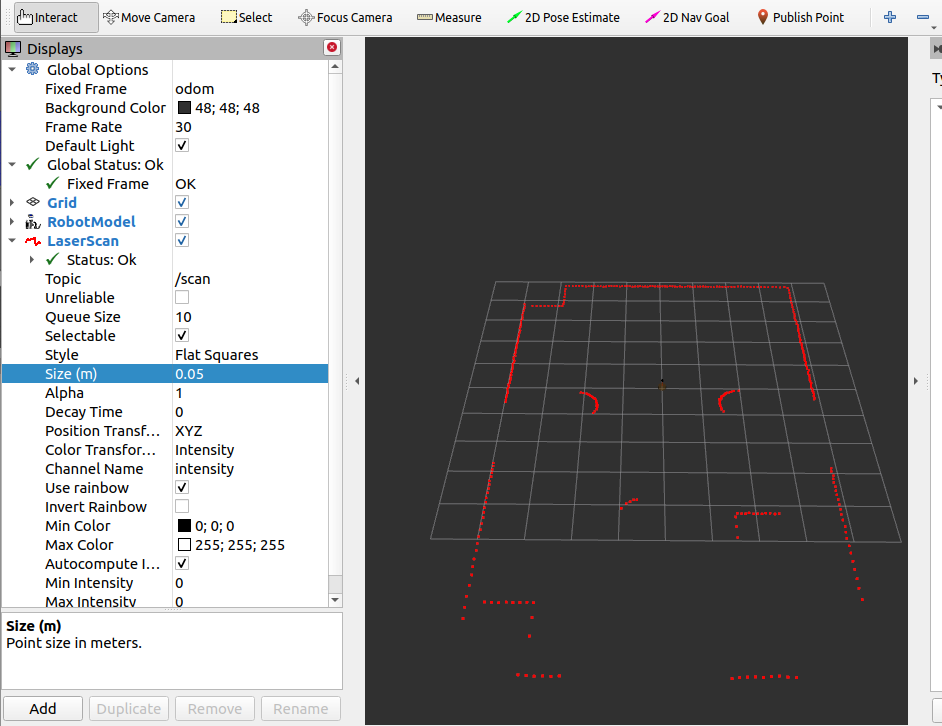
size可以改动标记的大小
参数解释
<gazebo reference="laser">
雷达关联的连杆
<frameName>laser</frameName>
雷达的坐标系,和连杆一样就行
<pose>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
xyz,rpy
<visualize>true</visualize>
雷达射线是否显示(gazebo里蓝色的)
<update_rate>5.5</update_rate>
雷达信息的更新频率(hz)
<samples>360</samples>
<resolution>1</resolution>
<min_angle>-3</min_angle>
<max_angle>3</max_angle>
分别是雷达发出射线的数量
每几个射线里有一个用于测距
扫描的左右弧度
<min>0.10</min>
<max>30.0</max>
<resolution>0.01</resolution>
雷达的最小可见范围和最大可见范围
精度
<type>gaussian</type>
<mean>0.0</mean>
<stddev>0.01</stddev>
高斯噪音
实际情况下雷达的测量并不总是准确的(可以参考高中物理的计算题),加入高斯噪音可以模拟这种误差
3.5 摄像头仿真
<robot name="my_sensors" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<!-- 被引用的link -->
<gazebo reference="camera">
<!-- 类型设置为 camara -->
<sensor type="camera" name="camera_node">
<update_rate>30.0</update_rate> <!-- 更新频率 -->
<!-- 摄像头基本信息设置 -->
<camera name="head">
<horizontal_fov>1.3962634</horizontal_fov>
<image>
<width>1280</width>
<height>720</height>
<format>R8G8B8</format>
</image>
<clip>
<near>0.02</near>
<far>300</far>
</clip>
<noise>
<type>gaussian</type>
<mean>0.0</mean>
<stddev>0.007</stddev>
</noise>
</camera>
<!-- 核心插件 -->
<plugin name="gazebo_camera" filename="libgazebo_ros_camera.so">
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
<updateRate>0.0</updateRate>
<cameraName>/camera</cameraName>
<imageTopicName>image_raw</imageTopicName>
<cameraInfoTopicName>camera_info</cameraInfoTopicName>
<frameName>camera</frameName>
<hackBaseline>0.07</hackBaseline>
<distortionK1>0.0</distortionK1>
<distortionK2>0.0</distortionK2>
<distortionK3>0.0</distortionK3>
<distortionT1>0.0</distortionT1>
<distortionT2>0.0</distortionT2>
</plugin>
</sensor>
</gazebo>
</robot>
rviz设置如下,可以看到摄像头的视野
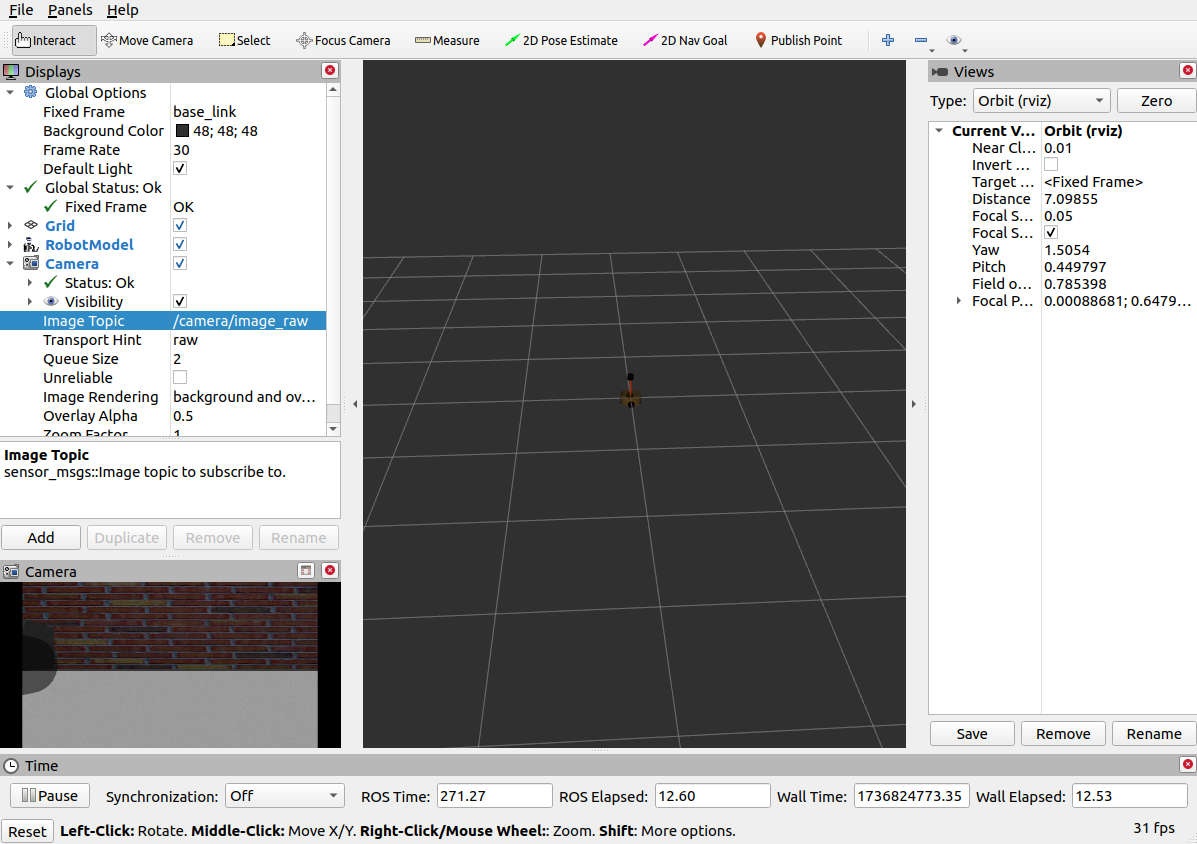
3.6深度相机
<robot name="my_sensors" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<gazebo reference="kinect link名称">
<sensor type="depth" name="camera">
<always_on>true</always_on>
<update_rate>20.0</update_rate>
<camera>
<horizontal_fov>${60.0*PI/180.0}</horizontal_fov>
<image>
<format>R8G8B8</format>
<width>640</width>
<height>480</height>
</image>
<clip>
<near>0.05</near>
<far>8.0</far>
</clip>
</camera>
<plugin name="kinect_camera_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_openni_kinect.so">
<cameraName>camera</cameraName>
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
<updateRate>10</updateRate>
<imageTopicName>rgb/image_raw</imageTopicName>
<depthImageTopicName>depth/image_raw</depthImageTopicName>
<pointCloudTopicName>depth/points</pointCloudTopicName>
<cameraInfoTopicName>rgb/camera_info</cameraInfoTopicName>
<depthImageCameraInfoTopicName>depth/camera_info</depthImageCameraInfoTopicName>
<frameName>kinect link名称</frameName>
<baseline>0.1</baseline>
<distortion_k1>0.0</distortion_k1>
<distortion_k2>0.0</distortion_k2>
<distortion_k3>0.0</distortion_k3>
<distortion_t1>0.0</distortion_t1>
<distortion_t2>0.0</distortion_t2>
<pointCloudCutoff>0.4</pointCloudCutoff>
</plugin>
</sensor>
</gazebo>
</robot>
kinect和camera可以设置在同一连杆上
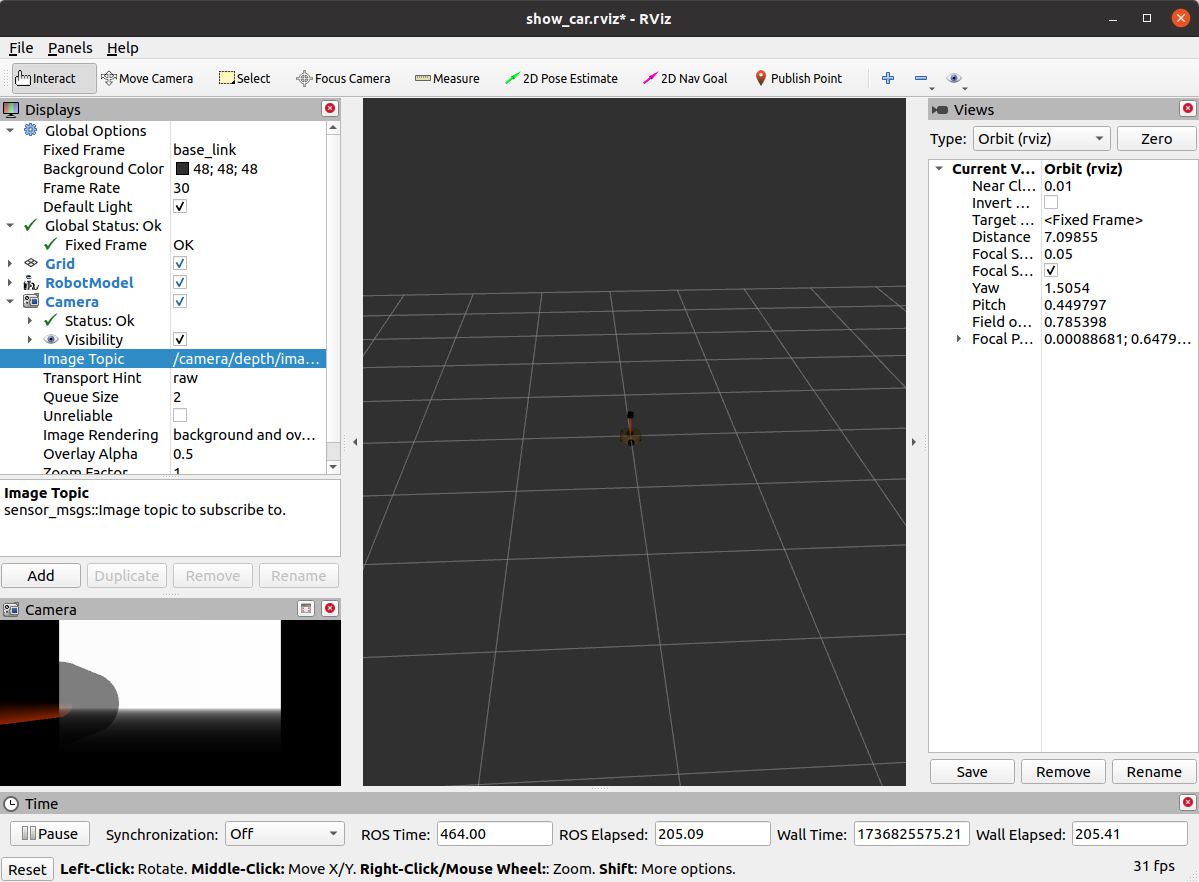
3.8 kinect点云
rviz中可以以点云的方式显示图形
但是启动点云时会发生这种情况(x轴和z轴都偏移了90度)
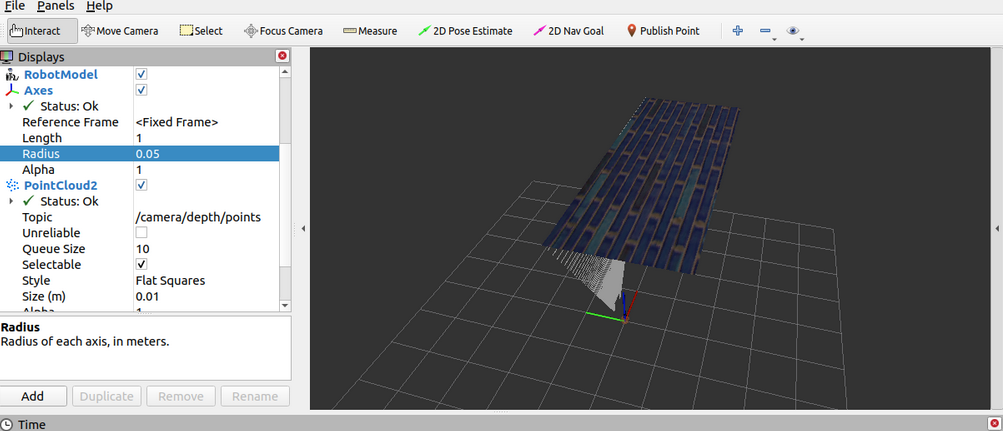 这是因为kinect中点云和图像数据分别使用了两套坐标系
这是因为kinect中点云和图像数据分别使用了两套坐标系
可以将坐标系进行修改和转换
kinect:
<frameName>support_depth</frameName>
rviz.launch
<node pkg="tf2_ros" type="static_transform_publisher" name="static_transform_publisher" args="0 0 0 -1.57 0 -1.57 /support /support_depth" />




















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








