! 面试题11:旋转数组中最小数字
yxc:二分不一定要有单调性,二分的本质是寻找某种性质的分界点。只要可以找到某种性质,使得区间的前半部分满足,后半部分不满足,那么就可以用二分把这个分界点找到。
本题中最重要的就是前段升序序列大于等于nums[0],后段升序序列应该小于nums[0],但是存在等于的,可以提前处理掉。由于需要处理后面这个相等的平台,导致时间复杂度为O(n),但如果不存在这种情况时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-RLxh3iIX-1637473830270)(D:\工作实习\new\offerme${img}\image-20211115094352671.png)]
//yxc版标准二分!赞 !
class Solution {
public:
int findMin(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size() - 1;
while(n > 0 && nums[0] == nums[n]) n--;
if(n < 0) return -1;
if(nums[n] >= nums[0]) return nums[0];
//删完重复后,只剩下第一个升序序列了
int l = 0, r = n;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(nums[mid] >= nums[0])
l = mid + 1;
else
r = mid;
}
return nums[l];
}
};
面试题12:矩阵中的路径
简单回溯
class Solution {
public:
int dx[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
bool dfs(int i, int j, int l, vector<vector<char>>& matrix, string & str)
{
if(l == str.size())
return true;
if(str[l] == matrix[i][j])
{
matrix[i][j] = '.';
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x < matrix.size() && x >= 0 && y < matrix[0].size() && y >= 0 && dfs(x, y, l + 1, matrix, str))
return true;
}
matrix[i][j] = str[0];
}
return false;
}
bool hasPath(vector<vector<char>>& matrix, string &str) {
int l = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < matrix[0].size(); j++)
{
if(matrix[i][j] == str[l])
{
if(str.size() == 1)
return true;
matrix[i][j] = '.';
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x < matrix.size() && x >= 0 && y < matrix[0].size() && y >= 0 && dfs(x, y, l + 1, matrix, str))
return true;
}
matrix[i][j] = str[l];
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
可以改进成从0开始!
class Solution {
public:
int dx[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
bool dfs(int i, int j, int l, vector<vector<char>>& matrix, string & str)
{
if(str[l] != matrix[i][j])
return false;
if(l == str.size() - 1)
return true;
matrix[i][j] = '.';
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x < matrix.size() && x >= 0 && y < matrix[0].size() && y >= 0 && dfs(x, y, l + 1, matrix, str))
return true;
}
matrix[i][j] = str[l];
return false;
}
bool hasPath(vector<vector<char>>& matrix, string &str) {
int l = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < matrix[0].size(); j++)
{
if(dfs(i, j, l, matrix, str))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
面试题13:机器人的运动范围
简单dfs
class Solution {
public:
int dx[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int thr, r, c;
bool check(int x, int y)
{
int s = 0;
while(x)
{
s += x % 10;
x = x / 10;
}
while(y)
{
s += y % 10;
y = y / 10;
}
if(s <= thr)
return true;
return false;
}
void dfs(int i, int j, int& ans, vector<vector<bool>>& st)
{
if(st[i][j] == true)
return ;
st[i][j] = true;
ans++;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 0 && x < r && y >= 0 && y < c && check(x, y))
dfs(x, y, ans, st);
}
}
int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols)
{
thr = threshold;
r = rows;
c = cols;
if(r == 0 && c == 0)
return 0;
vector<vector<bool>> st(rows, vector<bool>(cols, false));
int ans = 0;
dfs(0, 0, ans, st);
return ans;
}
};
面试题15:二进制中的1的个数
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1(int n) {
int ans = 0;
while(n)
{
if(n & 1)
ans++;
n = n >> 1;
}
return ans;
}
};
上面这种无法处理负数,如-1=0xFFFFFFFF,有32个1。每次右移会在最高位补1,保证是负数,那就导致永远存在1,死循环了。
解决方法是强制将n变成无符号整数,存储还是补码,但是解释不同,这样右移就是逻辑右移,在最高位补0。
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1(int n) {
int ans = 0;
unsigned int un = n;
while(un)
{
if(un & 1)
ans++;
un = un >> 1;
}
return ans;
}
};
另一个方法,就是将1不断循环左移,最多32次就会将1移出去变成0,然后就会结束循环。
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1(int n) {
int ans = 0, b = 1;
while(b)
{
if(n & b)
ans++;
b = b << 1;
}
return ans;
}
};
经典:将某个二进制最右侧1清零 like n = 1100, n -1 = 1011,就是最右侧1变0,1后面0变1,n & n -1 = 1000
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1(int n) {
int ans = 0;
while(n)
{
ans++;//统计多少次
n = n & (n - 1);//将某个二进制最右侧1清零
}
return ans;
}
};
面试题16:数值的整数次方
快速幂
int qkm(int a, int k, int p) //a^k % p
{
long long ans;
while(k)
{
if(k & 1)
ans = (long long) ans * a % p;
k = k >> 1;
a = (long long) a * a % p;
return ans;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
double Power(double b, int e) {
int s = 0;
long long ue;
if(e < 0)
{
s = 1;
ue = -(long long)e;
//e如果是负无穷取负会导致int越界
}
else
ue = e;
double ans = 1;
while(ue)
{
if(ue & 1)
ans *= b;
ue = ue >> 1;
b = b * b;
}
if(s)
ans = 1.0 / ans;
return ans;
}
};
面试题18:删除链表的节点
单链表删除一个节点通常需要遍历该链表找到链表的前一个节点,这就需要O(n)。但是现在要求O(1)的复杂度,因为给出了当前要删除的链表节点,所以可以将后面那个节点的值复制到要删除的,然后将要删除的下一个指向下下一个。
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
ListNode* nodeNext = node->next;
node->val = nodeNext->val;
node->next = nodeNext->next;
delete nodeNext;
}
};
如果是尾节点还是需要从头遍历的!
删除链表重复节点
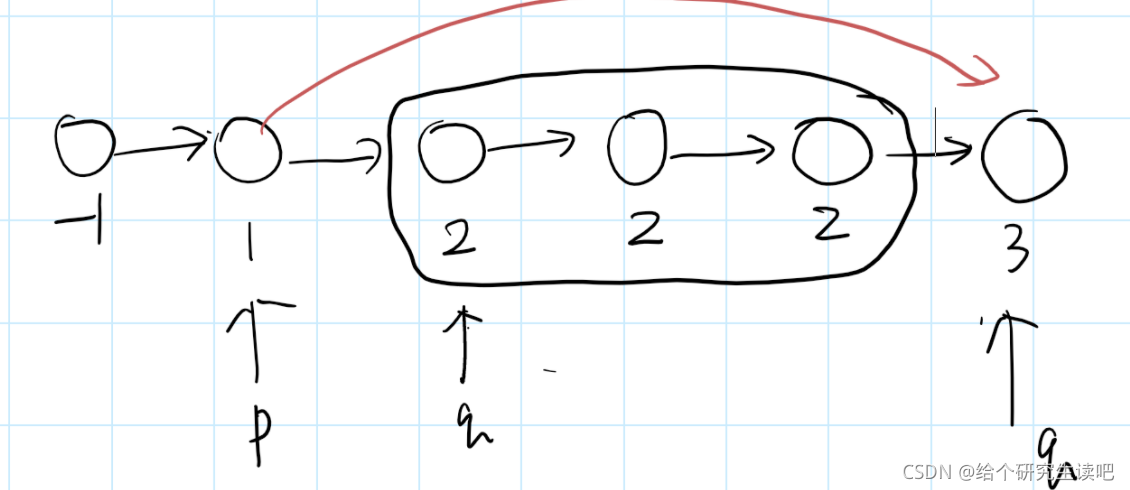
双指针,p指向上一个已完成的节点,q从p的下一个开始查找重复节点,直到和p->next->val不同,停止。如果p->next->next== q那就是不重复,因为p-next q 这两个不一样,但是如果不等就是有重复的,那就p直接指向和p->next不一样的q就可以了。
面试题21:调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
类似于快排,就是两个指针,l和r。l左侧的都是奇数,r右侧的都是偶数。如果碰见不是的,那就交换。
class Solution {
public:
void reOrderArray(vector<int> &array) {
int l = 0, r = array.size() - 1;
while(l < r)
{
while(l < r && array[l] % 2 == 1) l++;
while(l < r && array[r] % 2 == 0) r--;
if(l < r) swap(array[l], array[r]);
}
}
};
面试题22:链表中倒数第K个节点
我用栈做的哈哈哈哈,终于记起stack了!复杂度是O(n + k)。当然也可以是遍历两边,第一遍找出长度,第二遍找到第n-k个。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* findKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, int k) {
stack<ListNode* > s;
int n = 0;
ListNode* p = pListHead;
while(p != nullptr)
{
s.push(p);
p = p->next;
n++;
}
if(k > n)
return nullptr;
while(k--)
{
p = s.top();
s.pop();
}
return p;
}
};
快慢指针做法,就是快指针先走k-1,然后慢指针走。等快指针走到了n,慢指针也就是倒数第k个了。
重点就是相差k-1个!!!
*class Solution {
public:
ListNode* findKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, int k) {
ListNode *q = pListHead, *s = pListHead;
while(k--)
{
if(q != nullptr)
q = q->next;
else
return nullptr;
}
while(q != nullptr)
{
q = q->next;
s = s->next;
}
return s;
}
};
面试题23:链表中环的入口节点
首先判断链表中是否包含环?
方法一:哈希表
入口点就是第一个出现重复的节点
unordered_set.find(x) != end();
unordered_set.count(x) 是否存在x,存在返回1,不存在返回0
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode *head) {
unordered_set<ListNode*> hashset;
ListNode* p = head;
while(p)
{
if(hashset.find(p) != hashset.end())
//if(hashset.count(p))
return p;
else
hashset.insert(p);
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
};
方法二:快慢指针
快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,如果相遇就是存在环。相遇之后将first指向head,慢指针不动,继续一次走一步,再次相遇就是入口点。
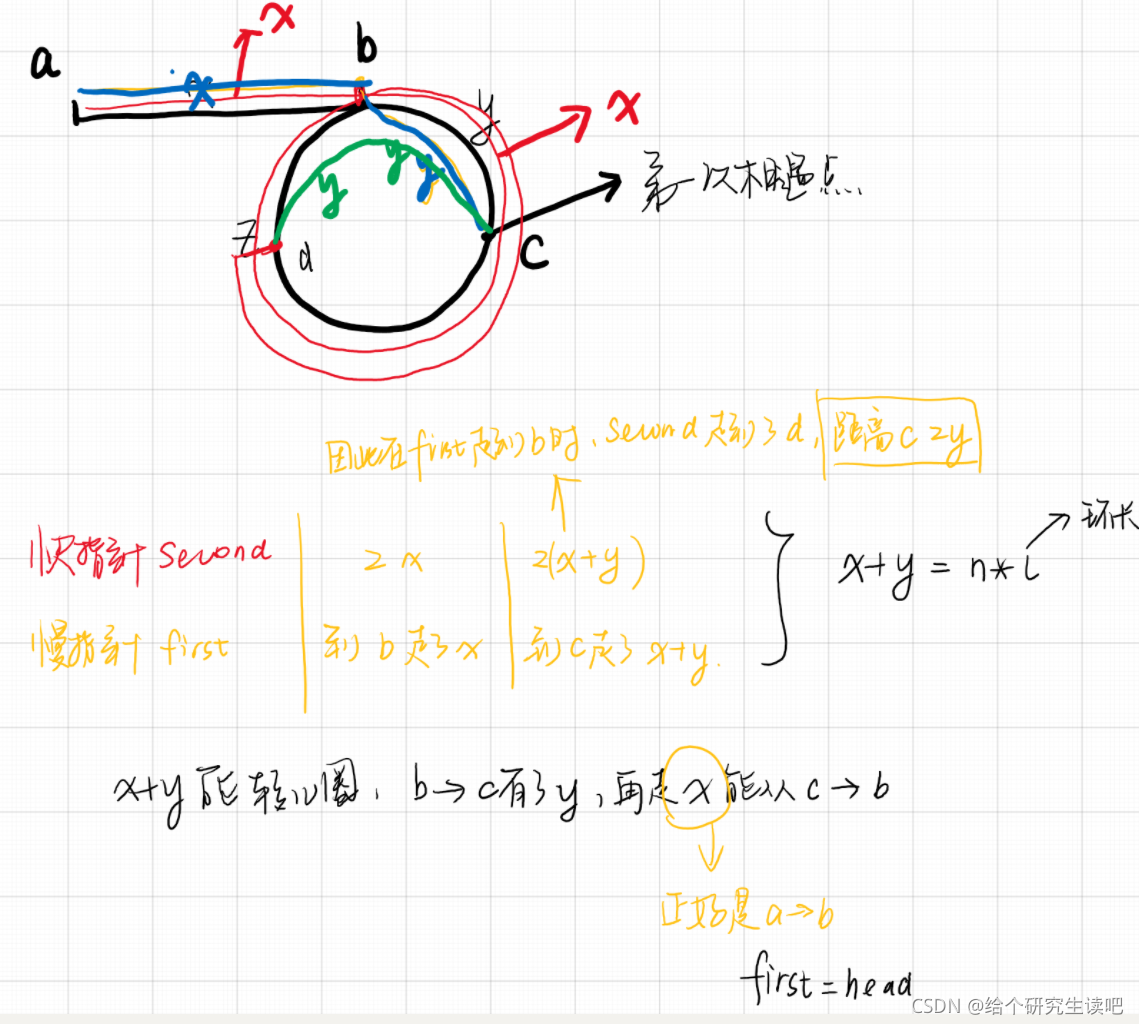
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *first = head, *second = head;
while(second && first)
{
first = first->next;
second = second->next;
if(second)
second = second->next;
if(second && second == first) //遇到了肯定是存在环
{
first = head;
while(first != second)
{
first = first->next;
second = second->next;
}
return first;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
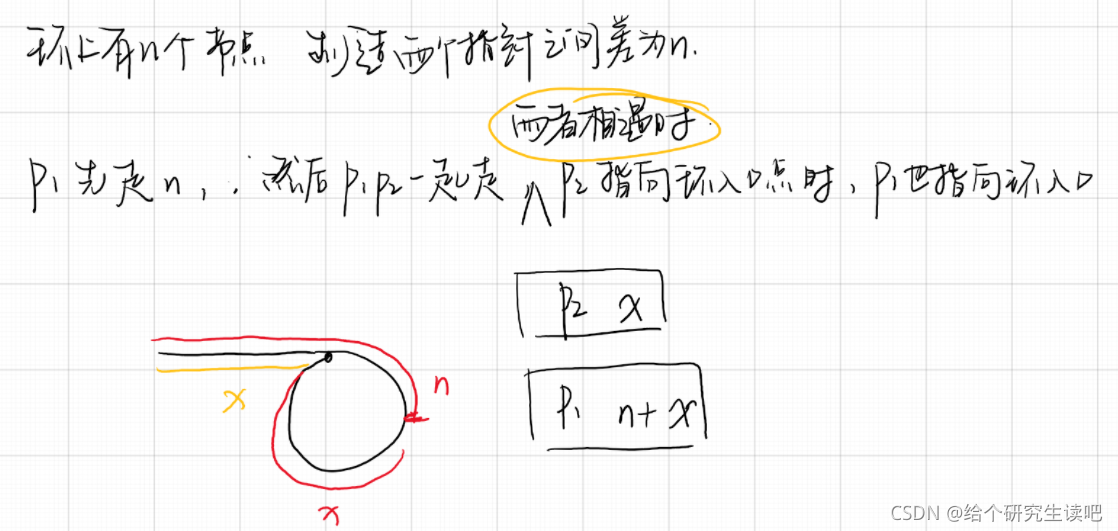
制造两个指针之前差为n的距离。
那就得先直到环上节点数,是否存在环,也就是上述的两个方法。
面试题25:合并两个有序链表
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* p = dummy;
while(l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL)
{
if(l1->val <= l2->val)
{
p->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
p = p->next;
}
else
{
p->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
p = p->next;
}
}
if(l1 != NULL)
p->next = l1;
if(l2 != NULL)
p->next = l2;
return dummy->next;
}
};
递归版:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if(l1 == nullptr)
return l2;
if(l2 == nullptr)
return l1;
ListNode* p = nullptr;
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
p = l1;
p->next = merge(l1->next, l2);
}
else
{
p = l2;
p->next = merge(l1, l2->next);
}
return p;
}
};
面试题26:判断树的子结构
class Solution {
public:
bool isSame(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2){
if(pRoot2 == nullptr)//root2匹配完成
return true;
if(pRoot1 == nullptr)//root2没完但是root1已经完成了
return false;
if(pRoot1->val != pRoot2->val)
return false;
return isSame(pRoot1->left, pRoot2->left) && isSame(pRoot1->right, pRoot2->right);
}
bool hasSubtree(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2) {
if(pRoot2 == nullptr || pRoot1 == nullptr)//空树不是任何树的子树
return false;
if(isSame(pRoot1, pRoot2)) //比较以proot1为根节点的子树是否和proot2匹配
return true;
else
return hasSubtree(pRoot1->left, pRoot2) || hasSubtree(pRoot1->right, pRoot2);
}
};
面试题27:二叉树的镜像
class Solution {
public:
void mirror(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
return;
TreeNode* tmp = root->right;
root->right = root->left;
root->left = tmp;
//swap(root->left, root->right);
mirror(root->left);
mirror(root->right);
}
};
面试题28:对称的二叉树
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
return isSymmetric(root, root);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* rootL, TreeNode* rootR)
{
if(rootR == nullptr && rootL == nullptr)
return true;
if(rootL == nullptr || rootR == nullptr)
return false;
if(rootL->val != rootR->val)
return false;
return isSymmetric(rootL->left, rootR->right) && isSymmetric(rootL->right, rootR->left);
}
};
面试题29:顺时针打印矩阵
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printMatrix(vector<vector<int> > matrix) {
if(matrix.empty()) return {};
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
vector<int> ans;
vector<vector<bool>> st(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
int x = 0, y = 0, d = 1;//从(0, 0)开始,初始方向为向右
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};//顺时针上右下左
for(int i = 0; i < m * n; i++)
{
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
st[x][y] = true;
int a = x + dx[d], b = y + dy[d];//下一个
if(a >= m || a < 0 || b >= n || b < 0 || st[a][b])//越界了或者访问过了就换一个方向
{
d = (d + 1) % 4;
a = x + dx[d];
b = y + dy[d];
}
x = a;
y = b;
}
return ans;
}
};
面试题30:包含min函数的栈
添加一个保存当前最小函数的辅助栈即可
class MinStack {
public:
stack<int> sdata, smin;
MinStack() {
while(sdata.size())
sdata.pop();
while(smin.size())
smin.pop();
}
void push(int x) {
sdata.push(x);
if(smin.size() == 0)
smin.push(x);
else
{
int t = smin.top();
if(x < t)
smin.push(x);
else
smin.push(t);
}
}
void pop() {
sdata.pop();
smin.pop();
}
int top() {
return sdata.top();
}
int getMin() {
return smin.top();
}
};
面试题31:栈的压入、弹出序列
压入一个值,就看看能否按照popV序列pop出一些东西来。如果最后栈中还有值,说明序列没有匹配上。
class Solution {
public:
bool isPopOrder(vector<int> pushV,vector<int> popV) {
if(pushV.empty() && popV.empty())
return true;
if(pushV.size() == 0 || popV.size() == 0 || pushV.size() != popV.size())
return false;
stack<int> s;
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < pushV.size(); i++)
{
s.push(pushV[i]);
while(s.size() && s.top() == popV[j])
{
s.pop();
j++;
}
}
return s.empty();
}
};
面试题32:从上到下打印二叉树
简单层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
return {};
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<int> ans;
q.push(root);
while(q.size())
{
TreeNode* t = q.front();
q.pop();
ans.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left != nullptr)
q.push(t->left);
if(t->right != nullptr)
q.push(t->right);
}
return ans;
}
};
分行从上到下打印二叉树
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-eSPWfQYf-1637851631800)(D:\工作实习\new\offerme${img}\image-20211121212148018.png)]
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
return {};
vector<vector<int>> ans;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(q.size())
{
int n = q.size();
vector<int> tmp;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
TreeNode* t = q.front();
q.pop();
tmp.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left != nullptr)
q.push(t->left);
if(t->right != nullptr)
q.push(t->right);
}
ans.push_back(tmp);
}
return ans;
}
};
之字形从上到下打印二叉树
巧用reverse!!
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
return {};
vector<vector<int>> ans;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
bool d = false;
while(q.size())
{
int n = q.size();
vector<int> tmp;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
TreeNode* t = q.front();
q.pop();
tmp.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left != nullptr)
q.push(t->left);
if(t->right != nullptr)
q.push(t->right);
}
if(d)
{
reverse(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
d = false;
}
else
d = true;
ans.push_back(tmp);
}
return ans;
}
};
面试题33:二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
class Solution {
public:
bool verifySequenceOfBST(vector<int> sequence) {
return dfs(sequence, 0, sequence.size() - 1);
}//最后一个是根, 左边比根小,右边比根大
bool dfs(vector<int>& s, int l, int r)
{
if(l >= r) return true;
int root = s[r];
int k = l;
while(k < r && s[k] < root) k++;
int i = k;
while(i < r)
{
if(s[i] < root)
return false;
i++;
}
return dfs(s, l, k - 1) && dfs(s, k, r - 1);
}
};
面试题34:二叉树中和为某一值的路径
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> tmp;
vector<vector<int>> findPath(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if(root == nullptr)
return {};
dfs(root, sum);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int sum)
{
if(root == nullptr)
return;
sum = sum - root->val;
tmp.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr && sum == 0)//左右节点都是nullptr才算是叶节点
ans.push_back(tmp);
dfs(root->left, sum);
dfs(root->right, sum);
tmp.pop_back();
sum = sum + root->val;
}
};
面试题35:复杂链表的复制
注意哈希表的使用
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *copyRandomList(ListNode *head) {
if(head == nullptr) return nullptr;
unordered_map<ListNode*, ListNode*> hashMap;
ListNode* newHead = new ListNode(head->val);
hashMap[head] = newHead;
ListNode* p = newHead, *q = head;
while(q->next != nullptr)
{
p->next = new ListNode(q->next->val);
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
hashMap[q] = p;
}
q = head, p = newHead;
while(q != nullptr)
{
if(q->random != nullptr)
p->random = hashMap[q->random];
q = q->next;
p = p->next;
}
return newHead;
}
};
一遍遍历,就是先把该节点需要连接的节点创建并保存在哈希表中,然后再连接
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *copyRandomList(ListNode *head) {
//先创建所需的节点,保存到哈希表中,然后再连接
if(head == nullptr) return nullptr;
unordered_map<ListNode*, ListNode*> hashMap;
hashMap[nullptr] = nullptr;//random可能为空
ListNode* newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* p = newHead, *q = head;
while(q)
{
if(!hashMap.count(q))
hashMap[q] = new ListNode(q->val);
if(!hashMap.count(q->random))
hashMap[q->random] = new ListNode(q->random->val);
p->next = hashMap[q];
p->next->random = hashMap[q->random];
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
return newHead->next;
}
};
面试题36:二叉搜索树与双向链表
中序遍历非常妙的一个做法!
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* pre, *head;
TreeNode* convert(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return head;
}
TreeNode* dfs(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
dfs(root->left);//左子树已经连接好
//操作root,将当前root和中序遍历前一个节点尾部连接
root->left = pre;
if(pre) pre->right = root;
else
head = root;
pre = root;//将root作为中序遍历最后一个节点
dfs(root->right);
}
};
面试题38:数字全排列
-
全不相同的数字全排列
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> ans; vector<int> tmp; int n; vector<vector<int>> permutation(vector<int>& nums) { n = nums.size(); vector<bool> st(n, false); dfs(0, nums, st); return ans; } void dfs(int cnt, vector<int>& nums, vector<bool>& st) { if(cnt == n) { ans.push_back(tmp); return ; } for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(!st[i]) { st[i] = true; tmp.push_back(nums[i]); dfs(cnt + 1, nums, st); tmp.pop_back(); st[i] = false; } } } }; -
有重复数字的全排列
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> ans; int n; vector<vector<int>> permutation(vector<int>& nums) { n = nums.size(); sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); vector<bool> st(n, false); vector<int> tmp(n); dfs(nums, 0, 0, st, tmp); return ans; } void dfs(vector<int>& nums, int u, int start, vector<bool>& st, vector<int>& tmp) { if (u == n) { ans.push_back(tmp); return; } for (int i = start; i < n; i ++ ) if (!st[i]) { st[i] = true; tmp[i] = nums[u]; if (u + 1 < n && nums[u + 1] != nums[u]) dfs(nums, u + 1, 0, st, tmp); else dfs(nums, u + 1, i + 1, st, tmp); st[i] = false; } } };面试题39:数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
排序,然后数组中间的那个就是
class Solution { public: int moreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int>& nums) { sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); int mid = nums.size() / 2; return nums[mid]; } };摩尔投票法:用相同的不断去抵消不同的,总能剩
class Solution { public: int moreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int>& nums) { int r = nums[0]; int cnt = 1; for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) { if(cnt == 0) { r = nums[i]; cnt = 1; } else { if(nums[i] == r) cnt++; else cnt--; } } return r; } };面试题40:最小的k个数
- 维护一个k个数的大顶堆, O(nlogk)
class Solution { public: vector<int> getLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int> input, int k) { priority_queue<int> q; vector<int> ans; for(int i = 0; i < input.size(); i++) { if(q.size() < k) q.push(input[i]); else { if(q.top() > input[i]) { q.pop(); q.push(input[i]); } } } while(q.size()) { ans.push_back(q.top()); q.pop(); } reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end()); return ans; } }; -
做k次快速排序,
面试题41:数据流中的中位数
不断获取数据流中的中位数,需要一直保持数据流有序。采用一个大顶堆存储数据流的前半部分,like 3 4 5(top),小顶堆保存数据流的后半部分like 6(top) 7 8。而且需要保证大顶堆和小顶堆之间数量差不能超过1。
class Solution {
public:
priority_queue<int> max_heap;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> min_heap;
void insert(int num){
max_heap.push(num);
while(min_heap.size() && max_heap.top() > min_heap.top())
{
int mi = min_heap.top();
int ma = max_heap.top();
min_heap.pop();
max_heap.pop();
min_heap.push(ma);
max_heap.push(mi);
}
while(max_heap.size() - min_heap.size() > 1)
{
min_heap.push(max_heap.top());
max_heap.pop();
}
}
double getMedian(){
if((min_heap.size() + max_heap.size()) % 2)
return max_heap.top();
else
return (max_heap.top() + min_heap.top()) / 2.0;
}
};
面试题42:连续子数组的最大和
- 动态规划
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int s = INT_MIN, ans = INT_MIN;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
if(s < 0)
s = nums[i];
else
s += nums[i];
ans = max(ans, s);
}
return ans;
}
}
面试题44:数字序列中某一位的数字
class Solution {
public:
int cntNum(int dig)
{
if(dig == 1)
return 10;
else
return 9 * pow(10, dig - 1);// 90 900
}
int cntBeginNum(int dig)
{
if(dig == 1)
return 0;
return pow(10, dig - 1);
}
int calIndex(int dig, int n)
{
long long start = cntBeginNum(dig);
long long num = start + n / dig;
int p = dig - n % dig;
for(int i = 1; i < p; i++)
num = num / 10;
return num % 10;
}
int digitAtIndex(int n) {
int dig = 1;//位数为1
while(1)
{
//计算位数为dig的有多少个数
long long num = cntNum(dig);
if(n < num * dig)
return calIndex(dig, n);
n = n - num * dig;
dig++;
}
return -1;
}
};
2147483647这个数字可能越界,注意使用long long 。在计算10位数字个数的时候,会越界。
面试题45:把数组排成最小的数
定义了一个新的比较方法,然后利用这个方法去排序。string a + string b < string b + string a则将a排在前面!
class Solution {
public:
bool static cmp(int a, int b)
{
if(to_string(a) + to_string(b) < to_string(b) + to_string(a))
return true;
return false;
}
string printMinNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
string ans;
if(!nums.size())
return ans;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end(), cmp);
for(int s: nums)
ans += to_string(s);
return ans;
}
};
面试题46:把数字翻译成字符串
dp[i] = dp[i + 1] + dp[i + 2]
12345使用递归可以翻译成 1 + 2345和 12 + 345,不过12得是两位数
class Solution {
public:
int getTranslationCount(string s) {
int n = s.size();
if(n == 0) return 0;
int dp[n];
memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if(i == n - 1)
dp[i] = 1;
else
dp[i] += dp[i + 1];
if(i < n - 2)
{
int n1 = s[i] - '0';
int n2 = s[i + 1] - '0';
int nn = n1 * 10 + n2;
if(nn >= 10 && nn <= 25)
dp[i] += dp[i + 2];
}
}
return dp[0];
}
};
面试题47:礼物的最大价值
dp[i] [j] = max(dp[i - 1] [j] , dp[i] [j - 1]) + grid[i] [j];
class Solution {
public:
int getMaxValue(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
int dp[m][n];
memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);
dp[0][0] = grid[0][0];
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++)
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + grid[i][0];
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++)
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1] + grid[0][j];
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++)
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++)
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j];
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
}
};
不开辟数组
class Solution {
public:
int getMaxValue(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++)
grid[i][0] += grid[i - 1][0];
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++)
grid[0][j] += grid[0][j - 1];
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++)
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++)
grid[i][j] += max(grid[i - 1][j], grid[i][j - 1]);
return grid[m - 1][n - 1];
}
};
面试题48:最长不含重复的子字符串
动态规划:dp[i]表示以i结尾的最长子字符串长度
如果之前没有出现过s[i]的话,dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1
如果之前出现了s[i]的话,找到与现在的距离d
如果d <= dp[i - 1],就说明之前出现的s[i]位于dp[i - 1]的那个序列中,现在dp[i]就变成了从之前出现的s[i]开始计算,即dp[i] = d
如果d > dp[i - 1],则说明之前出现的s[i]不在dp[i- 1]的那个序列中,现在dp[i]就还是dp[i - 1] + 1
最后取dp数组的最大值
class Solution {
public:
int longestSubstringWithoutDuplication(string s) {
int n = s.size(), ans = 1;
if(n == 0) return 0;
int pos[26], dp[n];
memset(pos, -1, sizeof pos);
memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
int idx = s[i] - 'a';
if(pos[idx] == -1)
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
else
{
int before = pos[idx];
int d = i - before;
if(d <= dp[i - 1])
dp[i] = d;
else
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
}
ans = max(ans, dp[i]);
pos[s[i] - 'a'] = i;
}
return ans;
}
};
绝妙双指针:i和j指向目前最长序列的开头和结尾
如果s[j]出现了两次,那就从s[i]开始删除直到删到使s[j]只出现一次!
class Solution {
public:
int longestSubstringWithoutDuplication(string s) {
int n = s.size(), ans = INT_MIN;
if(n == 0) return 0;
unordered_map<char, int> hash;
//统计目前最长序列中字符出现次数
for(int i = 0, j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
hash[s[j]]++;
while(hash[s[j]] > 1)
hash[s[i++]]--;
ans = max(ans, j - i + 1);
}
return ans;
}
};
面试题49:丑数
三路归并
class Solution {
public:
int getUglyNumber(int n) {
vector<int> u;
u.push_back(1);
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while(u.size() < n)
{
int num = min(2 * u[i], min(3 * u[j], 5 * u[k])); //按顺序加入
u.push_back(num);
if(num == 2 * u[i]) // 2 * 3
i++;
if(num == 3 * u[j]) // 3 * 2 不能用else, 相同的都需要后移
j++;
if(num == 5 * u[k])
k++;
}
return u.back();
}
};
面试题50:第一次只出现一次的字符
class Solution {
public:
char firstNotRepeatingChar(string s) {
int pos[256];
memset(pos, 0, sizeof pos);
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
pos[s[i]]++;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
if(pos[s[i]] == 1)
return s[i];
}
return '#';
}
};
注意不是仅仅是26个字母!也可以用哈希表做,我觉得不如数组快!
面试题52:两个链表的第一个公共结点
本题的关键在于:如果有公共节点,那么后面的节点都是相同的。因此可以让长的链表先走dif长度,然后再一起走,遇到相同的就是第一个公共节点了。因为先走dif的话就会一起走到最后一个,这样就同步了!
class Solution {
public:
int getLen(ListNode* head)
{
int len = 0;
while(head != nullptr)
{
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
ListNode *findFirstCommonNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
int la = getLen(headA), lb = getLen(headB), dif;
ListNode* lp, *sp;
if(la < lb)
{
lp = headB;
sp = headA;
dif = lb - la;
}
else
{
lp = headA;
sp = headB;
dif = la - lb;
}
while(dif--)
lp = lp->next;
while(lp != nullptr && sp != nullptr && lp != sp)
{
lp = lp->next;
sp = sp->next;
}
return lp;
}
};
面试题53:0到n-1中缺失的数字
class Solution {
public:
int getMissingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0) return 0;
int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;//找到右侧的最左边,yxc yyds!!!
if(nums[mid] > mid) //由于缺少x, x所在的右侧值会大于下标,即x + 1在下标x的位置
r = mid;
else //x所在的左侧值都和下标相同
l = mid + 1;
}
if(nums[r] == r) //如果缺失最后一个,like [0, 1]认为缺失2, 但结果会是r = n - 1 = 1, 需要++
r++;
return r;
}
};





















 2067
2067

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








