#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
/**
* @description: 法线采样
* @param cloud 输入点云
* @param cloud_filtered 滤波点云
* @param sample_ratio 采样比例
*/
void normalspacesample(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr& cloud, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr& cloud_filtered, int k, float sample_ratio)
{
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>); //创建用于最近邻搜索的KD-Tree
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>); //存储输出数据
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> normalEstimation; //创建法线估计向量
normalEstimation.setInputCloud(cloud); //输入点云
normalEstimation.setKSearch(k); //使用当前点周围最近的个数
normalEstimation.compute(*cloud_normals); //计算法线
//通过concatenateFields函数将point和normal组合起来形成PointNormal点云数据
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr cloud_with_normal(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);
pcl::concatenateFields(*cloud, *cloud_normals, *cloud_with_normal);
std::sort(cloud_with_normal->begin(), cloud_with_normal->end(), [](pcl::PointNormal pt1, pcl::PointNormal pt2) {return pt1.curvature>pt2.curvature; });
for (size_t i = 0; i < sample_ratio*cloud->size(); i++)
{
cloud_filtered->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(cloud_with_normal->points[i].x, cloud_with_normal->points[i].y, cloud_with_normal->points[i].z));
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("rabbit.pcd", *cloud);
normalspacesample(cloud, cloud_filtered, 10, 0.1f);
pcl::io::savePCDFile("mynormalspacesample.pcd", *cloud_filtered);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
原始点云:
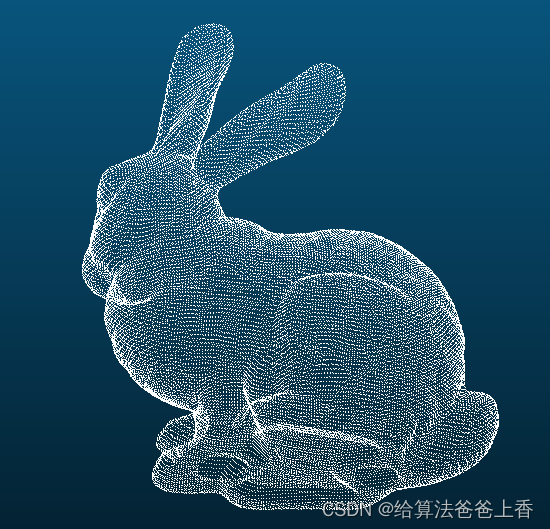
法线空间采样得到的点云:






 该代码示例展示了如何使用PCL库进行点云处理,包括法线估计、基于曲率的点云采样和滤波。首先,通过KdTree进行最近邻搜索,然后计算每个点的法线。接着,结合点云和法线信息,按曲率排序并按比例采样得到新的点云。最后,保存采样后的点云数据。
该代码示例展示了如何使用PCL库进行点云处理,包括法线估计、基于曲率的点云采样和滤波。首先,通过KdTree进行最近邻搜索,然后计算每个点的法线。接着,结合点云和法线信息,按曲率排序并按比例采样得到新的点云。最后,保存采样后的点云数据。

















 765
765












