这篇paper入选ECCV 2016 Oral,是目标检测领域代表性算法,第一作者Wei Liu博士毕业后现为自动驾驶公司Nuro的Lead Machine Learning Researcher。
本文的写作参考了arXiv上最新的版本,提交时间为Thu, 29 Dec 2016。由于网上已有太多中文解读SSD的文章,本文的出发点是总结归纳一些原文的主要思想,更多的细节解读可以参考文末的两个链接。
SSD的出发点是将bounding boxes的输出空间离散化为一系列default boxes(这些default boxes建立在feature map的每个单元格位置上,且拥有不同比例和尺度) (结论里表述为This representation allows us to efficiently model the space of possible box shapes.)
同时结合了多个不同分辨率(大小)的feature map的预测,有利于处理多尺度的目标。最终实现Allowing different default box shapes in several feature maps let us efficiently discretize the space of possible output box shapes.
预测时,网络的输出为每个default box在所有类别上各自的得分以及对该box形状的修正值。
性能:For 300 × 300 input, SSD achieves 74.3% mAP on VOC2007 test at59 FPS on a Nvidia Titan X, for512 × 512 input, SSD achieves 76.9% mAP.
网络结构如下:
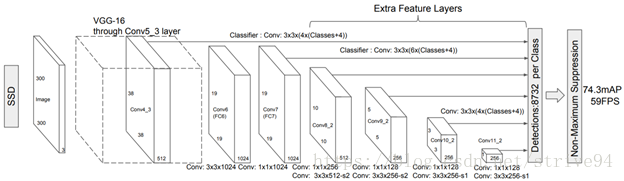
Inputsize: 300 × 300或者512 × 512 (Fast and Faster R-CNN 600 × 600, while YOLO is 448 × 448).
采用conv4_3, conv7, conv8_2, conv9_2, conv10_2, conv11_2的输出来预测location和confidence,6个feature map的大小分别是 ,
,
其上的default box的尺度分别是 ,
,
SSD300一共可以预测

个边界框(conv4_3, conv10_2, conv11_2的feature map上的每个位置预测4个default box;conv7, conv8_2, conv9_2预测6个)。
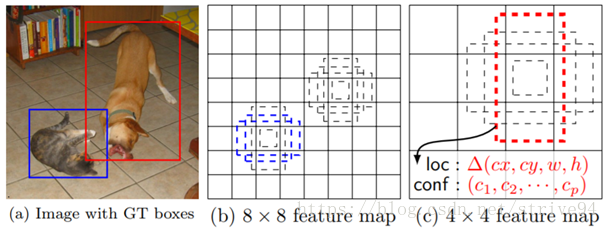
训练时,首先要匹配这些default boxes和ground truth boxes。
举例来说,上图b中的两个蓝色default box(即default box在原图上的投影)都match了ground truth中的猫,上图c中的红色default box(即default box在原图上的投影)match了ground truth中的狗。这三个default box均被划分为正样本,其余的default box被划分为负样本。
问:由feature map如何获得每个box的分类得分和形状修正值?
答:用一系列(个数 = (类别数 + 4) × feature map上每个位置default box的数量)大小为3 × 3的 convolutionalfilters(原文里也称convolutional predictor)处理每一张feature map。实质就是,default box和feature map之间是一种卷积的关系。
问:如何设置default box?
答:(Fortunately,within the SSD framework, the default boxes do not necessary need to correspond to the actual receptive fields of each layer. ) We design the tiling of default boxes so that specific feature maps learn to be responsive to particular scales of the objects.核心!
最终效果:多种feature map大小可以对应多种尺度物体的检测;一张feature map上多种比例的检测框对应物体的多种比例或形变。
在实际应用中,我们可以自定义以及优化default boxes的分布来更好的适用于特定的dataset,以获得更好的检测结果。
欢迎大家留言讨论更多的文章细节!
最后附上一些推荐的博客供参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33544892




 SSD算法通过在不同分辨率的特征图上设置多种比例和尺度的预设框(default boxes),实现了高效的目标检测。该方法能较好地处理多尺度目标,并在VOC2007数据集上取得了74.3% mAP的成绩,处理速度达到59 FPS。
SSD算法通过在不同分辨率的特征图上设置多种比例和尺度的预设框(default boxes),实现了高效的目标检测。该方法能较好地处理多尺度目标,并在VOC2007数据集上取得了74.3% mAP的成绩,处理速度达到59 FPS。
















 431
431

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








