先上结论:“指向派生类对象的基类指针”只能访问在抽象基类中声明(不非得要求在基类中定义过)的虚函数(virtual function),而不能访问派生类中自己新增的函数。
实验:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//define abstract class
class Shape
{
public:
virtual float area() const {return 0;}//抽象基类中的三个虚函数,其中一个是纯虚函数。
virtual float volume() const {return 0;}
virtual void shapeName() const=0;
};
class Point:public Shape
{
public:
Point(float=0,float=0);
void setPoint(float a,float b);
float getX()const {return x;}
float getY()const {return y;}
virtual void shapeName() const {cout<<"Point:";}
friend ostream& operator<< (ostream& o,const Point& p){
o<<"["<<p.x<<","<<p.y<<"]";
return o;
}
protected:
float x,y;
};
Point::Point(float a,float b):x(a),y(b){
}
void Point::setPoint(float a,float b){
x=a,y=b;
}
int main()
{
Point point(3.2,4.5);
point.shapeName();
cout<<point<<endl;
cout<<"------------------------------------------"<<endl;
Shape* p;
p=&point;
p->shapeName();
cout<<"x="<<p->getX()<<","<<"y="<<p->getY()<<endl; //此处妄想通过p指针访问派生类的新函数
cout<<"area="<<p->area()<<"/n"
<<"volume="<<p->volume()<<endl;
return 0;
}
在注释处已经指明。
错误如下:
C:\Users\11604\Desktop\my_cpp\Point.cpp In function 'int main()':
48 19
C:\Users\11604\Desktop\my_cpp\Point.cpp [Error] 'class Shape' has no member named 'getX'
48 41
C:\Users\11604\Desktop\my_cpp\Point.cpp [Error] 'class Shape' has no member named 'getY'
修改:对于派生类新增的函数,使用对象名point.getX()访问。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//define abstract class
class Shape
{
public:
virtual float area() const {return 0;}//抽象基类中的三个虚函数,其中一个是纯虚函数。
virtual float volume() const {return 0;}
virtual void shapeName() const=0;
};
class Point:public Shape
{
public:
Point(float=0,float=0);
void setPoint(float a,float b);
float getX()const {return x;}
float getY()const {return y;}
virtual void shapeName() const {cout<<"Point:";}
friend ostream& operator<< (ostream& o,const Point& p){
o<<"["<<p.x<<","<<p.y<<"]";
return o;
}
protected:
float x,y;
};
Point::Point(float a,float b):x(a),y(b){
}
void Point::setPoint(float a,float b){
x=a,y=b;
}
int main()
{
Point point(3.2,4.5);
point.shapeName();
cout<<point<<endl;
cout<<"------------------------------------------"<<endl;
Shape* p;
p=&point;
p->shapeName();
//cout<<"x="<<p->getX()<<","<<"y="<<p->getY()<<endl; //此处修改为通过point对象访问派生类的新函数
cout<<"x="<<point.getX()<<","<<"y="<<point.getY()<<endl; //此处妄想通过p指针访问派生类的新函数
cout<<"area="<<point.area()<<"\n" //此处继承下来的函数也改为point对象修改
<<"volume="<<p->volume()<<endl;
return 0;
}
编译通过,结果如下:
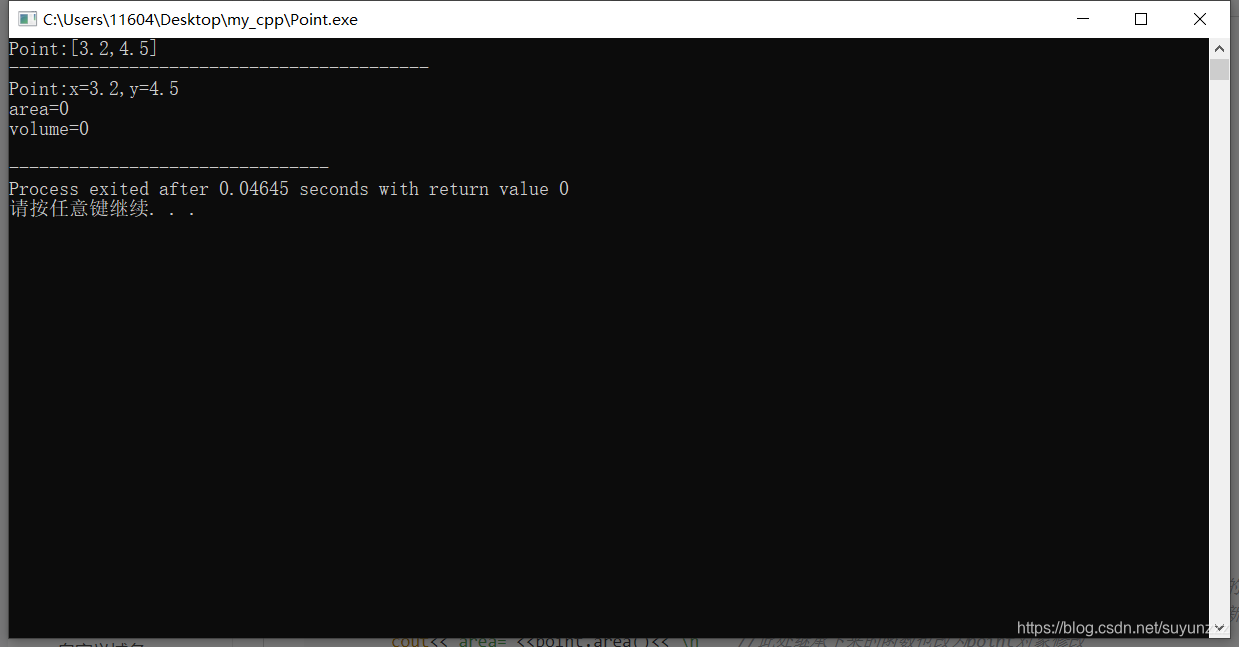
总结:对于所有函数无论是继承的还是新增的都可以通过对象访问,但是对于派生类新增的函数(没有在抽象基类中声明为虚函数的函数)只能通过 派生类对象访问。








 本文探讨了C++中指向派生类对象的基类指针访问限制,强调此类指针只能访问在基类中声明的虚函数,而无法访问派生类新增的成员函数。通过实例演示了如何正确访问派生类的新增函数。
本文探讨了C++中指向派生类对象的基类指针访问限制,强调此类指针只能访问在基类中声明的虚函数,而无法访问派生类新增的成员函数。通过实例演示了如何正确访问派生类的新增函数。

















 46
46

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










