首先下载point-transformer的代码:https://github.com/POSTECH-CVLab/point-transformer
由于该仓库使用的cuda和torch版本较低,需要对源代码进行一些改动:
lib/pointops/src/aggregation/aggregation_cuda.cpp、
lib/pointops/src/grouping/grouping_cuda.cpp、
lib/pointops/src/interpolation/interpolation_cuda.cpp、lib/pointops/src/knnquery/knnquery_cuda.cpp、lib/pointops/src/sampling/sampling_cuda.cpp、
lib/pointops/src/subtraction/subtraction_cuda.cpp这些文件把
#include <THC/THC.h>
修改为
#include <ATen/ATen.h>
导出onnx模型
为了能导出合适的onnx模型,
lib/pointops/src/sampling/sampling_cuda_kernel.h修改为
#ifndef _SAMPLING_CUDA_KERNEL
#define _SAMPLING_CUDA_KERNEL
#include <vector>
#include <torch/serialize/tensor.h>
#include <ATen/cuda/CUDAContext.h>
void furthestsampling_cuda(int b, int n, at::Tensor xyz_tensor, at::Tensor offset_tensor, int new_offset, at::Tensor tmp_tensor, at::Tensor idx_tensor);
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
void furthestsampling_cuda_launcher(int b, int n, const float *xyz, const int *offset, int new_offset, float *tmp, int *idx);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
lib/pointops/src/sampling/sampling_cuda.cpp修改为
#include <ATen/ATen.h>
#include <torch/serialize/tensor.h>
#include <ATen/cuda/CUDAContext.h>
#include "sampling_cuda_kernel.h"
void furthestsampling_cuda(int b, int n, at::Tensor xyz_tensor, at::Tensor offset_tensor, int new_offset, at::Tensor tmp_tensor, at::Tensor idx_tensor)
{
const float *xyz = xyz_tensor.data_ptr<float>();
const int *offset = offset_tensor.data_ptr<int>();
float *tmp = tmp_tensor.data_ptr<float>();
int *idx = idx_tensor.data_ptr<int>();
furthestsampling_cuda_launcher(b, n, xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
}
lib/pointops/src/sampling/sampling_cuda_kernel.cu修改为
#include "../cuda_utils.h"
#include "sampling_cuda_kernel.h"
__device__ void __update(float *dists, int *dists_i, int idx1, int idx2) {
const float v1 = dists[idx1], v2 = dists[idx2];
const int i1 = dists_i[idx1], i2 = dists_i[idx2];
dists[idx1] = max(v1, v2);
dists_i[idx1] = v2 > v1 ? i2 : i1;
}
// input xyz: (n, 3), tmp: (b, n_max)
// ouput idx (m)
template <unsigned int block_size>
__global__ void furthestsampling_cuda_kernel(const float *xyz, const int *offset, int new_offset, float *tmp, int *idx)
{
__shared__ float dists[block_size];
__shared__ int dists_i[block_size];
int bid = blockIdx.x;
int start_n = 0;
int end_n = offset[0];
int start_m = 0;
int end_m = new_offset;
int old = 0;
const int stride = block_size;
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid == 0) idx[start_m] = start_n;
__syncthreads();
for (int j = start_m + 1; j < end_m; j++)
{
int besti = start_n;
float best = -1;
float x1 = xyz[old * 3 + 0];
float y1 = xyz[old * 3 + 1];
float z1 = xyz[old * 3 + 2];
for (int k = start_n + tid; k < end_n; k += stride)
{
float x2 = xyz[k * 3 + 0];
float y2 = xyz[k * 3 + 1];
float z2 = xyz[k * 3 + 2];
float d = (x2 - x1) * (x2 - x1) + (y2 - y1) * (y2 - y1) + (z2 - z1) * (z2 - z1);
float d2 = min(d, tmp[k]);
tmp[k] = d2;
besti = d2 > best ? k : besti;
best = d2 > best ? d2 : best;
}
dists[tid] = best;
dists_i[tid] = besti;
__syncthreads();
if (block_size >= 1024) {
if (tid < 512) {
__update(dists, dists_i, tid, tid + 512);
}
__syncthreads();
}
if (block_size >= 512) {
if (tid < 256) {
__update(dists, dists_i, tid, tid + 256);
}
__syncthreads();
}
if (block_size >= 256) {
if (tid < 128) {
__update(dists, dists_i, tid, tid + 128);
}
__syncthreads();
}
if (block_size >= 128) {
if (tid < 64) {
__update(dists, dists_i, tid, tid + 64);
}
__syncthreads();
}
if (block_size >= 64) {
if (tid < 32) {
__update(dists, dists_i, tid, tid + 32);
}
__syncthreads();
}
if (block_size >= 32) {
if (tid < 16) {
__update(dists, dists_i, tid, tid + 16);
}
__syncthreads();
}
if (block_size >= 16) {
if (tid < 8) {
__update(dists, dists_i, tid, tid + 8);
}
__syncthreads();
}
if (block_size >= 8) {
if (tid < 4) {
__update(dists, dists_i, tid, tid + 4);
}
__syncthreads();
}
if (block_size >= 4) {
if (tid < 2) {
__update(dists, dists_i, tid, tid + 2);
}
__syncthreads();
}
if (block_size >= 2) {
if (tid < 1) {
__update(dists, dists_i, tid, tid + 1);
}
__syncthreads();
}
old = dists_i[0];
if (tid == 0)
idx[j] = old;
}
}
void furthestsampling_cuda_launcher(int b, int n, const float *xyz, const int *offset, int new_offset, float *tmp, int *idx)
{
unsigned int n_threads = opt_n_threads(n);
switch (n_threads) {
case 1024:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<1024><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
case 512:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<512><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
case 256:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<256><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
case 128:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<128><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
case 64:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<64><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
case 32:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<32><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
case 16:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<16><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
case 8:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<8><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
case 4:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<4><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
case 2:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<2><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
case 1:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<1><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
break;
default:
furthestsampling_cuda_kernel<512><<<b, n_threads, 0>>>(xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
}
}
lib/pointops/src/knnquery/knnquery_cuda_kernel.h修改为
#ifndef _KNNQUERY_CUDA_KERNEL
#define _KNNQUERY_CUDA_KERNEL
#include <vector>
#include <torch/serialize/tensor.h>
#include <ATen/cuda/CUDAContext.h>
void knnquery_cuda(int m, int nsample, at::Tensor xyz_tensor, at::Tensor new_xyz_tensor, at::Tensor offset_tensor, int new_offset_, at::Tensor idx_tensor, at::Tensor dist2_tensor);
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
void knnquery_cuda_launcher(int m, int nsample, const float *xyz, const float *new_xyz, const int *offset, int new_offset, int *idx, float *dist2);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
lib/pointops/src/knnquery/knnquery_cuda.cpp修改为
#include <ATen/ATen.h>
#include <torch/serialize/tensor.h>
#include <ATen/cuda/CUDAContext.h>
#include "knnquery_cuda_kernel.h"
void knnquery_cuda(int m, int nsample, at::Tensor xyz_tensor, at::Tensor new_xyz_tensor, at::Tensor offset_tensor, int new_offset, at::Tensor idx_tensor, at::Tensor dist2_tensor)
{
const float *xyz = xyz_tensor.data_ptr<float>();
const float *new_xyz = new_xyz_tensor.data_ptr<float>();
const int *offset = offset_tensor.data_ptr<int>();
//const int *new_offset = new_offset_tensor.data_ptr<int>();
int *idx = idx_tensor.data_ptr<int>();
float *dist2 = dist2_tensor.data_ptr<float>();
knnquery_cuda_launcher(m, nsample, xyz, new_xyz, offset, new_offset, idx, dist2);
}
lib/pointops/src/knnquery/knnquery_cuda_kernel.cu修改为
#include "../cuda_utils.h"
#include "knnquery_cuda_kernel.h"
__device__ void swap_float(float *x, float *y)
{
float tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
__device__ void swap_int(int *x, int *y)
{
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
__device__ void reheap(float *dist, int *idx, int k)
{
int root = 0;
int child = root * 2 + 1;
while (child < k)
{
if(child + 1 < k && dist[child+1] > dist[child])
child++;
if(dist[root] > dist[child])
return;
swap_float(&dist[root], &dist[child]);
swap_int(&idx[root], &idx[child]);
root = child;
child = root * 2 + 1;
}
}
__device__ void heap_sort(float *dist, int *idx, int k)
{
int i;
for (i = k - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
swap_float(&dist[0], &dist[i]);
swap_int(&idx[0], &idx[i]);
reheap(dist, idx, i);
}
}
__device__ int get_bt_idx(int idx, const int *offset)
{
int i = 0;
while (1)
{
if (idx < offset[i])
break;
else
i++;
}
return i;
}
__global__ void knnquery_cuda_kernel(int m, int nsample, const float *__restrict__ xyz, const float *__restrict__ new_xyz, const int *__restrict__ offset, int new_offset, int *__restrict__ idx, float *__restrict__ dist2) {
// input: xyz (n, 3) new_xyz (m, 3)
// output: idx (m, nsample) dist2 (m, nsample)
int pt_idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (pt_idx >= m) return;
new_xyz += pt_idx * 3;
idx += pt_idx * nsample;
dist2 += pt_idx * nsample;
int bt_idx = 0;
int start;
if (bt_idx == 0)
start = 0;
else
start = offset[bt_idx - 1];
int end = offset[bt_idx];
float new_x = new_xyz[0];
float new_y = new_xyz[1];
float new_z = new_xyz[2];
float best_dist[100];
int best_idx[100];
for(int i = 0; i < nsample; i++){
best_dist[i] = 1e10;
best_idx[i] = start;
}
for(int i = start; i < end; i++){
float x = xyz[i * 3 + 0];
float y = xyz[i * 3 + 1];
float z = xyz[i * 3 + 2];
float d2 = (new_x - x) * (new_x - x) + (new_y - y) * (new_y - y) + (new_z - z) * (new_z - z);
if (d2 < best_dist[0]){
best_dist[0] = d2;
best_idx[0] = i;
reheap(best_dist, best_idx, nsample);
}
}
heap_sort(best_dist, best_idx, nsample);
for(int i = 0; i < nsample; i++){
idx[i] = best_idx[i];
dist2[i] = best_dist[i];
}
}
void knnquery_cuda_launcher(int m, int nsample, const float *xyz, const float *new_xyz, const int *offset, int new_offset, int *idx, float *dist2) {
// input: new_xyz: (m, 3), xyz: (n, 3), idx: (m, nsample)
dim3 blocks(DIVUP(m, THREADS_PER_BLOCK));
dim3 threads(THREADS_PER_BLOCK);
knnquery_cuda_kernel<<<blocks, threads, 0>>>(m, nsample, xyz, new_xyz, offset, new_offset, idx, dist2);
}
lib/pointops/functions/pointops.py修改为
from typing import Tuple
import torch
from torch.autograd import Function
import torch.nn as nn
import pointops_cuda
namespace = "pointtransformer"
class FurthestSampling(Function):
@staticmethod
def symbolic(g, xyz, offset, new_offset):
new_offset = torch.tensor(new_offset, dtype=torch.int32)
return g.op(f"{namespace}::furthestsampling", xyz, offset, new_offset, attr_i=new_offset)
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, xyz, offset, new_offset):
"""
input: xyz: (n, 3), offset: (b), new_offset: (b) torch.Size([47358, 3]) tensor([47358], dtype=torch.int32) tensor([11839], dtype=torch.int32)
output: idx: (m) torch.Size([11839])
"""
assert xyz.is_contiguous()
n, b, n_max = xyz.shape[0], offset.shape[0], int(offset[0])
for i in range(1, b):
n_max = max(offset[i] - offset[i-1], n_max)
# idx = torch.cuda.IntTensor(new_offset[b-1].item()).zero_()
# tmp = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(n).fill_(1e10)
idx = torch.zeros(new_offset[b-1], dtype=torch.int32, device="cuda")
tmp = torch.full((n,), 1e10, dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda")
pointops_cuda.furthestsampling_cuda(b, n_max, xyz, offset, new_offset[0], tmp, idx)
del tmp
return idx
furthestsampling = FurthestSampling.apply
class KNNQuery(Function):
@staticmethod
def symbolic(g, nsample, xyz, new_xyz, offset, new_offset):
nsample = torch.tensor(nsample, dtype=torch.int32)
return g.op(f"{namespace}::knnquery", nsample, xyz, new_xyz, offset, new_offset, outputs=2, attr_i=nsample)
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, nsample, xyz, new_xyz, offset, new_offset):
"""
input: xyz: (n, 3), new_xyz: (m, 3), offset: (b), new_offset: (b) torch.Size([47358, 3]) torch.Size([47358, 3]) torch.int32 torch.int32
output: idx: (m, nsample), dist2: (m, nsample)
"""
if new_xyz is None: new_xyz = xyz
assert xyz.is_contiguous() and new_xyz.is_contiguous()
m = new_xyz.shape[0]
idx = torch.cuda.IntTensor(m, nsample).zero_()
dist2 = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(m, nsample).zero_()
pointops_cuda.knnquery_cuda(m, nsample, xyz, new_xyz, offset, new_offset[0], idx, dist2)
return idx, torch.sqrt(dist2)
knnquery = KNNQuery.apply
class Grouping(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input, idx):
"""
input: input: (n, c), idx : (m, nsample)
output: (m, nsample, c)
"""
assert input.is_contiguous() and idx.is_contiguous()
m, nsample, n, c = idx.shape[0], idx.shape[1], input.shape[0], input.shape[1]
output = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(m, nsample, c)
pointops_cuda.grouping_forward_cuda(m, nsample, c, input, idx, output)
ctx.n = n
ctx.save_for_backward(idx)
return output
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
"""
input: grad_out: (m, c, nsample)
output: (n, c), None
"""
n = ctx.n
idx, = ctx.saved_tensors
m, nsample, c = grad_output.shape
grad_input = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(n, c).zero_()
pointops_cuda.grouping_backward_cuda(m, nsample, c, grad_output, idx, grad_input)
return grad_input, None
grouping = Grouping.apply
def queryandgroup(nsample, xyz, new_xyz, feat, idx, offset, new_offset, use_xyz=True):
"""
input: xyz: (n, 3), new_xyz: (m, 3), feat: (n, c), idx: (m, nsample), offset: (b), new_offset: (b)
output: new_feat: (m, c+3, nsample), grouped_idx: (m, nsample)
"""
assert xyz.is_contiguous() and new_xyz.is_contiguous() and feat.is_contiguous()
if new_xyz is None:
new_xyz = xyz
if idx is None:
idx, _ = knnquery(nsample, xyz, new_xyz, offset, new_offset) # (m, nsample) torch.Size([47358, 8])
n, m, c = xyz.shape[0], new_xyz.shape[0], feat.shape[1]
grouped_xyz = xyz[idx.view(-1).long(), :].view(m, nsample, 3) # (m, nsample, 3) torch.Size([47358, 8, 3])
grouped_xyz -= new_xyz.unsqueeze(1) # (m, nsample, 3)
grouped_feat = feat[idx.view(-1).long(), :].view(m, nsample, c) # (m, nsample, c)
if use_xyz:
return torch.cat((grouped_xyz, grouped_feat), -1) # (m, nsample, 3+c)
else:
return grouped_feat
class Subtraction(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input1, input2, idx):
"""
input: input1: (n, c), input2: (n, c), idx: (n, nsample)
output: (n, nsample, c)
"""
assert input1.is_contiguous() and input2.is_contiguous()
n, c = input1.shape; nsample = idx.shape[-1]
output = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(n, nsample, c).zero_()
pointops_cuda.subtraction_forward_cuda(n, nsample, c, input1, input2, idx, output)
ctx.save_for_backward(idx)
return output
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
"""
input: grad_out: (n, nsample, c)
output: grad_input1: (n, c), grad_input2: (n, c)
"""
idx, = ctx.saved_tensors
n, nsample, c = grad_output.shape
grad_input1 = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(n, c).zero_()
grad_input2 = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(n, c).zero_()
pointops_cuda.subtraction_backward_cuda(n, nsample, c, idx, grad_output, grad_input1, grad_input2)
return grad_input1, grad_input2, None
subtraction = Subtraction.apply
class Aggregation(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input, position, weight, idx):
"""
input: input: (n, c), position: (n, nsample, c), weight : (n, nsample, c'), idx: (n, nsample)
output: (n, c)
"""
assert input.is_contiguous() and position.is_contiguous() and weight.is_contiguous()
n, nsample, c = position.shape; w_c = weight.shape[-1]
output = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(n, c).zero_()
pointops_cuda.aggregation_forward_cuda(n, nsample, c, w_c, input, position, weight, idx, output)
ctx.save_for_backward(input, position, weight, idx)
return output
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
"""
input: grad_out: (n, c)
output: grad_input: (n, c), grad_position: (n, nsample, c), grad_weight : (n, nsample, c')
"""
input, position, weight, idx = ctx.saved_tensors
n, nsample, c = position.shape; w_c = weight.shape[-1]
grad_input = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(n, c).zero_()
grad_position = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(n, nsample, c).zero_()
grad_weight = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(n, nsample, w_c).zero_()
pointops_cuda.aggregation_backward_cuda(n, nsample, c, w_c, input, position, weight, idx, grad_output, grad_input, grad_position, grad_weight)
return grad_input, grad_position, grad_weight, None
aggregation = Aggregation.apply
def interpolation(xyz, new_xyz, feat, offset, new_offset, k=3):
"""
input: xyz: (m, 3), new_xyz: (n, 3), feat: (m, c), offset: (b), new_offset: (b)
output: (n, c)
"""
assert xyz.is_contiguous() and new_xyz.is_contiguous() and feat.is_contiguous()
idx, dist = knnquery(k, xyz, new_xyz, offset, new_offset)
dist_recip = 1.0 / (dist + 1e-8) # (n, 3)
norm = torch.sum(dist_recip, dim=1, keepdim=True)
weight = dist_recip / norm # (n, 3)
new_feat = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(new_xyz.shape[0], feat.shape[1]).zero_()
for i in range(k):
new_feat += feat[idx[:, i].long(), :] * weight[:, i].unsqueeze(-1)
return new_feat#torch.Size([739, 256])
class Interpolation(Function):
@staticmethod
def symbolic(g, xyz, new_xyz, input, offset, new_offset, k=3):
return g.op(f"{namespace}::interpolation2", xyz, new_xyz, input, offset, new_offset, k=3)
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, xyz, new_xyz, input, offset, new_offset, k=3):
"""
input: xyz: (m, 3), new_xyz: (n, 3), input: (m, c), offset: (b), new_offset: (b)
output: (n, c)
"""
assert xyz.is_contiguous() and new_xyz.is_contiguous() and input.is_contiguous()
idx, dist = knnquery(k, xyz, new_xyz, offset, new_offset) # (n, k), (n, k)
dist_recip = 1.0 / (dist + 1e-8) # (n, k)
norm = torch.sum(dist_recip, dim=1, keepdim=True)
weight = dist_recip / norm # (n, k)
n, c, m = new_xyz.shape[0], input.shape[1], input.shape[0]
output = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(n, c).zero_()
pointops_cuda.interpolation_forward_cuda(n, c, k, input, idx, weight, output)
ctx.m, ctx.k = m, k
ctx.save_for_backward(idx, weight)
return output
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
"""
input: xyz: (m, 3), new_xyz: (n, 3), input: (m, c), offset: (b), new_offset: (b)
output: (n, c)
"""
m, k = ctx.m, ctx.k
idx, weight = ctx.saved_tensors
n, c = grad_output.shape
grad_input = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(m, c).zero_()
pointops_cuda.interpolation_backward_cuda(n, c, k, grad_output, idx, weight, grad_input)
return None, None, grad_input, None, None, None
interpolation2 = Interpolation.apply
model/pointtransformer/pointtransformer_seg.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from lib.pointops.functions import pointops
class PointTransformerLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, share_planes=8, nsample=16):
super().__init__()
self.mid_planes = mid_planes = out_planes // 1
self.out_planes = out_planes
self.share_planes = share_planes
self.nsample = nsample
self.linear_q = nn.Linear(in_planes, mid_planes)
self.linear_k = nn.Linear(in_planes, mid_planes)
self.linear_v = nn.Linear(in_planes, out_planes)
self.linear_p = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(3, 3), nn.BatchNorm1d(3), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Linear(3, out_planes))
self.linear_w = nn.Sequential(nn.BatchNorm1d(mid_planes), nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(mid_planes, mid_planes // share_planes),
nn.BatchNorm1d(mid_planes // share_planes), nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(out_planes // share_planes, out_planes // share_planes))
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, pxo) -> torch.Tensor:
p, x, o = pxo # (n, 3), (n, c), (b)
x_q, x_k, x_v = self.linear_q(x), self.linear_k(x), self.linear_v(x) # (n, c)
x_k = pointops.queryandgroup(self.nsample, p, p, x_k, None, o, o, use_xyz=True) # (n, nsample, 3+c)
x_v = pointops.queryandgroup(self.nsample, p, p, x_v, None, o, o, use_xyz=False) # (n, nsample, c)
p_r, x_k = x_k[:, :, 0:3], x_k[:, :, 3:]
for i, layer in enumerate(self.linear_p): p_r = layer(p_r.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()).transpose(1, 2).contiguous() if i == 1 else layer(p_r) # (n, nsample, c)
w = x_k - x_q.unsqueeze(1) + p_r.view(p_r.shape[0], p_r.shape[1], self.out_planes // self.mid_planes, self.mid_planes).sum(2) # (n, nsample, c)
for i, layer in enumerate(self.linear_w): w = layer(w.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()).transpose(1, 2).contiguous() if i % 3 == 0 else layer(w)
w = self.softmax(w) # (n, nsample, c)
n, nsample, c = x_v.shape; s = self.share_planes
x = ((x_v + p_r).view(n, nsample, s, c // s) * w.unsqueeze(2)).sum(1).view(n, c)
return x
class TransitionDown(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, nsample=16):
super().__init__()
self.stride, self.nsample = stride, nsample
if stride != 1:
self.linear = nn.Linear(3+in_planes, out_planes, bias=False)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool1d(nsample)
else:
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_planes, out_planes, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(out_planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, pxo):
p, x, o = pxo # (n, 3), (n, c), (b)
if self.stride != 1:
n_o, count = [o[0].item() // self.stride], o[0].item() // self.stride
for i in range(1, o.shape[0]):
count += (o[i].item() - o[i-1].item()) // self.stride
n_o.append(count)
#n_o = torch.cuda.IntTensor(n_o)
idx = pointops.furthestsampling(p, o, n_o) # (m)
n_p = p[idx.long(), :] # (m, 3)
n_o = torch.cuda.IntTensor(n_o)
x = pointops.queryandgroup(self.nsample, p, n_p, x, None, o, n_o, use_xyz=True) # (m, 3+c, nsample)
x = self.relu(self.bn(self.linear(x).transpose(1, 2).contiguous())) # (m, c, nsample)
x = self.pool(x).squeeze(-1) # (m, c)
p, o = n_p, n_o
else:
x = self.relu(self.bn(self.linear(x))) # (n, c)
return [p, x, o]
class TransitionUp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes=None):
super().__init__()
if out_planes is None:
self.linear1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(2*in_planes, in_planes), nn.BatchNorm1d(in_planes), nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.linear2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(in_planes, in_planes), nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
else:
self.linear1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(out_planes, out_planes), nn.BatchNorm1d(out_planes), nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.linear2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(in_planes, out_planes), nn.BatchNorm1d(out_planes), nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
def forward(self, pxo1, pxo2=None):
if pxo2 is None:
_, x, o = pxo1 # (n, 3), (n, c), (b)
x_tmp = []
for i in range(o.shape[0]):
if i == 0:
s_i, e_i, cnt = 0, o[0], o[0]
else:
s_i, e_i, cnt = o[i-1], o[i], o[i] - o[i-1]
x_b = x[s_i:e_i, :]
x_b = torch.cat((x_b, self.linear2(x_b.sum(0, True) / cnt).repeat(cnt, 1)), 1)
x_tmp.append(x_b)
x = torch.cat(x_tmp, 0)
x = self.linear1(x)
else:
p1, x1, o1 = pxo1; p2, x2, o2 = pxo2
x = self.linear1(x1) + pointops.interpolation(p2, p1, self.linear2(x2), o2, o1)
return x
class PointTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, share_planes=8, nsample=16):
super(PointTransformerBlock, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(in_planes, planes, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(planes)
self.transformer2 = PointTransformerLayer(planes, planes, share_planes, nsample)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(planes)
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(planes, planes * self.expansion, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, pxo):
p, x, o = pxo # (n, 3), (n, c), (b)
identity = x
x = self.relu(self.bn1(self.linear1(x)))
x = self.relu(self.bn2(self.transformer2([p, x, o])))
x = self.bn3(self.linear3(x))
x += identity
x = self.relu(x)
return p, x, o
class PointTransformerSeg(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, blocks, c=6, k=13):
super().__init__()
self.c = c
self.in_planes, planes = c, [32, 64, 128, 256, 512]
fpn_planes, fpnhead_planes, share_planes = 128, 64, 8
stride, nsample = [1, 4, 4, 4, 4], [8, 16, 16, 16, 16]
self.enc1 = self._make_enc(block, planes[0], blocks[0], share_planes, stride=stride[0], nsample=nsample[0]) # N/1
self.enc2 = self._make_enc(block, planes[1], blocks[1], share_planes, stride=stride[1], nsample=nsample[1]) # N/4
self.enc3 = self._make_enc(block, planes[2], blocks[2], share_planes, stride=stride[2], nsample=nsample[2]) # N/16
self.enc4 = self._make_enc(block, planes[3], blocks[3], share_planes, stride=stride[3], nsample=nsample[3]) # N/64
self.enc5 = self._make_enc(block, planes[4], blocks[4], share_planes, stride=stride[4], nsample=nsample[4]) # N/256
self.dec5 = self._make_dec(block, planes[4], 2, share_planes, nsample=nsample[4], is_head=True) # transform p5
self.dec4 = self._make_dec(block, planes[3], 2, share_planes, nsample=nsample[3]) # fusion p5 and p4
self.dec3 = self._make_dec(block, planes[2], 2, share_planes, nsample=nsample[2]) # fusion p4 and p3
self.dec2 = self._make_dec(block, planes[1], 2, share_planes, nsample=nsample[1]) # fusion p3 and p2
self.dec1 = self._make_dec(block, planes[0], 2, share_planes, nsample=nsample[0]) # fusion p2 and p1
self.cls = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(planes[0], planes[0]), nn.BatchNorm1d(planes[0]), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Linear(planes[0], k))
def _make_enc(self, block, planes, blocks, share_planes=8, stride=1, nsample=16):
layers = []
layers.append(TransitionDown(self.in_planes, planes * block.expansion, stride, nsample))
self.in_planes = planes * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.in_planes, self.in_planes, share_planes, nsample=nsample))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _make_dec(self, block, planes, blocks, share_planes=8, nsample=16, is_head=False):
layers = []
layers.append(TransitionUp(self.in_planes, None if is_head else planes * block.expansion))
self.in_planes = planes * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.in_planes, self.in_planes, share_planes, nsample=nsample))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, pxo):
p0, x0, o0 = pxo # (n, 3), (n, c), (b)
x0 = p0 if self.c == 3 else torch.cat((p0, x0), 1)
p1, x1, o1 = self.enc1([p0, x0, o0])
p2, x2, o2 = self.enc2([p1, x1, o1])
p3, x3, o3 = self.enc3([p2, x2, o2])
p4, x4, o4 = self.enc4([p3, x3, o3])
p5, x5, o5 = self.enc5([p4, x4, o4])
x5 = self.dec5[1:]([p5, self.dec5[0]([p5, x5, o5]), o5])[1]
x4 = self.dec4[1:]([p4, self.dec4[0]([p4, x4, o4], [p5, x5, o5]), o4])[1]
x3 = self.dec3[1:]([p3, self.dec3[0]([p3, x3, o3], [p4, x4, o4]), o3])[1]
x2 = self.dec2[1:]([p2, self.dec2[0]([p2, x2, o2], [p3, x3, o3]), o2])[1]
x1 = self.dec1[1:]([p1, self.dec1[0]([p1, x1, o1], [p2, x2, o2]), o1])[1]
x = self.cls(x1)
return x
def pointtransformer_seg_repro(**kwargs):
model = PointTransformerSeg(PointTransformerBlock, [2, 3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
return model
编写导出onnx模型的代码:
import argparse
import collections
import torch
from util import config
from model.pointtransformer.pointtransformer_seg import pointtransformer_seg_repro as Model
def get_parser():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation')
parser.add_argument('--config', type=str, default='/home/tfy/document/point-transformer-master/config/s3dis/s3dis_pointtransformer_repro.yaml', help='config file')
parser.add_argument('opts', help='see config/s3dis/s3dis_pointtransformer_repro.yaml for all options', default=None, nargs=argparse.REMAINDER)
args = parser.parse_args()
cfg = config.load_cfg_from_cfg_file(args.config)
cfg = config.merge_cfg_from_list(cfg, args.opts)
return cfg
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = get_parser()
model = Model(c=args.fea_dim, k=args.classes).cuda()
names = [line.rstrip('\n') for line in open(args.names_path)]
checkpoint = torch.load(args.model_path, weights_only=False)
state_dict = checkpoint['state_dict']
new_state_dict = collections.OrderedDict()
for k, v in state_dict.items():
name = k[7:]
new_state_dict[name] = v
model.load_state_dict(new_state_dict, strict=True)
model.eval()
coord_part = torch.rand(47358, 3).to(torch.float32).to("cuda")
feat_part = torch.rand(47358, 3).to(torch.float32).to("cuda")
offset_part = torch.tensor([47358], device='cuda', dtype=torch.int32)
with torch.no_grad():
torch.onnx.export(model, ([coord_part, feat_part, offset_part]), "pointtransformer.onnx", opset_version=15)
导出的onnx模型结构如下:
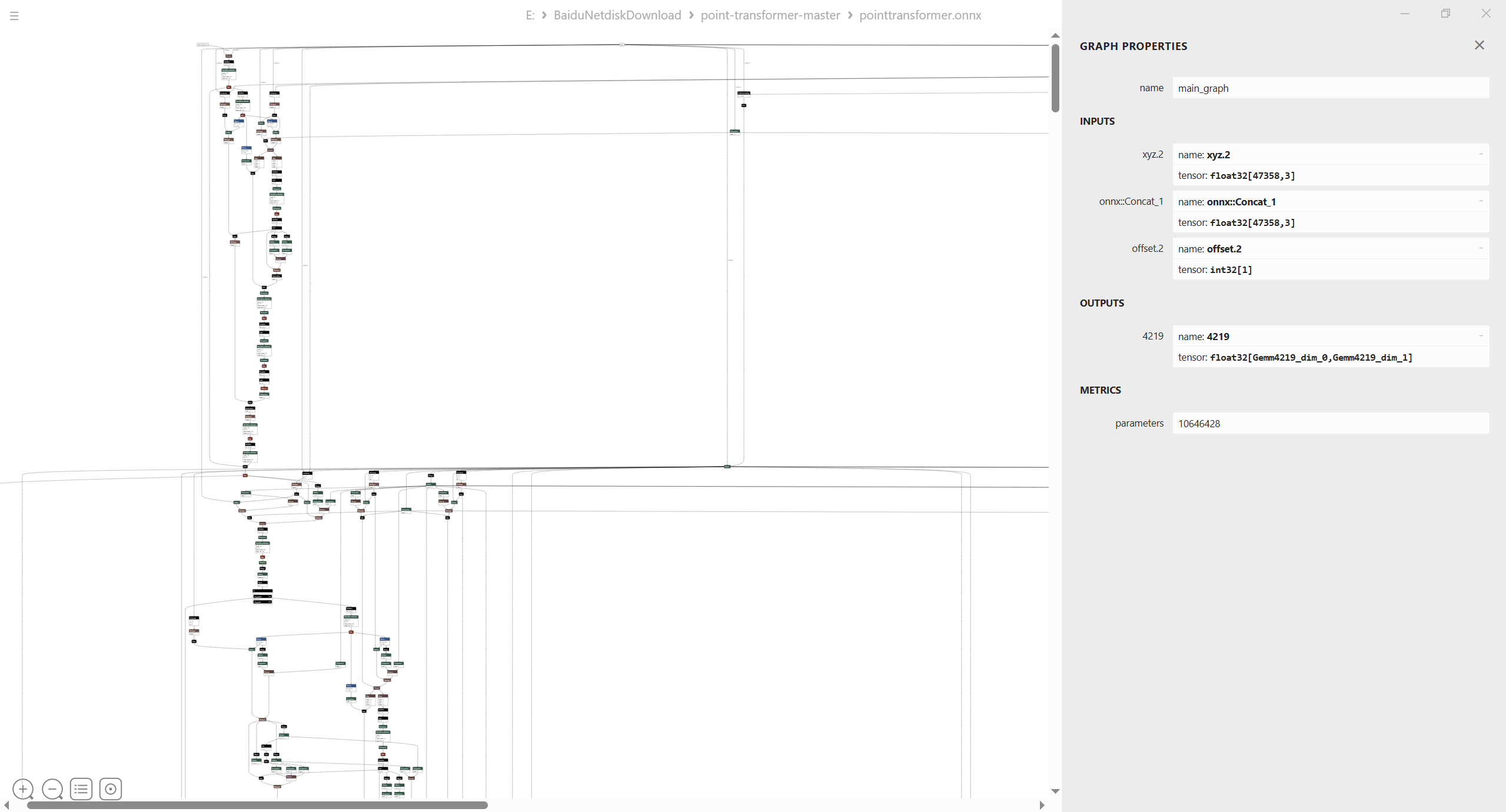
编写tensorrt自定义算子
furthestSampling自定义tensorrt算子编写
knnQuery自定义tensorrt算子编写
导出tensorrt模型
先用onnxslim简化模型:
onnxslim pointtransformer.onnx pointtransformer.onnx
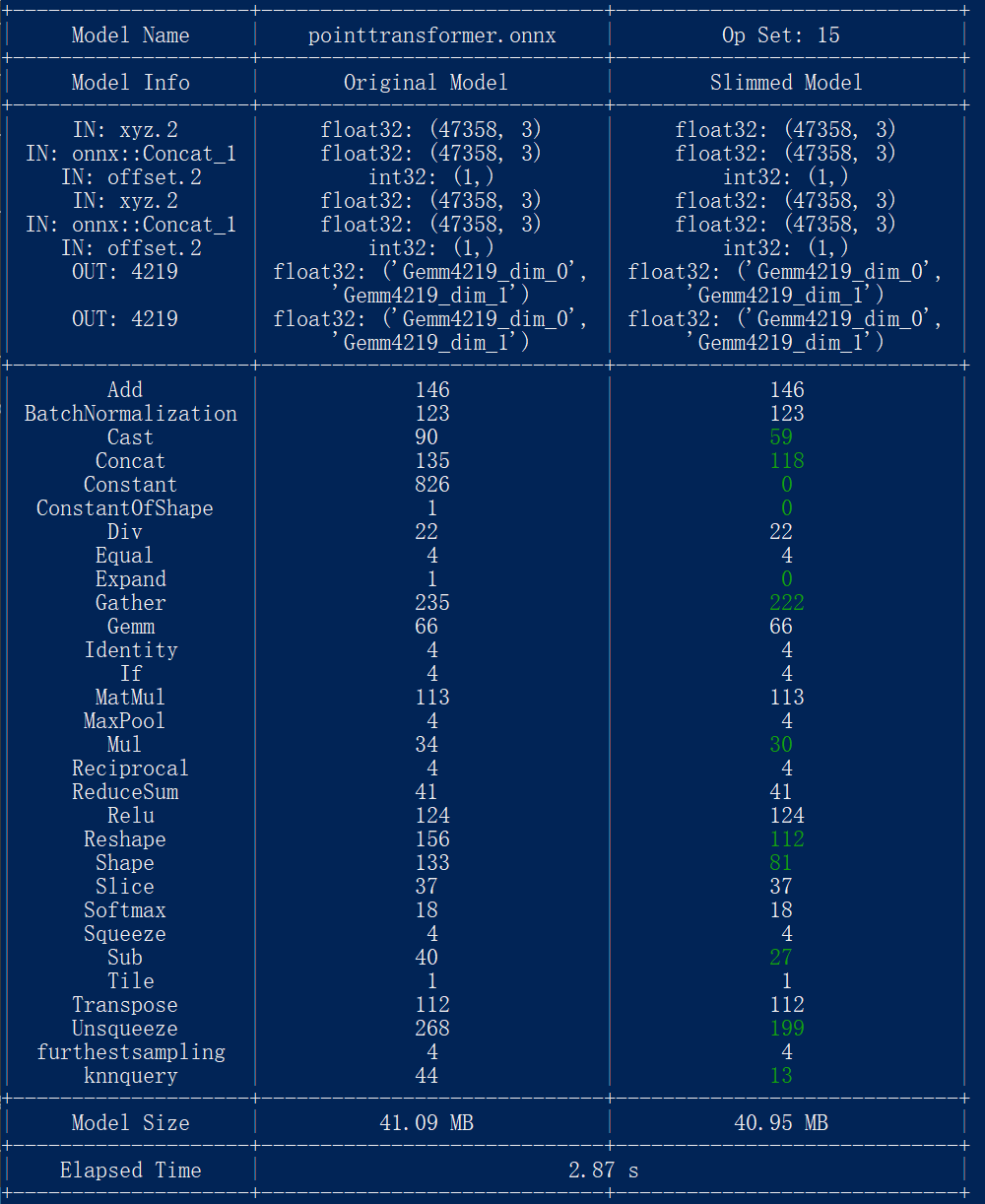
再执行:
TensorRT-10.6.0.26/bin/trtexec --onnx=pointtransformer.onnx --saveEngine=pointtransformer.engine
测试tensorrt模型
import numpy as np
import tensorrt as trt
import common
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
trt.init_libnvinfer_plugins(logger, "")
with open("pointtransformer.engine", "rb") as f, trt.Runtime(logger) as runtime:
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
context = engine.create_execution_context()
inputs, outputs, bindings, stream = common.allocate_buffers(engine)
coord_part = np.loadtxt("coord_part.txt").reshape(47358, 3).astype(np.float32) #(47358, 3)
feat_part = np.loadtxt("feat_part.txt").reshape(47358, 3).astype(np.float32) #(47358, 3)
offset_part = np.array([47358]).astype(np.int32)
np.copyto(inputs[0].host, coord_part.ravel())
np.copyto(inputs[1].host, feat_part.ravel())
np.copyto(inputs[2].host, offset_part)
output = common.do_inference(context,engine=engine, bindings=bindings, inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, stream=stream)
print(output)
tensorrt部署
from util.common_util import intersectionAndUnion
from util.voxelize import voxelize
import numpy as np
import tensorrt as trt
import common
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
trt.init_libnvinfer_plugins(logger, "")
with open("pointtransformer.engine", "rb") as f, trt.Runtime(logger) as runtime:
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
context = engine.create_execution_context()
inputs, outputs, bindings, stream = common.allocate_buffers(engine)
def input_normalize(coord, feat):
coord_min = np.min(coord, 0)
coord -= coord_min
feat = feat / 255.
return coord, feat
classes = 13
voxel_max = 80000
voxel_size=0.04
data = np.load("/home/tfy/document/point-transformer-master/dataset/s3dis/trainval_fullarea/Area_5_WC_1.npy") # xyzrgbl, N*7
coord, feat, label = data[:, :3], data[:, 3:6], data[:, 6]
idx_data = []
coord_min = np.min(coord, 0)
coord -= coord_min
idx_sort, count = voxelize(coord, voxel_size, mode=1)
for i in range(count.max()):
idx_select = np.cumsum(np.insert(count, 0, 0)[0:-1]) + i % count
idx_part = idx_sort[idx_select]
idx_data.append(idx_part)
pred = np.zeros((label.size, classes))
idx_size = len(idx_data)
idx_list, coord_list, feat_list, offset_list = [], [], [], []
for i in range(idx_size):
idx_part = idx_data[i]
coord_part, feat_part = coord[idx_part], feat[idx_part]
if voxel_max and coord_part.shape[0] > voxel_max:
coord_p, idx_uni, cnt = np.random.rand(coord_part.shape[0]) * 1e-3, np.array([]), 0
while idx_uni.size != idx_part.shape[0]:
init_idx = np.argmin(coord_p)
dist = np.sum(np.power(coord_part - coord_part[init_idx], 2), 1)
idx_crop = np.argsort(dist)[:voxel_max]
coord_sub, feat_sub, idx_sub = coord_part[idx_crop], feat_part[idx_crop], idx_part[idx_crop]
dist = dist[idx_crop]
delta = np.square(1 - dist / np.max(dist))
coord_p[idx_crop] += delta
coord_sub, feat_sub = input_normalize(coord_sub, feat_sub)
idx_list.append(idx_sub), coord_list.append(coord_sub), feat_list.append(feat_sub), offset_list.append(idx_sub.size)
idx_uni = np.unique(np.concatenate((idx_uni, idx_sub)))
else:
coord_part, feat_part = input_normalize(coord_part, feat_part)
idx_list.append(idx_part), coord_list.append(coord_part), feat_list.append(feat_part), offset_list.append(idx_part.size)
batch_num = int(np.ceil(len(idx_list)))
for i in range(batch_num):
s_i, e_i = i, min(i + 1, len(idx_list))
idx_part, coord_part, feat_part, offset_part = idx_list[s_i:e_i], coord_list[s_i:e_i], feat_list[s_i:e_i], offset_list[s_i:e_i]
idx_part = np.concatenate(idx_part)
coord_part = np.concatenate(coord_part)
feat_part = np.concatenate(feat_part)
offset_part = np.cumsum(offset_part)
np.copyto(inputs[0].host, coord_part.ravel())
np.copyto(inputs[1].host, feat_part.ravel())
np.copyto(inputs[2].host, offset_part)
output = common.do_inference(context,engine=engine, bindings=bindings, inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, stream=stream)
pred_part = output[0].reshape((offset_part[-1], classes))
pred[idx_part, :] += pred_part
pred = np.argmax(pred, axis=1)
intersection, union, target = intersectionAndUnion(pred, label, classes)
accuracy = sum(intersection) / (sum(target) + 1e-10)
print('Accuracy {accuracy:.4f}.'.format(accuracy=accuracy))
 Point-Transformer的TensorRT部署
Point-Transformer的TensorRT部署




























 2179
2179

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










